Anti-loosening quick-replacing nut
An anti-loosening and nut technology, applied in the direction of nuts, screws, bolts, etc., can solve the problems of poor anti-loosening performance of anti-loosening quick-change nuts and affecting the personal safety of staff.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
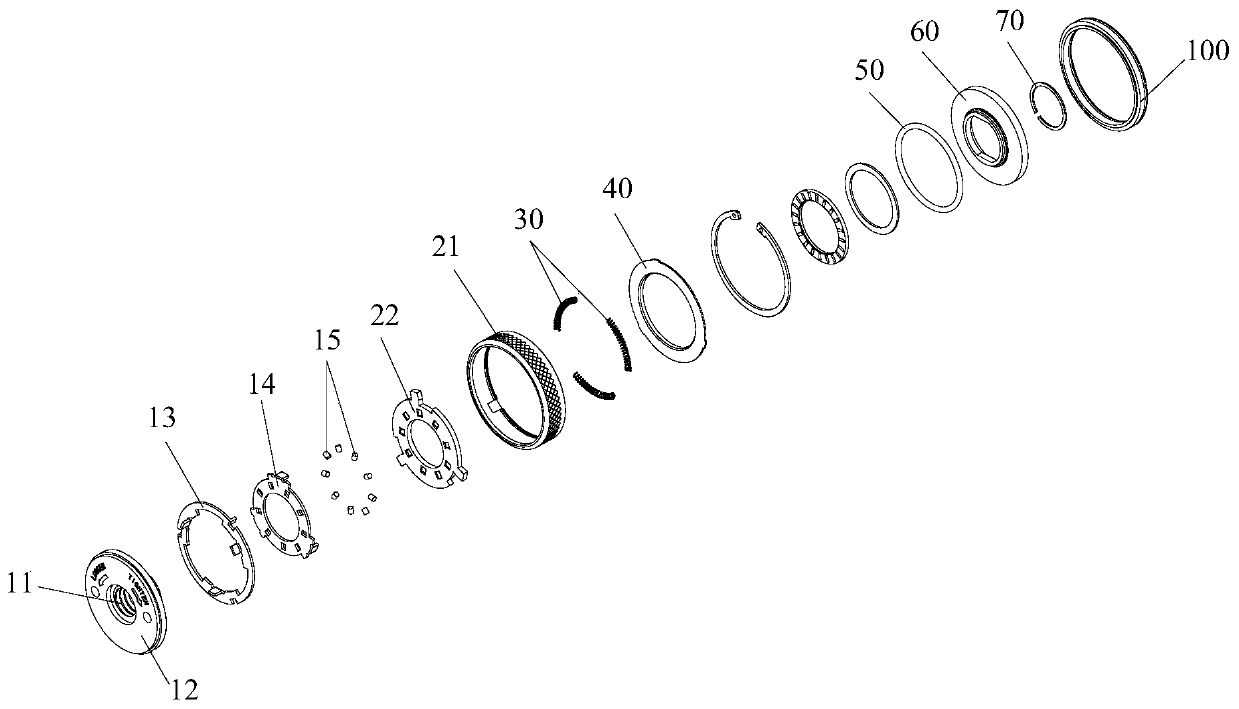
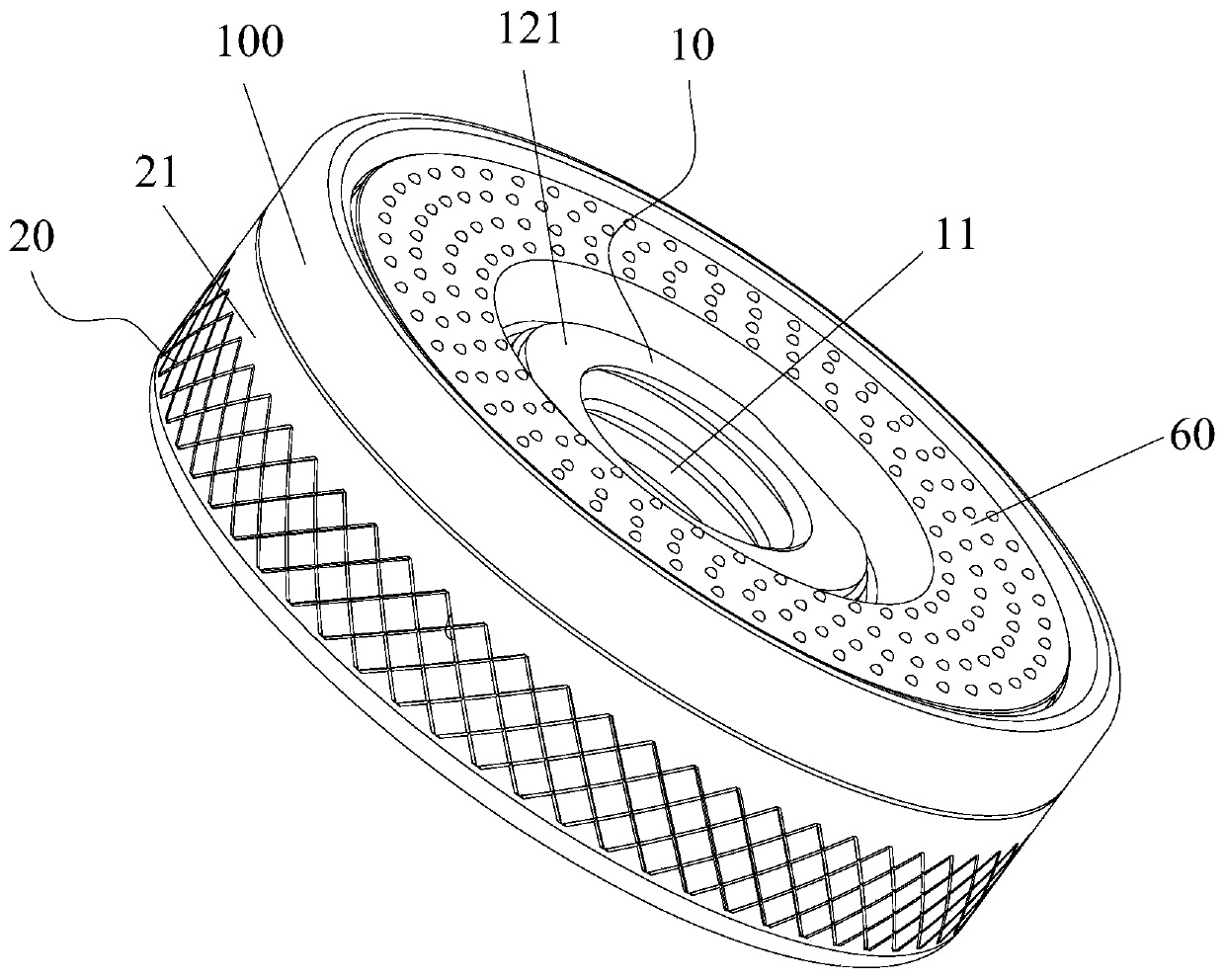
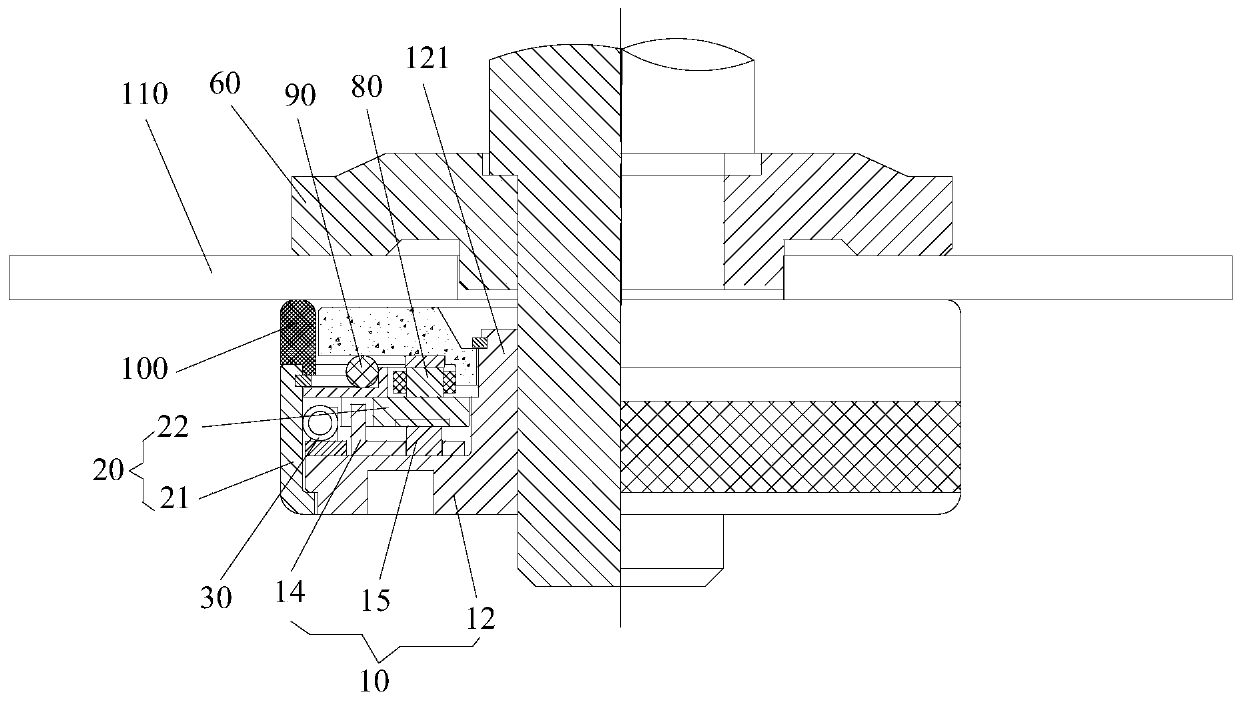
[0038] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the anti-loosening quick change nut includes a nut assembly 10 , a screw assembly 20 and an anti-loosening structure 100 . Wherein, the nut assembly 10 has an internal thread 11 . The screw assembly 20 includes a sleeve structure 21 and a partition structure 22. The sleeve structure 21 is sleeved outside the nut assembly 10. The partition structure 22 is detachably connected to the sleeve structure 21 and is located in the sleeve structure 21. The partition structure 22 is connected to the sleeve structure 21. The nut assembly 10 is non-rotatingly connected so that the screw assembly 20 has a static anti-rotation state relative to the nut assembly 10 . When the screw assembly 20 is in the anti-rotation state, the screw assembly 20 can drive the nut assembly 10 to rotate together. The anti-loosening structure 100 is arranged on the side of the screw assembly 20 facing the to-be-fastened piece 110 to increase the frictional force b...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The difference between the anti-loosening quick-change nut in the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the structure of the anti-loosening quick-change nut is different.
[0055] Such as Figure 4 to Figure 6 As shown, the nut assembly 10 includes a nut body 12, the nut body 12 has a through hole 123 and a mounting portion 124 communicating with the through hole 123, the inner wall of the through hole 123 has an internal thread 11, and the anti-loosening quick change nut also includes an auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 . Wherein, the auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 is arranged in the installation part 124, and the auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 is in contact with the to-be-fastener 110 pierced in the via hole 123, so as to increase the gap between the anti-loosening quick-change nut and the to-be-fastener 110. The frictional force prevents the anti-loosening quick-change nut from rotating relative to the component 110 to be fastened....
Embodiment 3
[0062] The difference between the anti-loosening quick-change nut in the third embodiment and the second embodiment is that the structure of the auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 is different.
[0063] Such as Figure 7 to Figure 10 As shown, the auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 includes a locking section 131 and a tapered section 132 connected in sequence, and the size of the tapered section 132 gradually increases along the direction from the locking section 131 to the tapered section 132 . Wherein, the tapered section 132 is connected with the mounting portion 124 to connect the auxiliary anti-loosening structure 130 with the nut body 12 , and the clamping section 131 is clamped with the component to be fastened 110 passing through the through hole 123 . In this way, when the anti-loosening quick-change nut is tightened on the component 110 to be fastened (such as the motor shaft), the clamping section 131 will be deformed to a certain extent, so that the frictio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com