Rolling freedom revolution stop mechanism for helicopter dynamic flight simulator
A stop mechanism and dynamic flight technology, applied in simulators, simulators of space navigation conditions, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient motor braking torque, potential safety hazards, and drop accidents, and achieve the purpose of overcoming the lack of motor braking torque , Ensure the safety of the machine and prevent the effect of relative rotation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
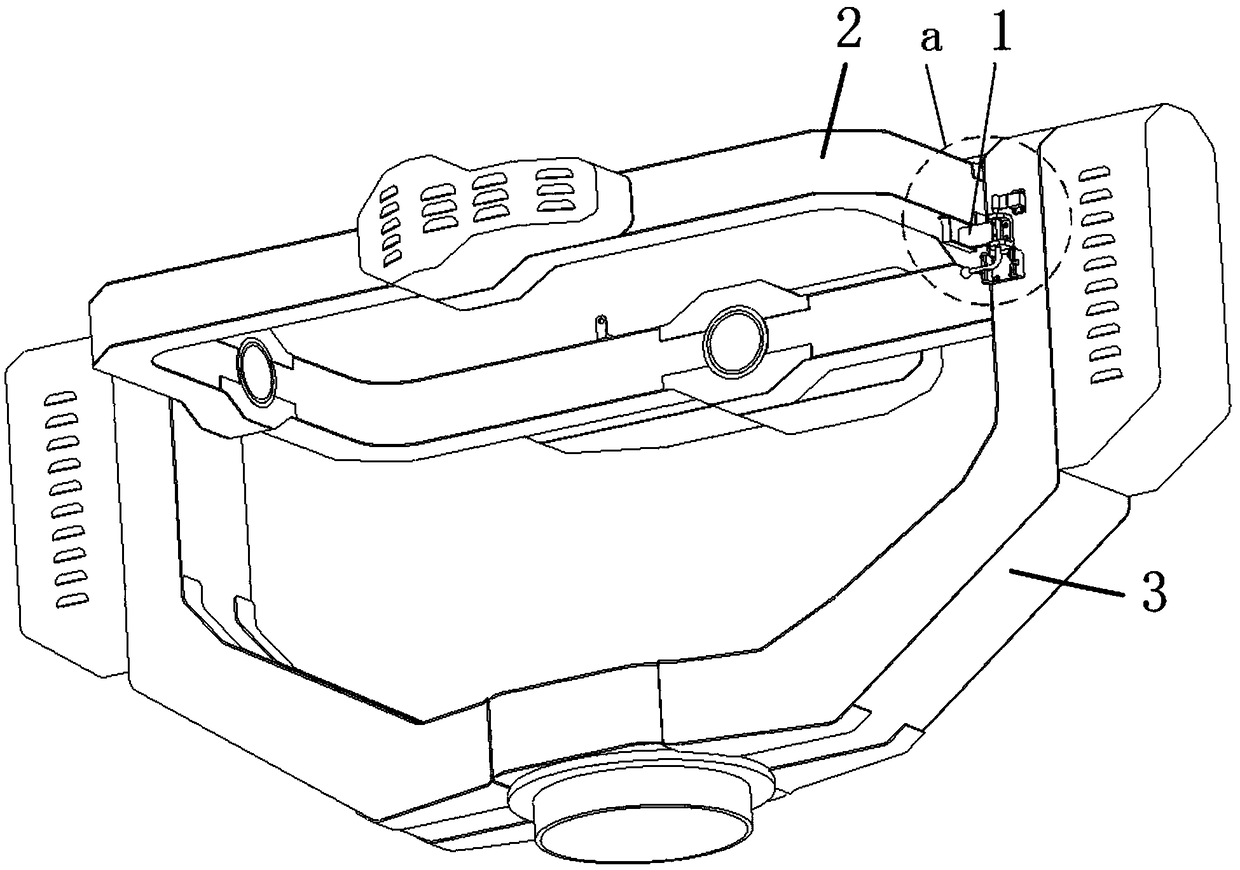
[0041] Example 1, such as figure 1 and figure 2 Shown:
[0042] The rotary stop mechanism for the rolling degree of freedom used in the helicopter dynamic flight simulator includes multiple sets of rotary stop mechanisms 1, and each set of rotary stop mechanisms 1 includes:
[0043] Rotatably connected to the deadbolt 13 installed on the yaw frame 3;
[0044] Fixedly installed on the roll frame 2 is a lock 111 that matches the size of the lock tongue 13; the lock tongue 13 snaps into the lock 111 to lock the position of the yaw frame 3 and the roll frame 2 at this time; the lock tongue 13 is disengaged When the buckle 111 is locked, the yaw frame 3 and the roll frame 2 can rotate relative to each other.
[0045]When the equipment is stationary, the rolling frame 2 and the yaw frame 3 can be locked by locking the tongue 13 into the buckle 111 to prevent the relative rotation of the rolling frame 2 and the yaw frame 3, overcome the shortcoming of insufficient braking torque ...
Embodiment 2
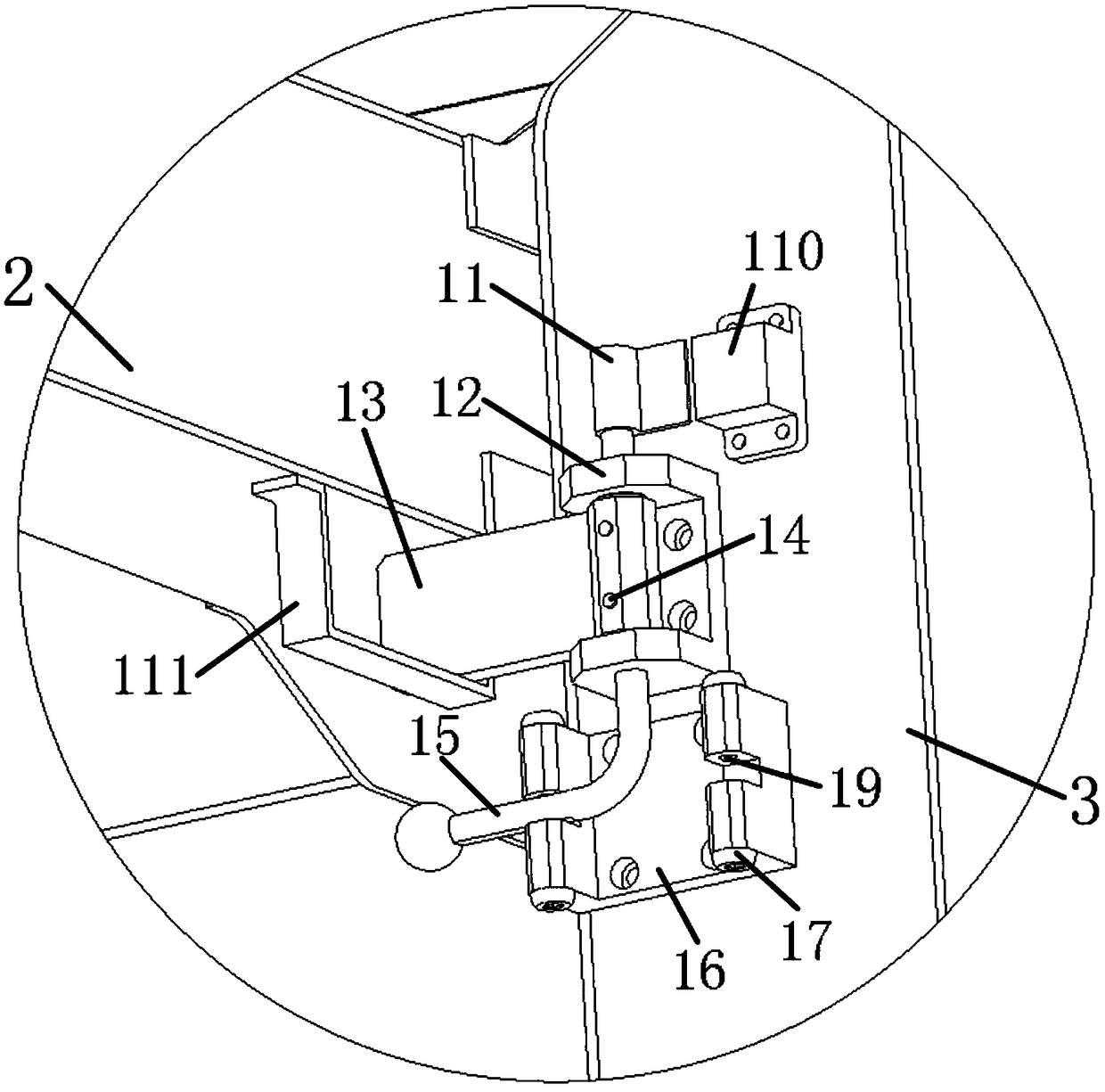
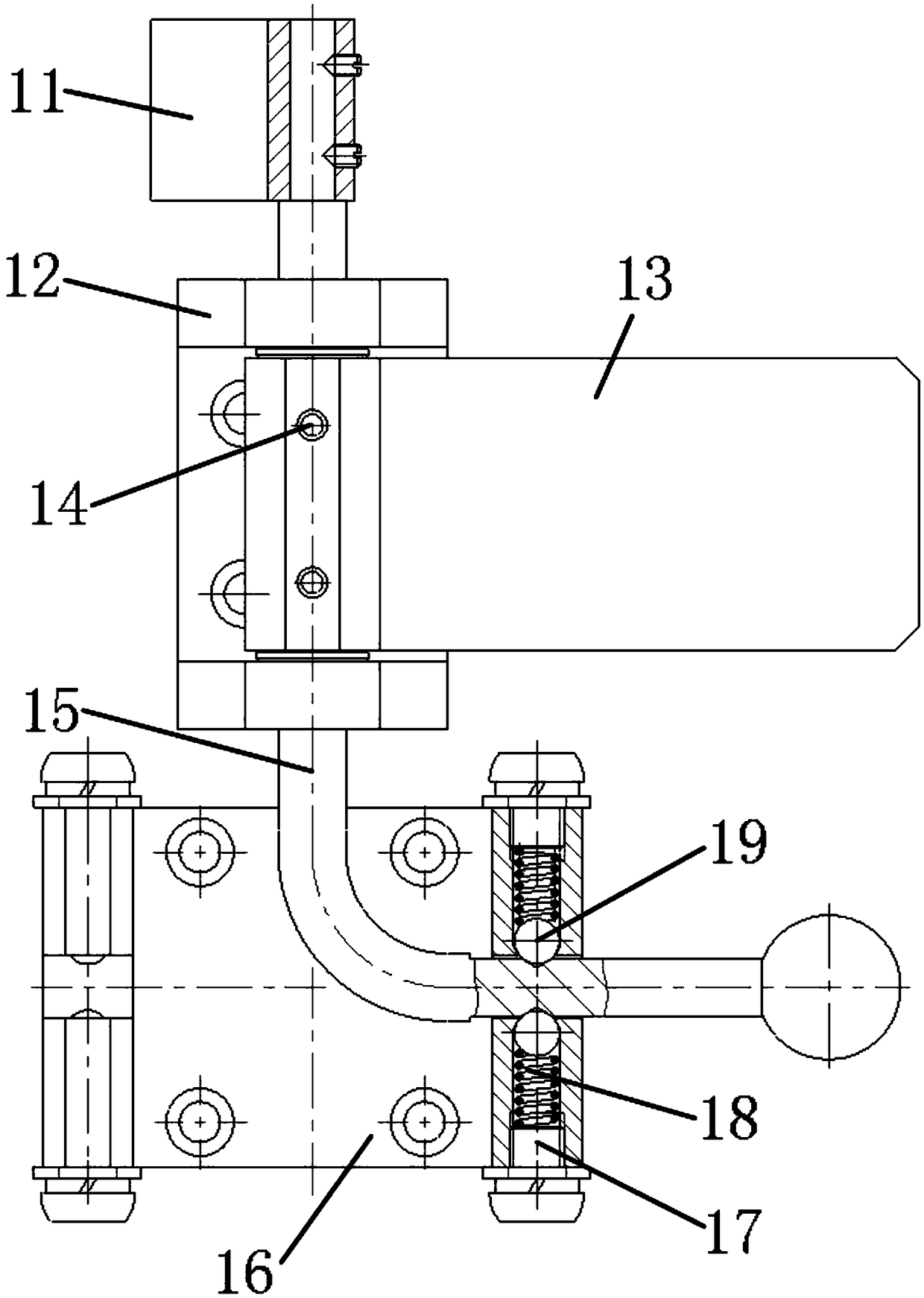
[0046] Example 2, such as figure 2 and image 3 Shown:
[0047] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that each group of rotation stop mechanism 1 also includes:
[0048] The rotating base 12; the rotating base 12 is a U-shaped structure, the bottom end of the rotating base 12 is fixed on the yaw frame 3, and the side wall of the rotating base 12 is provided with two opposite through holes;
[0049] Rotating shaft 15; the rotating shaft 15 has an L-shaped structure, the first end of the rotating shaft 15 passes through a through hole, the first end of the lock tongue 13 and the other through hole in turn, and the second end of the lock tongue 13 is used to match the lock buckle 111 For locking, the first end of the deadbolt 13 is placed in the notch of the rotating base 12 , and the first end of the deadbolt 13 is fixedly connected to the rotating shaft 15 through a plurality of pins 14 .
[0050] The setting of rotating base 12 can be convenient for t...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3, such as figure 2 and image 3 Shown:
[0052] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 2 is that each group of rotation stop mechanism 1 also includes:
[0053] Mounting plate 11; the mounting plate 11 is fixedly connected to the first end of the rotating shaft 15, and the measuring head of the proximity displacement sensor is installed on the mounting plate 11;
[0054] Sensor seat 110; the sensor seat 110 is fixedly installed on the yaw frame 3, the body of the proximity displacement sensor is installed on the sensor seat 110, and the body of the proximity displacement sensor matches the probe position of the proximity displacement sensor; when the dead bolt When 13 is stuck in the buckle 111, the body of the proximity displacement sensor approaches the probe of the proximity displacement sensor, and the probe of the proximity displacement sensor detects the signal of the body of the proximity displacement sensor; When 111 was disengaged, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com