Speaker verification method and system based on tensor structure and sparse representation
A technology of speaker confirmation and sparse representation, applied in the field of speaker recognition, can solve problems such as a large amount of memory, slow down the recognition process, limit the number of training samples, etc., to reduce the computational complexity and improve the confirmation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
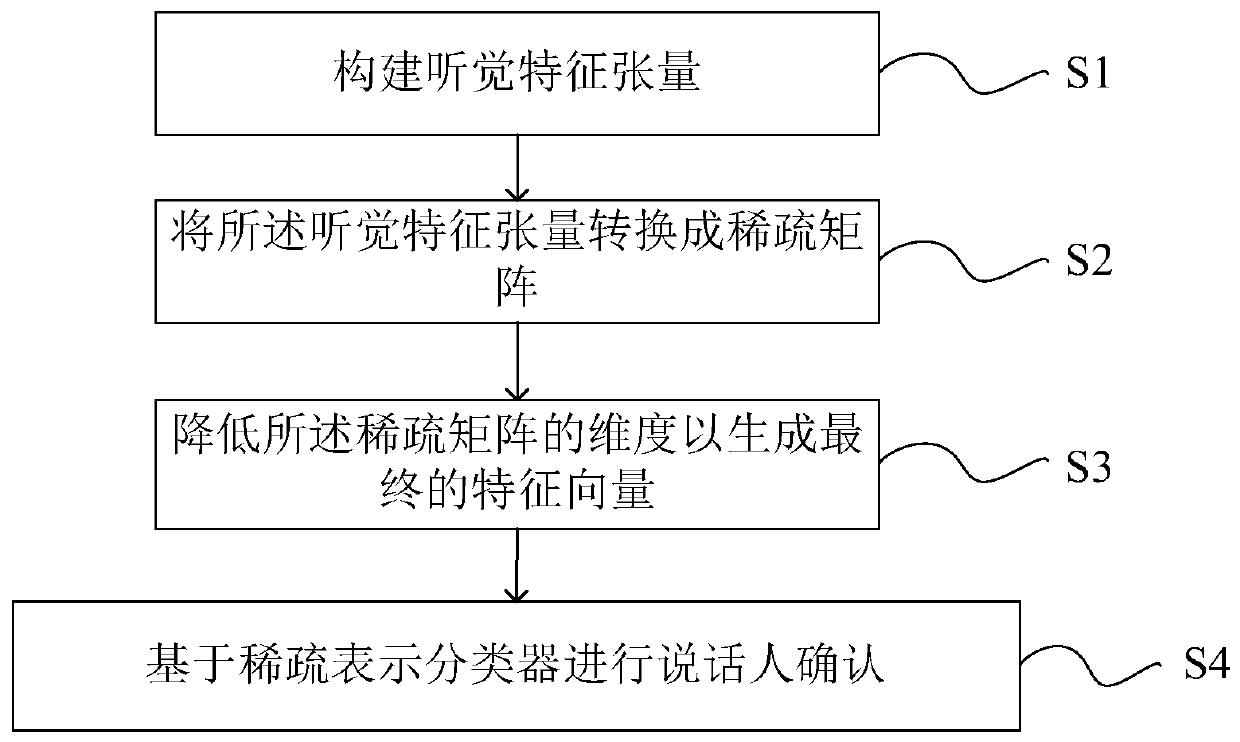
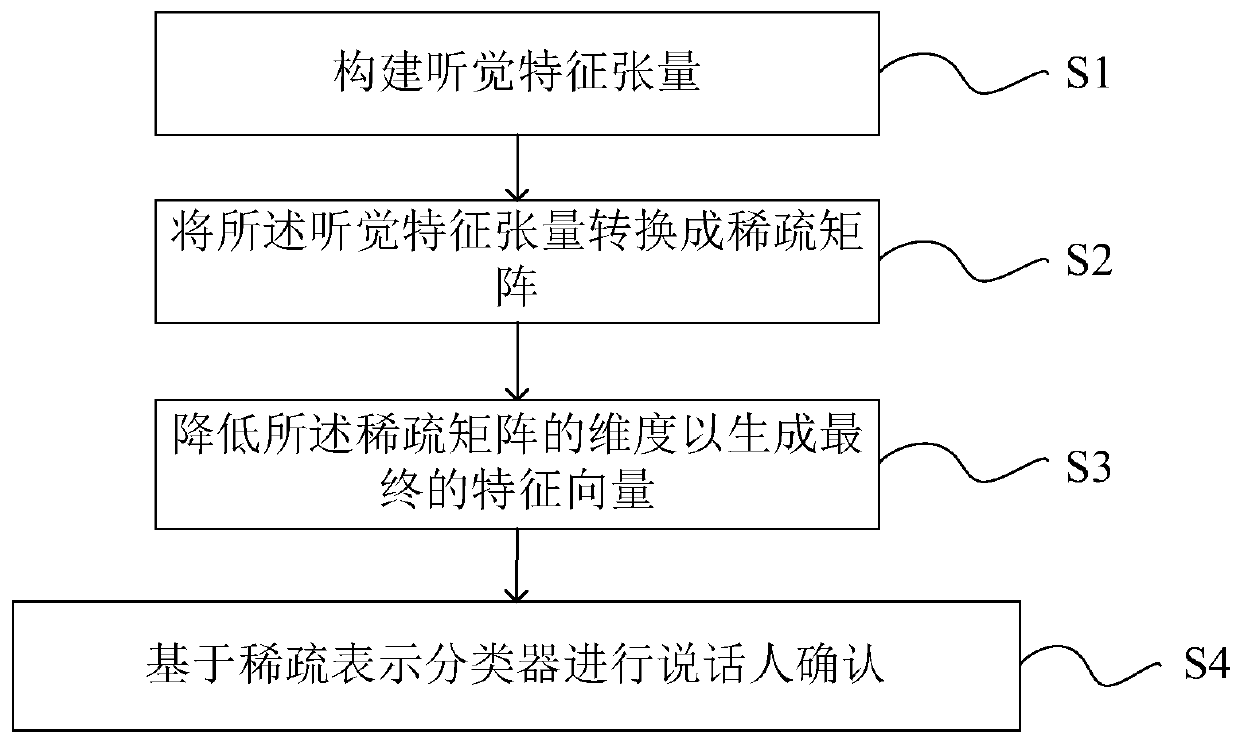
[0033] This embodiment provides a speaker confirmation method based on tensor structure and sparse representation, such as figure 1 shown, including steps:
[0034] S1. Construct an auditory feature tensor;
[0035] The present invention processes speech signals by simulating the auditory system of the human ear to obtain its power spectrum. In order to obtain robust features based on tensor structure, this embodiment models the obtained power spectra of different speakers as a third-order tensor quantity.
[0036] Specifically, the human ear can easily perform speaker recognition tasks and is insensitive to noise. In our feature extraction framework, we obtain frequency-selective information by mimicking the processes performed by the human ear in the auditory periphery and pathways.
[0037] First, the present invention extracts features by simulating the process of auditory periphery and pathway occurrence, such as outer ear, middle ear, basilar membrane, inner hair cell...
Embodiment 2
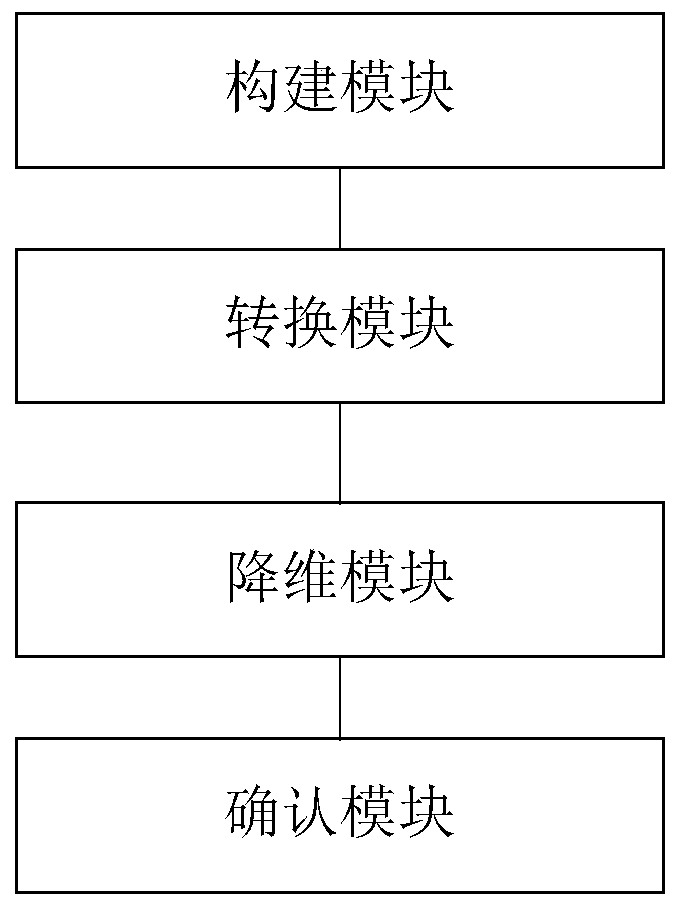
[0099] This embodiment provides a speaker confirmation system based on tensor structure and sparse representation, such as figure 2 shown, including:
[0100] Building blocks for constructing auditory feature tensors;
[0101] The present invention processes speech signals by simulating the auditory system of the human ear to obtain its power spectrum. In order to obtain robust features based on tensor structure, this embodiment models the obtained power spectra of different speakers as a third-order tensor quantity.
[0102] Specifically, the human ear can easily perform speaker recognition tasks and is insensitive to noise. In our feature extraction framework, we capture frequency-selective information by mimicking the processes performed by Ren in the auditory periphery and pathways.
[0103]First, the present invention extracts features by simulating the process of auditory periphery and pathway occurrence, such as outer ear, middle ear, basilar membrane, inner hair ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com