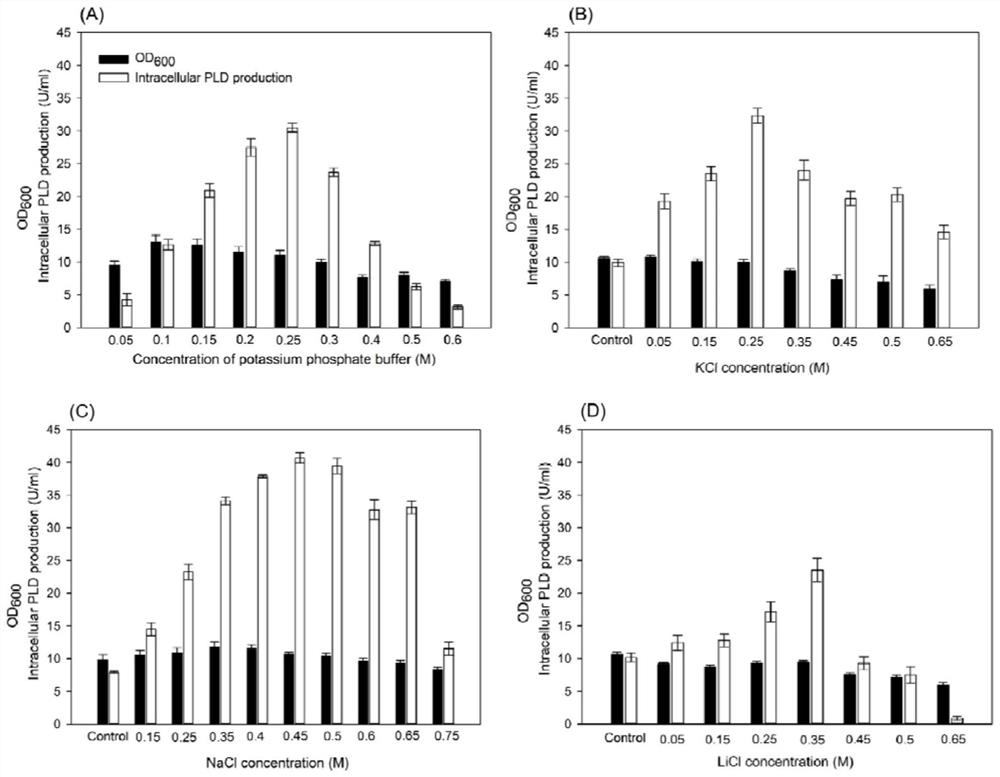
A method for producing phospholipase D by recombinant Escherichia coli
A technology of recombinant Escherichia coli and phospholipase, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of short synthesis time, cytotoxicity, cell lysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1. Construction of recombinant bacteria TOP10 / pBADKP-PLD
[0039] Using the plasmid pUC57-par (containing the par region sequence of pSC101 shown in SEQ ID No.1) as a template, by primer 1 and primer 2 (Table 1), the par sequence was amplified by PCR; to contain the arabinose promoter P BAD The plasmid pBADK was used as a template, and the plasmid pBADK backbone was amplified by PCR with primers 3 and 4 (Table 1); the par sequence and pBADK backbone obtained by the above two amplifications were used as primers and templates, respectively, for POE-PCR, and the product was directly Transformed into E.coli DH5α, colony PCR verification and sequencing, to obtain the vector pBADKP; the plasmid pUC57-PLD containing the codon-optimized Streptomycesantibioticus PLD gene sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2 and the vector pBADKP were passed through Nco I and Xba I double digestion, T4 ligase ligation, transformed into E.coli TOP10 (recA - ), the colony PCR was verified and ...
Embodiment 2
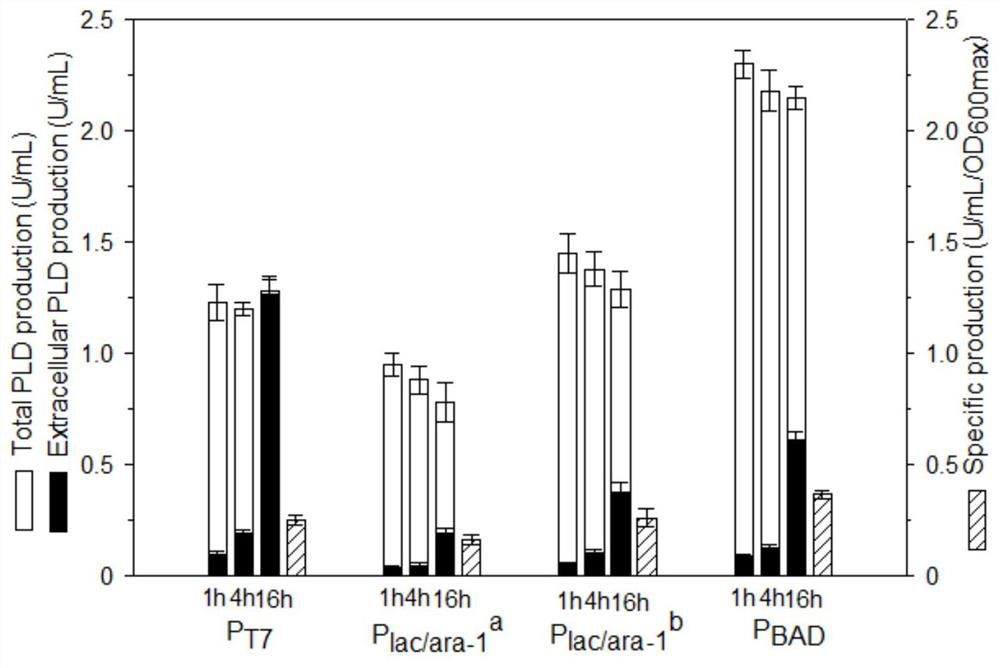
[0050] Example 2. Effect of promoter on phospholipase D expression.
[0051] Four promoters P T7 ,P lac / ara-1 a ,P lac / ara-1 b and P BAD It was used to investigate the expression of phospholipase D, and its activation strength decreased sequentially. where P lac / ara-1 a Partially activated by IPTG induction, P lac / ara-1 b Fully activated by IPTG and arabinose. Recombinant bacteria TOP10 / pBADKP-PLD was induced at 25°C for 16 hours, the results were as follows figure 1 shown. Under saturation induction, in the expression of PLD, P lac / ara-1 b and P BAD better than P T7 and P lac / ara-1 a , where P BAD Produces maximum PLD enzyme activity and specific yield. During the induction process, the PLD enzyme activities under all promoters almost reached the maximum after 1 hour of induction; after 16 hours of induction, the proportions of extracellular enzyme activities were 100%, 25%, 34% and 26%, respectively; process, the increase of extracellular enzyme activity ...
Embodiment 3
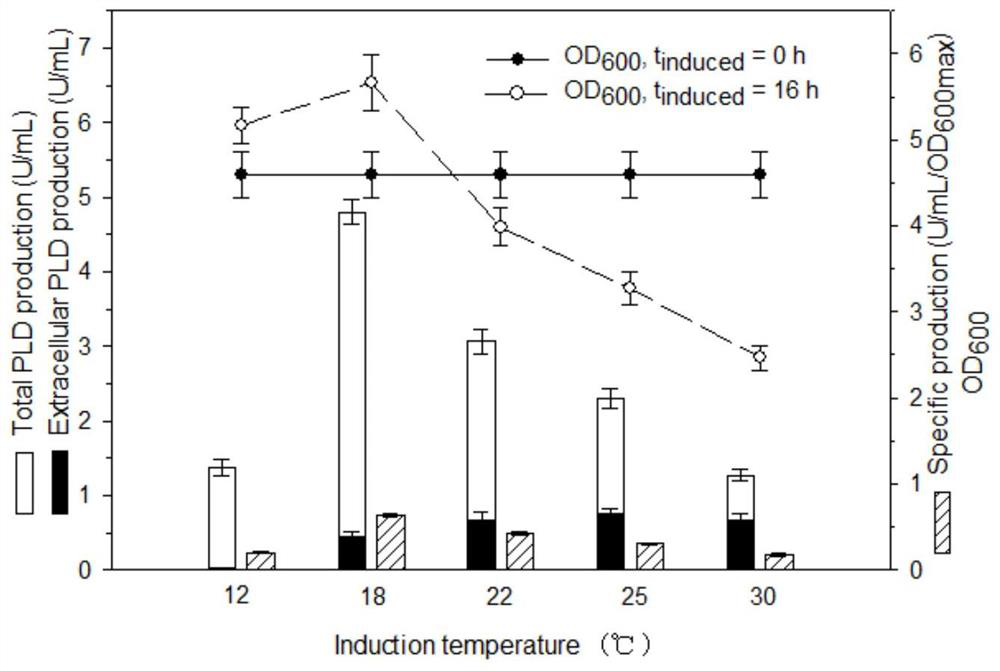
[0052] Example 3. Effect of Induction Temperature on Cell Growth and Phospholipase D Expression
[0053] In this experiment, TOP10 / pBADKP-PLD was cultured in TB medium at 37°C to OD 600 5 to 6, and then at 12°C, 18°C, 22°C, 25°C, 30°C and 37°C, respectively, to induce expression for 16 hours, and investigate the effect of induction temperature on the expression of PLD and biomass of TOP10 / pBADKP-PLD, the results are as follows figure 2 shown. Induction temperature significantly affected the expression of PLD and cell growth. The expression level was higher at 16-22°C, and the highest expression level appeared at 18°C. The specific productivity at 18°C was 3.8 times that at 30°C, and 92% of PLD appeared in the cell. Meanwhile, when the temperature was greater than 18°C, the expression of PLD decreased. The cell growth was significantly better at a moderate low temperature than at a high temperature, which reflected that a certain low temperature weakened the toxicity of P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com