Method for predicting and avoiding inbreeding degree in conventional breeding of macrobrachium nipponense
An inbreeding and conventional technology, applied in the fields of instruments, climate change adaptation, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in estimating and controlling the degree of inbreeding, difficult family technology, asynchronous mating, etc., to achieve reliable evaluation of genetic progress, Overcoming genetic decline, strong practical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
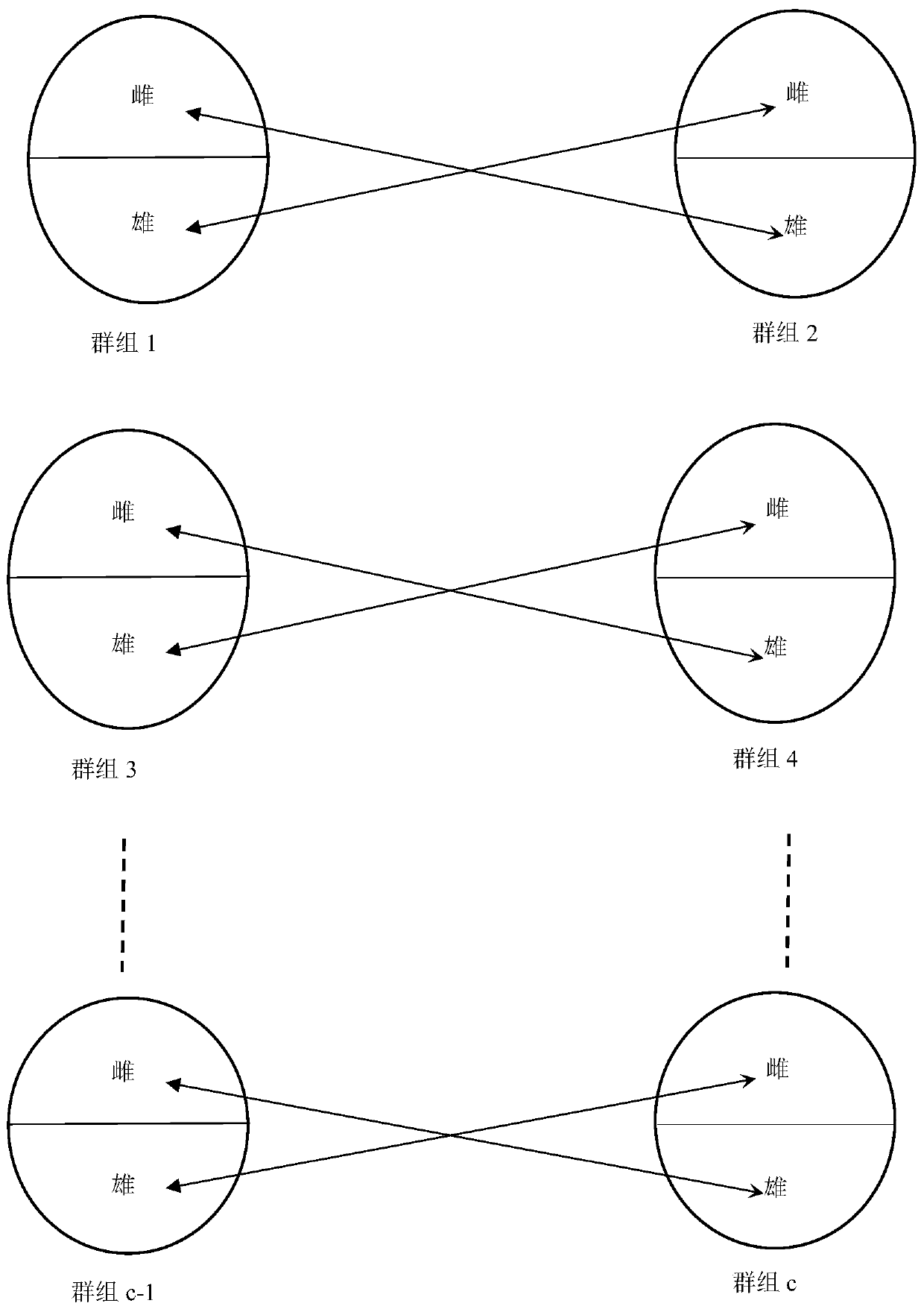
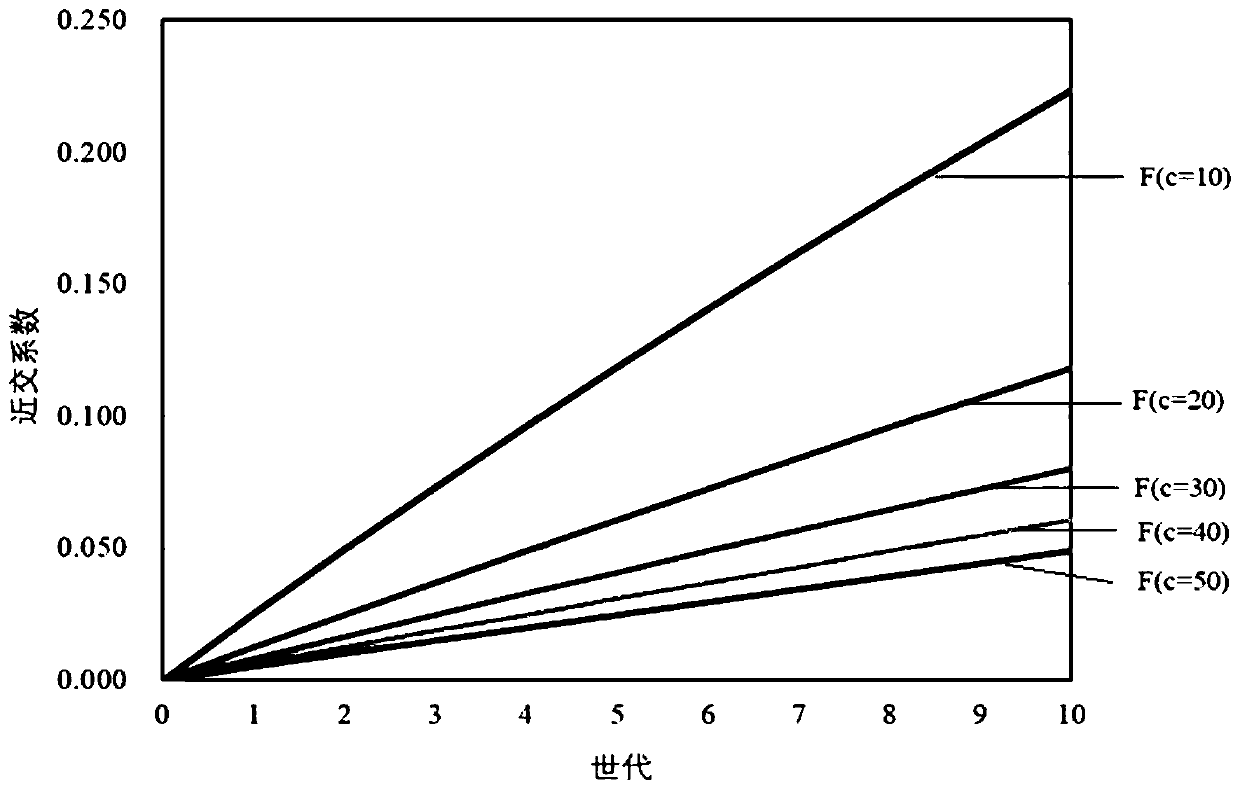
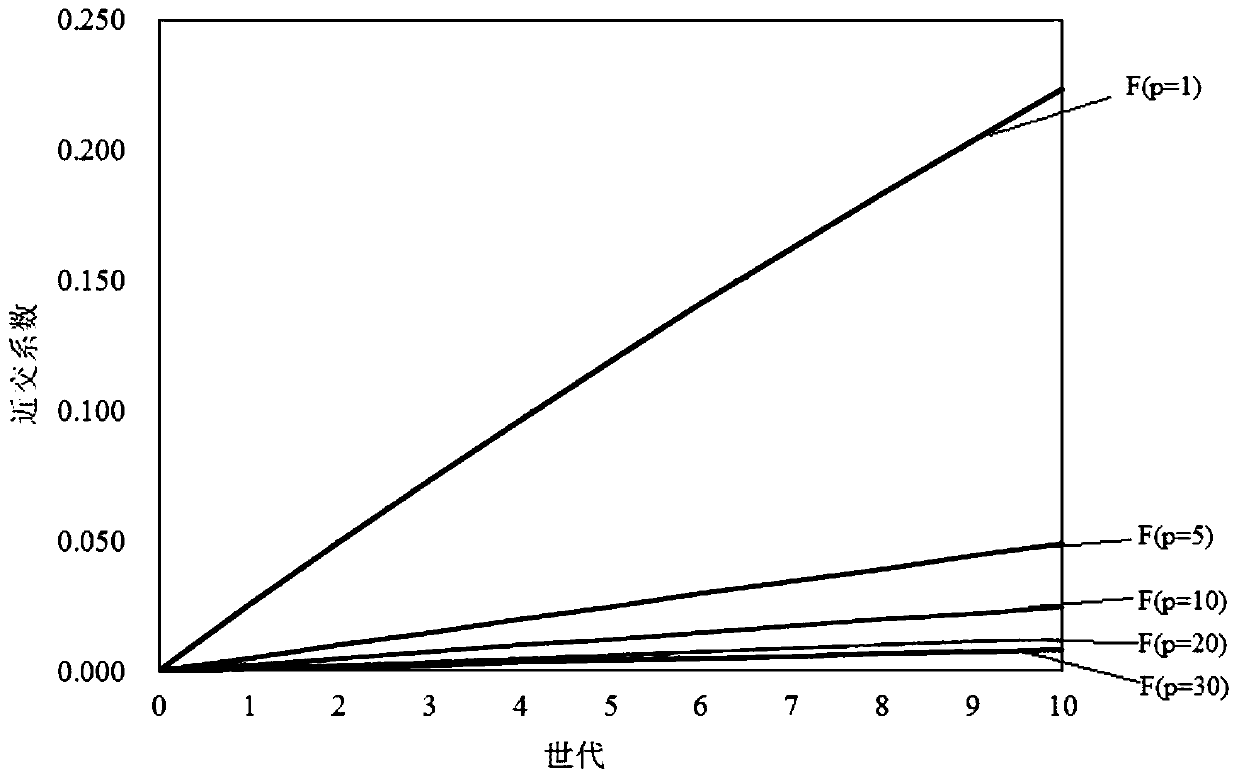
[0027] Embodiment: When the breeding strategy of Macrobrachium japonicus adopts the individual selection method to design the breeding program, it is necessary to monitor and control the degree of inbreeding, and the gene homozygosity caused by inbreeding will erode part of the genetic progress; the breeding target traits are caused by artificial selection pressure. Actual genetic progress achieved = expected genetic progress - inbreeding depression effect; the greater the degree of inbreeding, the greater the inbreeding depression effect, and the smaller the actual genetic progress. In order to maximize the genetic progress of breeding target traits, necessary measures must be taken to minimize the effect of inbreeding depression when formulating breeding programs; the effect of inbreeding depression can be measured by the inbreeding coefficient (inbreeding coefficient).
[0028] A method for predicting and avoiding the degree of inbreeding in Macrobrachium japonicus conventio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com