A colorimetric assay for ascorbic acid based on degradable nanozymes
An ascorbic acid and nano-enzyme technology, which is used in material analysis by observing the effect on chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of using cost advantages and portability advantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
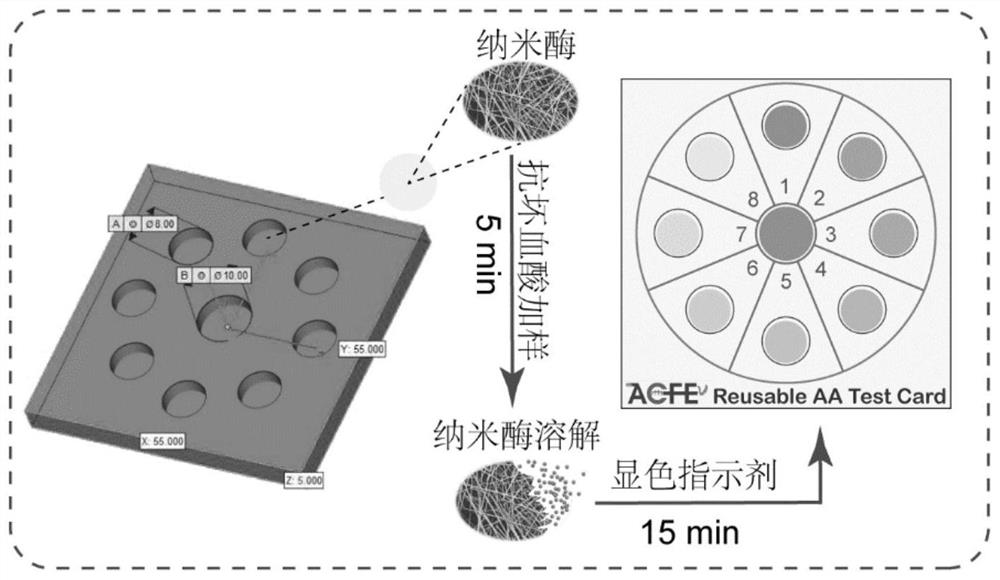
[0039] (1) Use cellulose filter paper to prepare a circular test paper piece with a diameter of 0.6 cm, and fully soak it in an aqueous solution of manganese oxyhydroxide (MnOOH) nanowires at a concentration of 10 μg / mL, then take out the test paper piece, and take it out after 15 minutes The test paper sheet was vacuum-dried for 6 hours, and then stored in a sealed container at room temperature to prepare a degradable nano-enzyme test paper sheet;
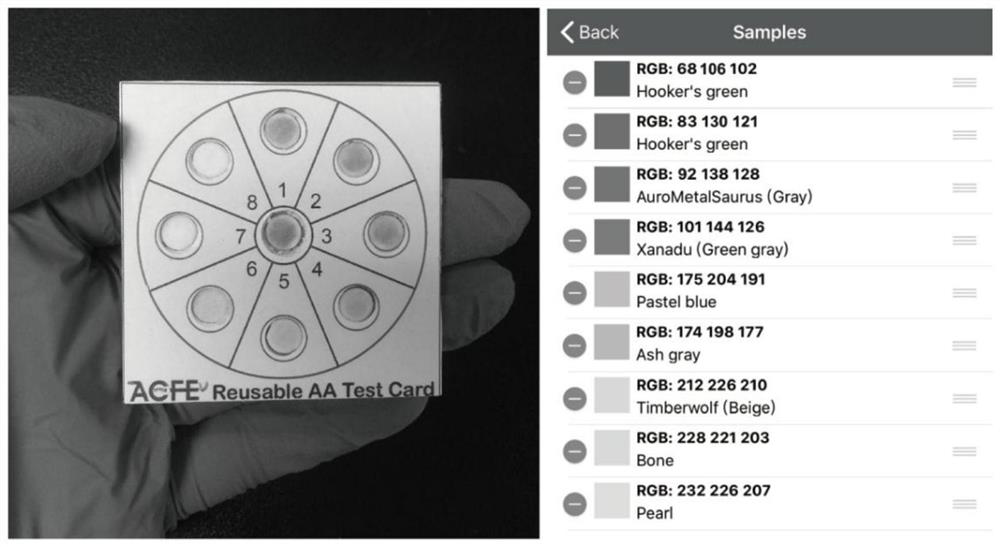
[0040] (2) Prepare 8 sample grooves (diameter 8mm, groove depth 1.5mm) and 1 blank control groove (diameter 10mm, groove depth 1.5mm) on the substrate, and embed the degradable nanozyme test paper made by S1 into In the sample slot of the substrate, the detection card is obtained;
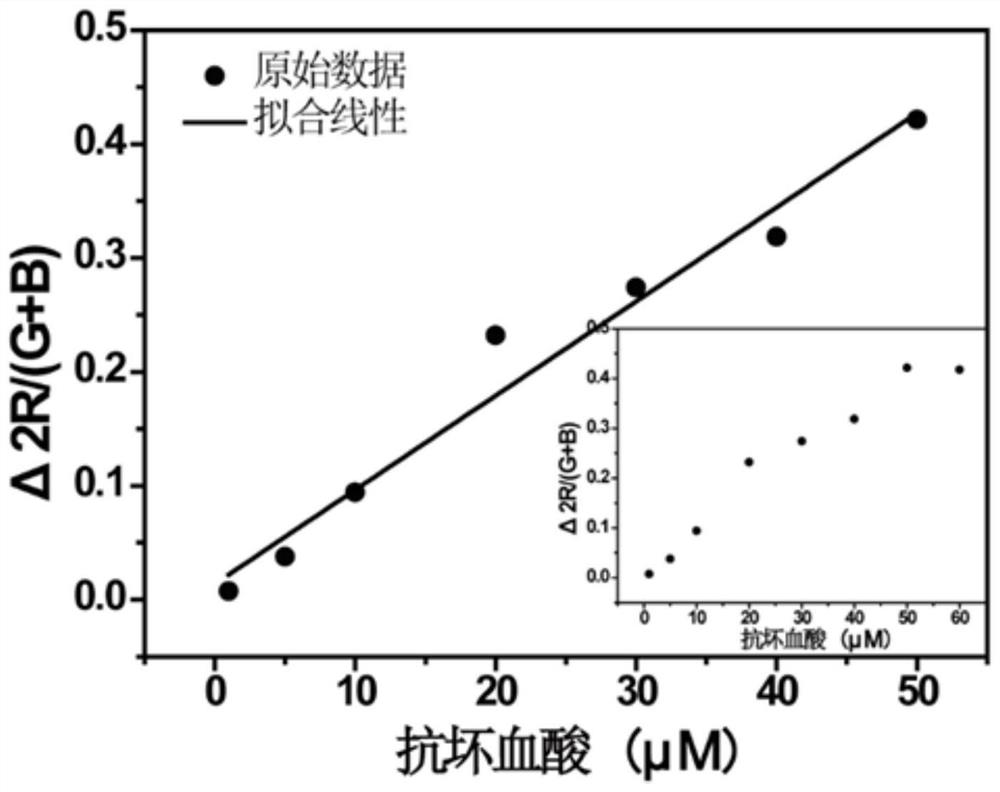
[0041] (3) Ascorbic acid solutions with concentrations of 1 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM, 30 μM, 40 μM, 50 μM and 60 μM were respectively prepared and added dropwise to the sample slots of the test card prepared in S2, and the dropping amount was 10 μL for e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com