Duck plague virus ge gene seamless deletion strain dpv CHv-ΔgE and its construction method
A duck plague virus and construction method technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as residual bases and residual MiniF elements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1 Preparation of duck plague virus gE gene traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE
[0052] Duck plague virus gE gene traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE, its construction method comprises the following steps:
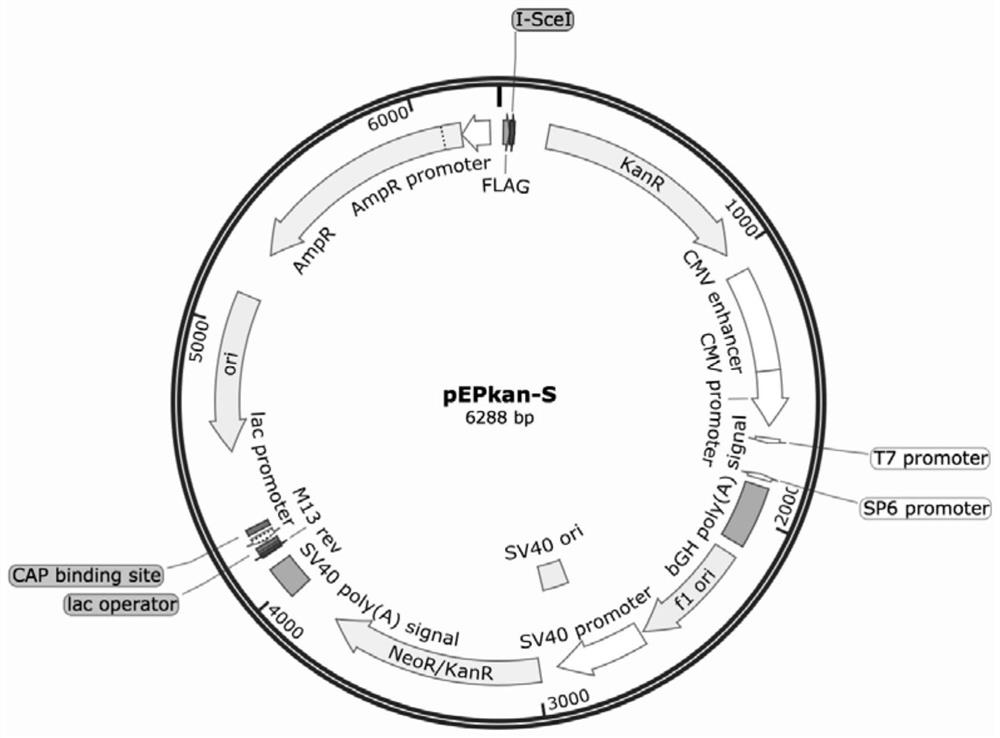
[0053] 1. Prepare GS1783 electroporation competent, electrotransform pBAC-DPV plasmid
[0054] (1) Escherichia coli with pBAC-DPV plasmid was revived in LB solid medium containing chloramphenicol, cultured overnight at 37°C; single colonies were inoculated in LB liquid medium containing chloramphenicol, and cultivated overnight at 37°C;
[0055] (2) Extract the pBAC-DPV plasmid according to the operating instructions of the QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kit;
[0056] (3) Resuscitate GS1783 frozen-preserved bacteria in LB solid medium, culture overnight at 30°C;
[0057] (4) Pick a single colony of GS1783 and inoculate it in 5 mL of LB liquid medium, and culture it overnight at 30°C to obtain a seed solution;
[0058] (5) Add 5mL seed liquid to 100mL LB liquid m...
Embodiment 2
[0160] Example 2 Detection of virus quantity after inoculation of 7-day-old ducks with traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE
[0161] The gE gene and MiniF element traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE was inoculated into DEF cells at 0.01 MOI, and the cells were collected 120 hours after inoculation, frozen and thawed twice, and TCID was determined 50 Afterwards, 7-day-old ducks were inoculated with 2MOI of DPV CHv-ΔgE deletion virus, and the blood, liver, and spleen of the ducks were collected at 24h, 48h, 72h, and 96h respectively, and the tissues were extracted according to the instructions of TaKaRa MiniBEST ViralRNA / DNA Extraction Kit Ver.5.0 DNA. Use identification primers gE-F and gE-R to carry out PCR amplification to detect whether the duck liver virus is a gE gene deletion virus 48 hours after challenge, use UL30QPCR to identify primers and Taq probes, and QPCR to detect blood, liver and spleen at different time points virus count. The results showed that DPV CHv-Δg...
Embodiment 3
[0162] The determination of the growth curve of DPV CHv-ΔgE of embodiment 3 traceless deletion strain
[0163] 1. Determination of one-step growth curve
[0164] The parental virus DPV CHv and the gE gene traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE were inoculated into DEF cells at 2 MOI respectively, and the supernatant and cells were collected 6h, 12h, 18h, and 24h after inoculation, and each time point was repeated three times. After the collection was complete, the freeze-thaw was repeated twice, and the virus titer was detected in a 96-well plate. The results showed that the deletion of the gE gene would not significantly affect the replication of the DPV CHv virus.
[0165] 2. Determination of multi-step growth curve
[0166] The parental virus DPV CHv and gE gene traceless deletion strain DPV CHv-ΔgE were inoculated into DEF cells at 0.01 MOI respectively, and the supernatant and cells were collected 12h, 24h, 48h, and 72h after inoculation, and each time point was repeated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com