Stem cells expressing mesenchymal and neuronal markers, compositions thereof, and methods of preparation thereof
A composition and technology of dental pulp stem cells, applied in the field of neurological diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
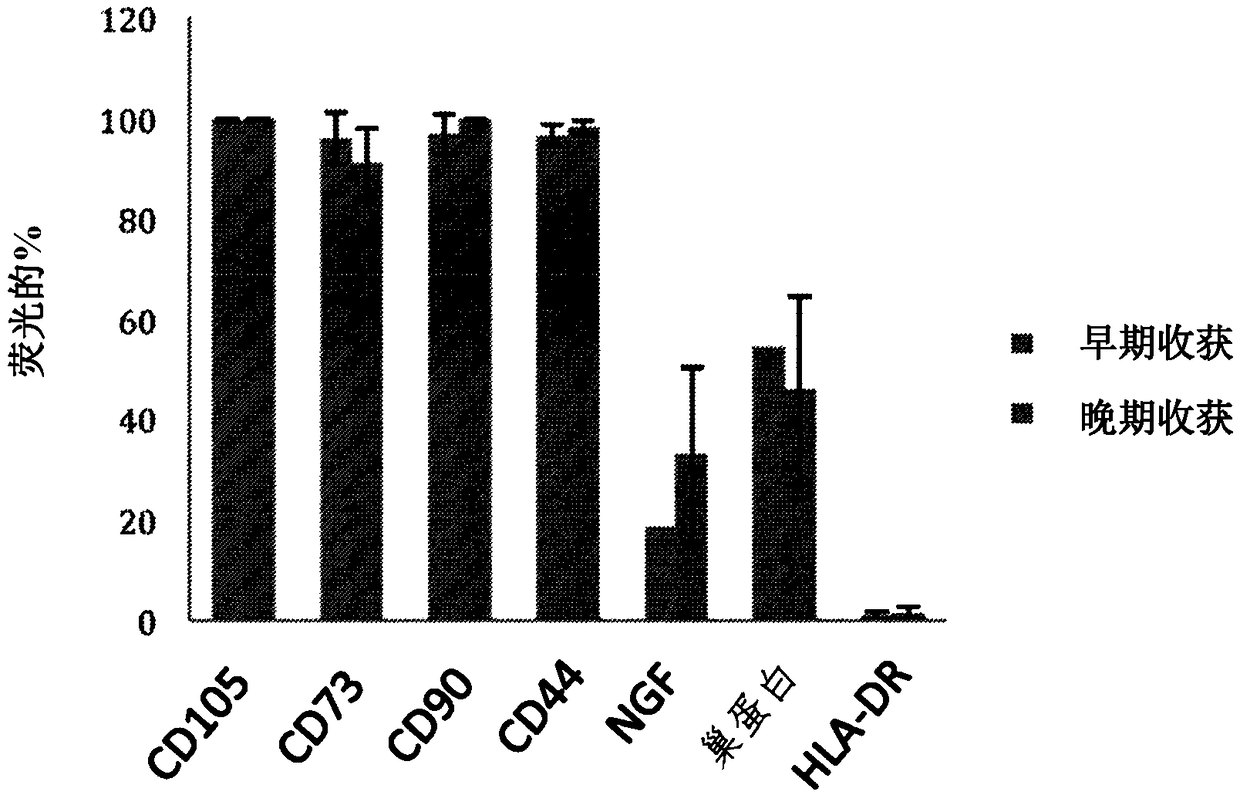
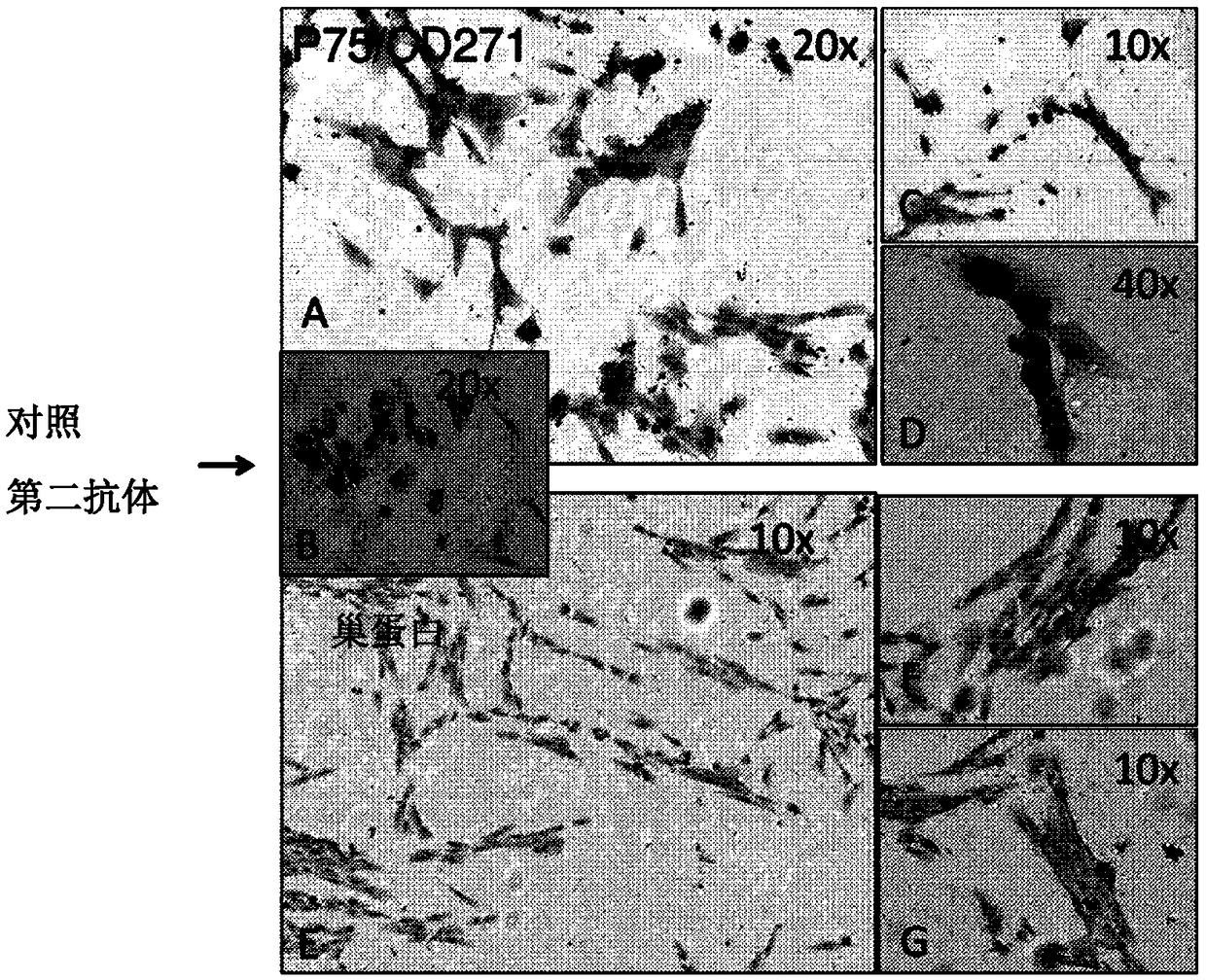
[0176] Example 1: Characterization of Early and Late Harvest IDPSCs and Derivation of Neural and Glial Cells from Early and Late Harvest IDPSCs
[0177] Characterization of Early and Late Harvest IDPSCs
[0178] To characterize hIDPSC properties, early (n=8) and late (n=4) harvests (Table 1) were harvested for flow cytometric analysis of mesenchymal markers CD13, CD105, CD73, CD90, CD44. Using 2×10 5 cells for FACS experiments. Cells were washed twice with PBS (without calcium and magnesium), and the tested antibodies were added for 15 minutes at room temperature. Cells were then washed twice with cold PBS and analyzed by Becton-Dickinson flow cytometry. The fluorescence of PE(FL2), FITC(FL1), APC(FL4) was detected at emission wavelengths of 575nm, 53nm and 600nm, respectively.
[0179] Table 1. List of cells used in FACS experiments
[0180]
[0181] Cells from both early and late harvests expressed high levels of mesenchymal markers. Both populations are negative fo...
Embodiment 2
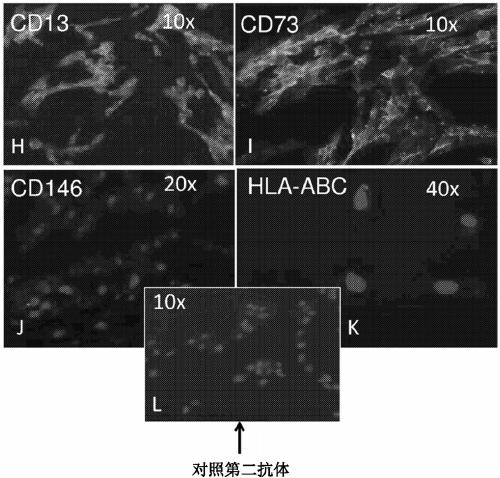
[0198] Example 2. Expression of CD146 and CD13 in early stage (EP) and late stage (LP) hIDPSCs
[0199] CD146 and CD13 expression was analyzed by flow cytometry in EP-hIDPSCs and LP-hIDPSCs. Figure 7 The results in showed that CD13 was expressed in 52% of EP-hIDPSCs and 95% of LP-hIDPSCs. These results suggest that in vitro DP harvest and hIDPSC passaging yields increased numbers of hIDPSCs expressing CD13 and lacking CD146 expression.
Embodiment 3
[0200] Comparison of embodiment 3.IDPSC and SHED
[0201] MSCs from different sources such as bone marrow and adipose tissue respond differently to different stimuli (Fraser JK et al., 2006). Culture conditions (eg, medium supplemented with human or fetal calf serum (FCS) or serum-free) may also affect the differentiation potential of MSCs even of the same origin (Lindroos et al., 2011; Lizier et al., 2012). Differences in differentiation efficiency likely largely reflect the heterogeneity of the MSC population (ie, the presence of different subpopulations) (Ho et al., 2008; Tormin et al., 2009; Mareddy et al., 2009; Rada et al., 2011). Different isolation and culture protocols used by different populations may explain the predominance of specific MSC subpopulations with different differentiation potential (Ho et al., 2008; Pevsner-Fischer et al., 2011; Rada et al., 2011).
[0202] SHED and IDPSC have different isolation methods and come from different stem cell niches. Ther...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com