Gravity-magnetic interface inversion-based geodetic heat flow estimation method
An inversion algorithm and interface technology, which is used in electrical/magnetic exploration, re-radiation of sound waves, geophysical measurements, etc. It can solve the iterative convergence instability of the inversion algorithm, damage the high-frequency information of the data, and reduce the accuracy of the inversion results. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0109] Such as figure 1 As shown in , a method for estimating terrestrial heat flow based on gravity-magnetic interface inversion includes the following steps:
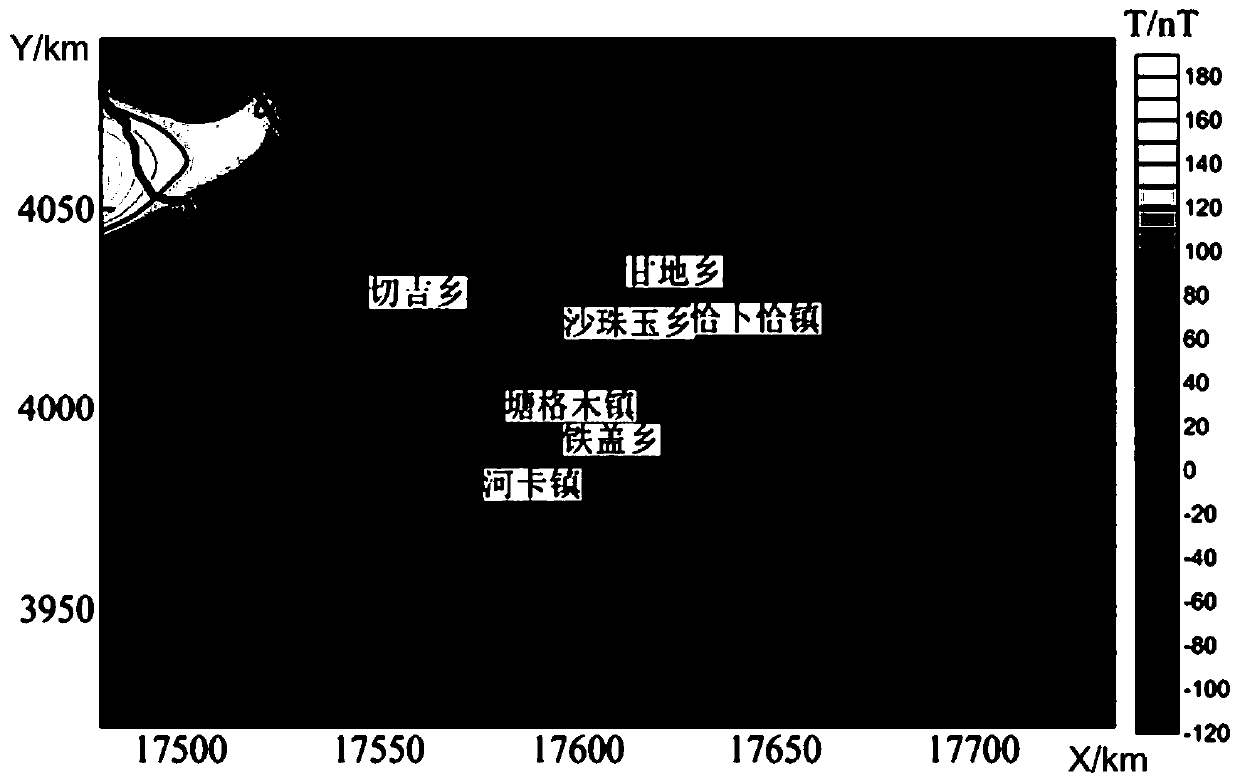
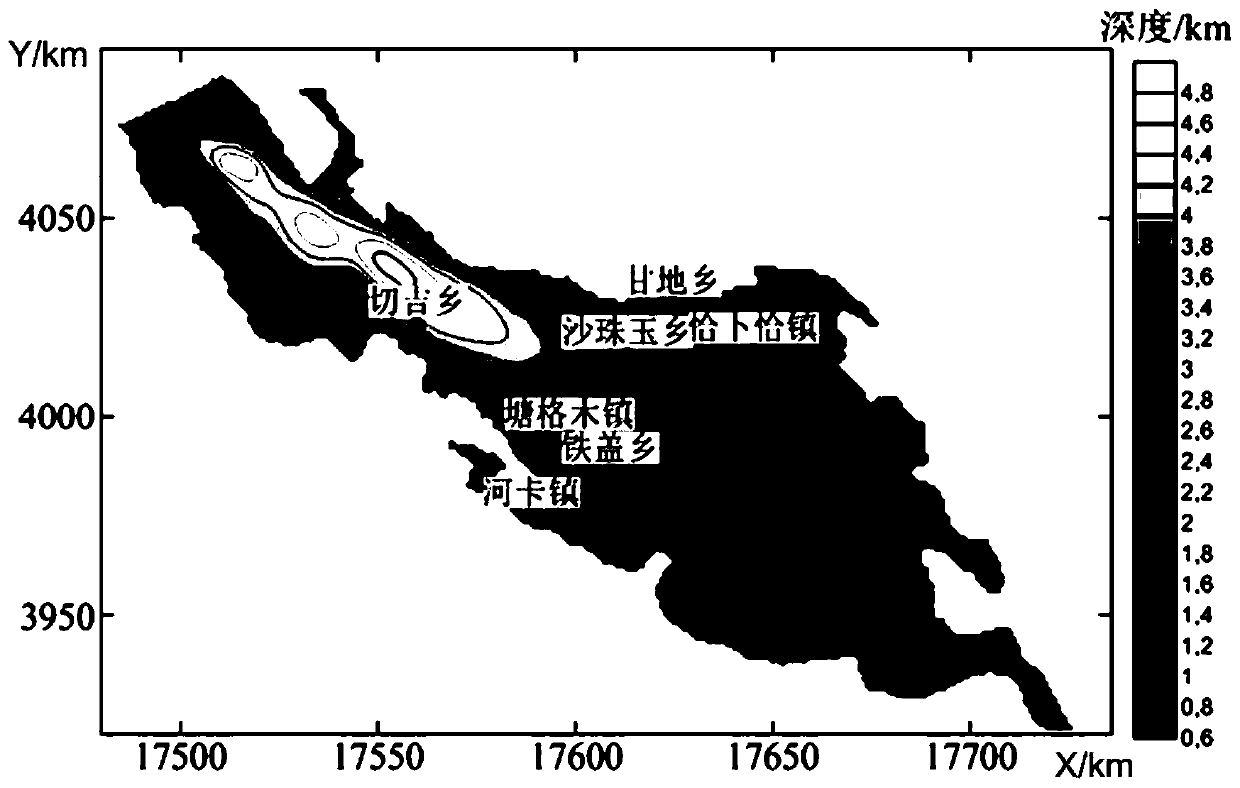
[0110] (S1) Utilize the improved Parker-Oldenburg interface inversion algorithm to invert the gravity and magnetic data to obtain the Curie and Moho surfaces, and the inversion algorithms of the Moho surface and Curie are respectively:
[0111]
[0112] Among them, h 0 Indicates the average depth of the upper and lower interfaces, Δh 2 and Δh 1 Indicates the difference between the upper and lower interfaces and the average depth, s indicates the iteration step size, ρ 0 Indicates the remaining density of the surface geological medium, ω indicates the circular wave number, F[] indicates the Fourier transform of the gravity anomaly, Δg indicates the gravity anomaly, G indicates the gravitational constant, and a indicates the density variation index with depth;
[0113]
[0114]where Δz represents the magnetic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com