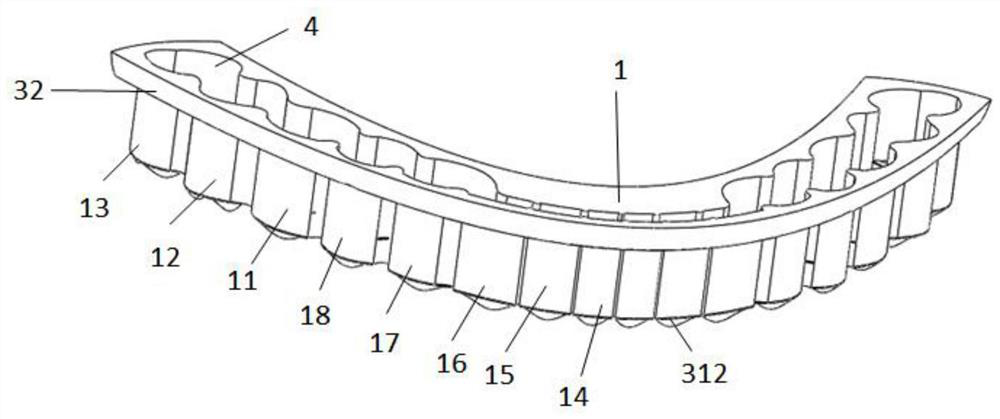
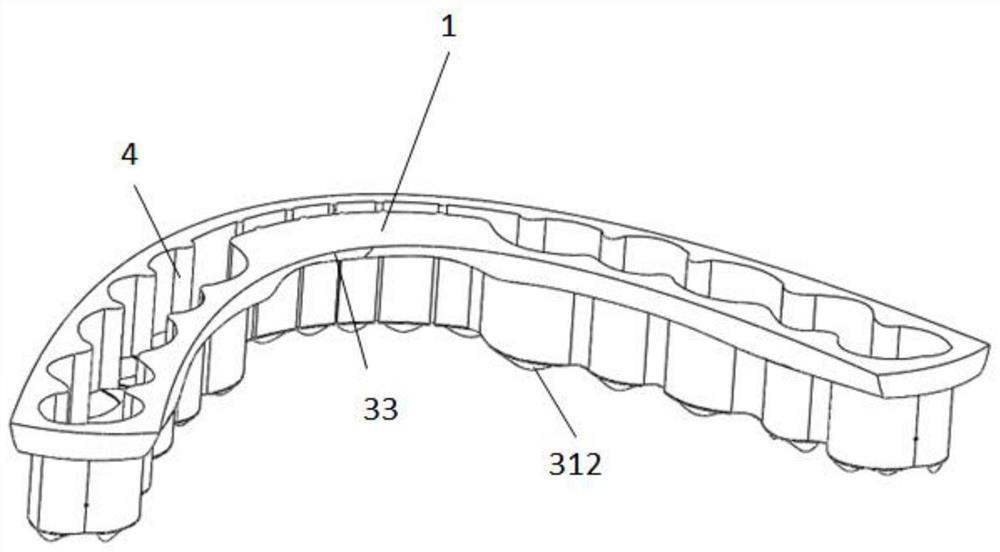
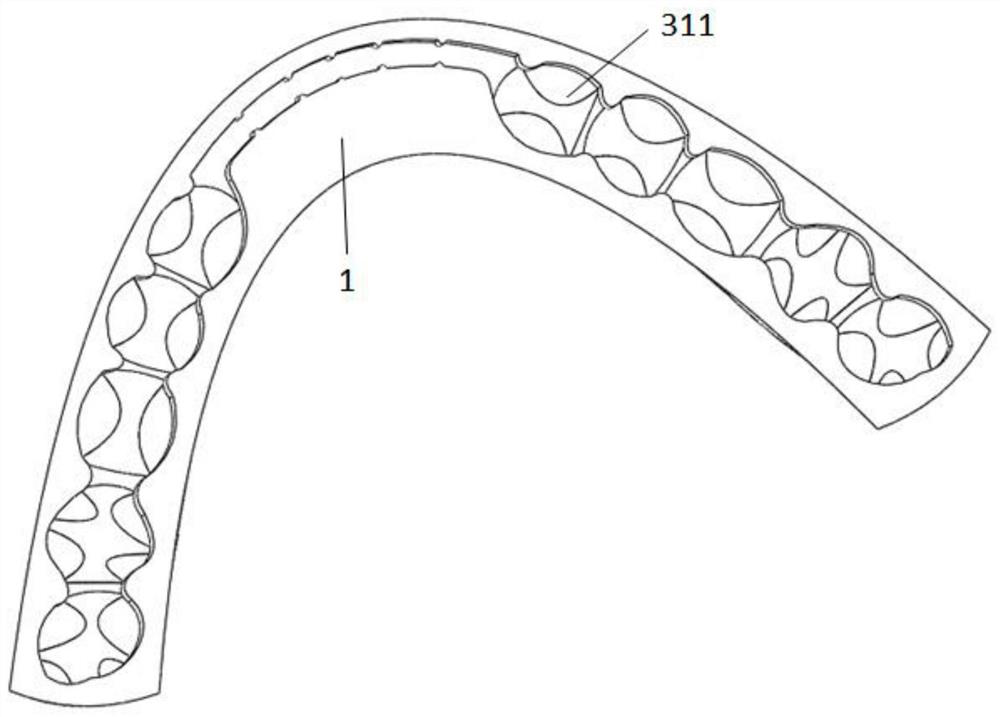
3D printed occlusal splint for the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders and its preparation method
A temporomandibular joint and 3D printing technology, which is applied in the field of oral cavity and medical equipment, can solve the problems of single design of treatment equipment, complex treatment procedures, and poor accuracy of equipment, and achieve a highly targeted, high-quality, simple and convenient use Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1 A preparation method of a 3D printed occlusal splint for the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders
[0067] A method for preparing a 3D printed occlusal splint for treating temporomandibular joint disorders, specifically:
[0068] (1) Data Acquisition and Processing
[0069] 1. Cone beam CT was used to shoot the patient's craniomaxillofacial; cone beam CT applied DICOM3.0 format, and the slice thickness was set to 1.25mm; the shooting range was from the supraorbital rim to the mandibular rim.
[0070] 2. Use a 3D scanner to scan the data of the maxillary dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusion of the upper and lower dentition; use a 3D scanner to scan the data of the upper dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusion of the upper and lower dentition. The range is: the scanning range of the maxillary dentition is the upper dentition including at least the entire tooth surface of two pairs of symmetrical molars and the upper palate; the scanni...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2 A preparation method of a 3D printed occlusal splint for the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders
[0081] A method for preparing a 3D printed occlusal splint for treating temporomandibular joint disorders, specifically:
[0082] (1) Data Acquisition and Processing
[0083] 3. Use cone beam CT to shoot the patient's craniomaxillofacial; cone beam CT uses DICOM3.0 format, and the slice thickness is set to 1.25mm; the shooting range is from the upper orbital edge to the lower edge of the mandible
[0084] 4. Use a 3D scanner to scan the data of the maxillary dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusal dentition; use a 3D scanner to scan the data of the upper dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusion of the upper and lower dentition. The range is: the scanning range of the mandibular dentition is the entire tooth surface of the teeth corresponding to the upper dentition; the scanning range of the upper and lower dentition is the outer surface of...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Example 3 A preparation method of a 3D printed occlusal splint for the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders
[0097] A method for preparing a 3D printed occlusal splint for treating temporomandibular joint disorders, specifically:
[0098] (1) Data Acquisition and Processing
[0099]5. Use cone-beam CT to shoot the patient's craniomaxillofacial; cone-beam CT uses DICOM3.0 format, and the slice thickness is set to 1.25mm; the shooting range is from the upper orbital edge to the lower edge of the mandible
[0100] 6. Use a three-dimensional scanner to scan the data of the maxillary dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusal dentition respectively; use a 3D scanner to scan the data of the upper dentition, mandibular dentition, and occlusion of the upper and lower dentition respectively The scope is: when the upper and lower dentition are occlusal, the scanning range is the outer surface of the upper and lower dentition; the 3D scanner is Smartoptics, 3shape o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com