Plant site-directed recombination method mediated by repeated fragments
A technology for plant cells and transgenic plants, applied in the field of site-directed recombination of plants mediated by repeat fragments, can solve the problems of low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
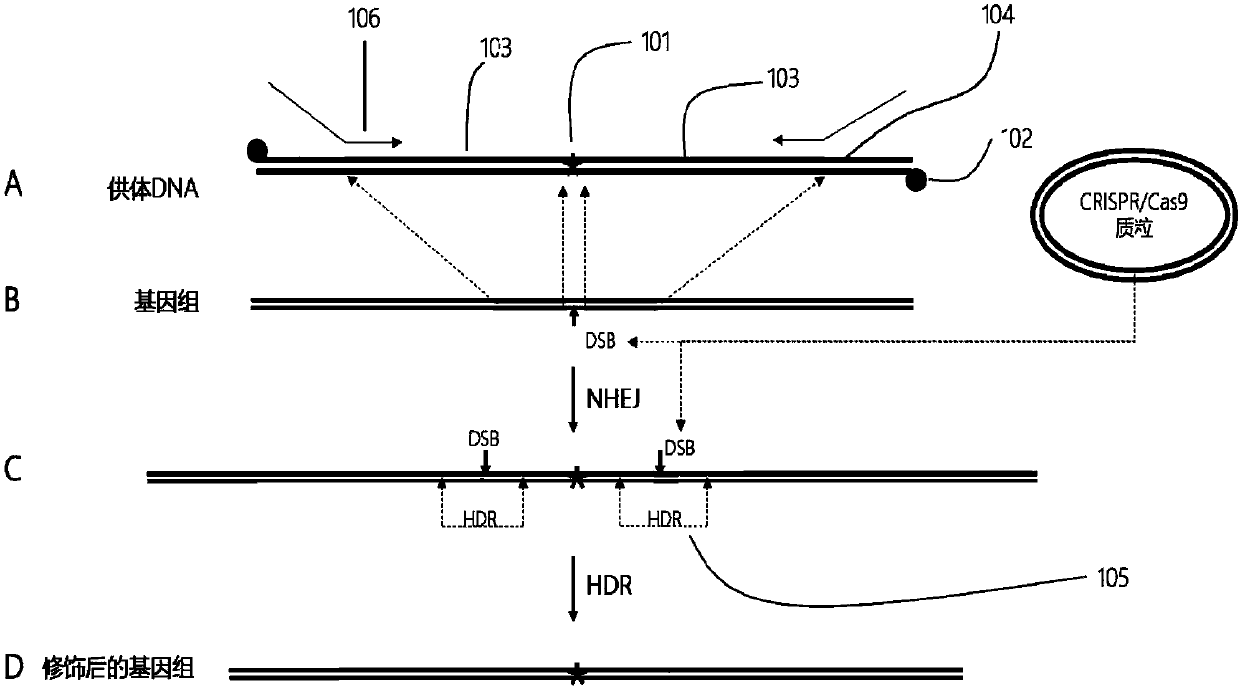
[0184] 1) For the preparation of shorter donor DNA (usually within 120bp), the modified oligonucleotide single strand can be directly synthesized and annealed directly to generate double-stranded donor DNA;
[0185] 2) For the preparation of longer donor DNA, primers modified by thiolation can be used to obtain by PCR amplification ( figure 1 );
[0186] 3) Or directly prepare by cutting exogenous DNA such as plasmids.
[0187] Preparation of site-directed cutting nuclease DNA construct
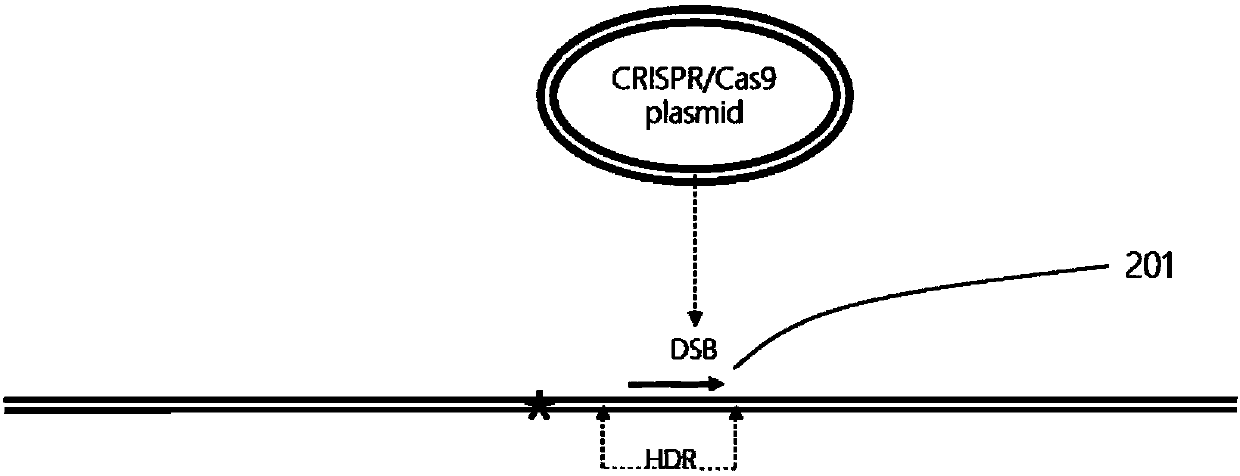
[0188] ZFN, Talen, and CRISPR / Cas9 technologies can all make site-directed cuts in plant genomes to generate double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs). Therefore, DNA elements expressing these three site-directed cutting nucleases can all be used in the present invention. The DNA element can be a plasmid or a linear fragment. Since the CRISPR / Cas9 technology is relatively simple and efficient, the present invention prefers CRISPR / Cas9 to make site-specific cuts on the plant genome.
[0189] Reagen...
Embodiment 1
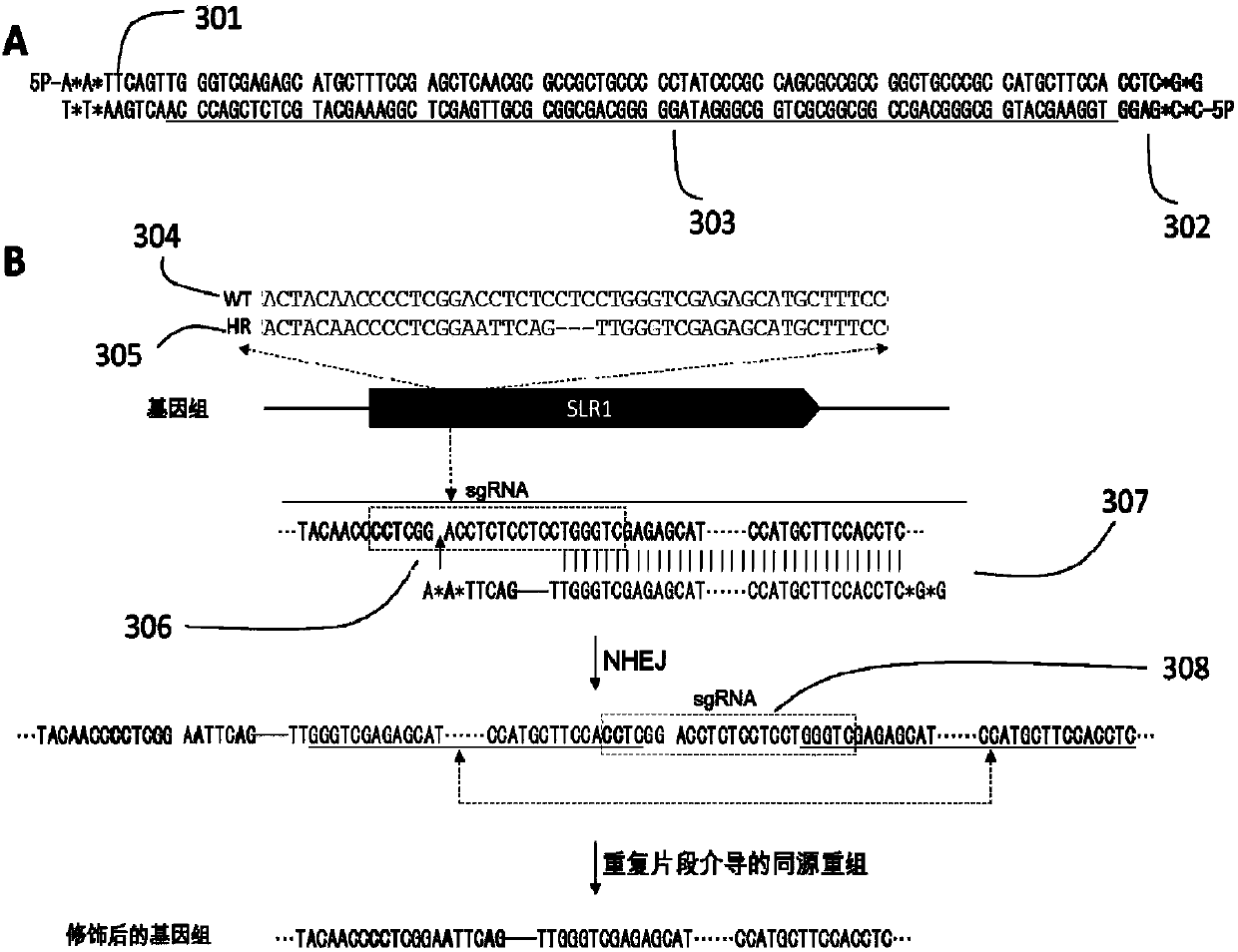
[0228] Example 1 Rice SLR1 Gene Base Replacement
[0229] Using the modified DNA fragment synthesized in vitro as the donor DNA fragment, combined with CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the multiple bases in the rice SLR1 gene were precisely replaced and deleted. The specific operation process is as follows.
[0230] CRISPR / Cas9 vector preparation
[0231] The target gRNA-1 (SEQ ID NO.:) was designed for the region to be replaced of the rice SLR1 gene, and the gRNA-1 guide sequence was constructed into the rice CRISPR / Cas9 vector, wherein the OSU6-gRNA-1 sequence is shown in the sequence listing (SEQ ID NO. NO.: 2).
[0232] Donor fragment design and in vitro preparation
[0233] Such as image 3 As shown in A and 3B, the end of the donor DNA can be phosphorylated and thio-modified (5'P stands for phosphorylation modification at the 5' end, and * stands for inter-base thio-modification) to promote NHEJ; 82bp in the fragment and The sequence of the SLR1 target site is homologous; af...
Embodiment 2
[0246] Example 2 The fixed-point knock-in experiment of GFP
[0247] The DNA fragment amplified by PCR was used as the donor DNA fragment, and combined with CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the GFP gene was knocked into the 3' end of the rice highly expressed genes ACT1 and GST1 to form a fusion protein. The specific operation process is as follows.
[0248] CRISPR / Cas9 vector preparation
[0249] Target gRNA-2 and gRNA-3 (SEQ ID NO.: 9, 10) were designed for the 3' ends of rice ACT1 and GST1 genes respectively, and these two guide sequences were constructed into rice CRISPR / Cas9 vectors, wherein OSU6-gRNA- 2 and OSU6-gRNA-3 sequences are shown in the sequence listing (SEQ ID NO.: 11, 12).
[0250] Design and preparation of donor DNA fragments
[0251] Such as Figure 5 As shown in A, the donor DNA is amplified by PCR, and the primers used for the amplification are shown in the table below. Wherein, the donor DNA fragment (sequence 9, 1528bp) knocked in by primer ACT1-F1 and NOS-R1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com