A multi-path routing method based on link lifetime and energy consumption prediction
A time-to-live and multi-path technology, applied in the field of the Internet of Things, can solve problems such as large energy consumption, prolonged average end-to-end time, and short network life time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
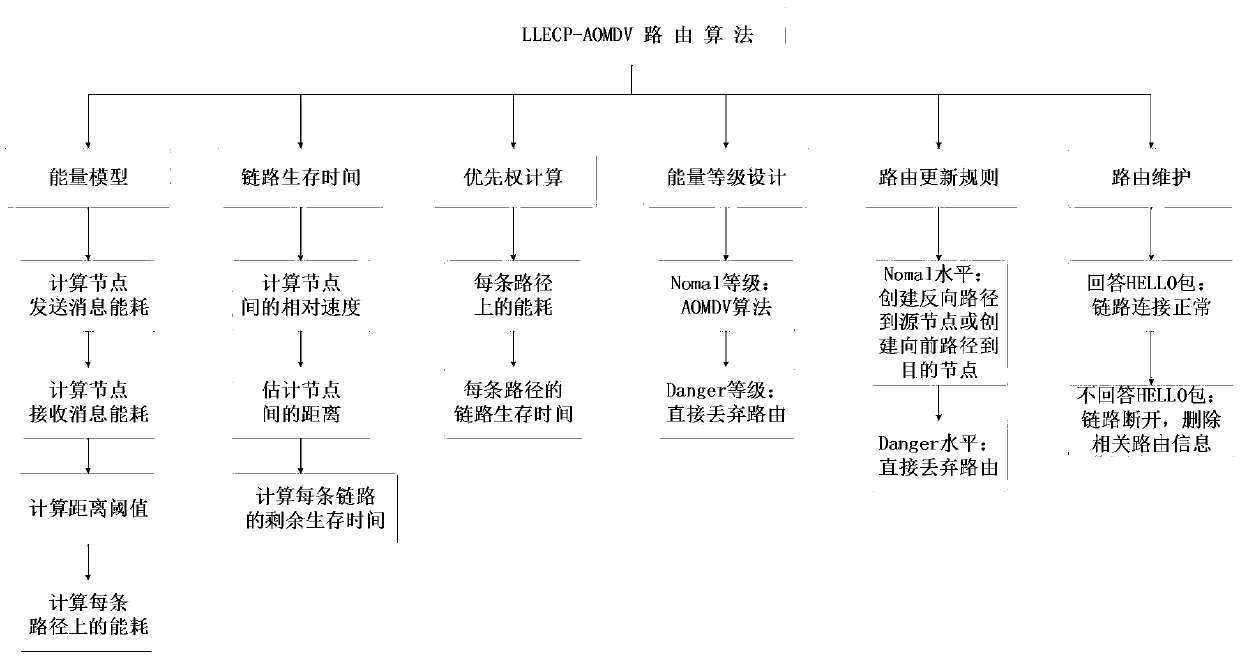
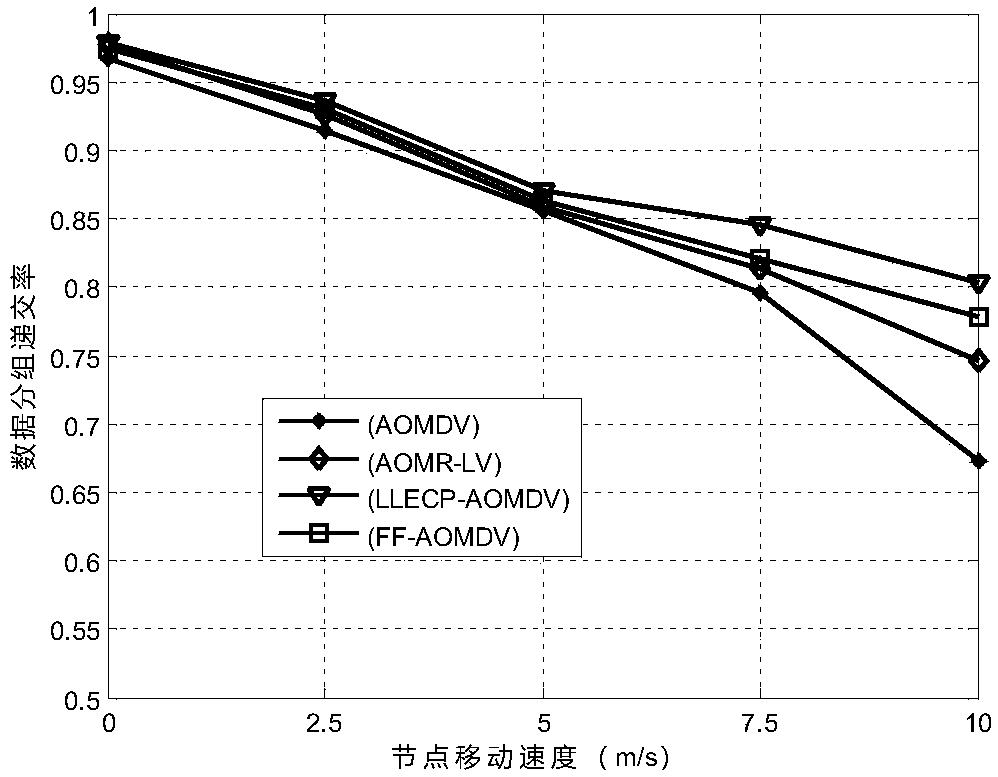
[0036] The method designed in this embodiment uses the NS-2 platform to carry out simulation experiments on this method. The method was compared with AOMDV, AOMR-LV and FF-AOMDV methods. In different data packet sizes, different node speeds and different simulation times, the simulation experiments are carried out on the data packet delivery rate, average end-to-end delay and energy consumption between nodes, and the LLECP-AOMDV method is analyzed in network survival time and energy consumption. and average end-to-end delay. See attached figure 1 , the specific implementation process is detailed as follows:
[0037] 1. Priority path selection strategy:
[0038] In step 1.1 of the present invention, an energy consumption model of a node is established.
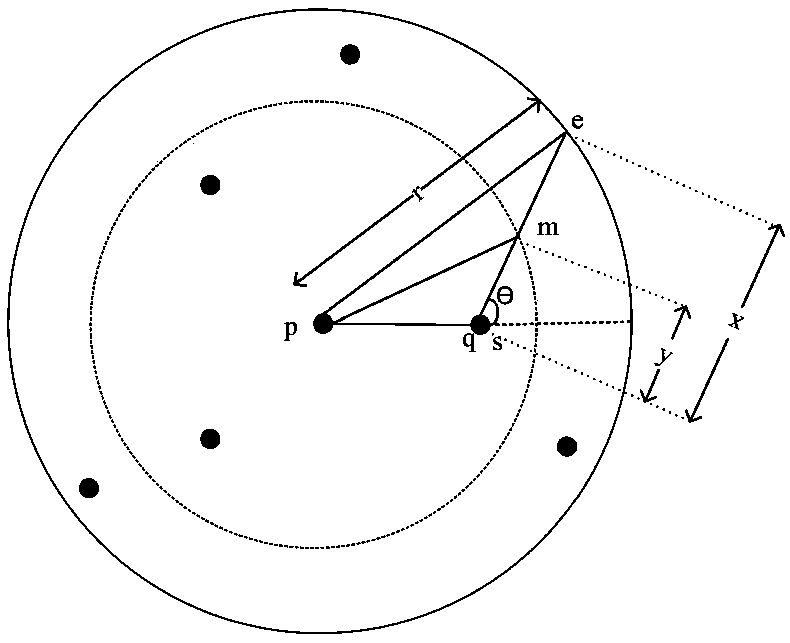
[0039] In MANET, once the energy of a node is exhausted, the link will be broken, so the lifetime of the link is directly related to the energy of the node, and the choice of routing path should take the energy consumption ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com