MOS transistor driver circuit
A drive circuit and MOS tube technology, applied in electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of slow switching speed of IGBT drive circuit, poor electrical isolation performance of MOS tube rapid shutdown, and prone to false triggering, etc., to achieve Enhanced anti-interference characteristics, easy development and use, and fast switching speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
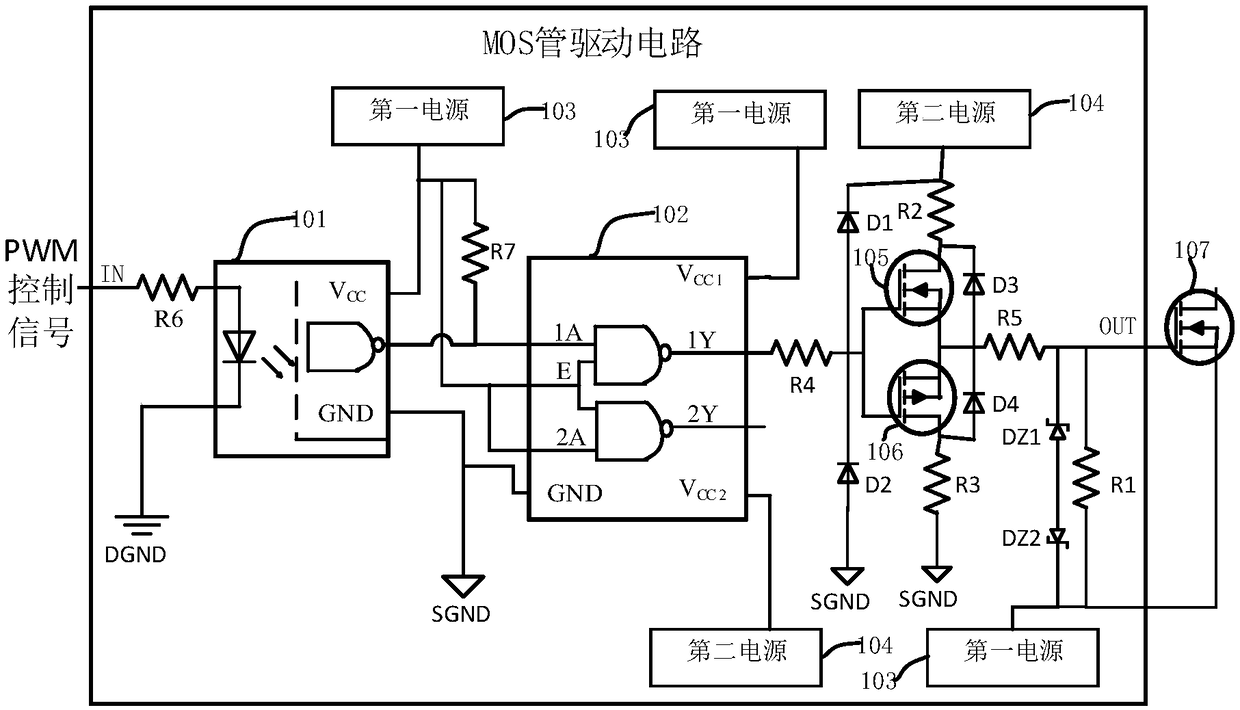
[0021] The MOS transistor drive circuit of this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, the driving circuit is used to drive the target NMOS transistor 107. The driving circuit includes a photocoupler 101, a level driver 102, an NMOS transistor 105, a PMOS transistor 106, and a first resistor R1. The photocoupler 101 The anode is connected to the PWM control signal input end, the cathode is grounded, the collector of the optocoupler 101 is respectively connected to the input end of the level driver 102 and the first power supply 103, and the emitter of the optocoupler 101 is grounded. The output terminals of the level driver 102 are respectively connected to the gate of the NMOS transistor 105 and the gate of the PMOS transistor 106, the drain of the NMOS transistor 105 is connected to the second power supply 104, and the PMOS transistor 106 The drain of the NMOS transistor 105, the source of the PMOS transistor 106, and one end of the first resistor R1 are all connected to the...
Embodiment 2
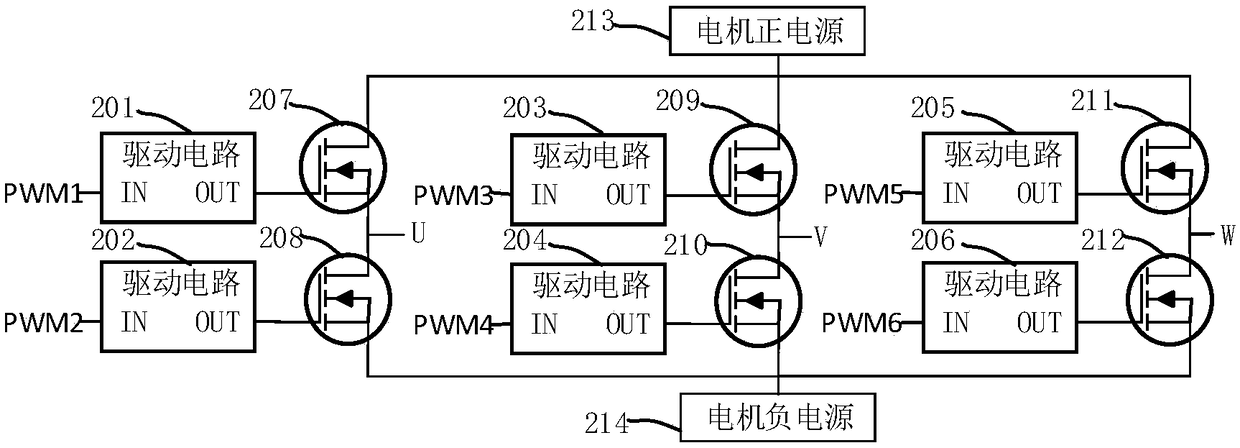
[0039] In this embodiment, six MOS transistor driving circuits as in Embodiment 1 are used to drive six target NMOS transistors, thereby forming a driving circuit capable of driving a three-phase motor. Such as figure 2 As shown, the drive circuits 201-206 are the MOS transistor drive circuits of Embodiment 1, and the external PWM1-PWM6 control signals pass through the input terminals of the drive circuits 201-206 respectively (such as figure 2 IN shown) is input into the driving circuits 201-206, and then through the output terminals of the driving circuits 201-206 (such as figure 2 OUT shown) to respectively drive the target NMOS tubes 207-212, the motor positive power supply 213 and the motor negative power supply 214 provide power for the target NMOS tubes 207-212, and U, V, W are respectively connected to the U of the three-phase motor. phase, V phase, W phase. figure 2 In the above, for the sake of simplicity and clarity, the connection between the sources of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com