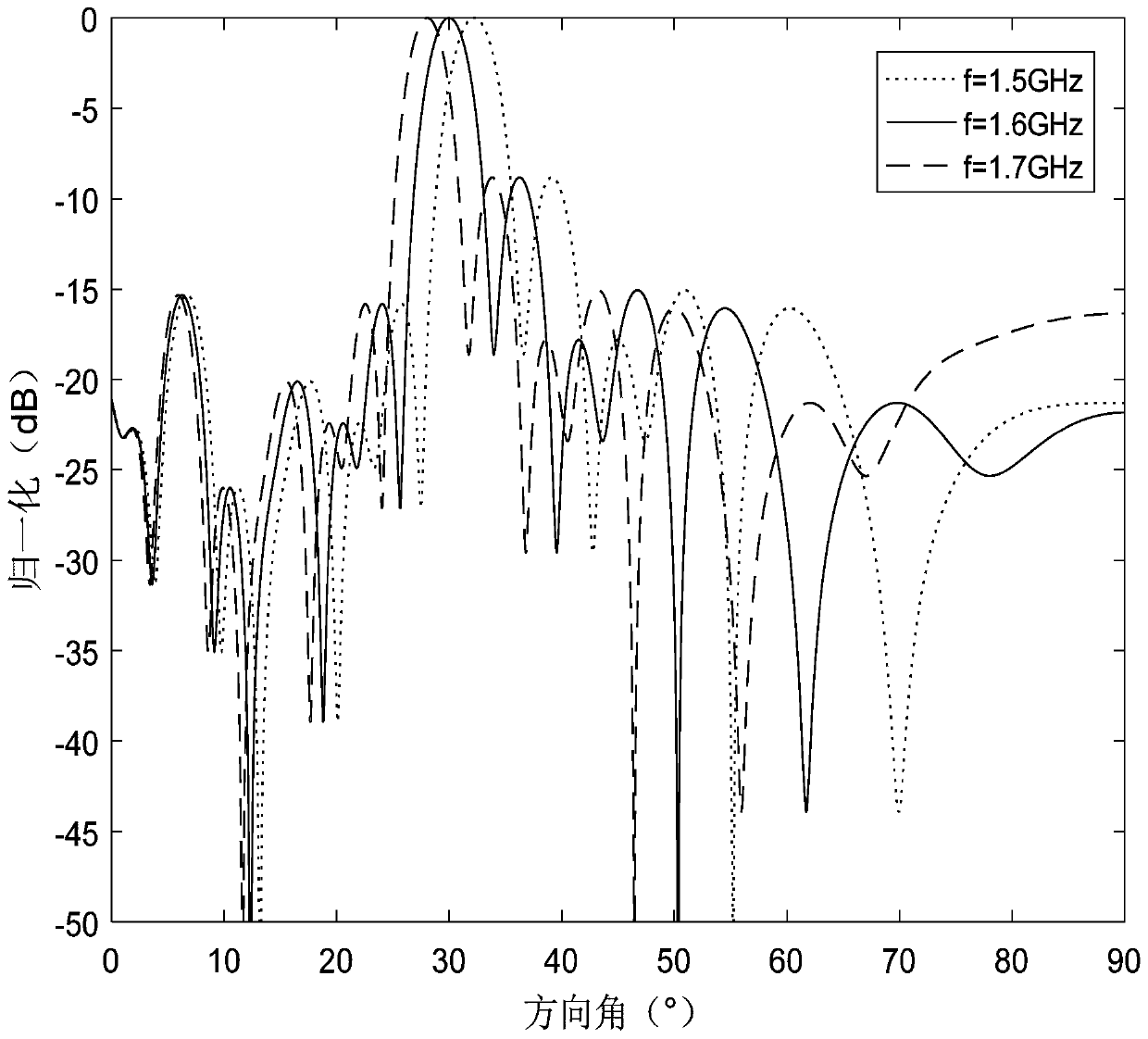
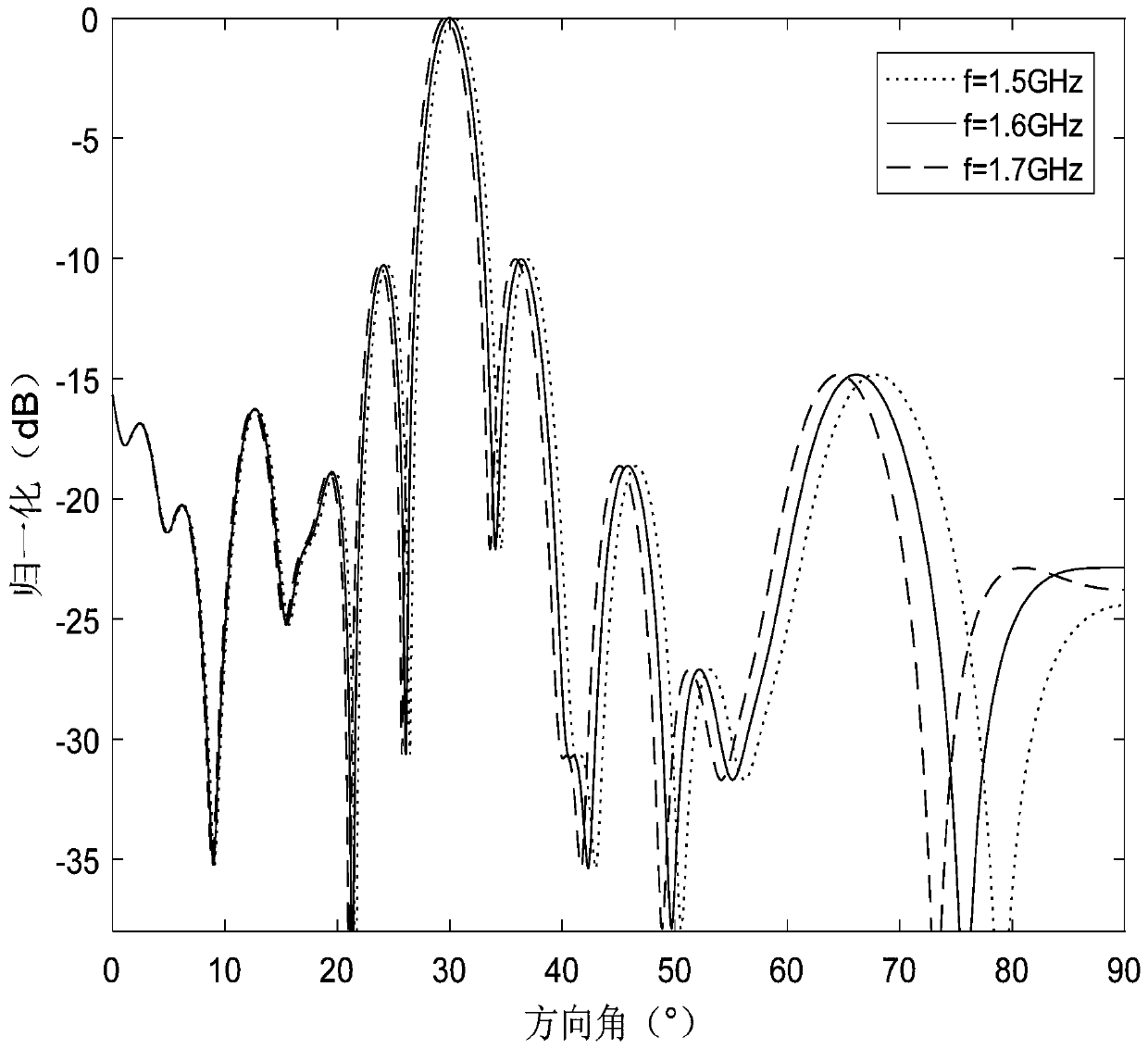
Design method for forming an optimal weight by self-adaptive wave beams of a uniform-power broadband signal
An adaptive beam and broadband signal technology, applied in wireless communication, space transmit diversity, network planning, etc., can solve the problem of large pointing error of pattern beam pointing and adaptive interference suppression, and achieve improved interference nulling and good correction effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] Specific implementation mode 1: The specific process of the design method for the optimal weight value of the adaptive beamforming of the uniform power broadband signal in this implementation mode is as follows:
[0021] Step 1. Construct the expression of uniform power broadband signal in any array;
[0022] Step 2, applying the expression of the uniform power broadband signal in the arbitrary array in the step 1 to the uniform linear phased array to obtain the covariance matrix of the useful signal, the interference signal and the noise signal;
[0023] Step 3: Substituting the covariance matrix of useful signal, interference signal, and noise signal obtained in step 2 into the linearly constrained minimum variance criterion to obtain optimal adaptive weights.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that in the step one, the expression of the uniform power broadband signal in any array is constructed; the specific process is:
[0025] Suppose the source of the uniform power broadband signal is s(t), the bandwidth of the uniform power broadband signal is B, and the center frequency of the uniform power broadband signal is f 0 , and the power spectral density of s(t) obeys the uniform distribution, that is, the power spectral density function of the signal s(t) is p s (f);
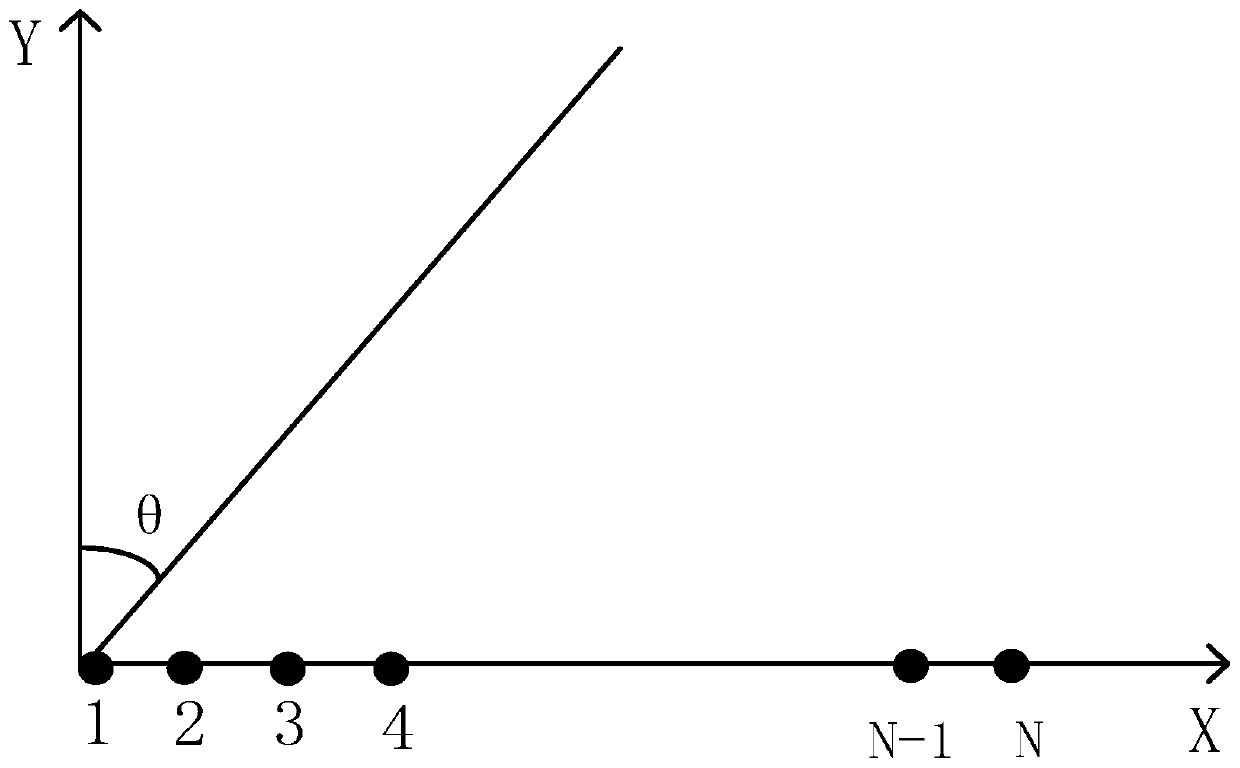
[0026] Assume that there are N array elements in an array (this array can be any array, an array of uniform power spectral density broadband signals), the first array element is located at the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system, and the coordinates of any array element in the array can be expressed as z i =(x i ,y i ),
[0027] where i=1,2,...,N,x i is the abscissa of the array element, y i...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the power spectral density function p of the signal s(t) s (f) The expression is:
[0045]
[0046] Among them, t is the time variable, p s (f) is the power spectral density function of the signal s(t), f is the frequency variable, and p is the power spectral density of the signal s(t).
[0047] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com