Laser radar
A lidar and laser technology, applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of large ranging, limited field of view of the lens, limited radar installation position and function use, etc., to meet the requirements of miniaturization, accuracy and ease of implementation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
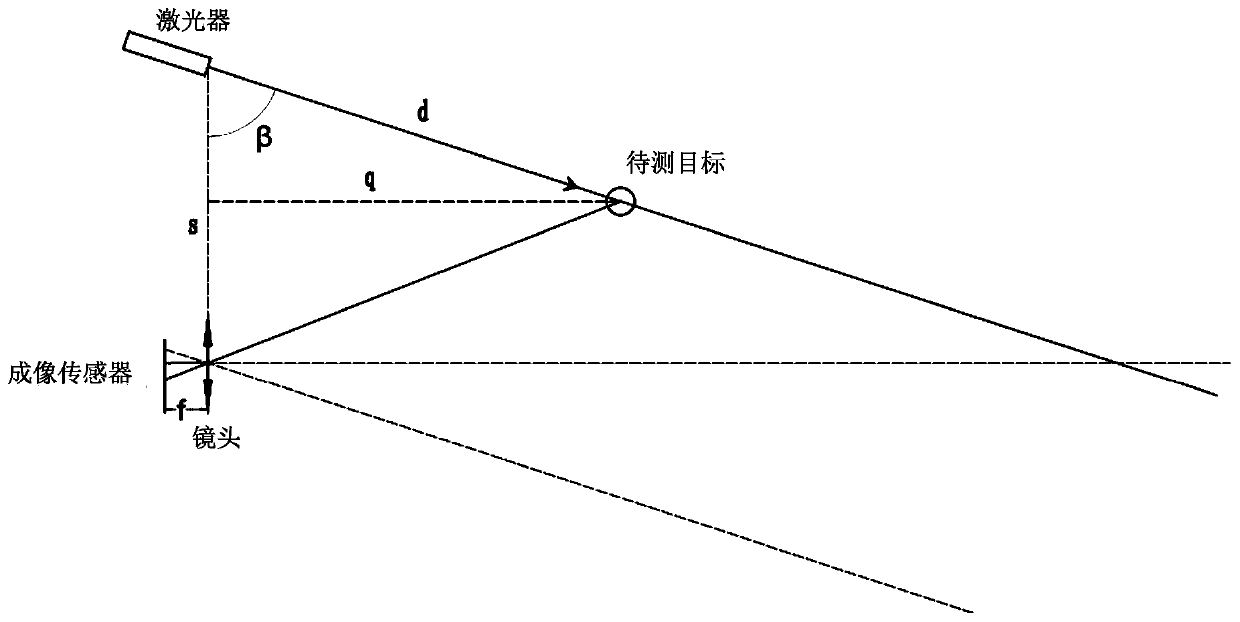
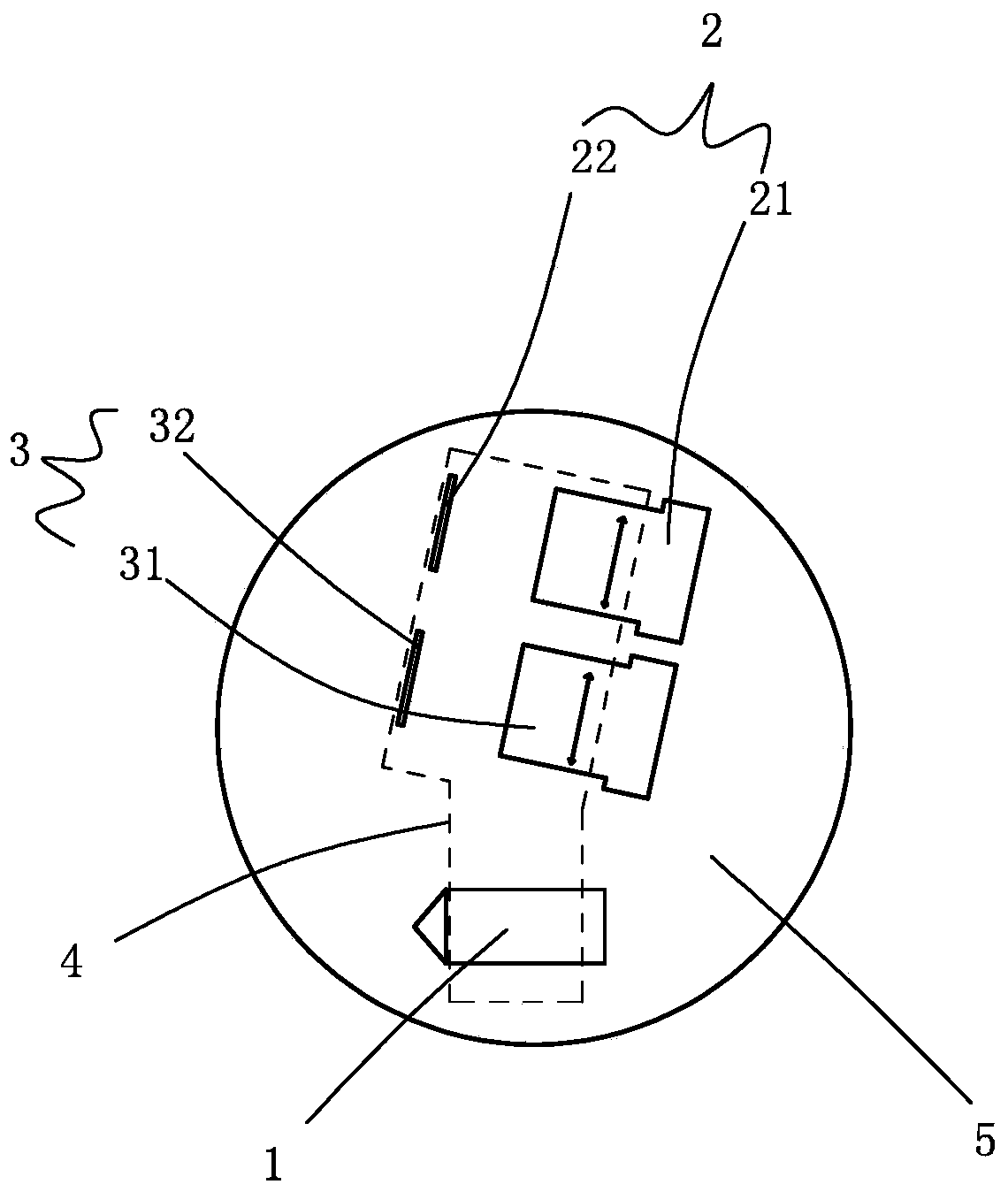
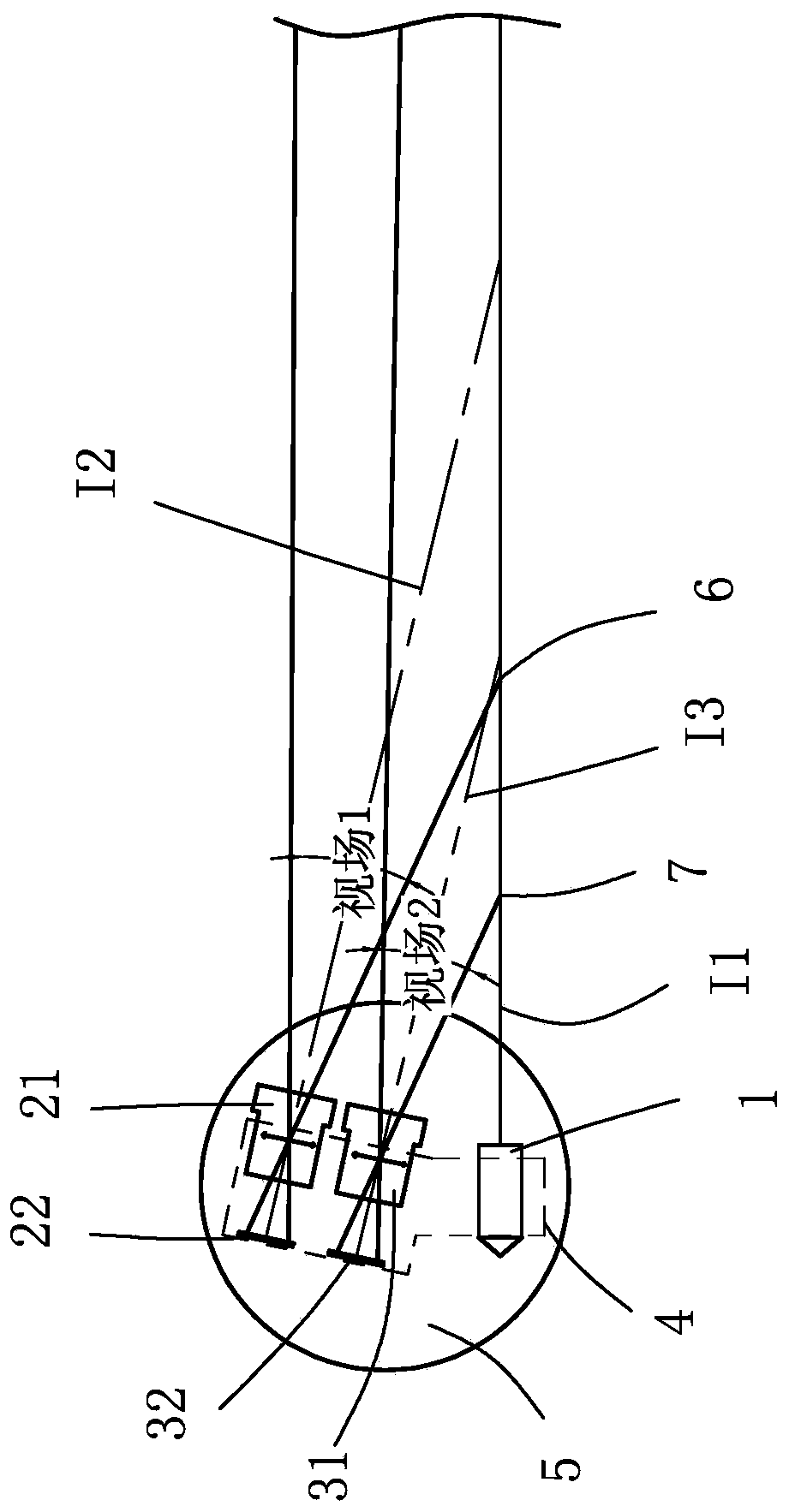
[0032] Such as figure 2 and 3 As shown, a laser radar includes a laser 1 and a receiving system. The laser 1 is used to emit laser light to the target to be measured, and the receiving system is used to receive the laser light reflected back from the target to be measured. For specific principles, please refer to the background technology. Here No more details.
[0033] The receiving system includes a first receiving system 2 and a second receiving system 3, the first receiving system 2 is spaced apart from the laser 1, and the second receiving system 3 is arranged between the first receiving system 2 and the laser 1, The first receiving system 2 is used to receive the laser light reflected back by the target to be measured within the range from the first near point 6 to the first far point (not shown in the figure), the first far point can be taken as infinity, but considering In actual use, it is generally not necessary to detect the infinite distance. In this embodiment,...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the receiving system includes a first receiving system, a second receiving system and a third receiving system, the first receiving system is set at intervals from the laser, and the second receiving system is set at Between the first receiving system and the laser, the third receiving system is arranged between the second receiving system and the laser, and the first receiving system is used to receive the target to be measured within the range from the first near point to the first far point The reflected laser light, the second receiving system is used to receive the laser light reflected back from the target to be measured within the range from the second near point to the second far point, and the third receiving system is used to receive the third near point to the third For the laser reflected back by the target to be measured within the range of the far point, the distance from the third near point to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com