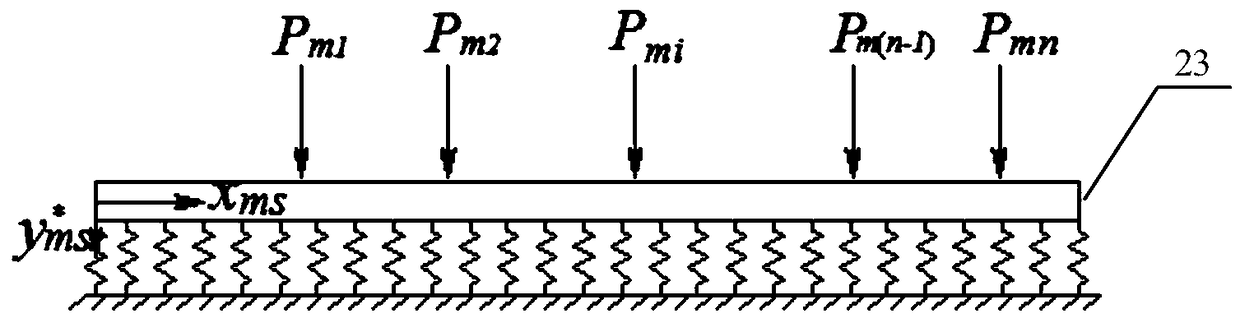
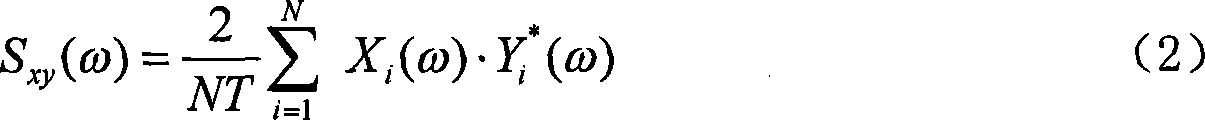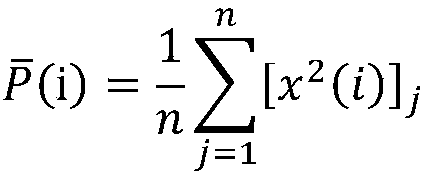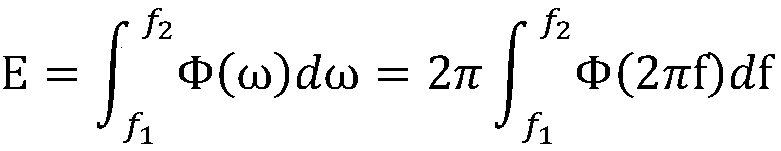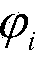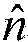Patents
Literature
121 results about "Spectral density function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
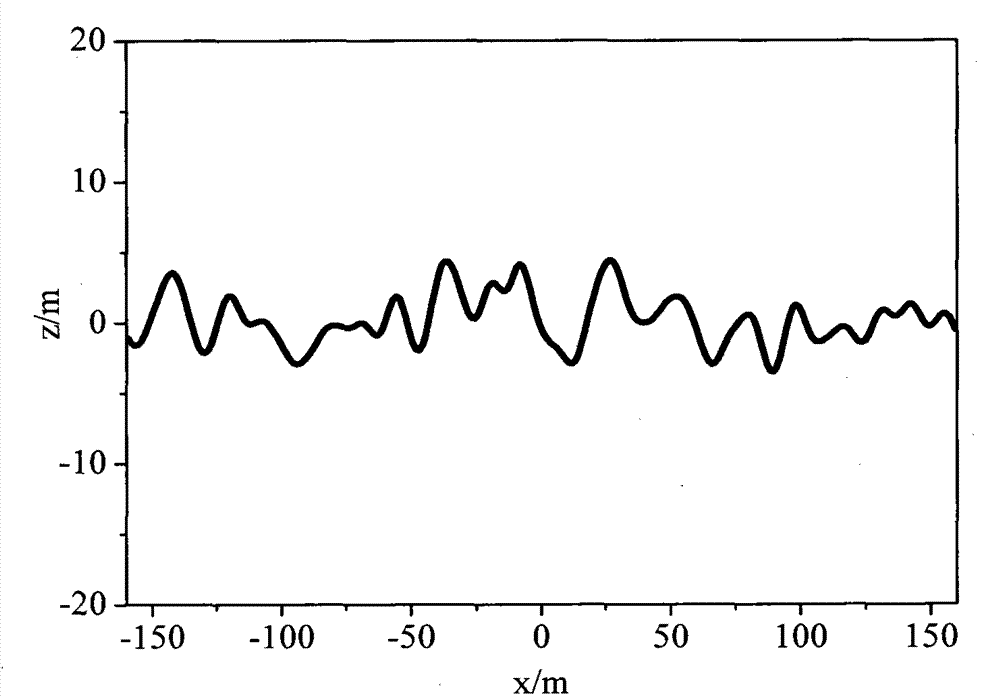
The Power Spectral Density (PSD) function is useful in analyzing surface roughness. This function provides a representation of the amplitude of a surface’s roughness as a function of the spatial frequency of the roughness. Spatial frequency is the inverse of the wavelength of the roughness features.
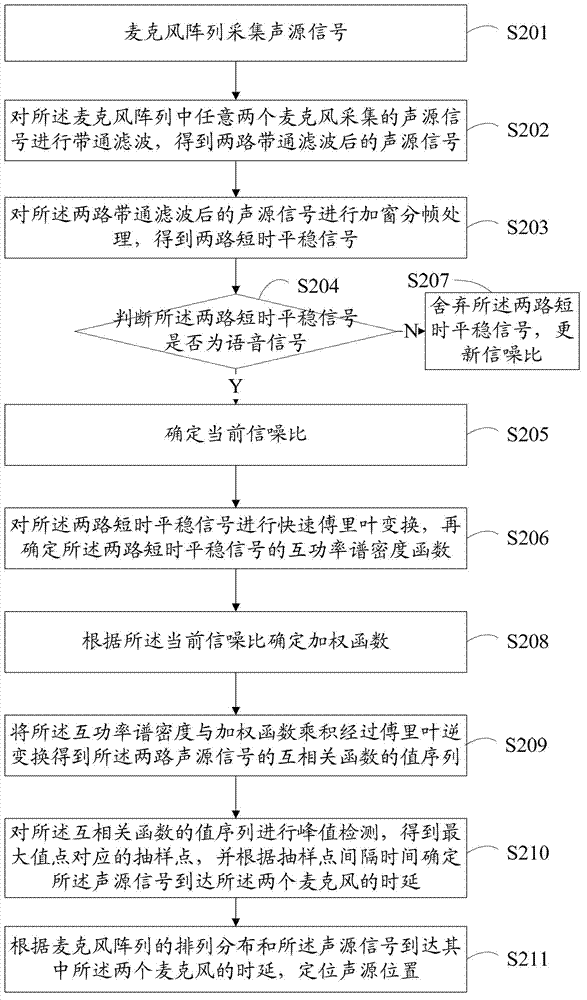
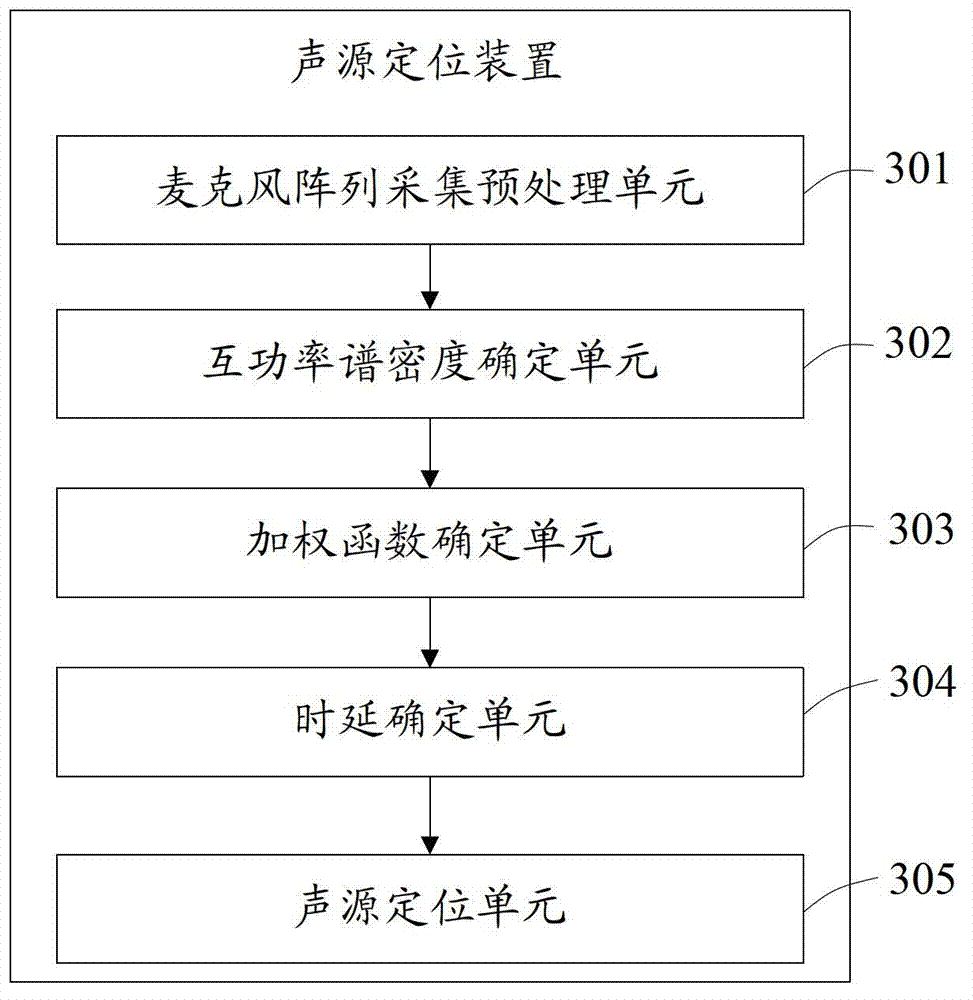
Sound source locating method and device
ActiveCN102854494AHigh positioning accuracyGet Accurate LatencyPosition fixationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Sound sources
The invention is suitable for the technical field of sound processing and provides a sound source locating method and device. The method comprises the steps of: collecting sound source signals by utilizing a microphone array and preprocessing the sound source signals collected by any two microphones; confirming a cross-power spectral density function of the two sound source signals; confirming a weighting function adjusted along with the variation of the present signal to noise ratio; confirming a sequence of values of the cross-correlation function of the two sound source signals according to the cross-power spectral density function and the weighting function; confirming the time delay of the sound source singles to two microphones according to the maximum value of the cross-correlation function; and locating the sound source positions according to the permutation distribution of the microphone array and the time delay of the sound source signals to the any two microphones. According to the method and the device, the adopted weighting function can be correspondingly adjusted along with the variation of the present signal to noise ratio to ensure that under the environment that the signal to noise ratio of a sound source is changed, the time delay of the sound source can be accurately obtained through correspondingly adjusting the weighting function, and therefore, the sound source locating accuracy is improved.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
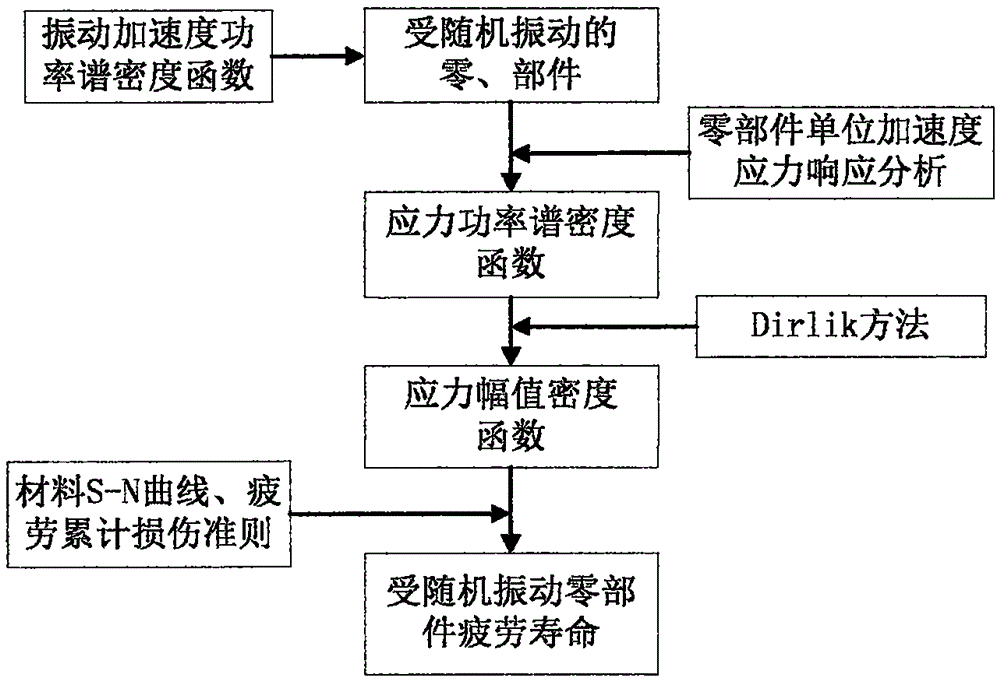
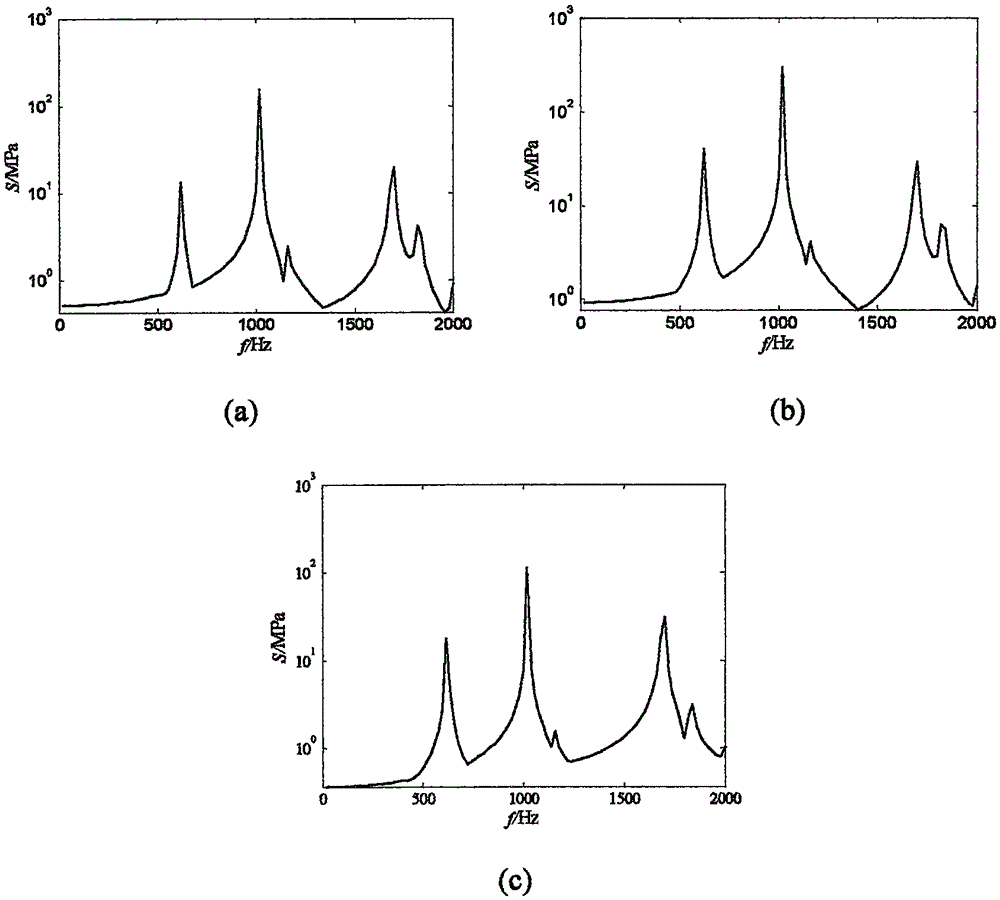
Analysis method for testing fatigue life of components based on vibration signals
InactiveCN105651478ASolve the problem that it is difficult to directly obtain structural stress amplitude informationExtended service lifeVibration testingLoad timeEngineering
Owner:QINGDAO R & D INST XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Acquiring system eigenfunction and signal feature value method
InactiveCN101158623AStructural/machines measurementFrequency analysisFourier transform on finite groupsCurve fitting
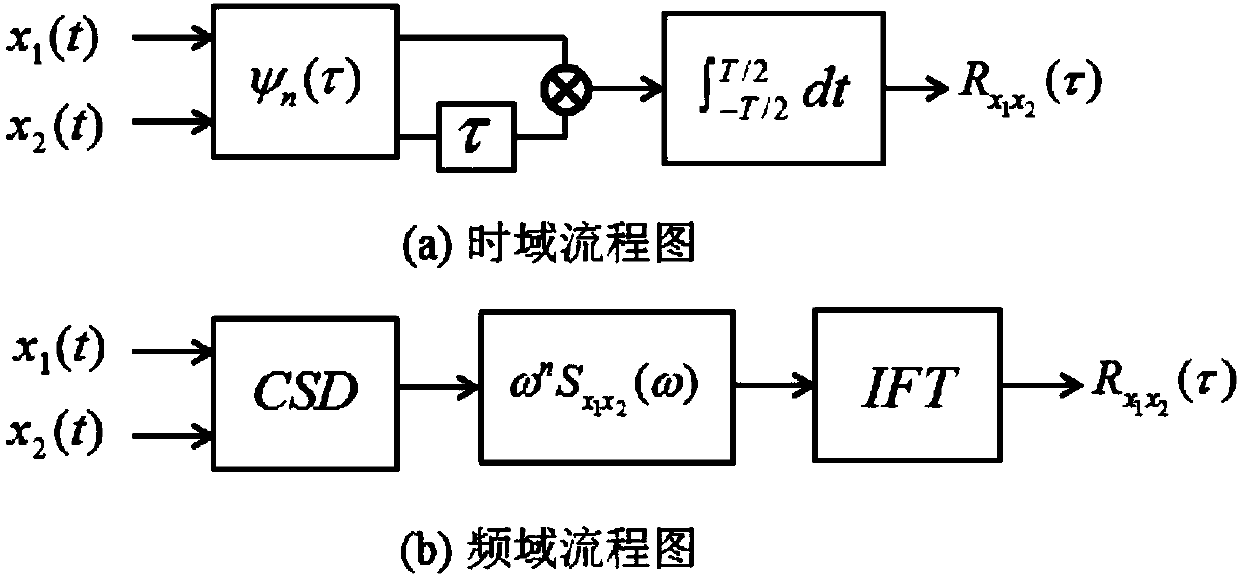
A method of catching systematic eigenfunctions and signal eigenvalues under the condition of only response output available belongs to the parametric recognition technique in dynamic test field. The technique is a method of adopting cross spectral density functions of each response point instead of frequency response functions to perform time-frequency filtering and the parametric recognition of frequency domain, and includes the following steps: (1) carrying out analytic calculation of the cross spectral density functions of different metering signal of output points; (2) analyzing and calculating the nonorthogonal wavelets in the time-frequency domain according to the cross spectral calculating result; (3) inversing the fourier transformation to gain the time-frequency analyse coefficient; (4) adding a rectangular window to perform the time-frequency filtering; (5) calculating the cross spectrum of the output signal after filtering as the systematic function for recognition; (6) performing curvefitting to obtain the systematic parameter; the technique improves the recognition precision of the systematic parameters, precisely recognizes modal parameters, is simple and convenient, and is suitable for the dynamic analyses, the performance verification and the failure diagnosis of large civil engineering establishments such as large and complex mechanical equipments under operation status, high-rise buildings, bridges, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
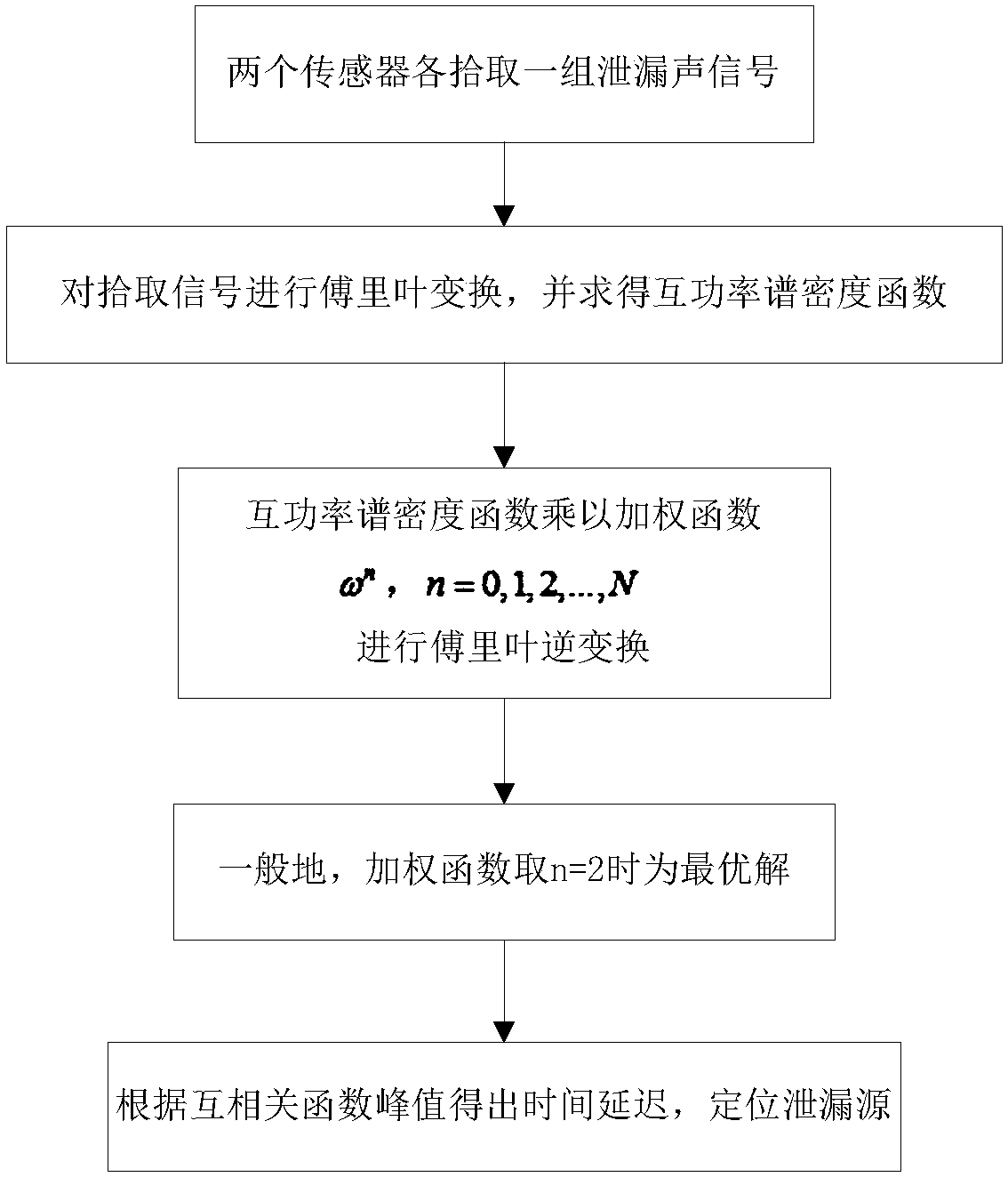
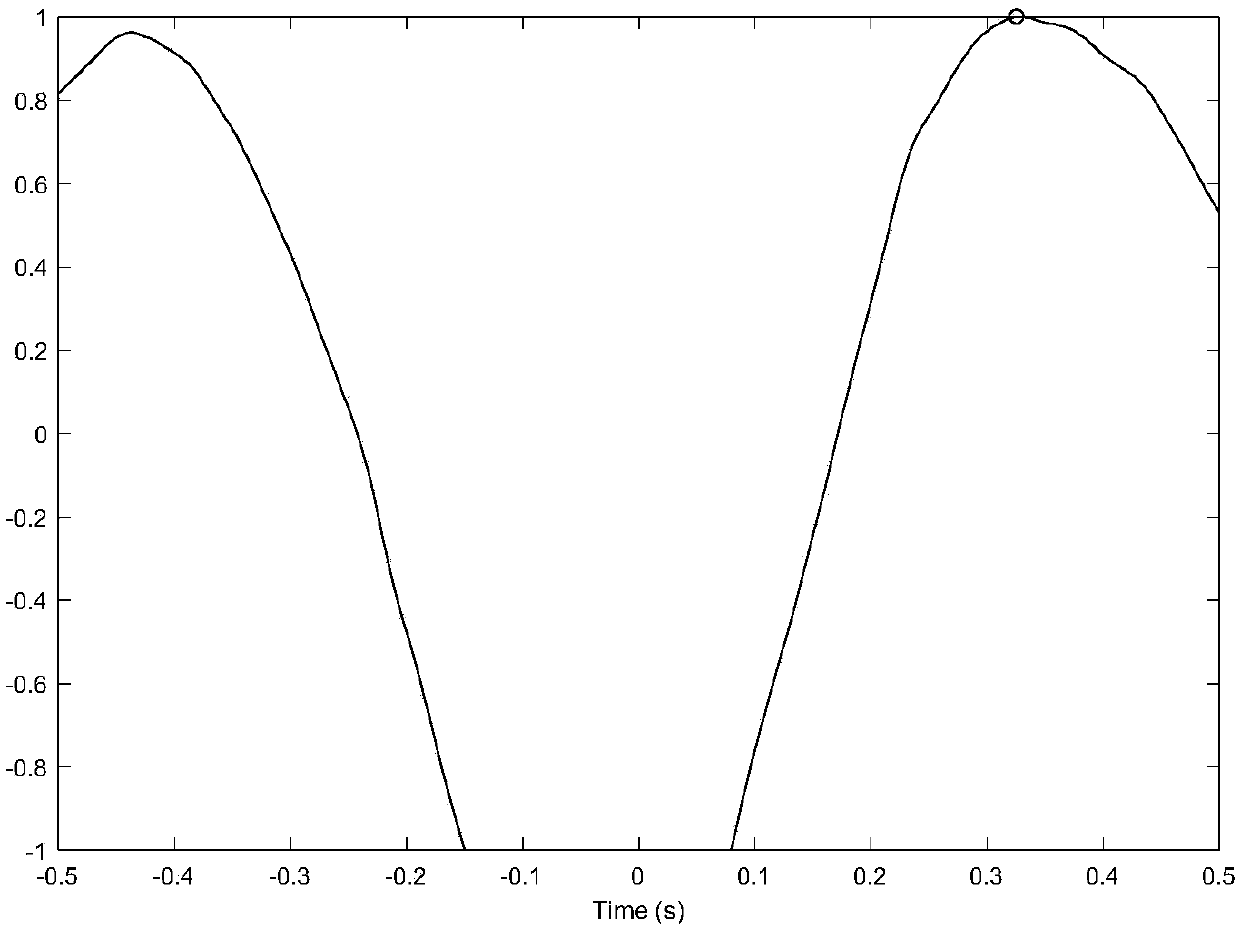
Pipeline leakage location method based on cross-correlation
ActiveCN108332063ALow professional knowledge requirementEasy to implementPipeline systemsHydrophoneTime domain
The invention discloses a pipeline leakage location method based on cross-correlation. The method is implemented on the basis of the following detection device: two sensors are mounted on a to-be-detected pipeline and are acceleration sensors or hydrophones; each sensor is connected with a data acquisition unit which is used for synchronously acquiring leak acoustic signals transmitted in a fluiddue to pipeline leakage. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring leak acoustic time-domain signals picked by the two sensors, and calculating a cross power spectral density function; weighting the cross power spectral density function, performing inverse Fourier transform to obtain a cross-correlation function, acquiring time delay estimation corresponding to a peak value of the cross-correlation function, and accordingly, reversely deriving the distance between a leak point and a first sensor with a location formula. According to the method, filtering processing is not needed forsensor signals, the influence of reflection can be eliminated effectively, and pipeline leakage can be located more accurately under complicated working conditions.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
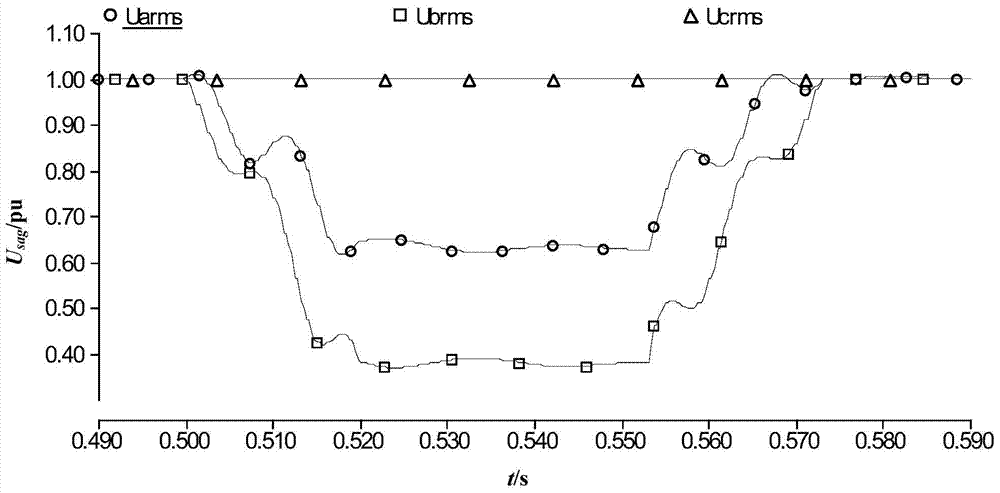
Method for identifying voltage sag reason
InactiveCN103578050AReduce the number of samplesGood effectData processing applicationsComplex mathematical operationsTime domainPower grid
The invention provides a method for identifying a voltage sag reason. The method for identifying the voltage sag reason comprises the following steps of (1) using the discrete Fourier transform to calculate a spectral density function, converting the voltage in a time domain to the voltage in a frequency domain, (2) calculating the characteristic quantity related to identification of the voltage sag reason, (3) defining a sag phase number N1, judging whether swell and a sag combination N3 exist or not, and (4) identifying the voltage sag reason. The method for identifying the voltage sag reason is comprehensive and higher in adaptability to changes of voltage sags, and can be easily improved, verification is carried out on the basis of really-measured data of a power grid, and the calculation result has better engineering practicability.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
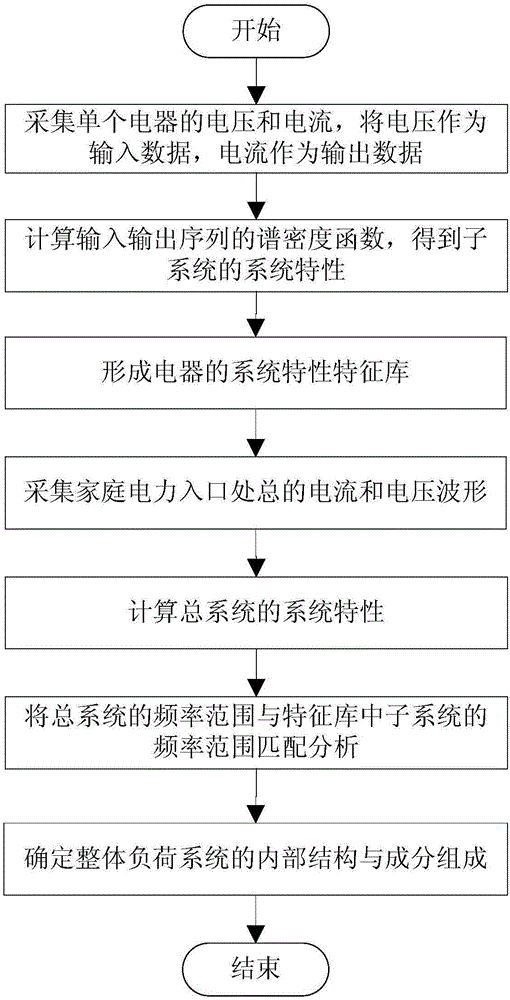
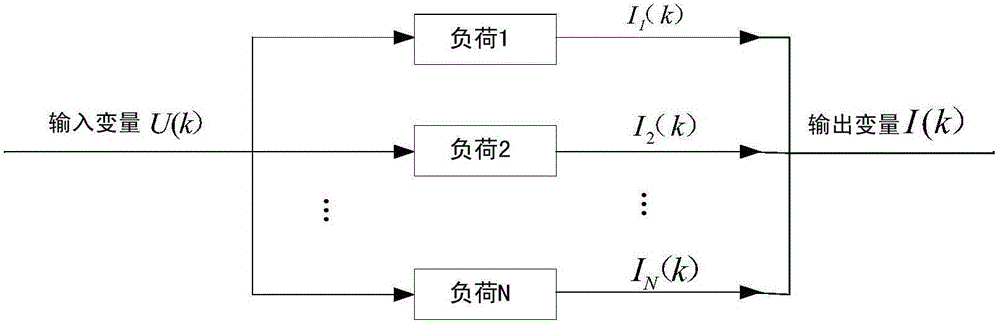
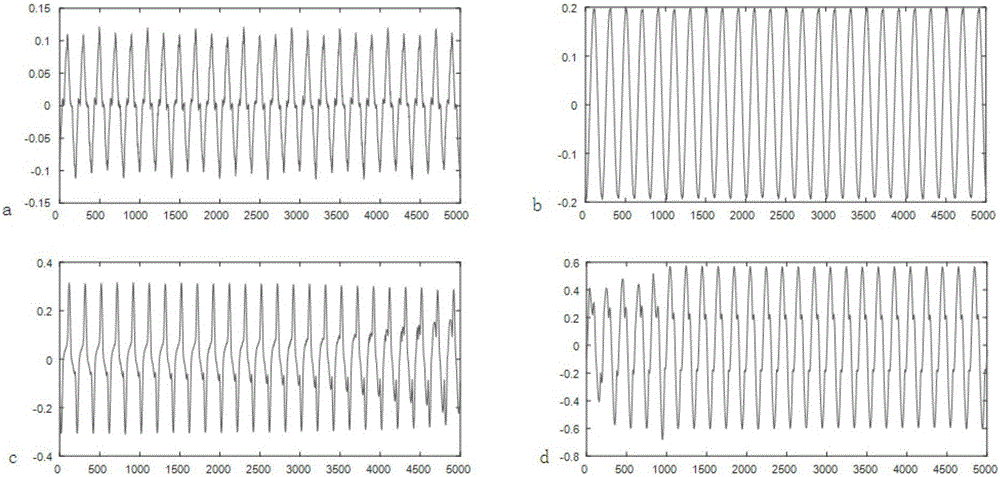
Non-intrusive household appliance identification method
InactiveCN106093630AImprove accuracyImprove recognition efficiencyElectrical testingPower flowEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power load identification, and in particular relates to a non-invasive household appliance identification method. Household appliance devices are taken as a separate system. Current and voltage waveforms of single household appliance are collected. Voltage is used as input data. Current is used as output data. The output response of the system under input action is measured. The spectral density function of input and output sequences is calculated to acquire the system characteristics of a sub system. The system characteristic feature library of household appliances is formed. General current and voltage waveforms at the entrance of household electric power are collected, and the system characteristics of the general system are calculated. Matching analysis is carried out on the frequency range of the frequency response of the general system and the frequency range of the frequency response of sub systems in the feature library to determine the internal structure and composition of the overall load system to realize the identification of household appliances. According to the invention, the kind of household appliances can be effectively identified through measured data, and the method has the advantages of simple algorithm and high accuracy, and is robust to dynamic fluctuation of load power.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and terminal device
InactiveCN108318129AImprove discrimination accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTerminal equipmentCorrelation function
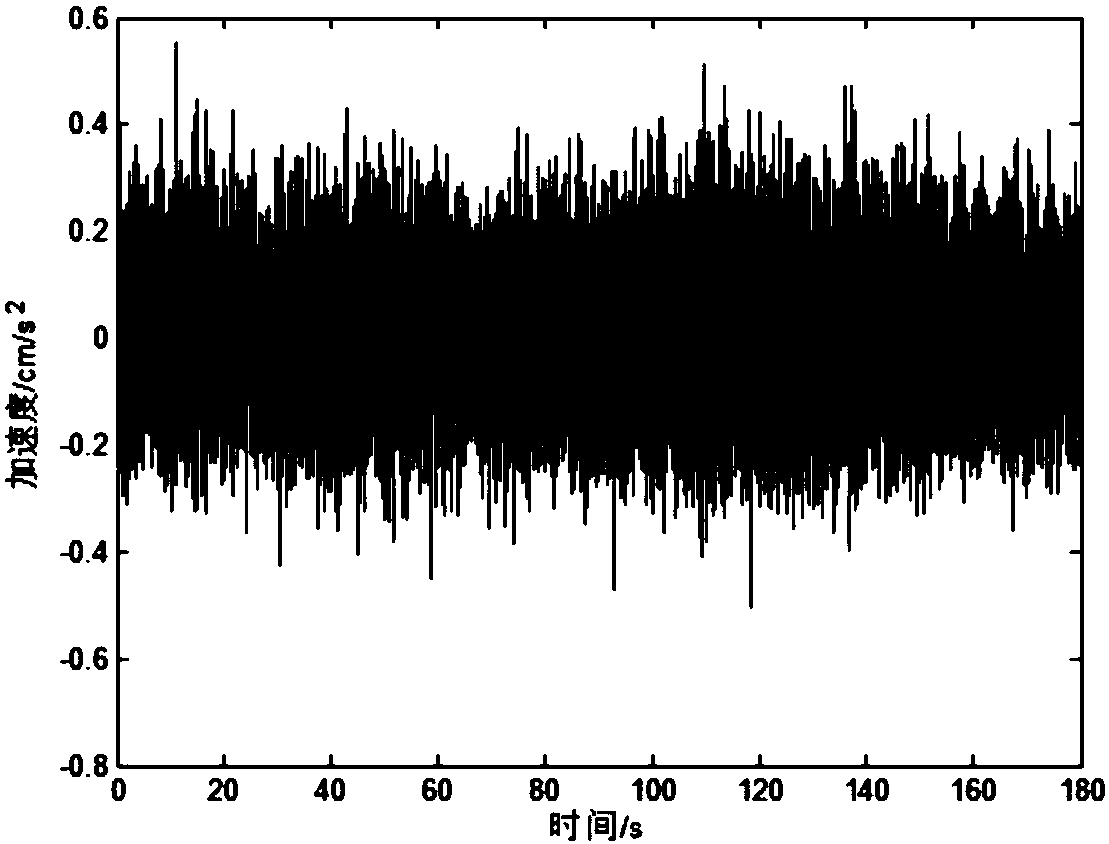
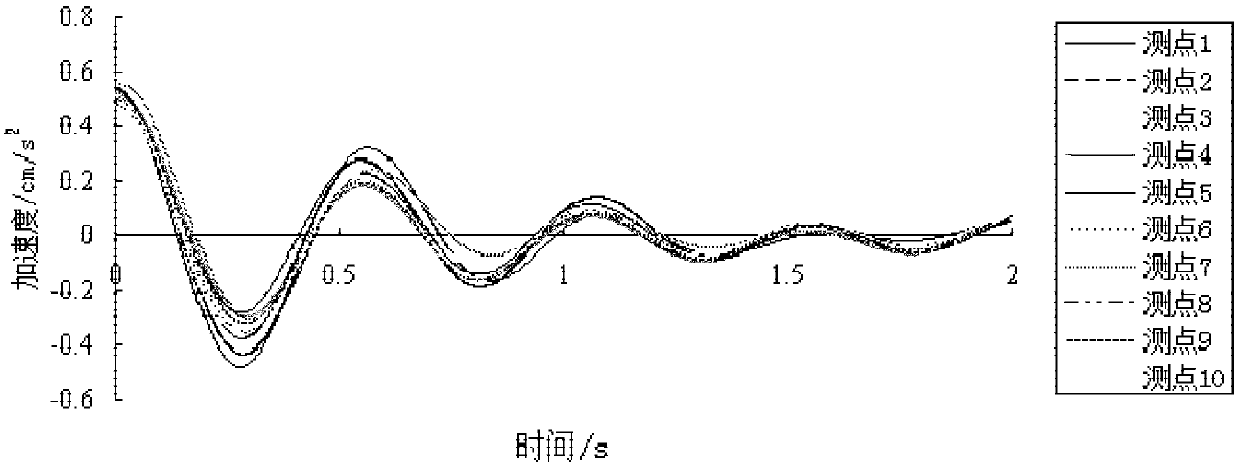
The invention belongs to the bridge monitoring technical field and provides a bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and a terminal device. The method includesthe following steps that: the monitoring data of the structure of a bridge under an environmental excitation condition are obtained through data acquisition devices disposed in a plurality of measuring points of the bridge; the NExT (natural excitation technique) is adopted, at first, the cross power spectrum density function of the monitoring data is calculated, and Fourier inverse transformation is performed on the cross power spectrum density function, so that the cross-correlation function of the monitoring data is obtained, the cross-correlation function is adopted as the input data of amodal parameter identification algorithm, so that modal parameter identification can be carried out, and a stability diagram can be drawn; the auto-power spectrum density function and cross-power spectrum density function of the monitoring data of the measuring points are calculated, the auto-power spectra and cross-power spectra of all the measuring points are summated, and the auto-spectra andthe cross spectra are summated in the same order of magnitude, so that the sum function of the power spectra can be obtained; and a diagram of the sum function, and true and false modal parameters canbe discriminated according to the stability diagram of the sum function. According to the method, the stability diagram method and a power spectrum summation peak method are combined to perform bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination, so that discrimination accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
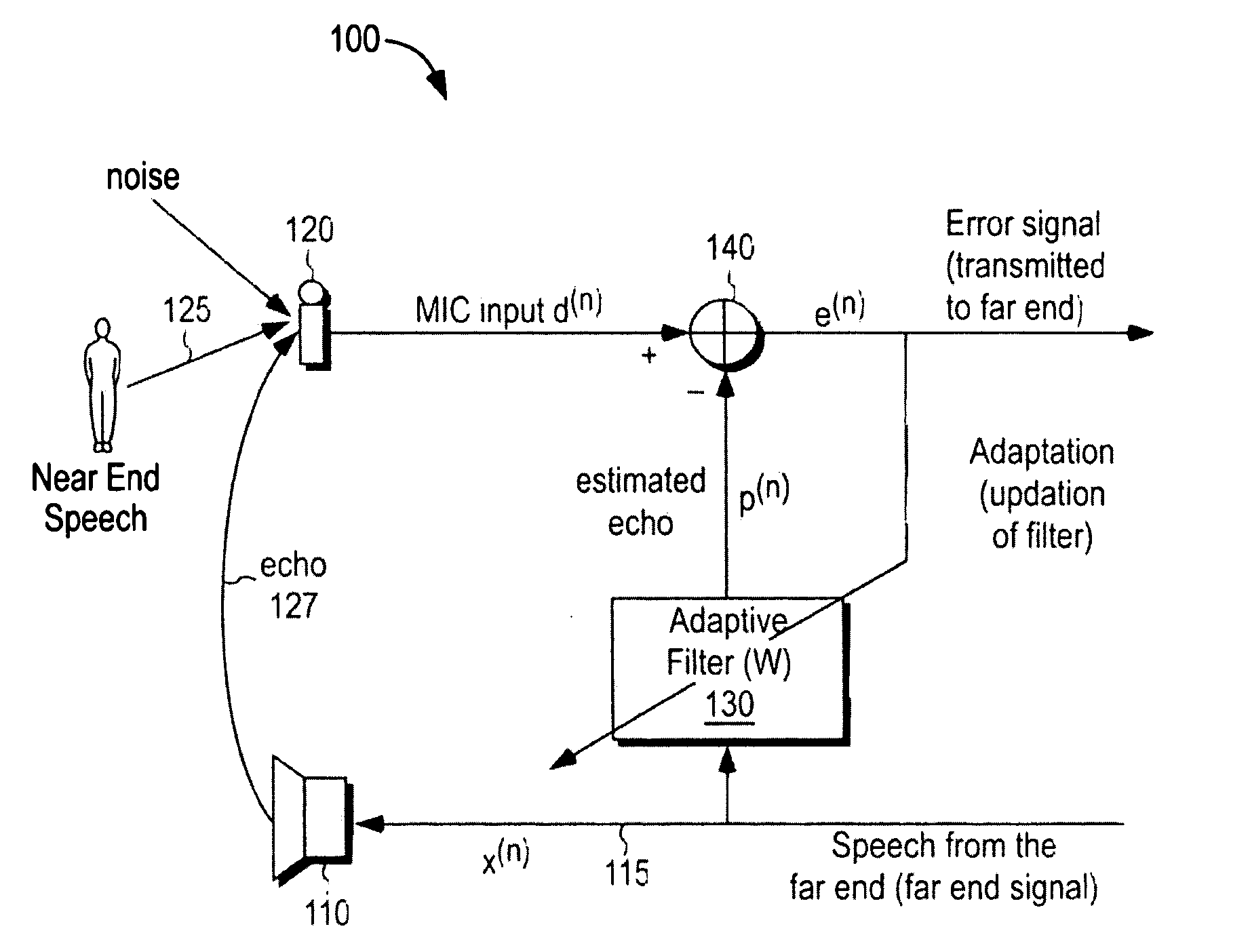
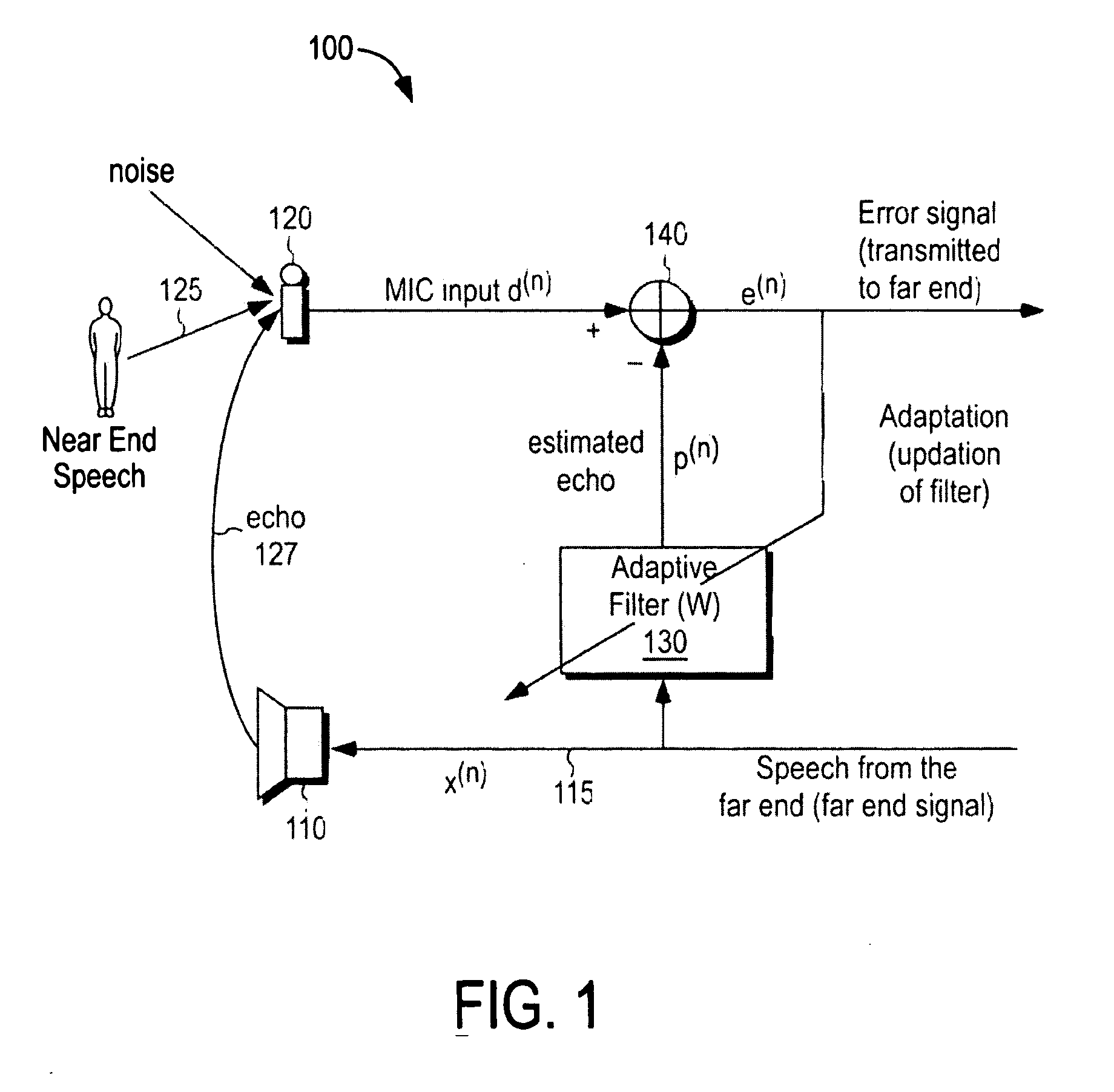
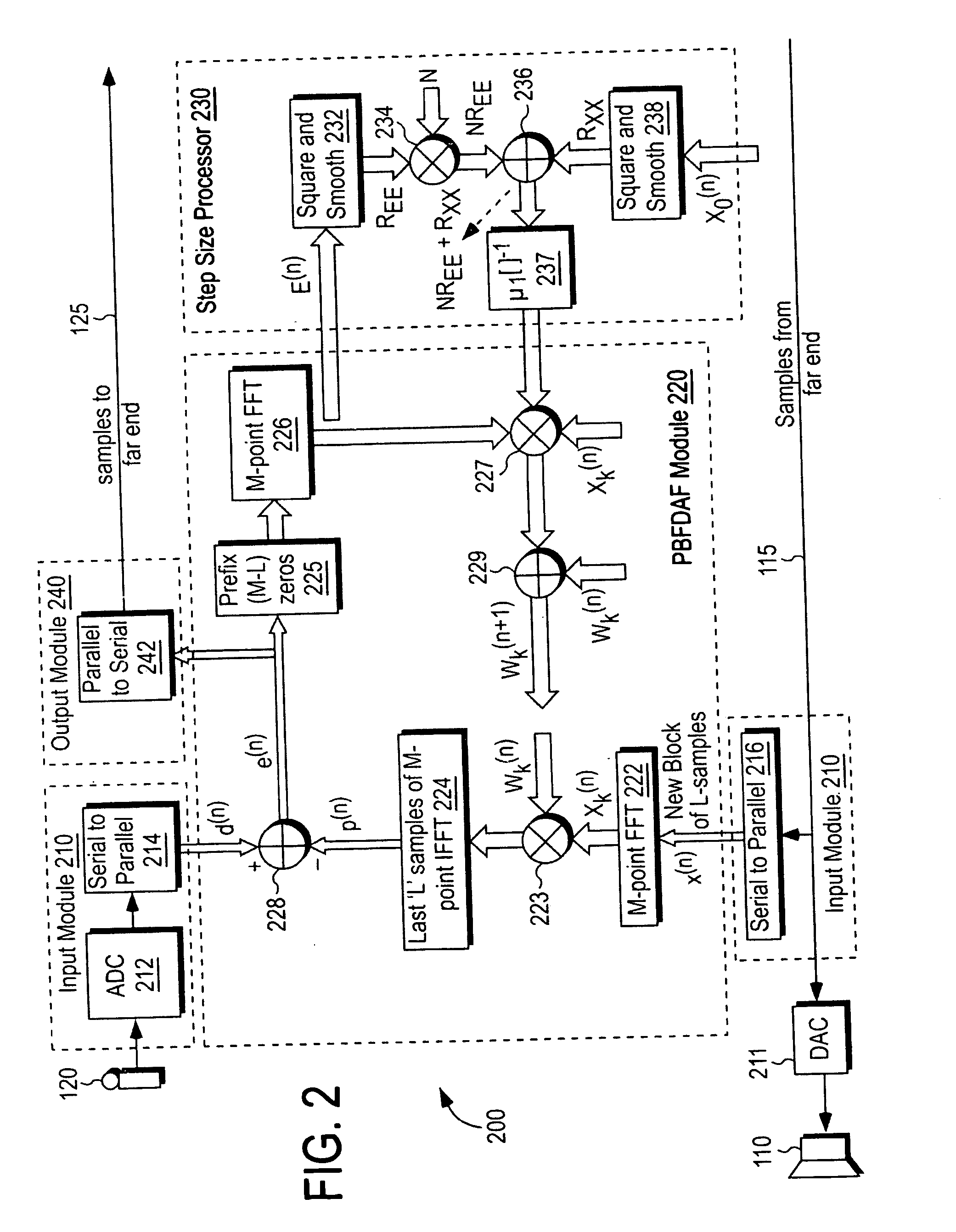
Method, apparatus and articles incorporating a step size control technique for echo signal cancellation
A novel technique for canceling echo signal in teleconferencing applications. In one example embodiment, a low complexity double-talk and noise robust frequency domain adaptive filter is used to cancel the echo signal during the teleconferencing applications. The adaptive filter computes step sizes using power spectral density functions of error and far end signals using an equation, which does not require a single talk / double detectors and a voice activity detector. The computed step sizes are then used by the adaptive filter (PBFDAF) to cancel the echo signal.
Owner:LTIMINDTREE LTD
Method and device for measuring dynamic light scattering nanoparticles based on band-pass filtering
InactiveCN102297823AReduce acquisition speedReduce the amount of data collectedParticle size analysisBandpass filteringPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for measuring dynamic light scattering nano-particles based on bandpass filtering. According to the invention, lasers are radiated on nano-particles performing Brownian motions in a solution. The scattered lights of the particles are directly detected; or the scattered lights of the particles are interfered with part of the original lights, and are detected; or the scattered lights are fed-back into a laser-tube cavity, self mixing is occurred, and self mixing signals are detected. Signals output by a photoelectric detector are pre-amplified, and are simultaneously delivered into a circuit formed by components of an M route buffer, bandpass filters with different central frequencies, and an RMS root-mean-square processor, which are connected in series, such that signal root-mean-square values at different frequencies with a number of M are obtained. The values are sampled by an A / D collecting card, such that power spectrum density functions at different frequencies with a number of M are obtained. With the method and the apparatus provided by the invention, a problem in prior arts of poor robustness of inverse calculations caused by seriously ill-conditioned coefficient matrix is solved. With the method and the apparatus provided by the invention, requirements on data collecting speed, data collecting amount, storage amount andprocessing amount are reduced; data processing time is reduced; and rapid measuring of nano-particle sizes can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
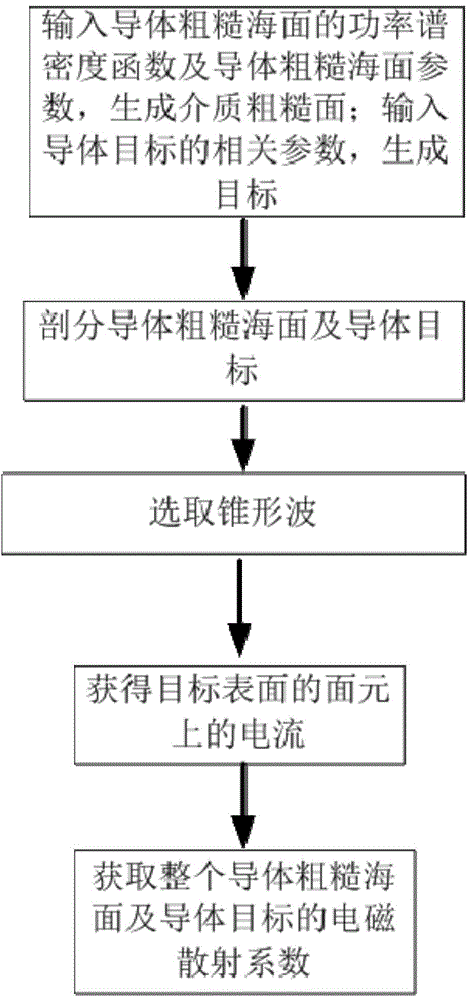
Electromagnetic scattering simulation method of one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and two-dimensional conductor target
InactiveCN104573289ASimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorClassical mechanics
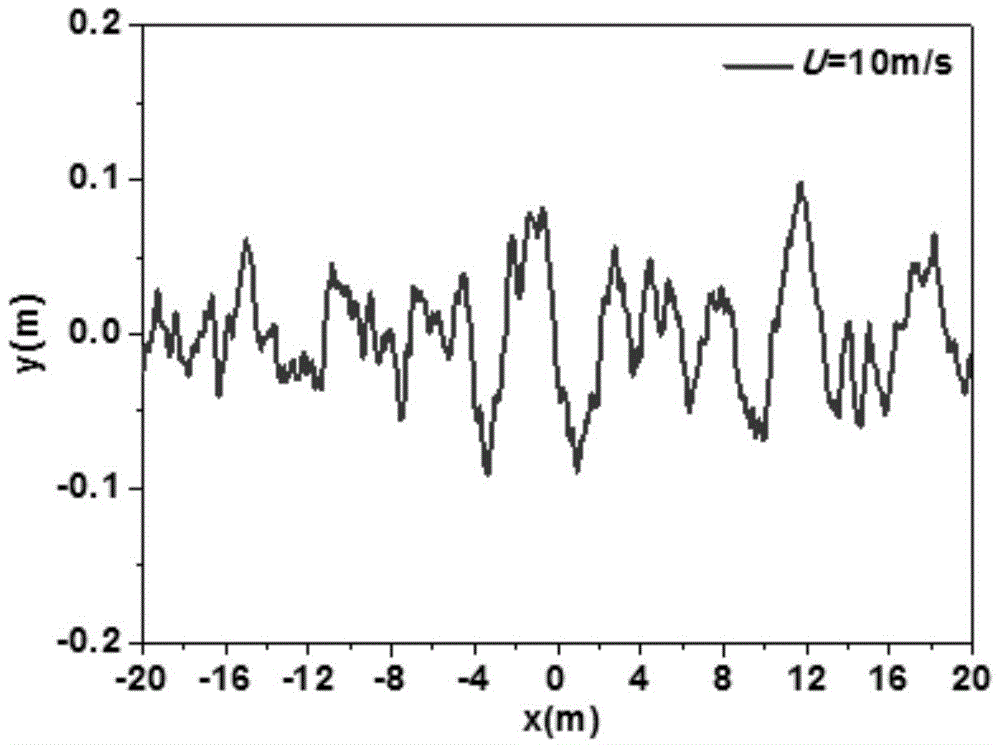
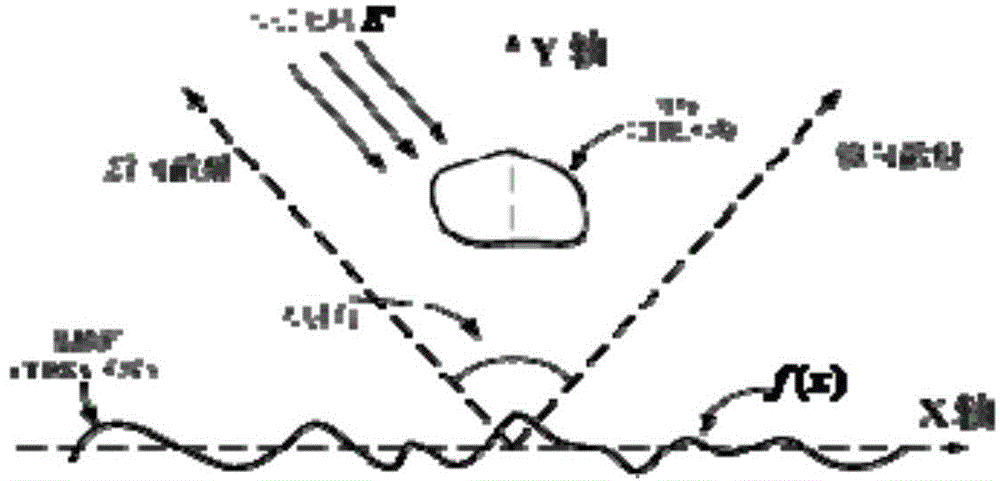
The invention relates to an electromagnetic scattering simulation method of a one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and a two-dimensional conductor target. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting a power spectral density function of the one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and a rough sea surface parameter, modeling the one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface to generate a one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface; (2) subdividing the one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and a two-dimensional infinite long conductor target under the irradiation of an incident wave; (3) incoming a conical wave to the one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and the two-dimensional infinite long conductor target; (4) according to the boundary conditions in the electromagnetic field, acquiring a time stepping equation of a display format of the incident wave one-dimensional conductor rough sea surface and the two-dimensional infinite long conductor target under the incidence; and (5) solving out a two-dimensional transient far field according to the numerical value of the current response of the target changing along the time. The method disclosed by the invention has the following beneficial effects that the interaction of the rough sea surface and the electromagnetic wave of the target is visually represented; and the composite electromagnetic scattering of the rough sea surface and the target under different wind speeds is simulated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for multi-sound localization
ActiveCN108198568AAvoid mutual interferenceAvoid interferenceSpeech analysisPosition fixationSound sourcesBase frequency
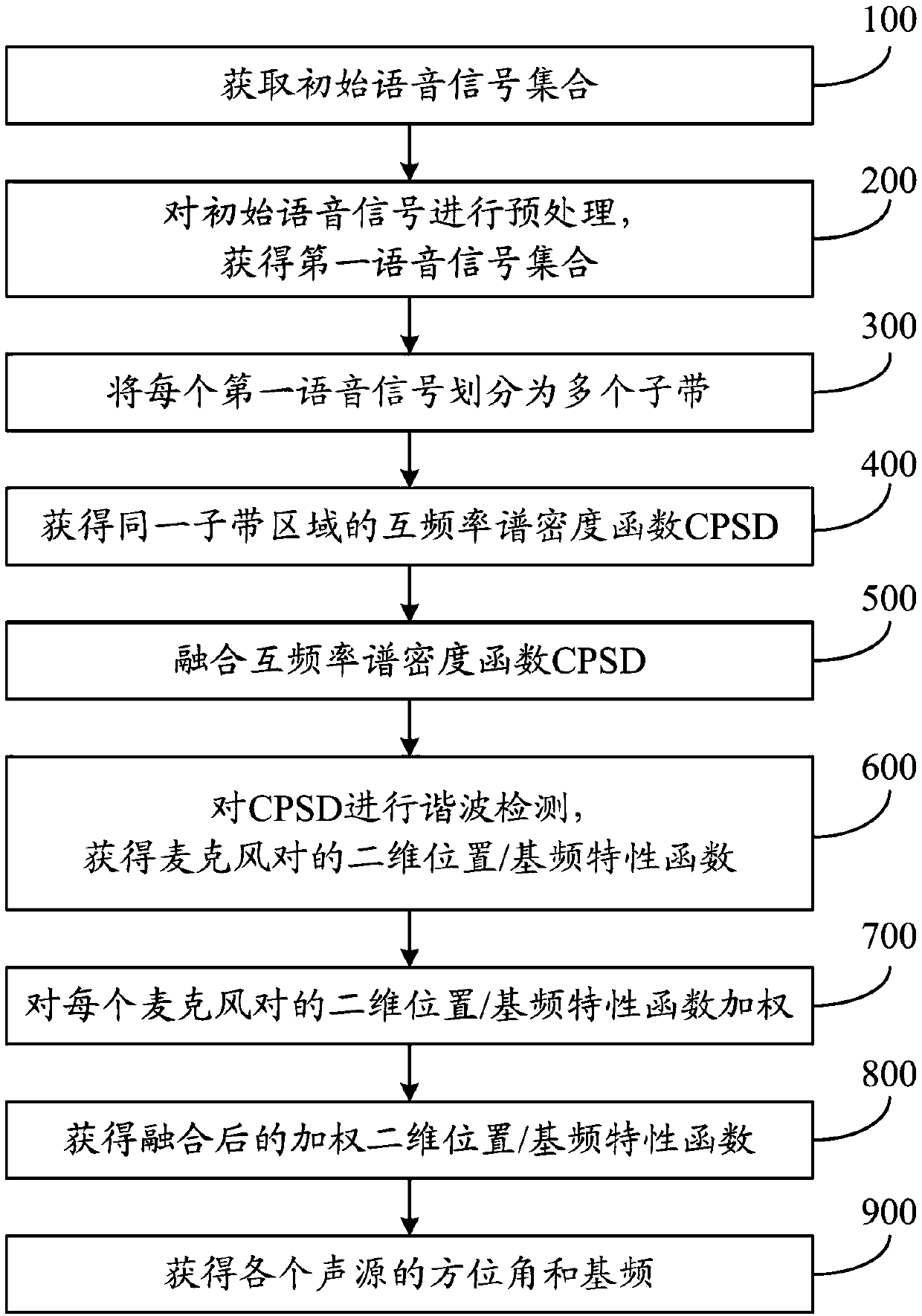
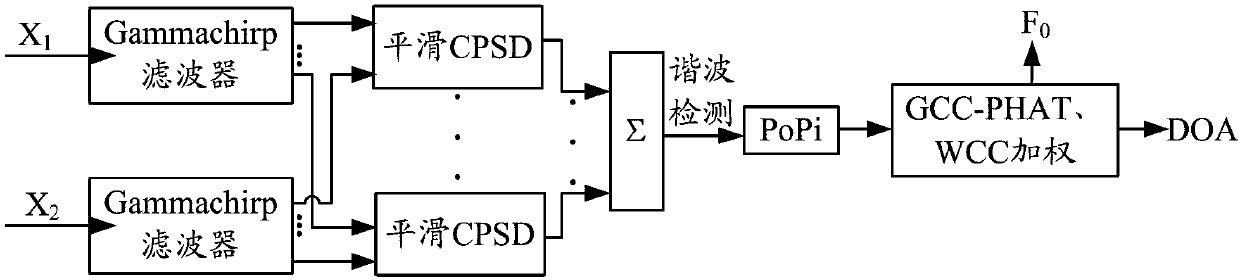
The invention discloses a method and a system for multi-sound localization. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an initial voice signal set; pre-processing each initial voice signal; dividing the pre-processed signals into a plurality of sub-bands via a basilar membrane filter; acquiring a cross-power spectral density functions of a same sub-band; fusing the cross-power spectral density functions of all sub-bands; acquiring a two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function of a microphone pair corresponding to each first voice signal; acquiring the two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function of each microphone pair; acquiring a fused weighted two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function; and confirming azimuth angles and base frequencies of various sound sources within a preset threshold range in accordance with a function value of the fused weighted two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function. According to the method and the system provided by the invention, mutual interference between sound signals is avoided and localization accuracy is improved. Moreover, the method and the system are relatively high in reverberation resistance, and locations of the various sound sources can be accurately estimated under a circumstance of strong reverberation.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on multi-zone model moment method
InactiveCN103400004AReduce memory requirementsSmall scaleSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceRadar
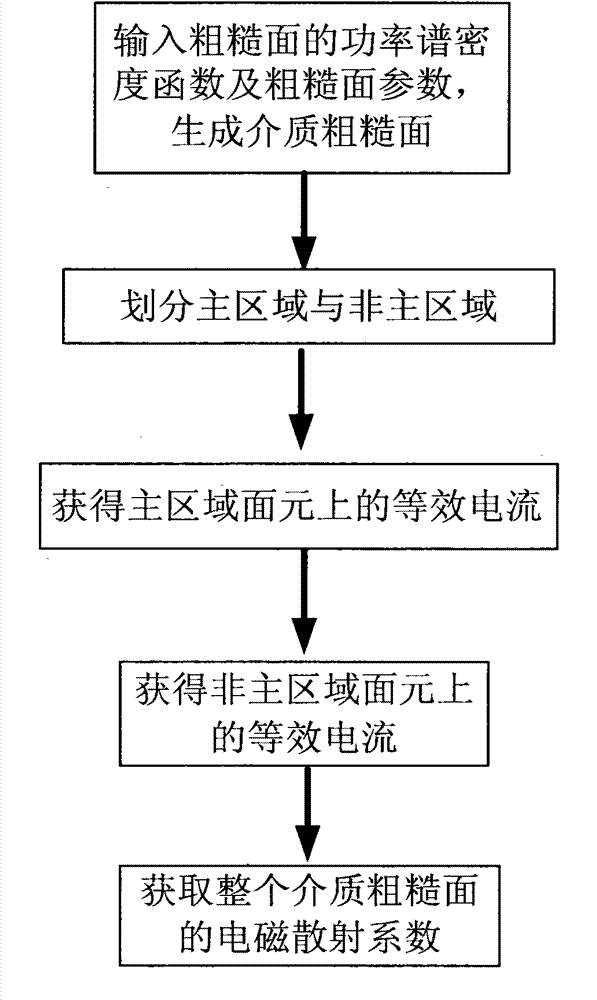
The invention discloses a medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on a multi-zone model moment method. The method includes the steps of inputting a medium rough surface power spectral density function and rough surface parameters, obtaining position coordinates of N scattering surface elements on a rough surface through a Monte Carlo method, dividing the rough surface into a main zone and a non-main zone, obtaining equivalent current on the surface elements of the two zones respectively, obtaining an electromagnetic scattering coefficient of the rough surface, and achieving medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation. According to the method, zone division is performed on the rough surface, a boundary integral equation is built through the moment method in the main zone which has large influences on scattering results, the equivalent current of the main zone is obtained, the equivalent current is obtained approximately in the non-main zone, the number of unknown quantities is lowered under the premise that certain accuracy is guaranteed, internal storage is reduced, calculation efficiency is improved, the technical problem of actual large-zone medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation is solved, and the method is applied to rough surface radar scattering property study in the fields of national defense and civil use.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Recognition method of motor imagery EEG (electroencephalograph) signal based on energy characteristics
PendingCN108280414AImprove classification accuracyShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionEnergy basedClassification methods
The invention relates to a recognition method of motor imagery EEG (electroencephalograph) signals based on energy characteristics. The recognition method of the motor imagery EEG signals based on theenergy characteristics includes the steps of collecting EEG signals from subjects as sample sets during the time when the subjects are completely relaxed and when the subjects are conducting motion imagination, denoising the EEG signals of these sample sets and acquiring the average power of the EEG signals, acquiring the energy values of the Mu (8-12 Hz) band and the Beta (18-25 Hz) band of theEEG signals as the eigenvalues during the motion imaging state and the fully relaxed state based on Fourier transform and using the energy spectral density function, and conducting online optimizationof parameters of classification methods to realize the recognition of the motor imagery EEG signals with the characteristics as input and using a support vector machine classification method based ona radial basis kernel function as well as using an improved grid optimization algorithm. The recognition method of the motor imagery EEG signals based on the energy characteristics has the advantagesof consuming short time, guaranteeing high accuracy and providing a new idea for real-time BCI (bulk current injection) implementation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for tracking targets with hyper-spectral data
ActiveUS7212652B1Enhances low signal to noise ratio (SNR) trackingLow signal noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrequency spectrumSource spectrum
In the present invention, the histogram model used in H-PMHT is extended to treat the problem of tracking using hyper-spectral data. Completely general spectral density functions are handled via the use of non-parametric methods. The present invention is not restricted to derivations based on knowledge of the spectral character of the source being tracked. The source spectrum can be estimated in a non-parametric fashion based on an initial track, and this allows the invention to adapt to the source spectrum in situ. The resulting method has improved crossing track performance on sources that have some degree of spectral distinction and will perform no worse than regular H-PMHT on sources that have identical spectral densities.
Owner:US SEC NAVY THE
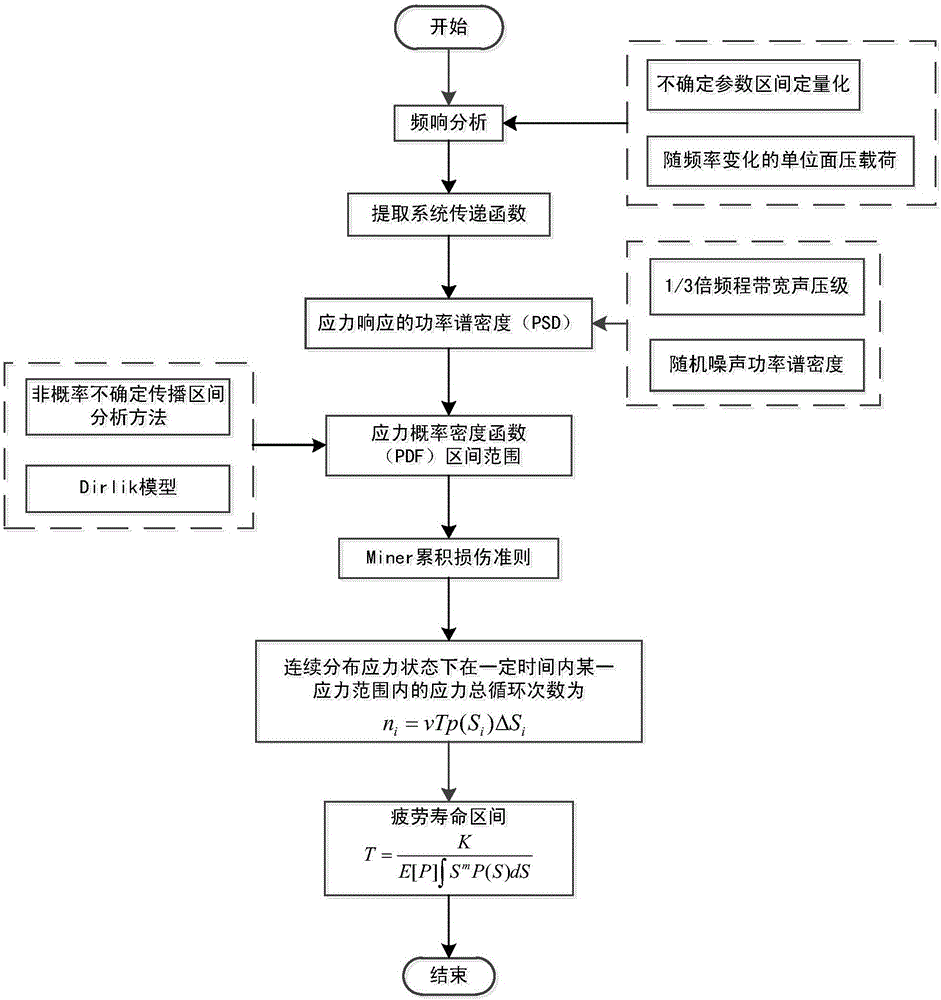
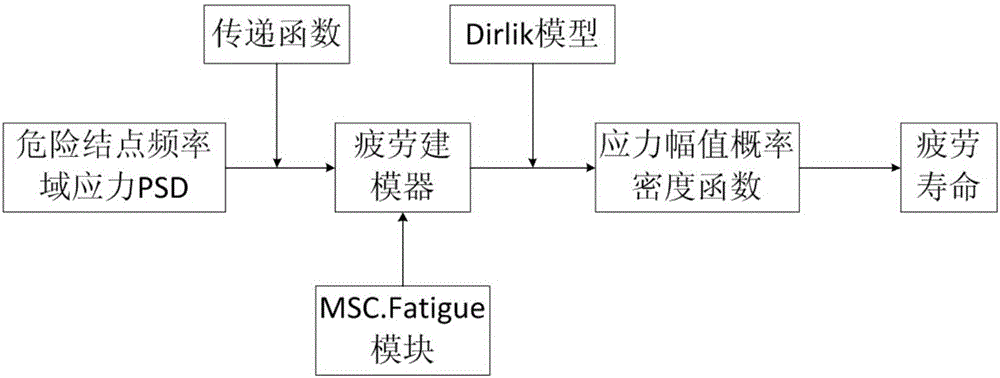
Estimation method for sound vibration fatigue life containing uncertain metal structure
ActiveCN105760577AMake up for and perfect limitationsEasy to solveGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDispersityRandom noise
The invention discloses an estimation method for a sound vibration fatigue life containing an uncertain metal structure.According to the method, firstly, a finite element analytical model of a metal structure is established, the uncertain effect of material and structure characteristic parameters under finite sample conditions is considered, and a systematic transfer function is obtained based on the frequency response analytical theory; secondly, according to the characteristics of random noise loads, a mean square root response and stress power spectral density function (PSD) of displacement and stress of all key nodes is obtained through an SRSS method for typical broadband steady ergodic random noise loads; thirdly, in combination with a Dirlik model, an interval uncertain propagation second-order Taylor series expansion method and an analytical method for vibration fatigue within a frequency domain, the relation between a rain flow amplitude probability density function and the power spectral density function is set up; finally, the Miner linear accumulative damage theory is used for obtaining an interval range of the sound vibration fatigue life containing the uncertain metal structure.Dispersity of the structure and material parameters is taken into full consideration during calculation of the structural life excited by typical random noise, and therefore the obtained fatigue life is more reasonable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
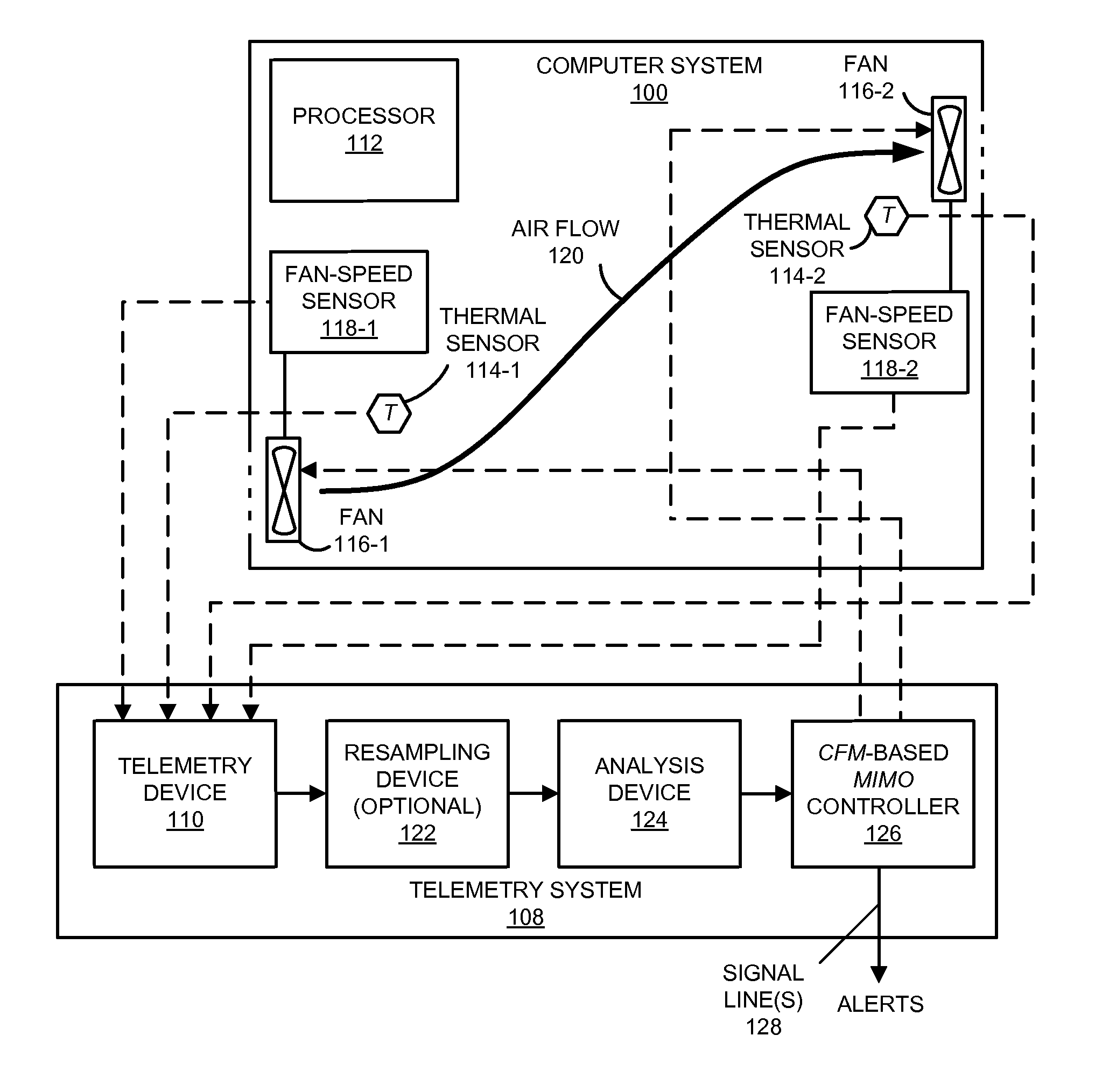
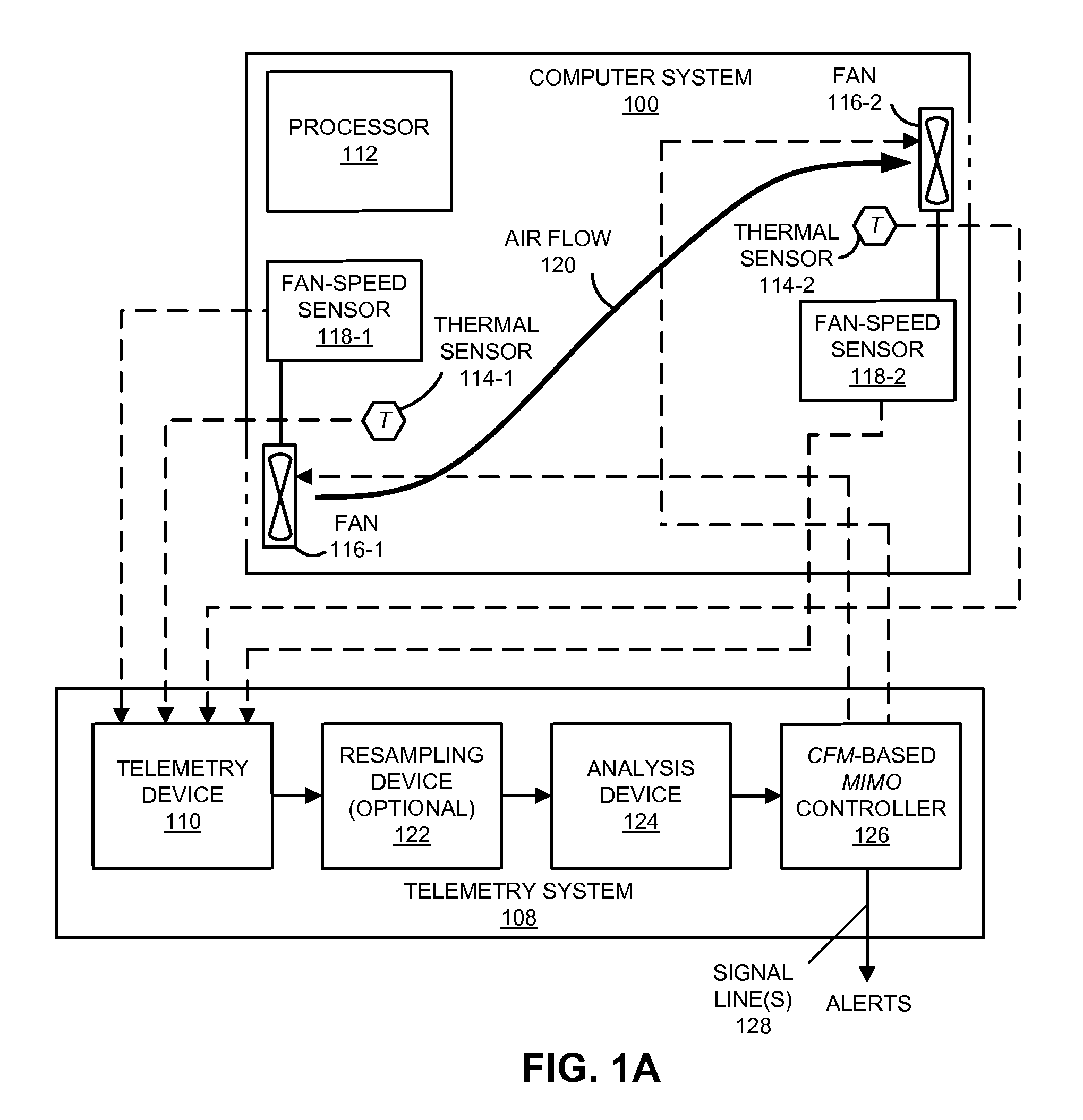
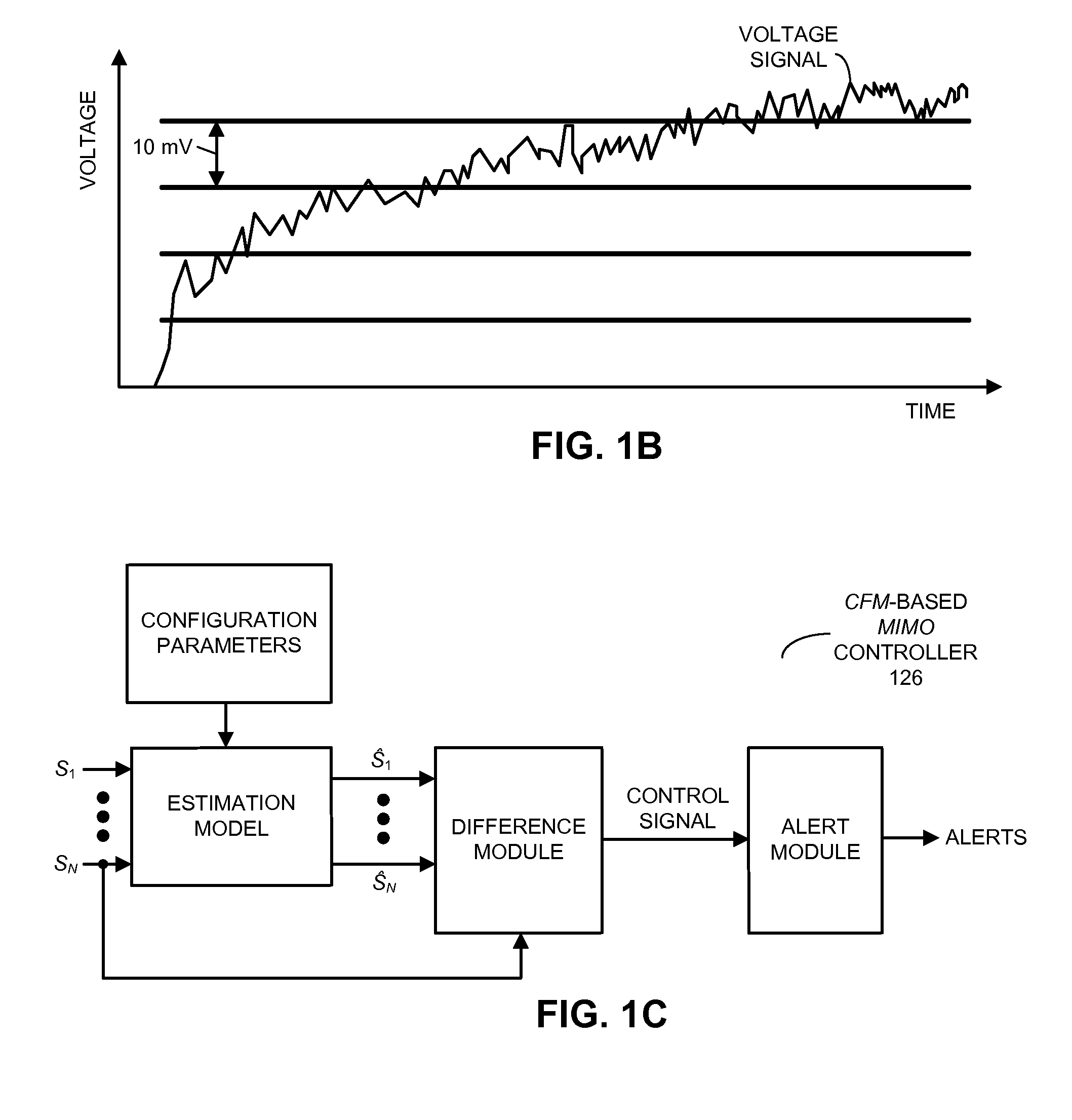
Cooling-control technique for use in a computer system
ActiveUS8164434B2Facilitates above-described operationThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTControl signalCoolant flow
A method for providing control signals to a fan in a computer system is described. During the method, an electronic device receives temperature measurements and a fan-speed measurement performed in the computer system. Using a pattern-recognition model, the electronic device validates the measurements, and excludes any inaccurate measurements, such as those associated with drifting or failed sensors. Next, the electronic device determines control signals for a fan in the computer system using a model of coolant flow in the computer system and / or a slope of a phase-frequency curve of a cross power spectral density function corresponding to a pair of temperature profiles measured, as a function of time, by a pair of thermal sensors. Then, the determined control signals are provided to the fan.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Modeling method of rough surface microwave band bidirectional reflectance distribution function
InactiveCN103699810AAvoid measurement constraintsImprove limitationsSpecial data processing applicationsScattering cross-sectionFast optimization
The invention discloses a modeling method of rough surface microwave band bidirectional reflectance distribution function. The modeling method comprises the following steps of: generating a rough surface by a Monte Carlo method according to power spectral density function of rough surface; calculating unit radar cross section sigma 0 of the rough surface by a moment method; obtaining a bidirectional reflectance distribution function of the rough surface according to the relation between the rough surface scattering coefficient and the bidirectional reflectance distribution function; modeling a five-parameter empirical model according to the obtained bidirectional reflectance distribution function; selecting optimal standard according to the model parameters, optimizing the parameters of the five-parameter model to obtain empirical parameters; according to the empirical parameters obtained by optimization, modeling a rough surface bidirectional reflectance distribution function through the five-parameter empirical model. Compared with the prior art, the modeling method provided by the invention has the advantages of fast optimization speed, high modeling precision and strong universality, and can be used for study on features of rough surface microwave band bidirectional reflectance distribution function.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and device for calculating track irregularity at bridge pier settlement and electronic apparatus
InactiveCN109190312AUneven fastNot smooth and accurateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringElectron
The invention provides a method and device for calculating track irregularity at a bridge pier settlement and an electronic apparatus, which relate to the technical field of high-speed railways. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the vertical deformation of a bridge at the settlement of a bridge pier; inputting the vertical deformation into the mapping analytical model of bridge vertical deformation and track deformation, and calculating the track deformation caused by pier settlement. The mapping analytical model is a model reflecting the corresponding relationship between vertical deformation and track deformation of the bridge. The track irregularity power spectral density function is determined and the track irregularity graph is generated by fitting the track irregularity power spectral density function with numerical analysis method. According to the track deformation and track irregularity diagram, the track irregularity diagram at the pier settlement is obtained. The method and device for calculating the track irregularity at the bridge pier settlement provided by the embodiment and the electronic apparatus can accurately obtain the track irregularity at abridge pier settlement.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of evaluating inhibition of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) process on errors under different frequencies
The invention relates to a method of evaluating the inhibition of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) process on errors under different frequencies. The method includes the steps of S1, building a formula (1), PSDaft=(1-H)(1-H)<*>*PSDbef, for smoothing spectral function H, PSDaft and PSDbef according to the power spectral density functions PSDbef and PSDaft before and after optical element polishing, with (1-H)<*> being a conjugate to (1-H) and the symbol * being an operator used for obtaining the conjugate; S2, subjecting the formula (1) to bilateral modulo operation according to complex operation algorithms to obtain a power spectral density function expression (2), PSDaft=|(1-H)|2*PSDbef, for polished surface shape data; S3, solving the formula (2) according to |H|<1 due to the fact that the smoothing spectral function H is for Fourier transform after function normalization is removed, thus establishing a smoothing spectral function H formula (3); expressing the inhibition of the PCCOS process on errors under different frequencies as a frequency normalization function, calculating smoothing spectral function curves according to the PSDbef and PSDaft obtained before and after polishing, and evaluating the magnitude of the inhibition of the CCOS process on the errors under different frequencies according to values of the smoothing spectral function curves.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
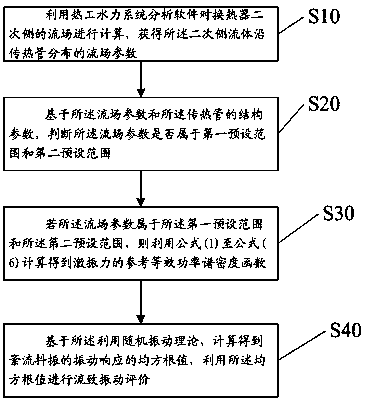
Method for calculating turbulence buffeting responses of heat exchanger
ActiveCN104392067AAnalysis input is reasonableReasonable analysis resultsSpecial data processing applicationsSystems analysisDensity based
The invention discloses a method for calculating turbulence buffeting responses of a heat exchanger. The method comprises steps as follows: a flow field of a secondary side of the heat exchanger is calculated by thermotechnical hydraulic system analysis software to obtain parameters of flow fields, distributed along a heat exchange pipe, of flow on the secondary side; on the basis of the parameters of the flow fields and the structure parameters of the heat exchange pipe, whether the parameters of the flow fields belong to a first preset range and a second preset range is judged; if the parameters of the flow fields belong to the first preset range and the second preset range, a reference equivalent power spectral density function of exciting force is calculated by means of formula (1)-(6); a root-mean-square value of the turbulence buffeting vibration responses is calculated by means of the random vibration theory based on a density function, flow-induced vibration evaluation is performed by means of the root-mean-square value, and the technical effects of more reasonable input and more accurate analysis result during calculation analysis of turbulence buffeting responses of the heat exchanger are achieved.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics
ActiveCN109100692AAvoid artificial reflexesImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationPhysical opticsSimulation
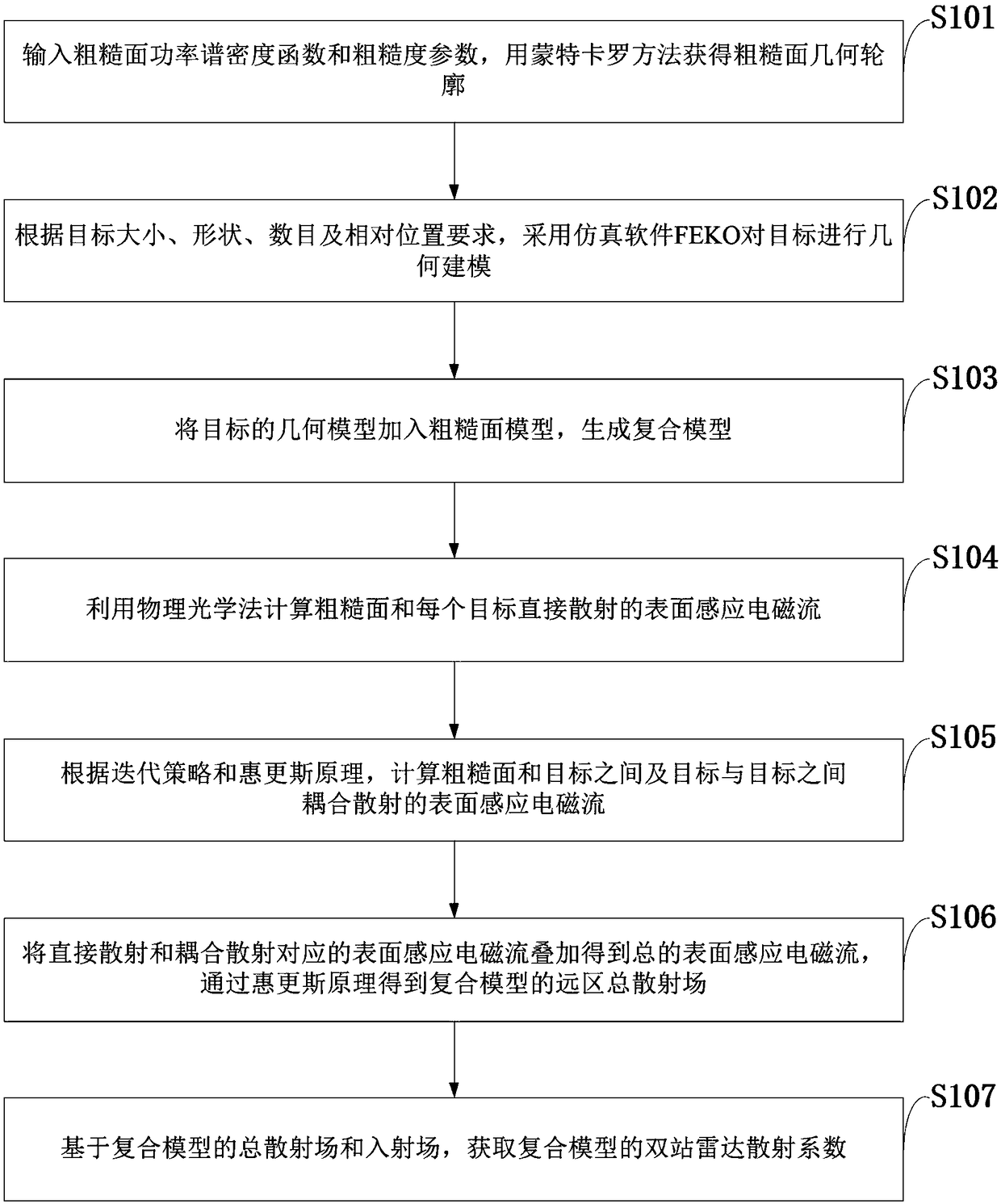
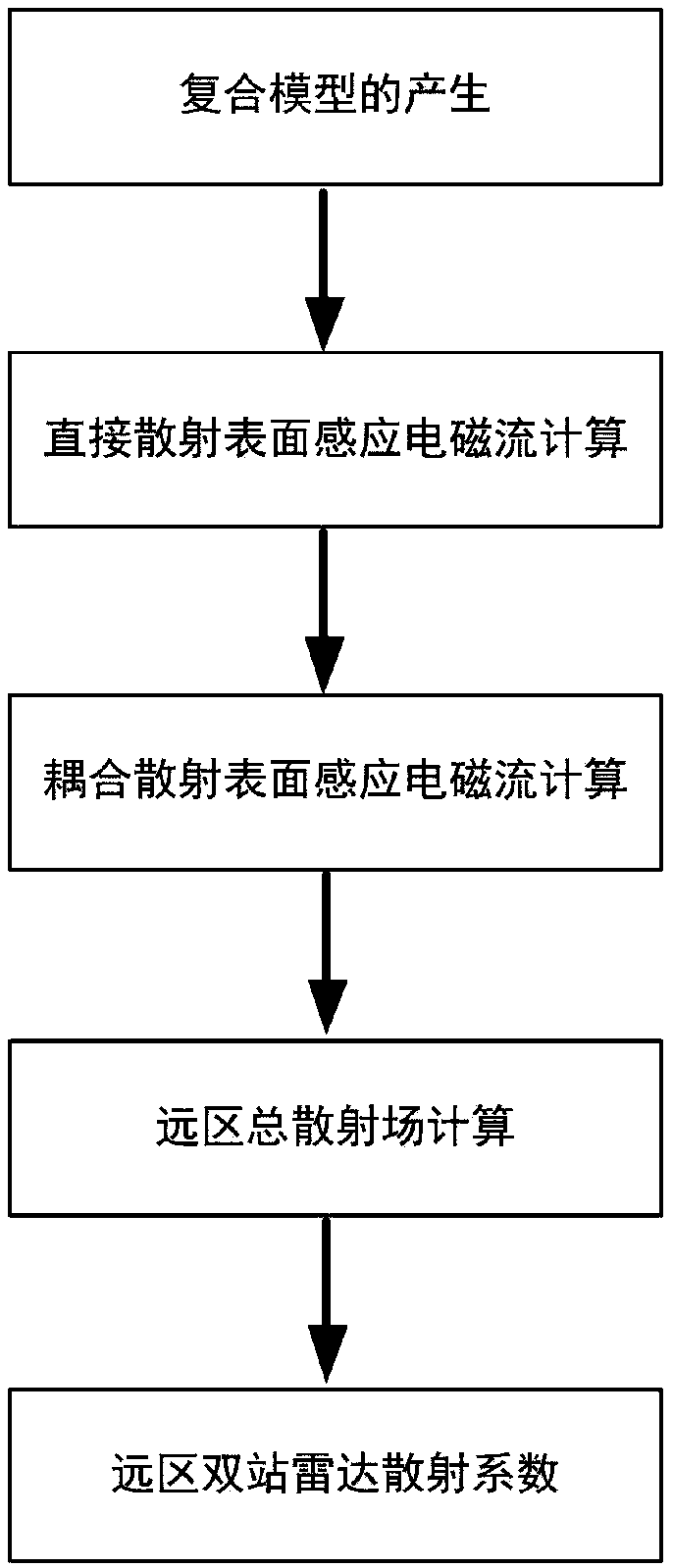
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar electromagnetic simulation, and discloses a rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a rough surface power spectral density function and a roughness parameter, obtaining a rough surface geometric contour by the Monte Carlo method; using the simulation software FEKO to geometrically model the targets; adding the geometric models of the targets to the rough surface model to generate a composite model; using the physical opticsmethod to calculate the surface induced electromagnetic current directly scattered by the rough surface and each target; calculating the surface-induced electromagnetic current between the rough surface and the targets and between the targets according to the iterative strategy and Huygens principle; obtaining a far-field total scattering field of the composite model by the Huygens principle; andobtaining a two-station radar scattering coefficient of the composite model based on the total scattering field and the incident field of the composite model. The rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics has the advantages such as low memory requirement, high simulation efficiency and strong versatility of the simulation method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
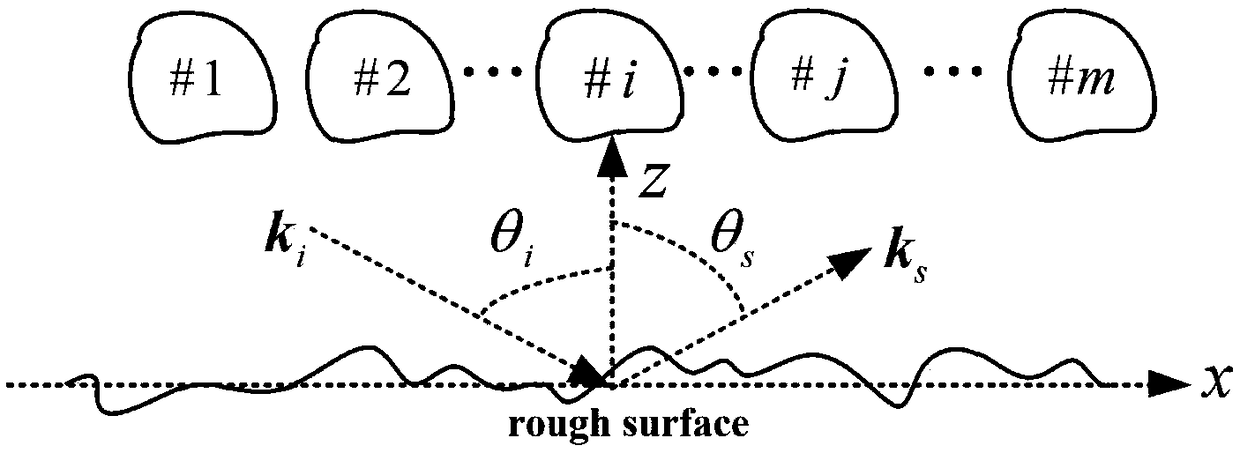
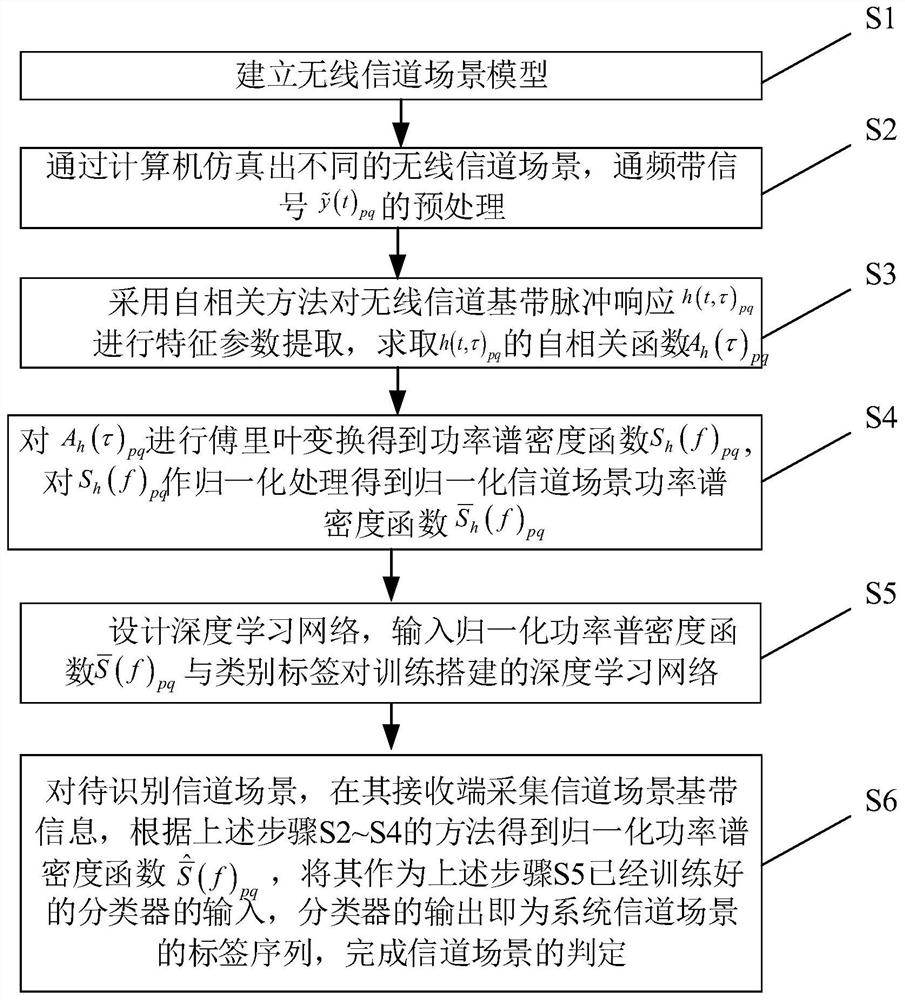
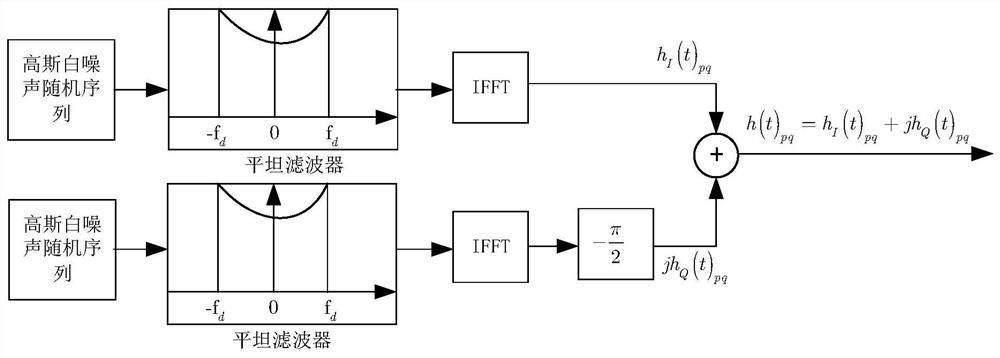
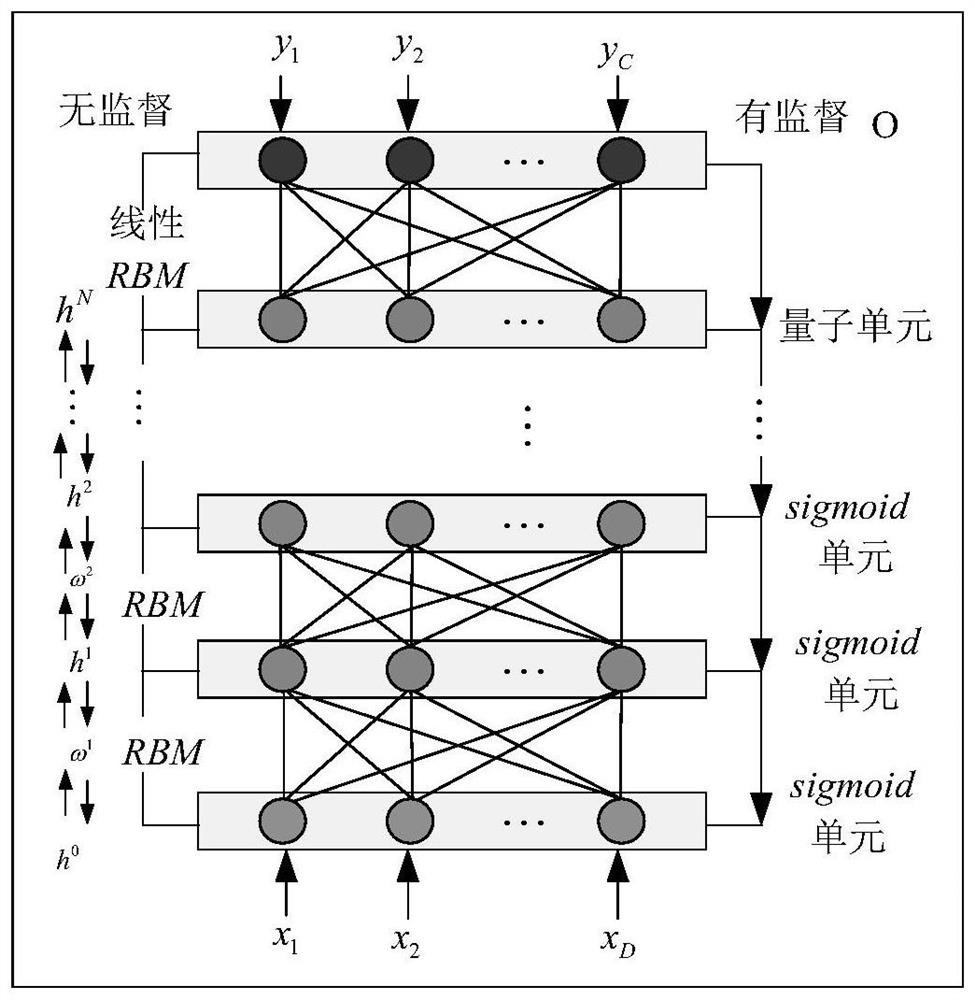
Wireless channel scene identification method and system
ActiveCN111835444AExpand the scope of recognitionImprove classification abilityTransmission monitoringWireless communicationAlgorithmEngineering
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
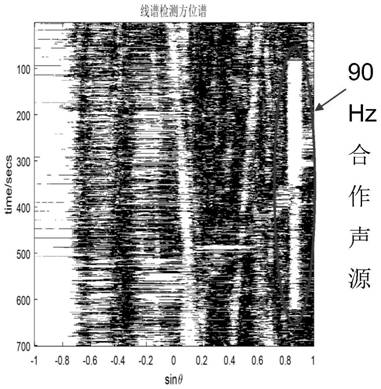
Line spectrum extraction method based on target characteristics
ActiveCN111665489AImprove robustnessHigh speedWave based measurement systemsTarget signalComputational physics
The invention provides a line spectrum extraction method based on target characteristics, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a broadband target signal to be converted into a space-time two-dimensional power spectrum density function, extracting frequency domain power spectrum line information through processing of a frequency domain power spectrum density function, and obtaining a targetsignal strong line spectrum; selecting an estimated scanning azimuth angle on the spatial-temporal power spectral density without the influence of the strong line spectrum, and calculating a mean value of energy distribution in a strip along a wave number direction to obtain a power spectrum estimation map of a scanning azimuth target signal; and extracting line spectrum information of each orientation on the power spectrum estimation graph, and compounding the obtained scanning orientation line spectrum and the target signal strong line spectrum in the orientation direction to obtain the line spectrum characteristics of a specific target. According to the method, target power spectrum information does not need to be predicted in advance; the application range is wide, and extraction of strong line spectrum components and weak target line spectrum components can be included; the speed is high, the real-time performance is good, and the algorithm robustness is high; simulation and seatest data prove that the method is effective.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
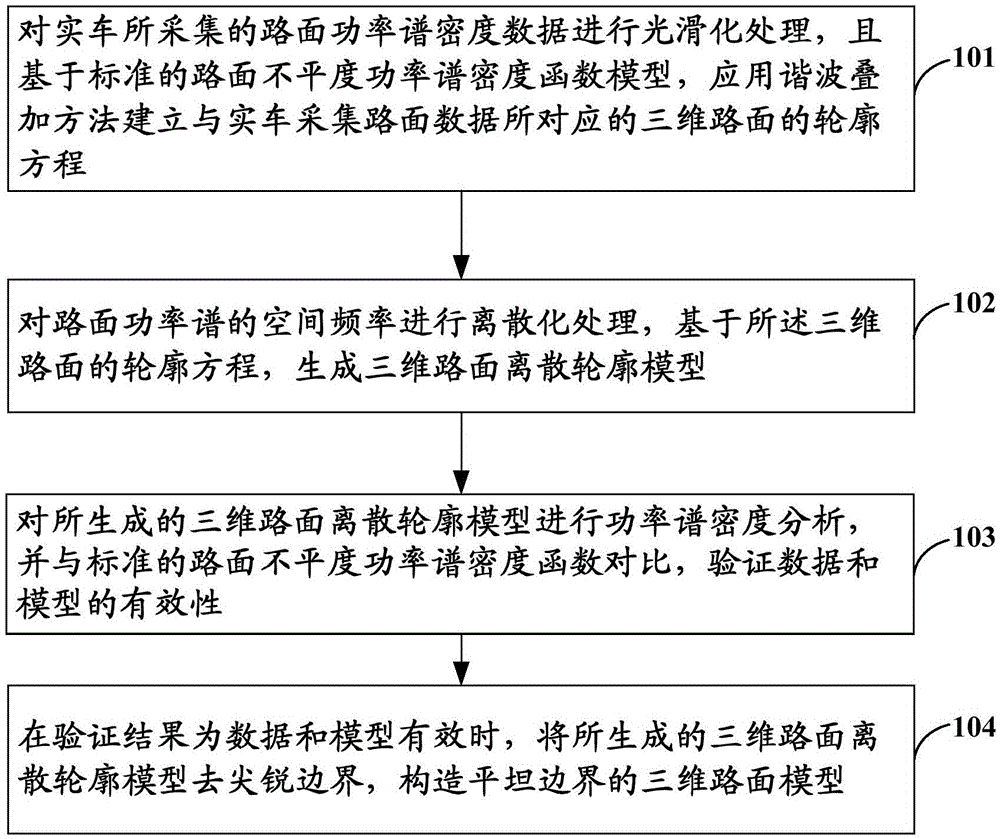
Method and system for generating three-dimensional road profile
InactiveCN105427375ARigorous theoryAccurate calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHarmonicSimulation
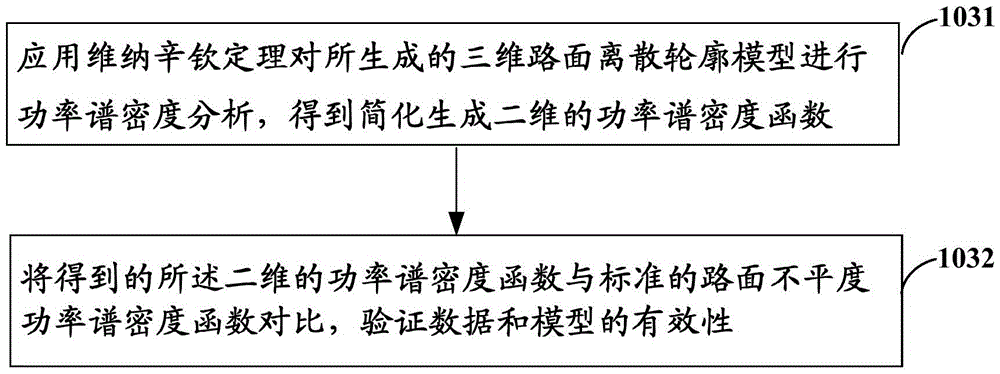
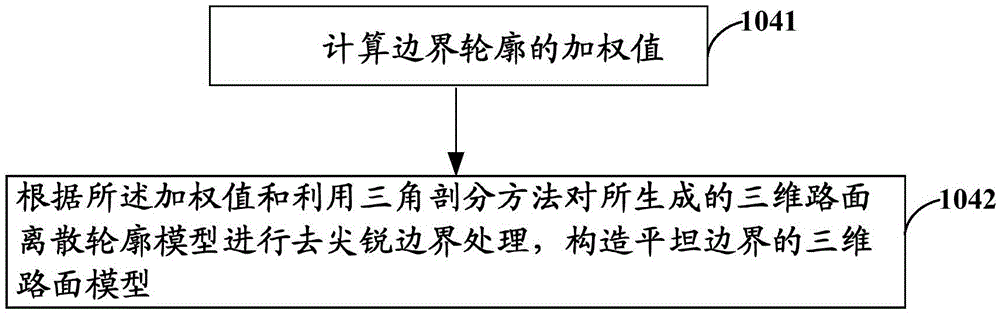
The invention provides a method and a system for generating a three-dimensional road profile. The method comprises: smoothing road power spectral density data acquired by a real vehicle, and establishing a profile equation of a three-dimensional road corresponding to the road data acquired by the real vehicle by using a harmonic superposition method based on a standard road unevenness power spectral density function model; discretizing the spatial frequency of road power spectra, and generating a three-dimensional road discrete profile model based on the profile equation of the three-dimensional road; performing power spectral density analysis on the generated three-dimensional road discrete profile model, and comparing with a standard road unevenness power spectral density function to verify the validity of the data and the model; and when the data and the model are valid, removing sharp boundaries from the generated three-dimensional road discrete profile model, thus constructing a three-dimensional road model with flat boundaries. The method and the system are simple and theoretically strict, and have strong passing ability to simulation test calculation.
Owner:BAIC GRP ORV CO LTD
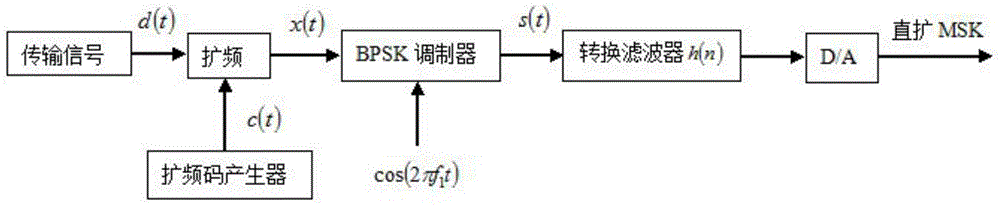
Method for generating direct-spread MSK (minimum shift keying) signals and conversion filter design method
ActiveCN104639100AAvoid strict balance requirementsEasy to implementDigital technique networkMean squareEngineering
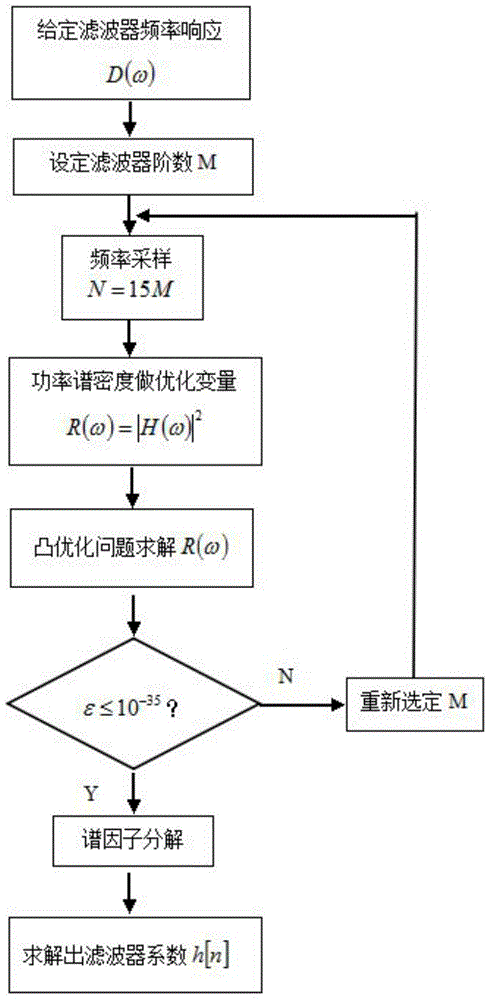
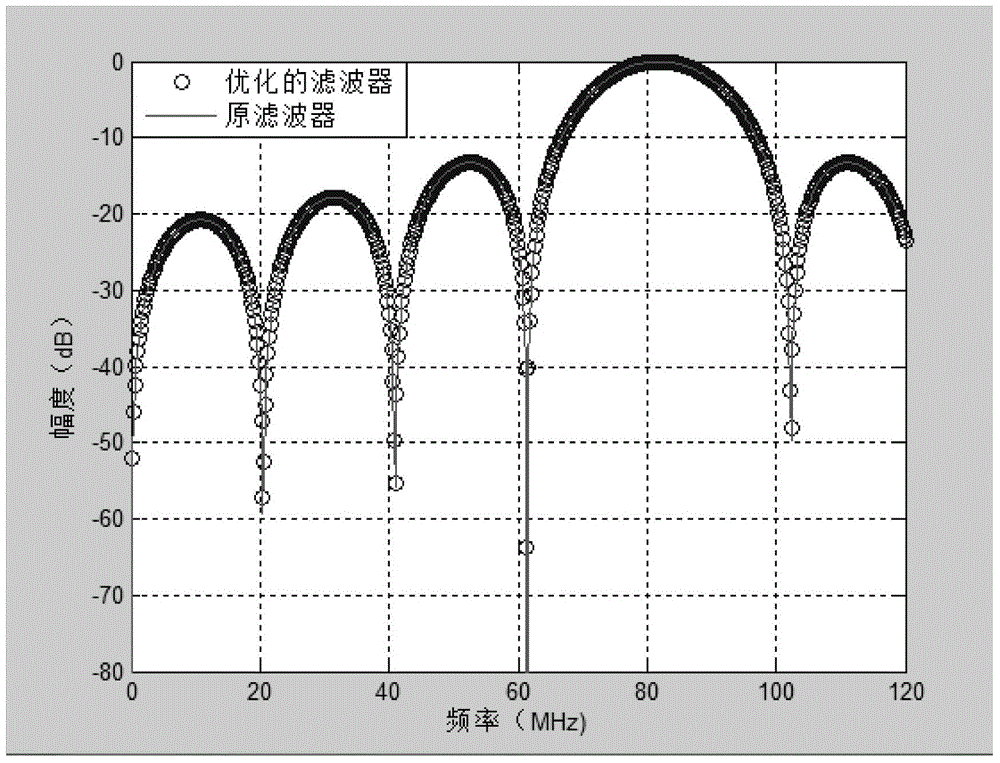
The invention provides a design method for a conversion filter generating direct-spread MSK (minimum shift keying) signals. The method comprises the following steps that a Chebyshev approximation convex optimization model of the conversion filter is built; the proper frequency sampling point number is determined, and the semi-infinite conditions of a conversion filter model is estimated by utilizing frequency sampling; the Chebyshev approximation convex optimization model is resolved, and a power spectral density function is solved; the filter order is selected, the power spectral density value of the conversion filter is calculated, and in addition, whether the power spectral density value meets the design requirements or not is judged according to the mean square error value; if the optimized power spectral density value meets the design requirements, the coefficient of the conversion filter is solved by a spectral factorization method through the power spectral density value. The design method for the conversion filter provided by the invention has the advantages that the filter order is smaller, and the occupied resources of hardware of the conversion filter are fewer.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
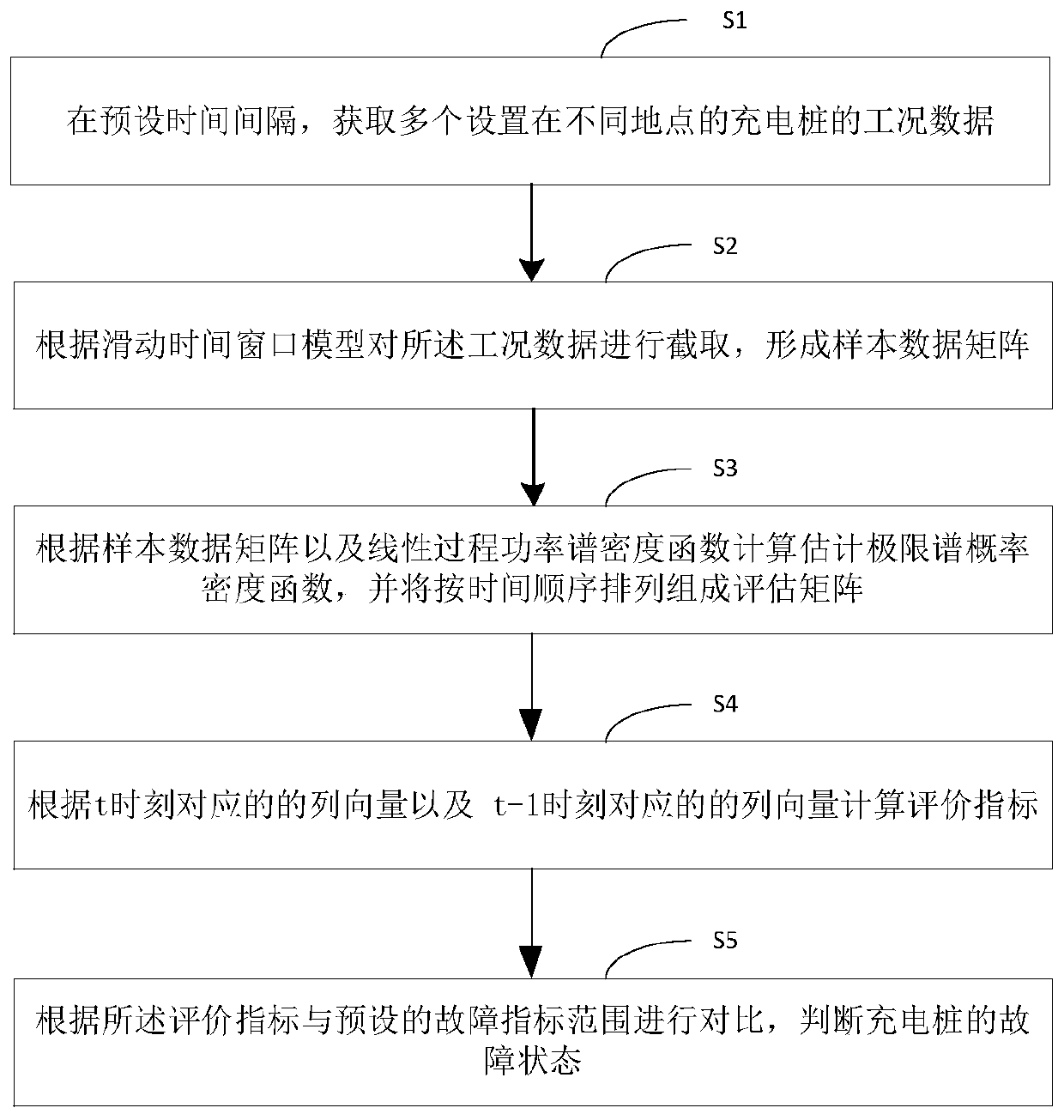
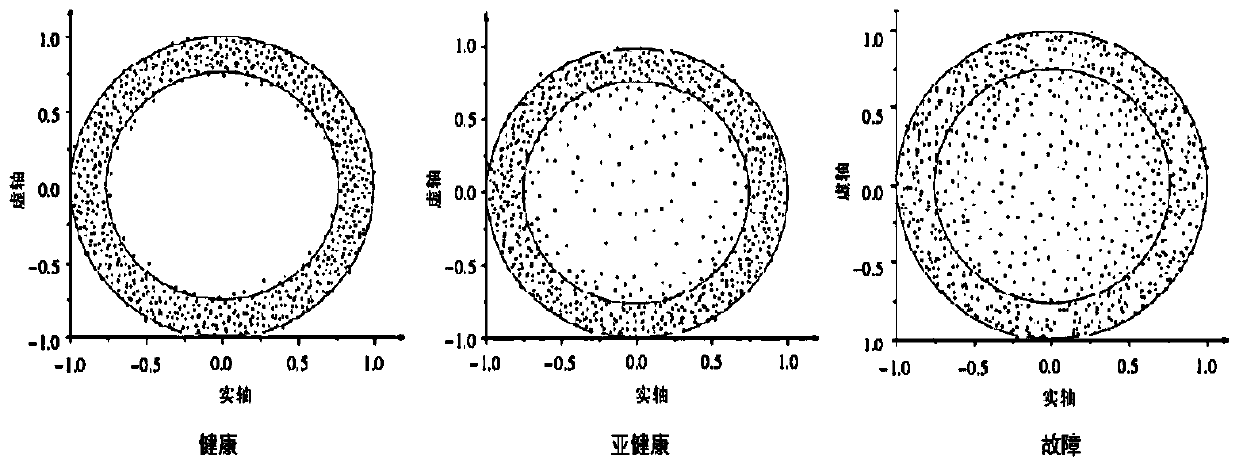
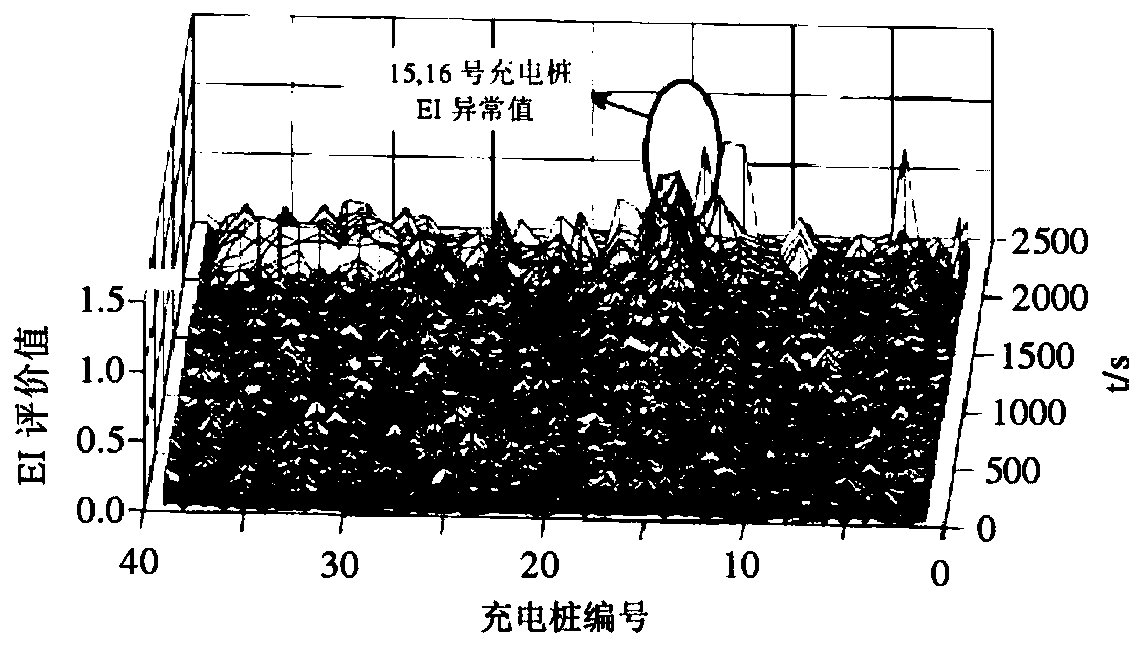
Evaluation method of charging pile state
ActiveCN110466381ALow failure rateEasy maintenanceCharging stationsElectric vehicle charging technologySliding time windowCaret
The invention discloses an evaluation method of a charging pile state. The method comprises the steps that working condition data of a plurality of charging piles arranged at different places are acquired at a preset time interval; the working condition data are intercepted according to a sliding time window model to form a sample data matrix X caret t; an estimated limit spectrum probability density function h caret (x) is calculated according to the sample data matrix X caret t and a linear process power spectral density function, and h caret (x) is arranged according to the chronological order to form an evaluation matrix H caret (x); an evaluation index is calculated according to a column vector nt of H caret (x), corresponding to the moment t, and a column vector nt-1 of H caret (x),corresponding to the moment t-1; and according to the evaluation index, compared with a preset fault index range, the fault state of the charging piles is judged. According to the evaluation method ofthe charging pile state, the inner link between the working condition of the charging piles and various influence factors can be analyzed, the pre-judgment before a fault occurs is made, the fault probability of the charging piles is reduced, and the maintenance of the charging pile is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +2
Multi-point seismic oscillation synthesis method and system
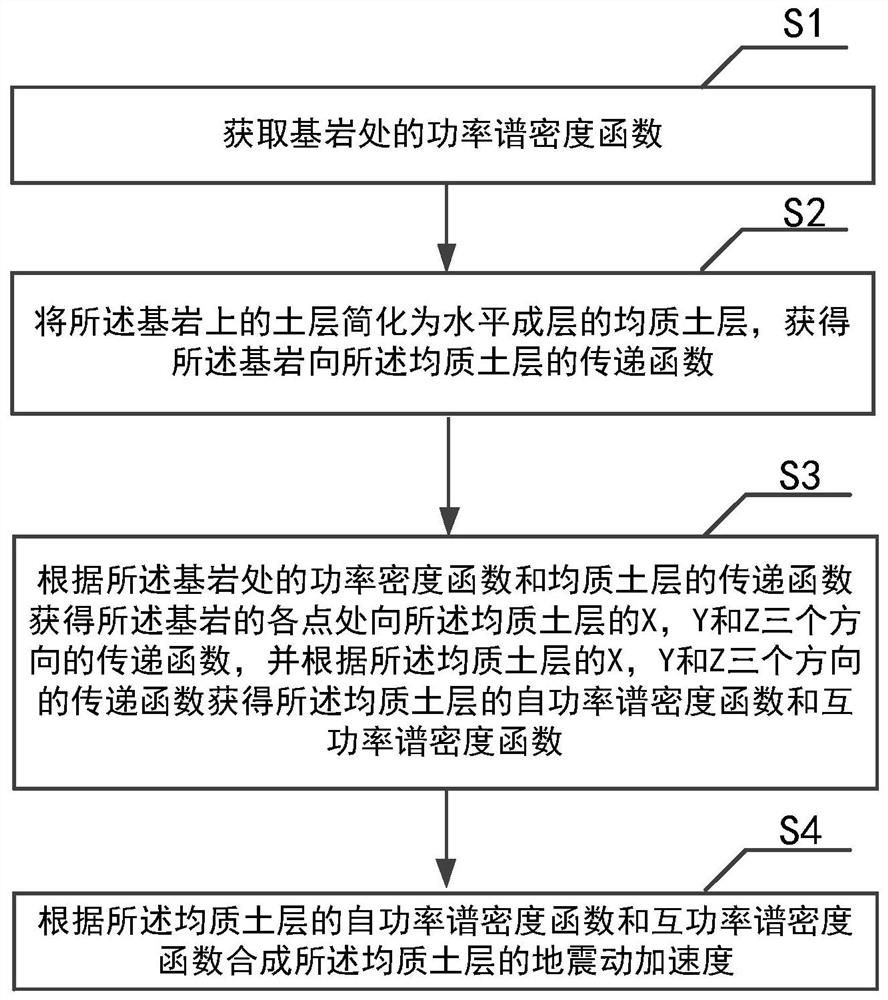
PendingCN112069569AResearch on the Realization of Multiple Incidence AnglesIn line with the actual situationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBedrockClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to the related technical field of seismic oscillation detection, and discloses a multi-point seismic oscillation synthesis method, which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a power spectral density function at a bedrock; S2, simplifying a soil layer on the bed rock into a homogeneous soil layer which is horizontally layered to acquire a transfer function from a bed rock to the homogeneous soil layer; S3, according to the power density function of the bedrock and the transfer function of the homogeneous soil layer, obtaining transfer functions of the homogeneous soil layer from each point of the bedrock in the X, Y and Z directions, and further obtaining a self-power spectral density function and a cross-power spectral density function of the homogeneous soillayer; and S4, synthesizing the seismic oscillation acceleration of the homogeneous soil layer according to the self-power spectral density function and the cross-power spectral density function of the homogeneous soil layer. The invention further provides a multi-point seismic oscillation synthesis system. By means of the method and system, accurate representation of seismic oscillation can be achieved, meanwhile, the requirement of the system for the professional level of a user is low, and research and design efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
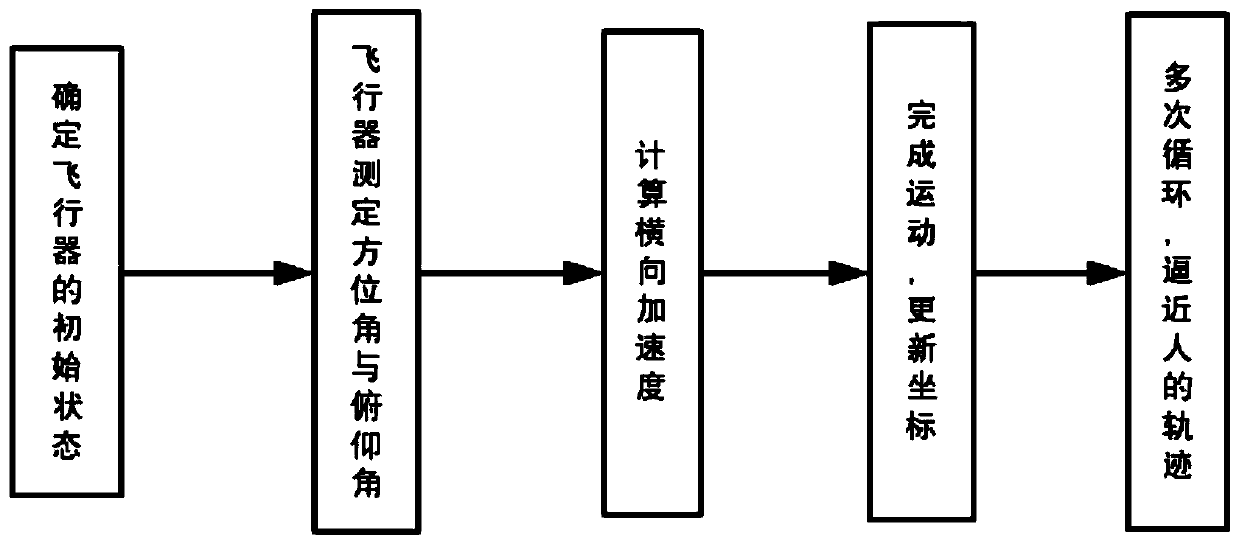
UAV control method for automatically following signal source
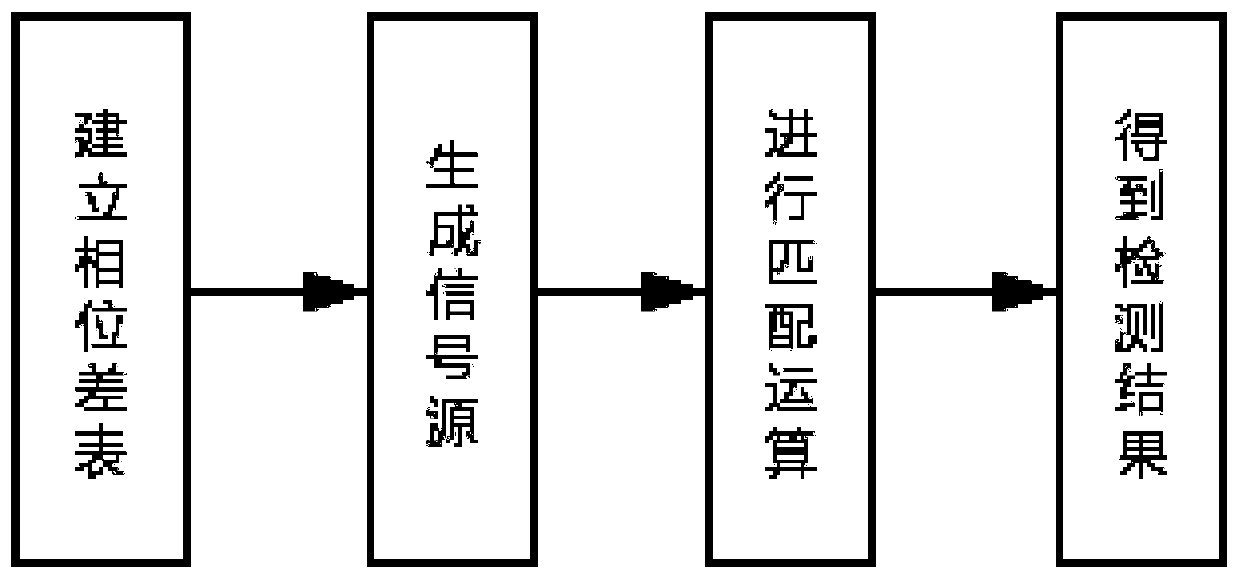
The invention provides an UAV control method for automatically following a signal source. The method is characterized by finding the direction of the signal source by using a phase difference measurement algorithm based on a cross-spectral density function and using correlation interferometry in a radio direction finding technique; establishing a sample library of the phase differences by using the structure of an antenna array, and attaching its corresponding elevation angle and azimuth angle to shorten the direction finding time; performing data matching on the measured phase difference to obtain a true pitch angle and a true azimuth angle to locate a target; and approximating a human motion trajectory by using a UAV path guidance algorithm. The method has the characteristics of stable operation, simple and effective steps and real-time control. In practical applications, an automatic following system using the control method can make a police UAV follow a police to carry out law enforcement, can save a lot of police resources, and is very suitable to be popularized and applied in daily police practices.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
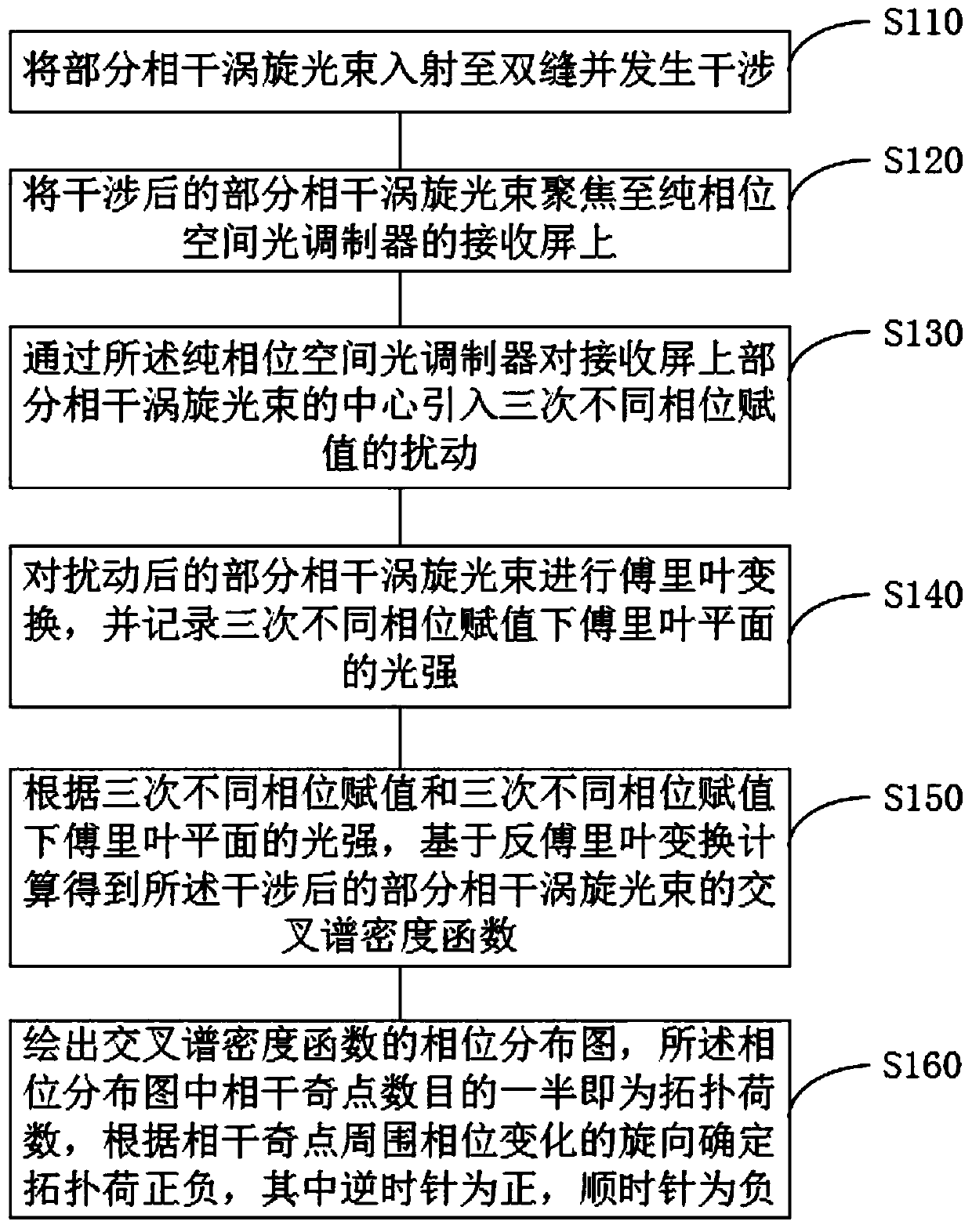
Method and system for measuring topological charges and positive and negative values of partially coherent vortex beams
ActiveCN111412983ARealize measurementLess stringent requirementsOptical measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
The invention discloses a method and a system for measuring topological charges and positive and negative values of partially coherent vortex light beams. The method comprises the following steps: enabling the partially coherent vortex light beams to enter double slits and generate interference; focusing the partially coherent vortex light beams after interference to a receiving screen of a pure phase spatial light modulator through a lens; introducing disturbance of three times of different phase assignment to the center of the partially coherent vortex light beams on the receiving screen through a pure phase spatial light modulator; carrying out fourier transform on the disturbed partially coherent vortex light beams, wherein the light intensity of a Fourier plane under three times of different phase assignment is recorded; according to the three times of different phase assignment and the light intensity of the Fourier plane under the three times of different phase assignment, basedon inverse Fourier transform, calculating to obtain a cross spectral density function of the partially coherent vortex beams after double-slit interference and focusing. Coherent singular points canbe directly observed from a phase distribution diagram of the cross spectral density function, and therefore the topological charges and positive and negative values of the partially coherent vortex beams are obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Frequency offset estimating method and receiver employing the same
InactiveUS20060146961A1Carrier regulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCarrier signalHardware complexity
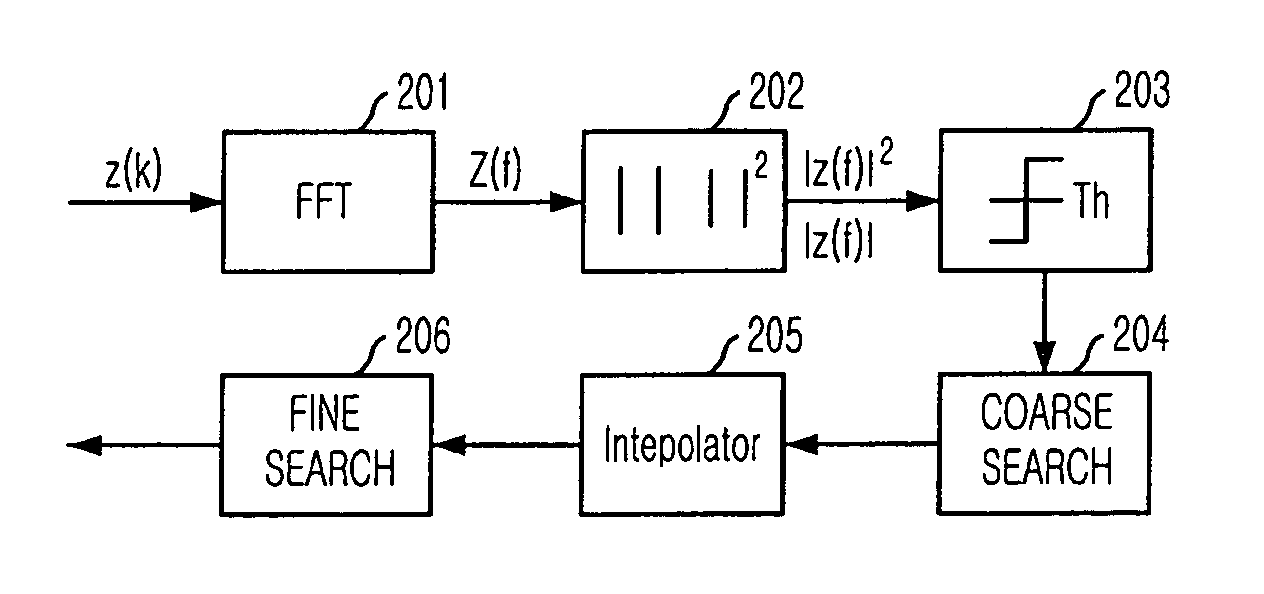
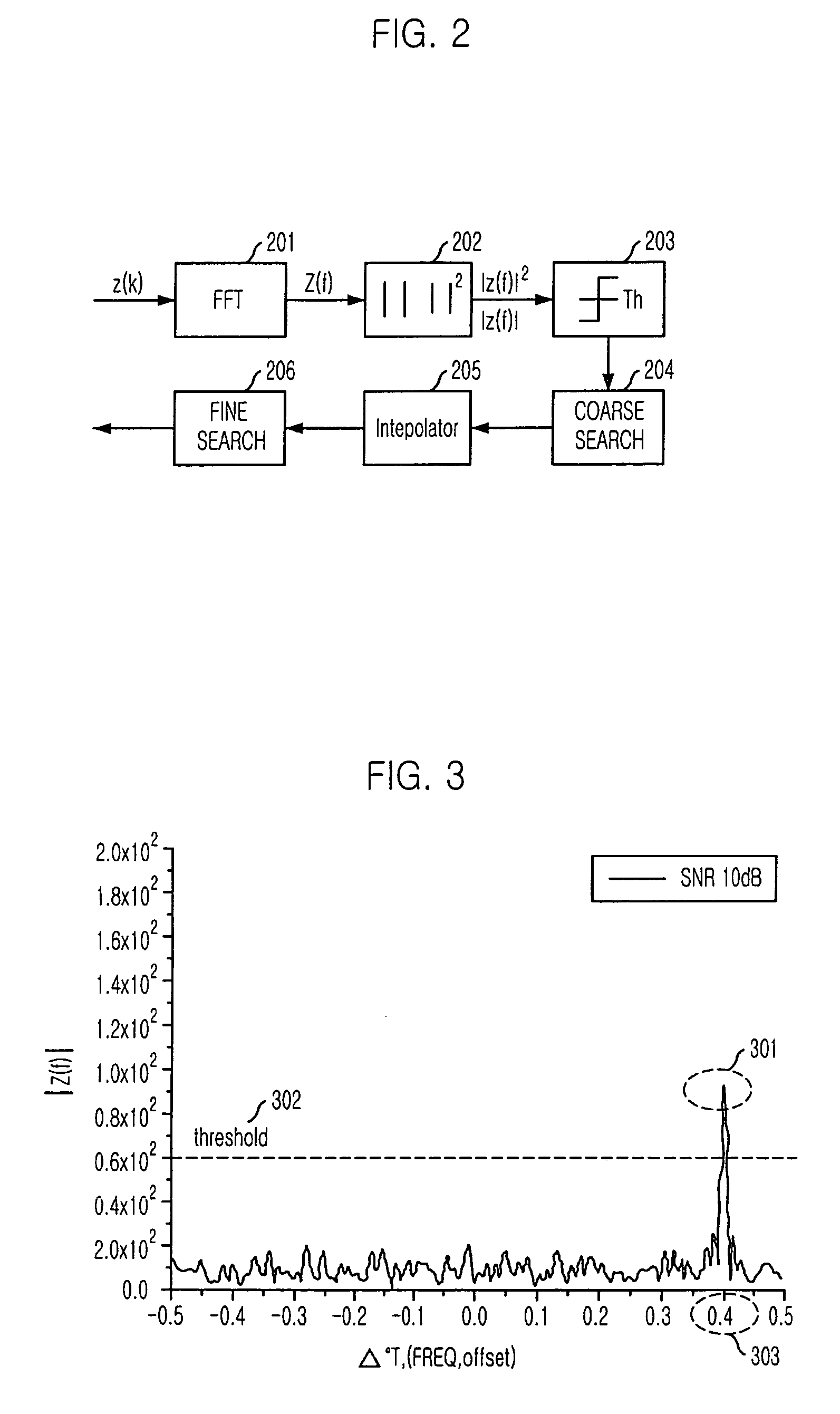
Provided is a method for estimating carrier wave or doppler frequency offset based on an approximated quadratic non-linear function in fine search, and a receiver employing the method. The method for estimating frequency offset includes the steps of: a) extracting more than three discrete samples in an order where the discrete samples are close to a maximum value of a power spectrum density function; b) inducing a quadratic non-linear function by using the extracted discrete samples; and c) estimating the frequency offset from a maximum point of the quadratic non-linear function. The technology of the present research makes it possible to exactly estimate frequency offset without increasing hardware complexity in estimation of carrier wave or doppler frequency offset.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com