Reasonable width determination method for gob-side entrydriving narrow coal pillar based on fracture evolution
A technology for fracture evolution and determination method, which is applied in earthwork drilling, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc. It can solve problems such as gas exceeding the limit, gas entering gob-side roadway, safety accidents, etc., and achieve isolation of gobs gas, increase coal mining rate, and the effects of safe and efficient mining
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be noted that the following examples are only used to illustrate the present invention, and do not limit the present invention.
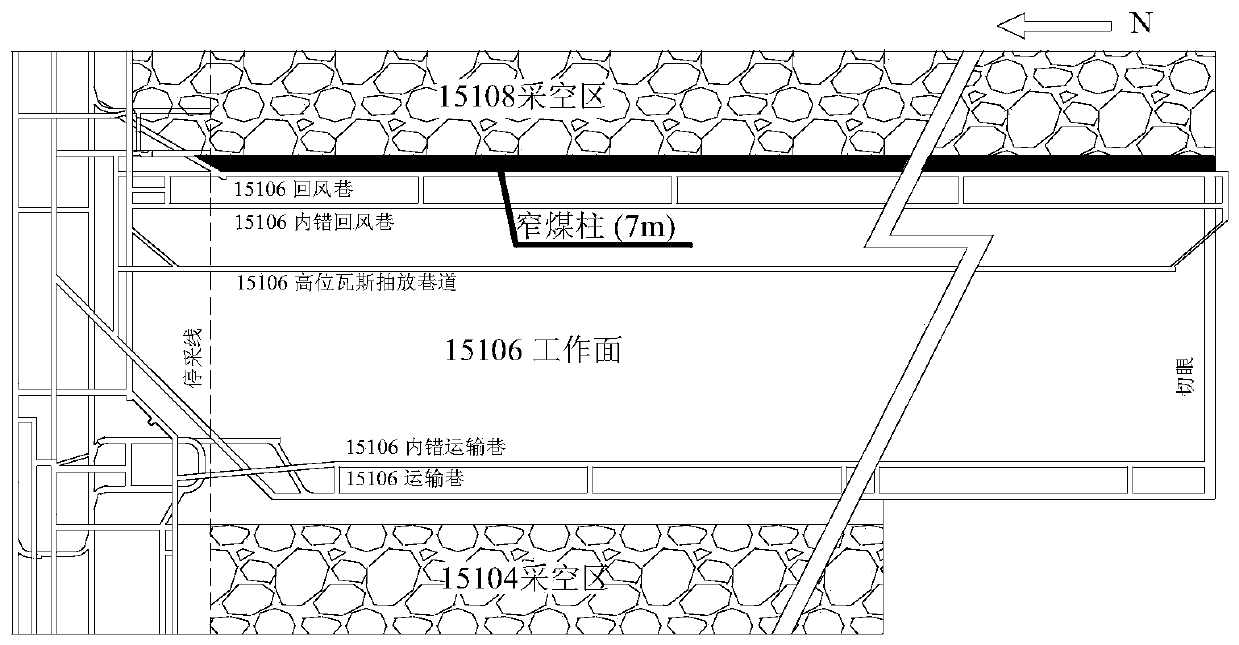
[0031] A method for determining the reasonable width of narrow coal pillars in gob-side entry based on fracture evolution. Figure 12 shown, including the following steps:
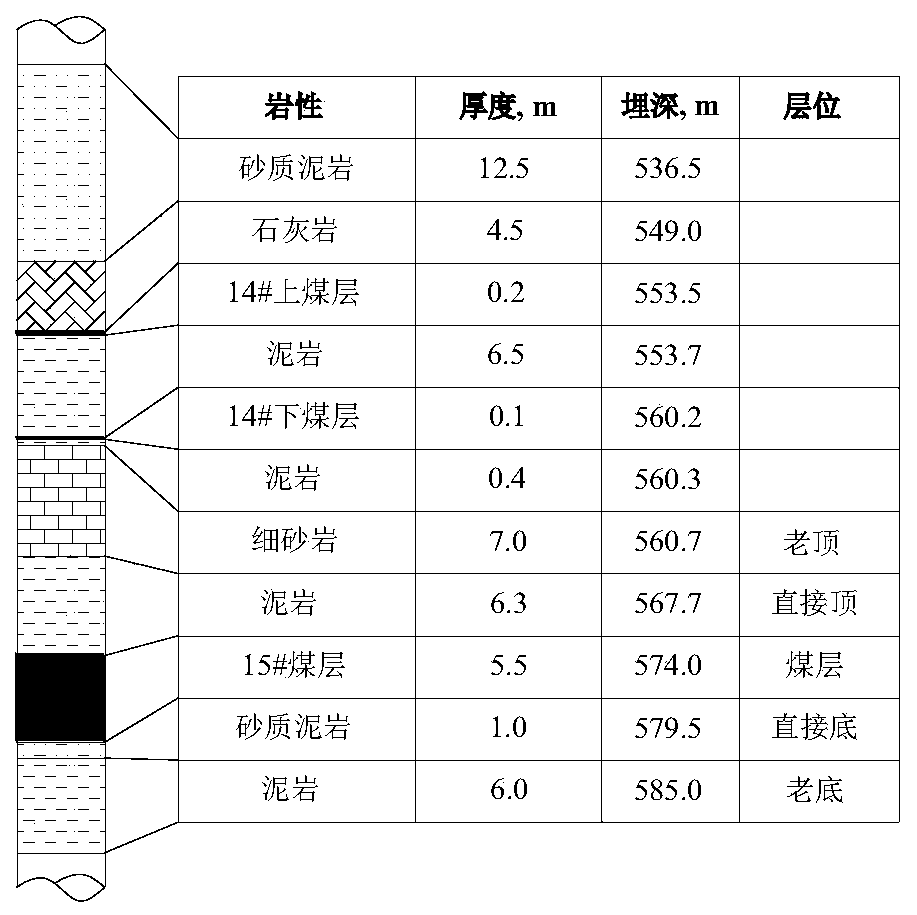
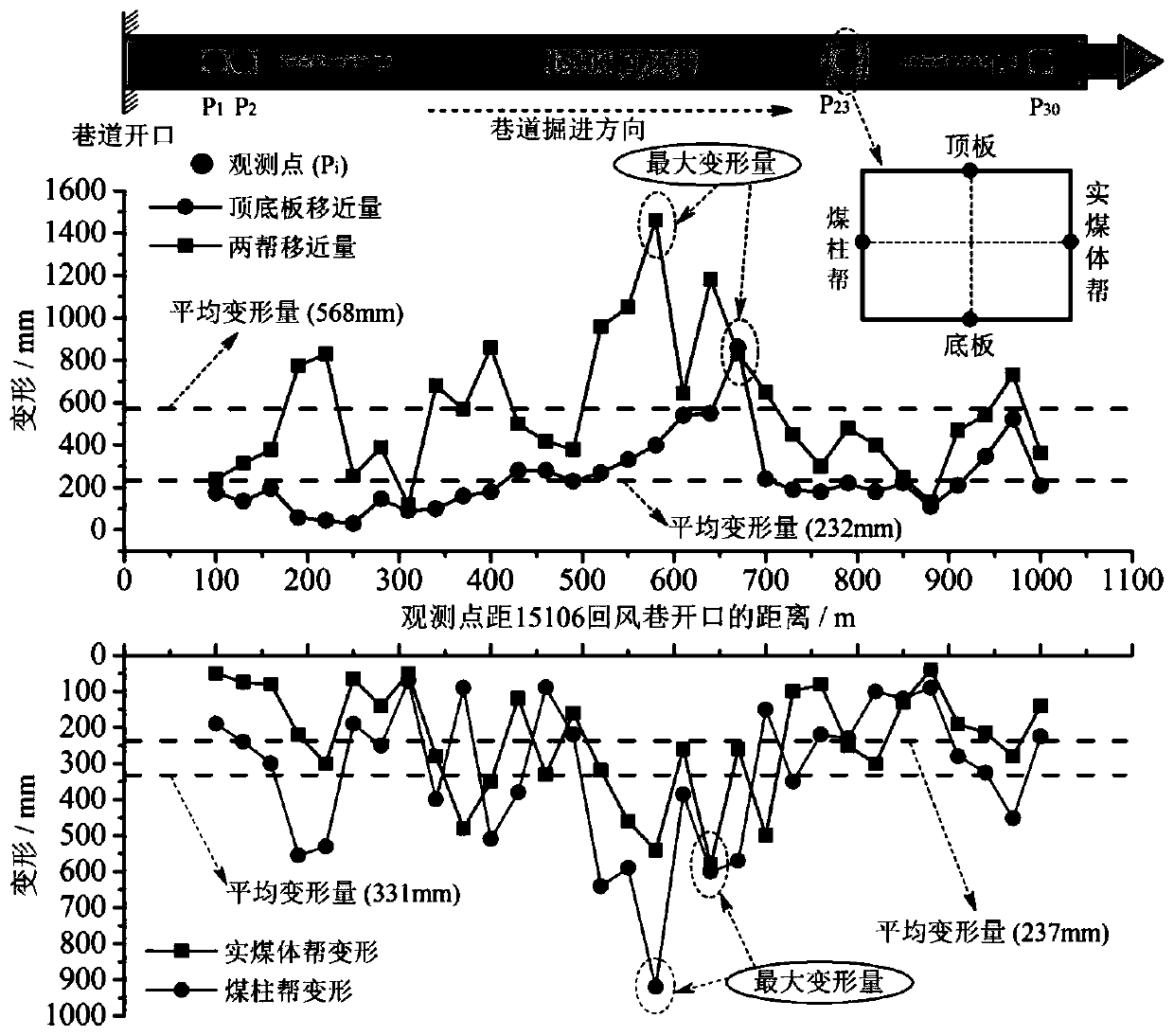
[0032] S1. On-site observation of roadway deformation and coal pillar fissure distribution characteristics: In the process of gob-side excavation, the roadway surface displacement observation station is arranged by the method of cross-point arrangement, and the distance of the roadway roof and floor is measured and recorded with a tape measure. The observation period of the two gangs is once a day; after the roadway is excavated, the mining borehole peeper is used to detect the distribution characteristics of the cracks in the narrow co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com