Non-contact type ridge waveguide, micro-strip and coupling slot probe transition circuit
A non-contact, ridged waveguide technology, applied in circuits, waveguide devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as operating bandwidth limitations, achieve low-loss transition, strong electric field signals, and avoid effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
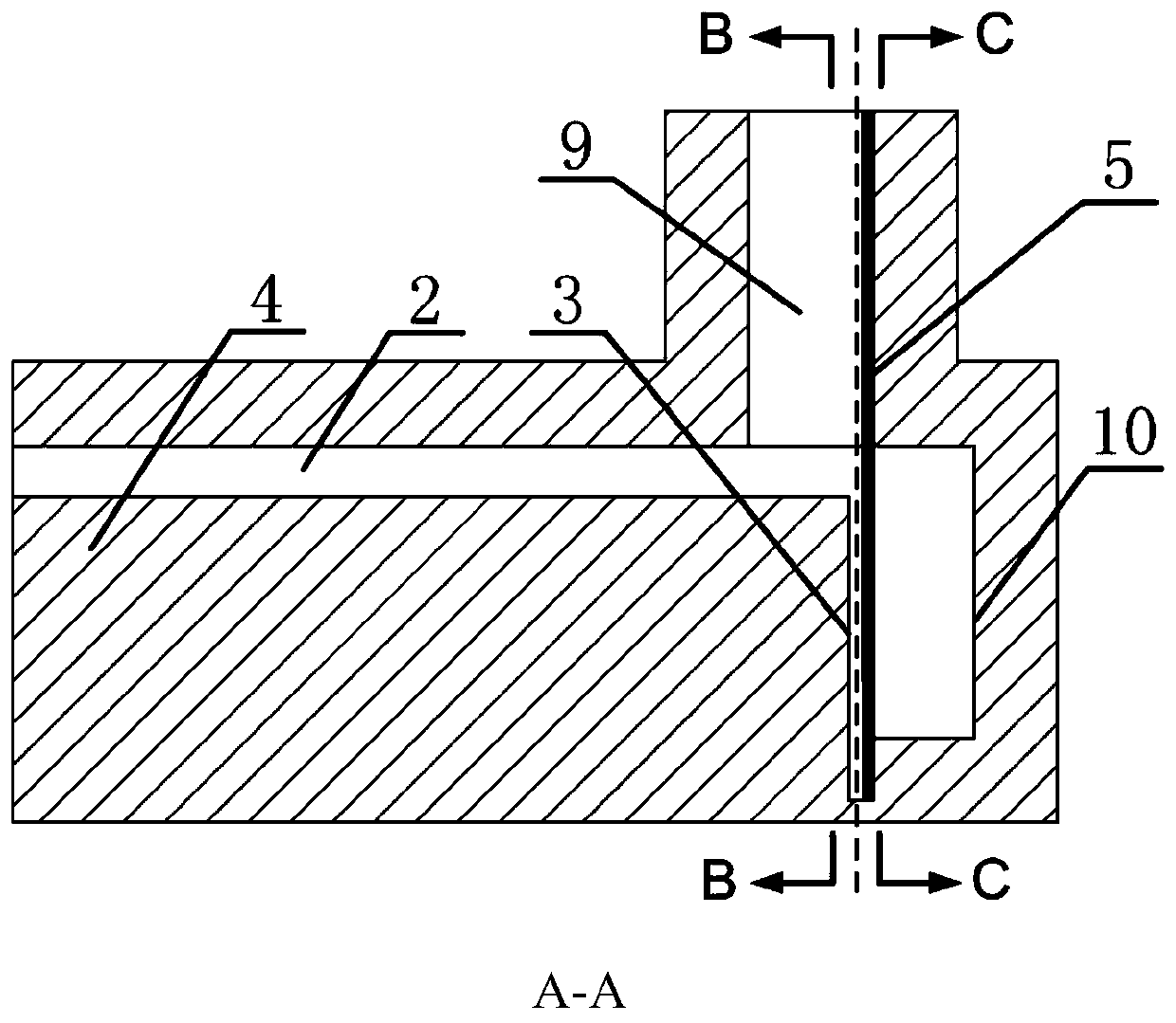
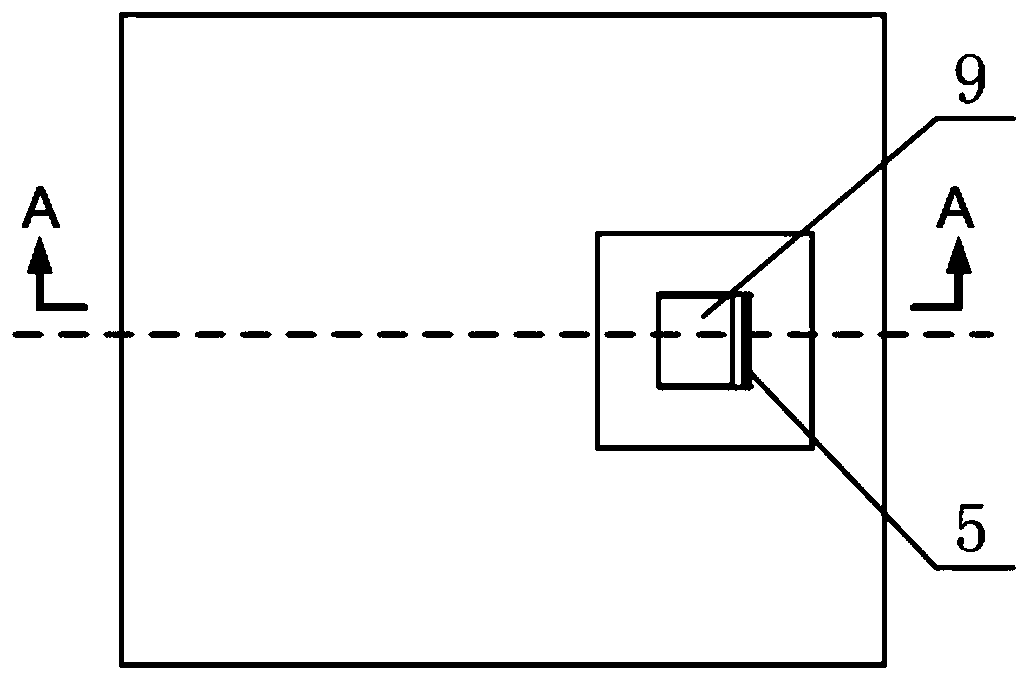
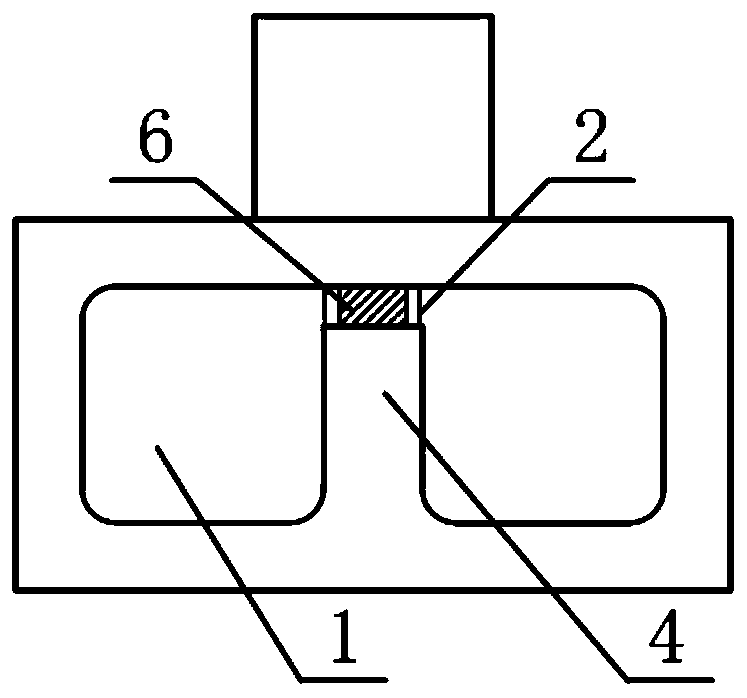
[0017] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 5 . In the preferred embodiment described below, a non-contact ridge waveguide microstrip coupling slot probe transition structure includes: a single ridge waveguide composed of a waveguide ridge back 4 is fabricated in a rectangular waveguide 1, perpendicular to the center of the upper end plane of the rectangular waveguide 1 The windowed waveguide 9 of the line, the waveguide back gap 2 formed by the upper end plane of the waveguide ridge 4 and the upper bottom plane of the rectangular waveguide 1, and the microstrip probe 6 inserted into the window channel of the windowed waveguide 9. It is characterized in that: the waveguide ridge 4 extends below the window at the bottom of the windowed waveguide 9, cuts down and turns vertically to form a section of the ridge open end 3, and is a microstrip substrate inserted downward from the side wall of the window terminal of the windowed waveguide 9 5 is divided into a waveguide coupling slot and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com