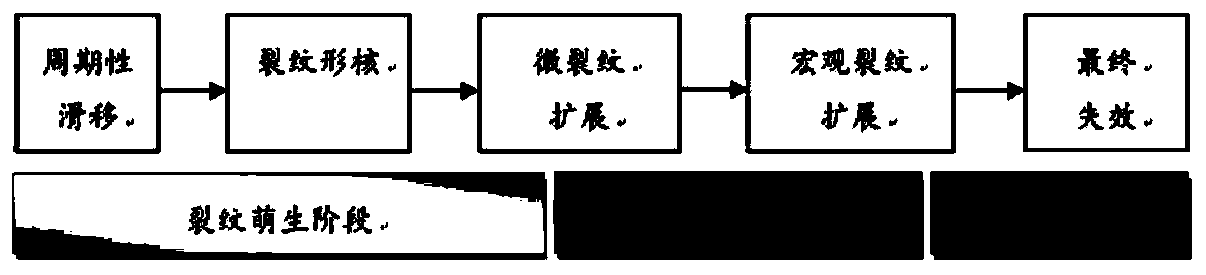
Method for establishing crystal plastic constitutive model in face-centered cubic material fatigue process
A face-centered cubic, constitutive model technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems that cannot consider mesoscopic plastic evolution, material damage, etc., and achieve important scientific significance and engineering application value , good compatibility and portability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The specific embodiments of the present invention are described below so that those skilled in the art can understand the present invention, but it should be clear that the present invention is not limited to the scope of the specific embodiments. For those of ordinary skill in the art, as long as various changes Within the spirit and scope of the present invention defined and determined by the appended claims, these changes are obvious, and all inventions and creations using the concept of the present invention are included in the protection list.
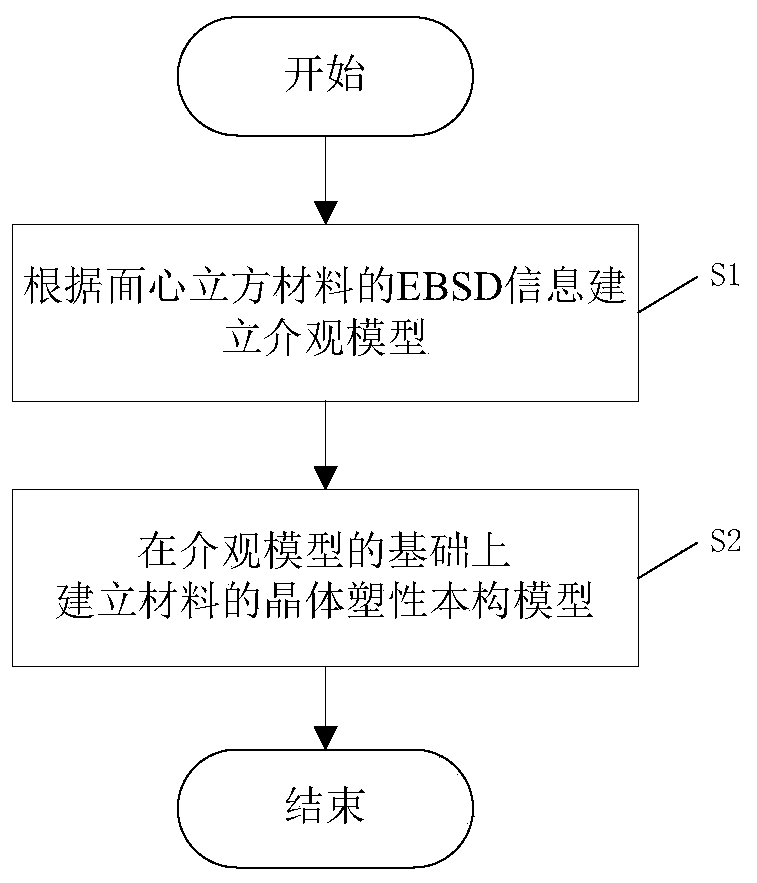
[0055] Such as figure 2 As shown, a method for establishing a crystal plastic constitutive model in the fatigue process of a face-centered cubic material includes the following steps:
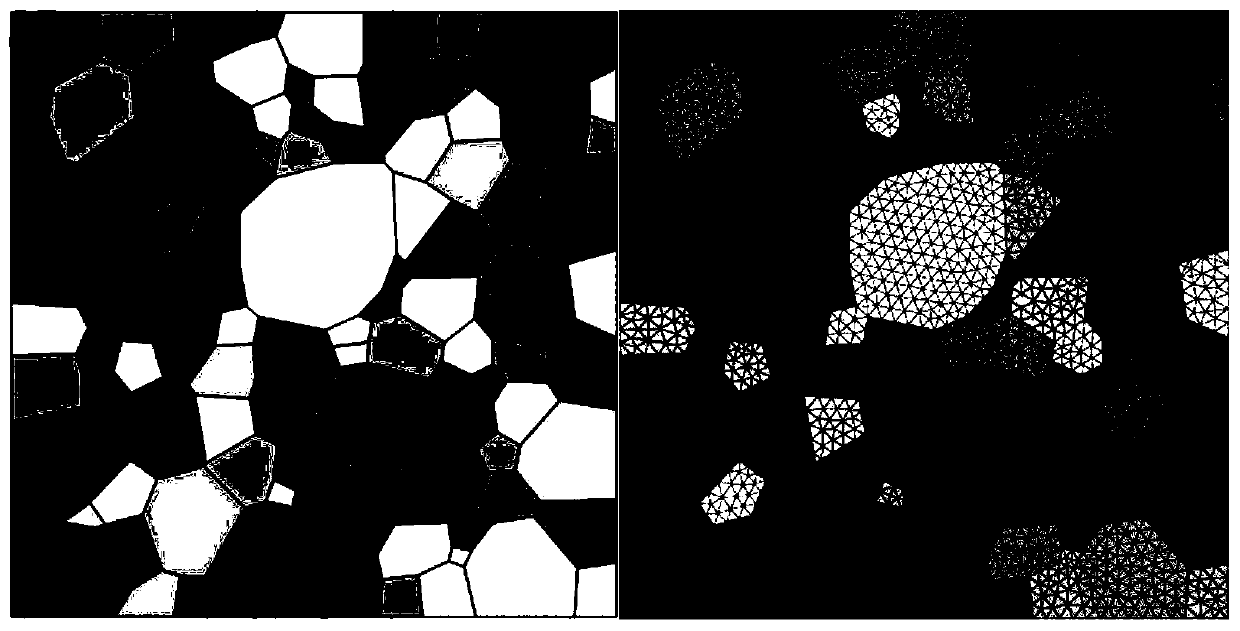
[0056] S1. Establish a mesoscopic model through the EBSD (Electron Backscatter Diffraction) information of the face-centered cubic material; the specific steps are:
[0057] S11. According to the EBSD information of the face-centered cubic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com