Commercial vehicle anti-burst tire assembly and commercial vehicle tire burst control system
A technology for run-flat tires and control systems, applied in tire measurement, tire inflation valve, tire parts, etc., can solve the problems of low configuration of commercial vehicles, difficult to practical application of commercial vehicles, etc., to achieve low impact force and delay the deterioration of accidents time and improve driving safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
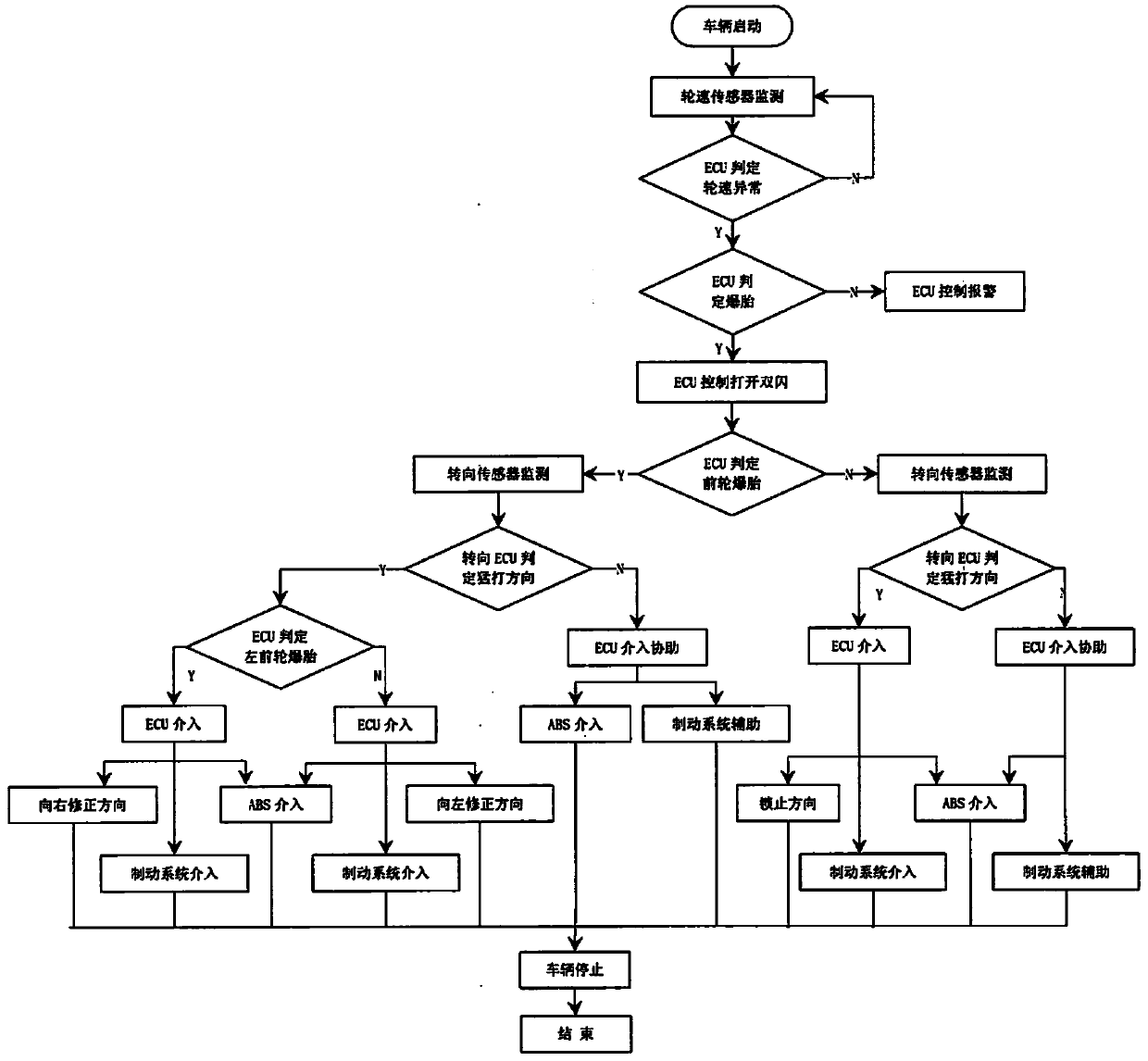
[0033] The specific embodiment of the present invention will be described in further detail by describing the embodiments below with reference to the accompanying drawings, the purpose is to help those skilled in the art to have a more complete, accurate and in-depth understanding of the concept and technical solutions of the present invention, and contribute to its implementation.
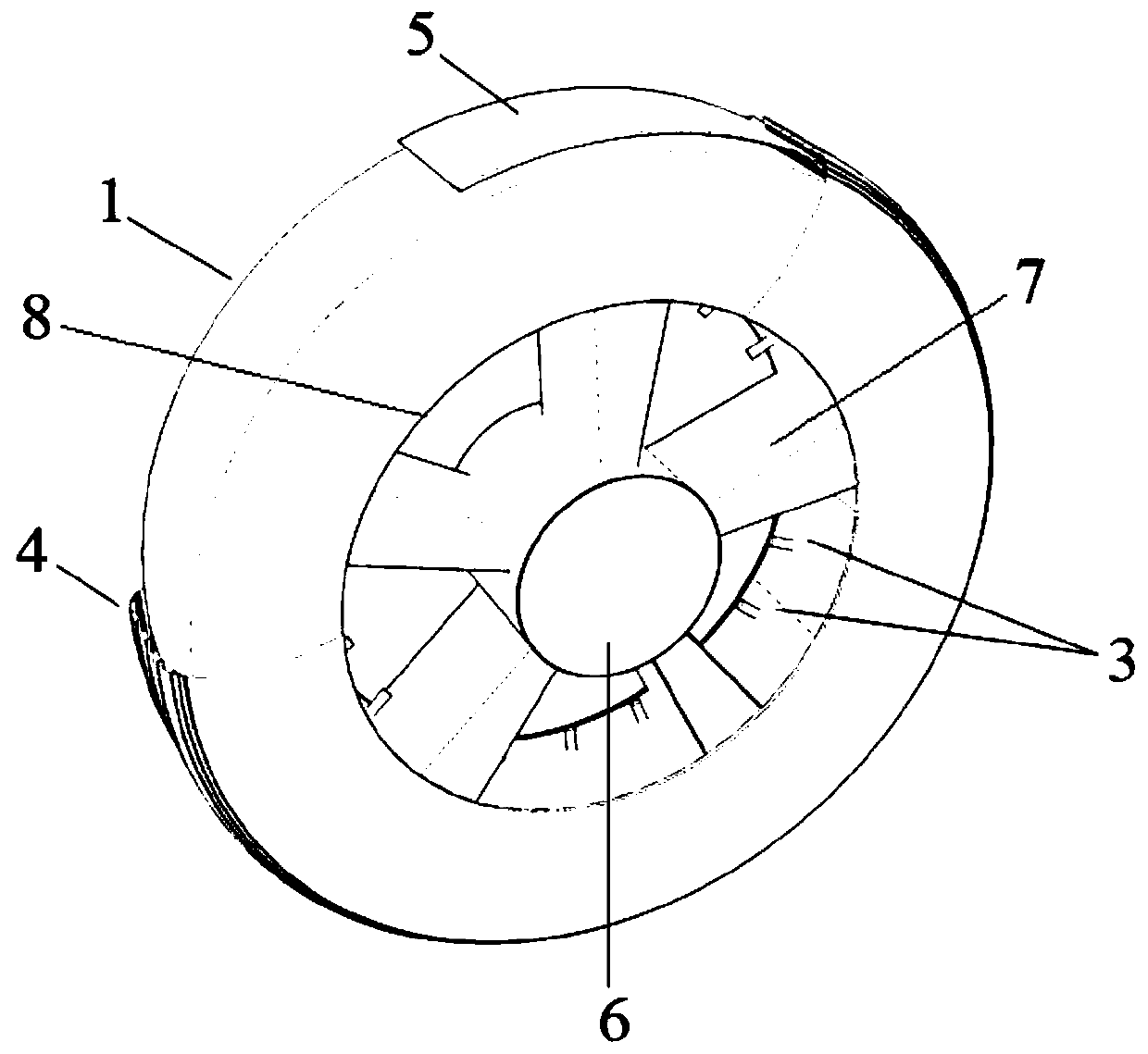
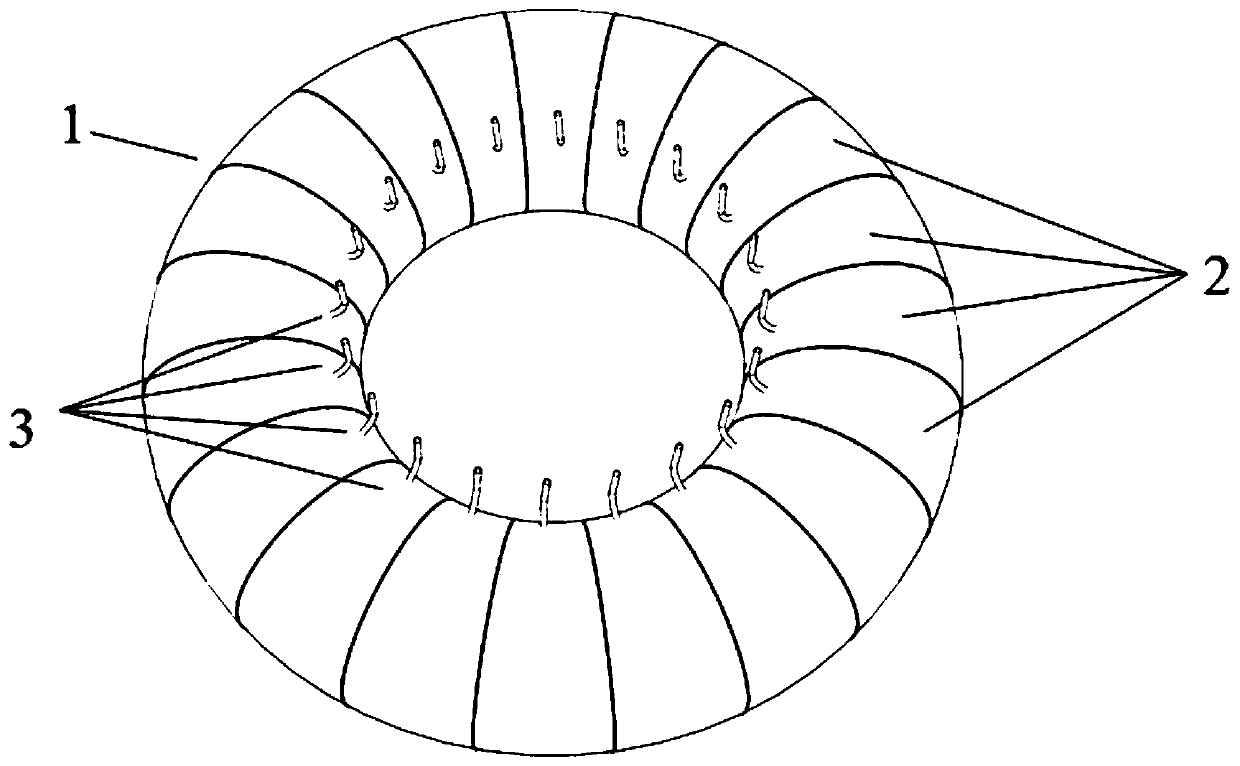
[0034] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a commercial vehicle run-flat tire assembly, comprising a rigid wheel, a pad 5, a cover tire 4 arranged on the rigid wheel, an inner tube 1 arranged inside the cover tire 4 and a diaphragm 2 arranged inside the inner tube 1 , the diaphragm 2 divides the inner cavity of the inner tube 1 into a plurality of independent air storage chambers, and two adjacent air storage chambers are not connected.
[0035] Specifically, as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the rigid wheel mainly includes a rim 8, a hub 6 and a spoke 7, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com