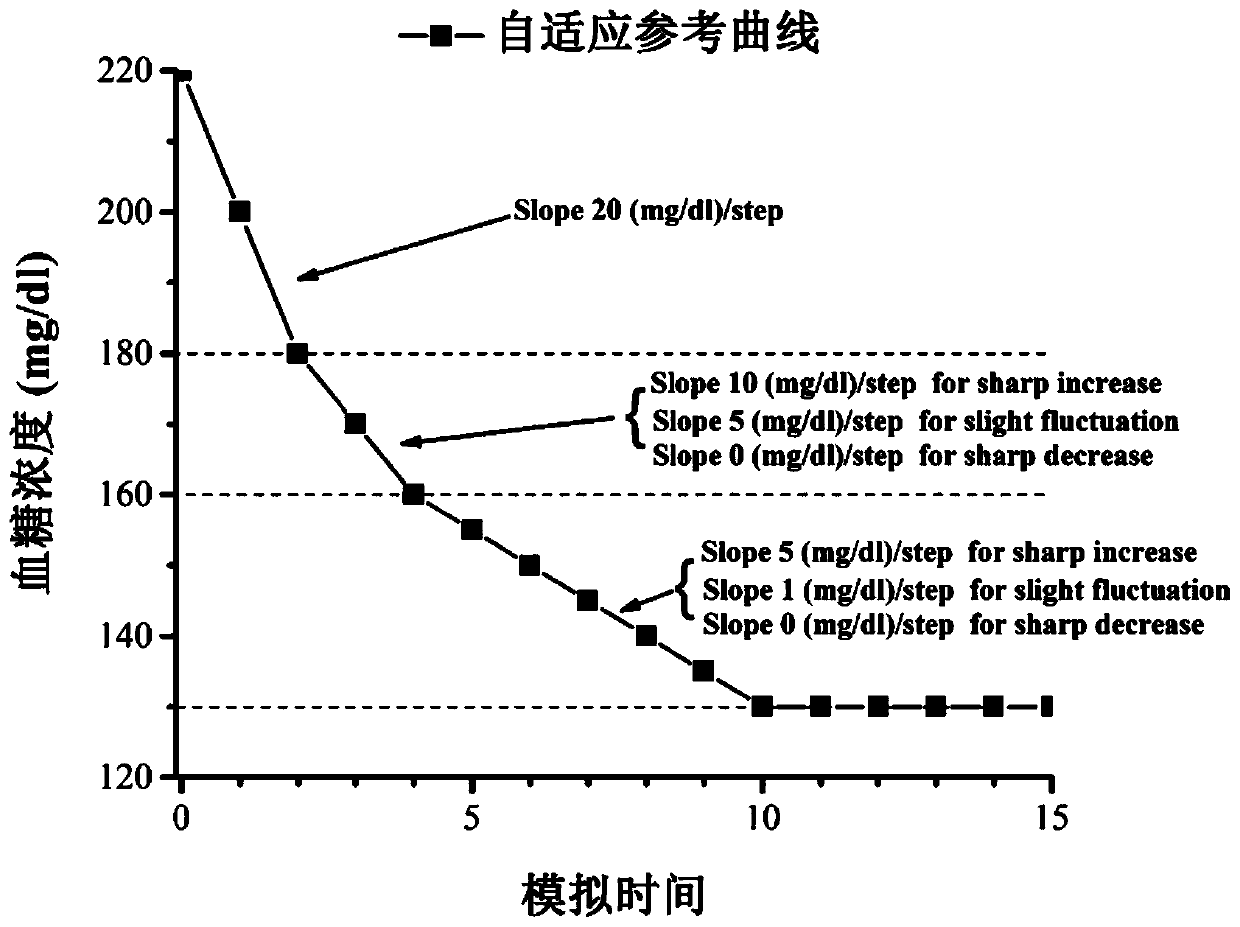
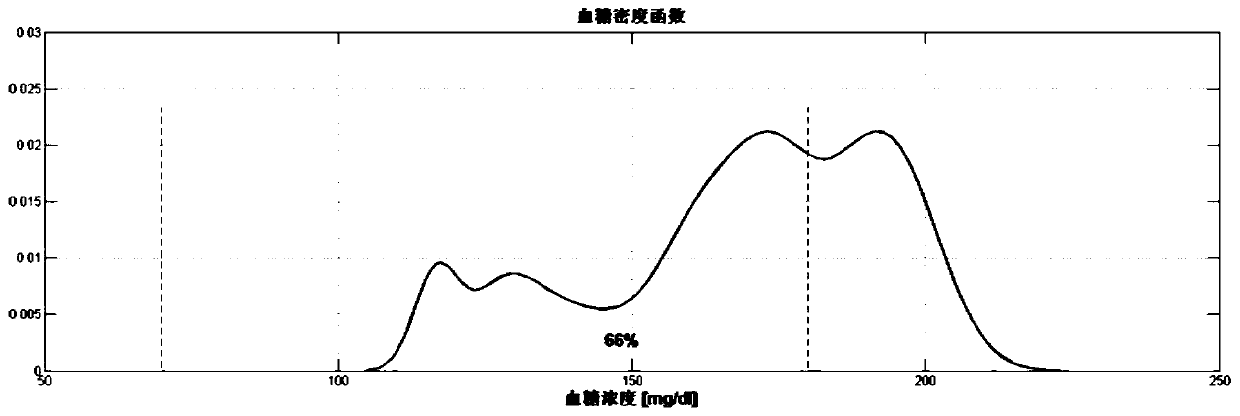
Generalized predictive control insulin infusion amount calculating method based on adaptive reference curve strategy
A generalized predictive control and reference curve technology, applied in adaptive control, flow control, pressure infusion, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve control effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
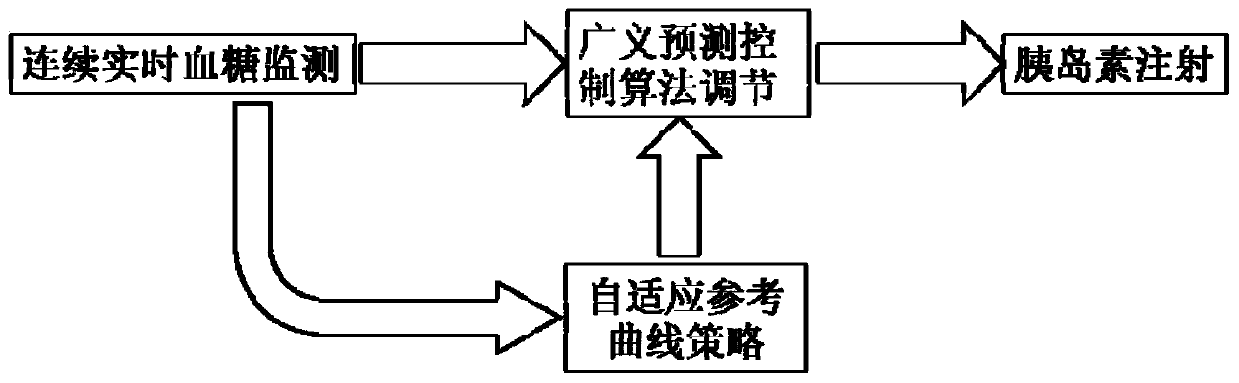
[0102] Such as figure 1 As shown, a generalized predictive control insulin infusion calculation method based on the adaptive reference curve strategy includes the following steps:
[0103] S1: According to the current blood sugar value, the predicted value of future blood sugar changes is obtained through the CARIMA model;
[0104] Through the CARIMA model and the Diophantine equation, the following equation is obtained:
[0105] y(k+j)=G j (z -1 )Δu(k+j-1)+F j (z -1 )y(k)(j=1,2...n)
[0106]In the formula, y(k) represents the blood glucose level at time k; y(k+j) represents the predicted value of blood glucose level j steps ahead at time k; Δu(k+j-1) represents the blood glucose level of the insulin pump at time k Control input increment; n represents the maximum prediction length; G j (z -1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the control input increment of the insulin pump at time k; F j (z -1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the blood sugar value;
[010...
Embodiment 2
[0140] Such as figure 1 As shown, a generalized predictive control insulin infusion calculation method based on the adaptive reference curve strategy includes the following steps:
[0141] S1: According to the current blood sugar value, the predicted value of future blood sugar changes is obtained through the CARIMA model;
[0142] Through the CARIMA model and the Diophantine equation, the following equation is obtained:
[0143] y(k+j)=G j (z -1 )Δu(k+j-1)+F j (z -1 )y(k)(j=1,2...n)
[0144] In the formula, y(k) represents the blood glucose level at time k; y(k+j) represents the predicted value of blood glucose level j steps ahead at time k; Δu(k+j-1) represents the blood glucose level of the insulin pump at time k Control input increment; n represents the maximum prediction length; G j (z -1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the control input increment of the insulin pump at time k; F j (z -1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the blood sugar value;
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0178] Such as figure 1 As shown, a generalized predictive control insulin infusion calculation method based on the adaptive reference curve strategy includes the following steps:
[0179] S1: According to the current blood sugar value, the predicted value of future blood sugar changes is obtained through the CARIMA model;
[0180] Through the CARIMA model and the Diophantine equation, the following equation is obtained:
[0181] y(k+j)=G j (z -1 )Δu(k+J-1)+F j (z -1 )y(k)(j=1,2...n)
[0182] In the formula, y(k) represents the blood glucose level at time k; y(k+j) represents the predicted value of blood glucose level j steps ahead at time k; Δu(k+j-1) represents the blood glucose level of the insulin pump at time k Control input increment; n represents the maximum prediction length; G j (z- 1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the control input increment of the insulin pump at time k; F j (z -1 ) represents the weight coefficient of the blood sugar value;
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com