Ground fault point positioning method and device for rail transit traction auxiliary converter
A technology for auxiliary converters and ground faults, which is applied in the field of rail transit, can solve problems such as complex internal structures, equipment loss, and heavy workload, and achieve the goals of improving operational safety and reliability, avoiding serious damage, and improving maintenance efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0070] In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present application clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present application. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of the embodiments of this application, not all of them. Based on the embodiments in this application, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of this application.
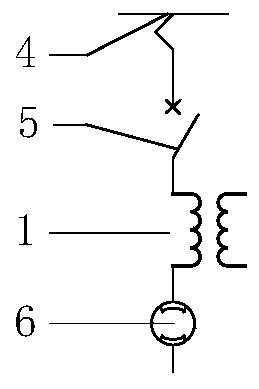
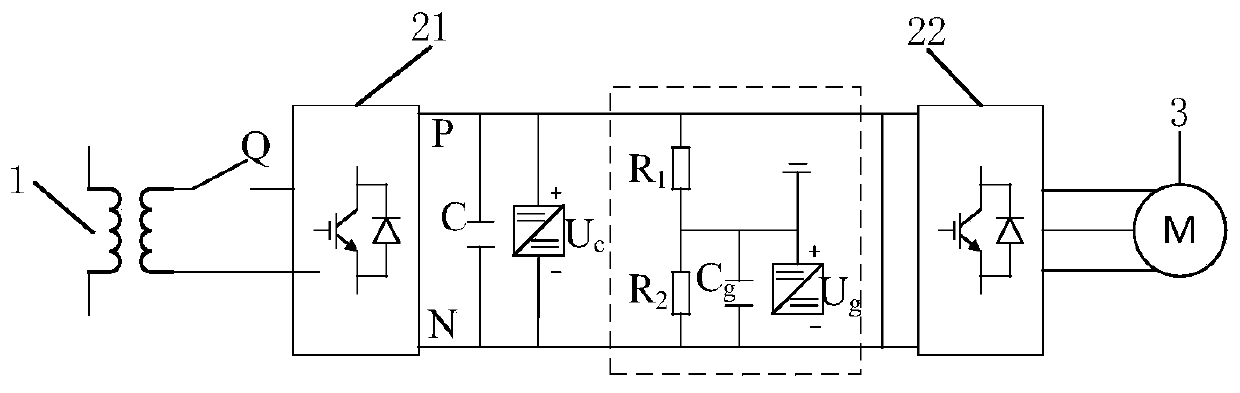
[0071] Considering that the traditional ground detection method of traction auxiliary converter does not have the function of automatically locating the ground fault point, and because the internal structure of the converter is complex and there are many components, manual troubleshooting is cumbersome; For transformers, if the ground fault cannot be quickly l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com