Detection method of SNP site of SMA gene
A detection method and site technology, which can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of low sensitivity, high cost, and poor efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
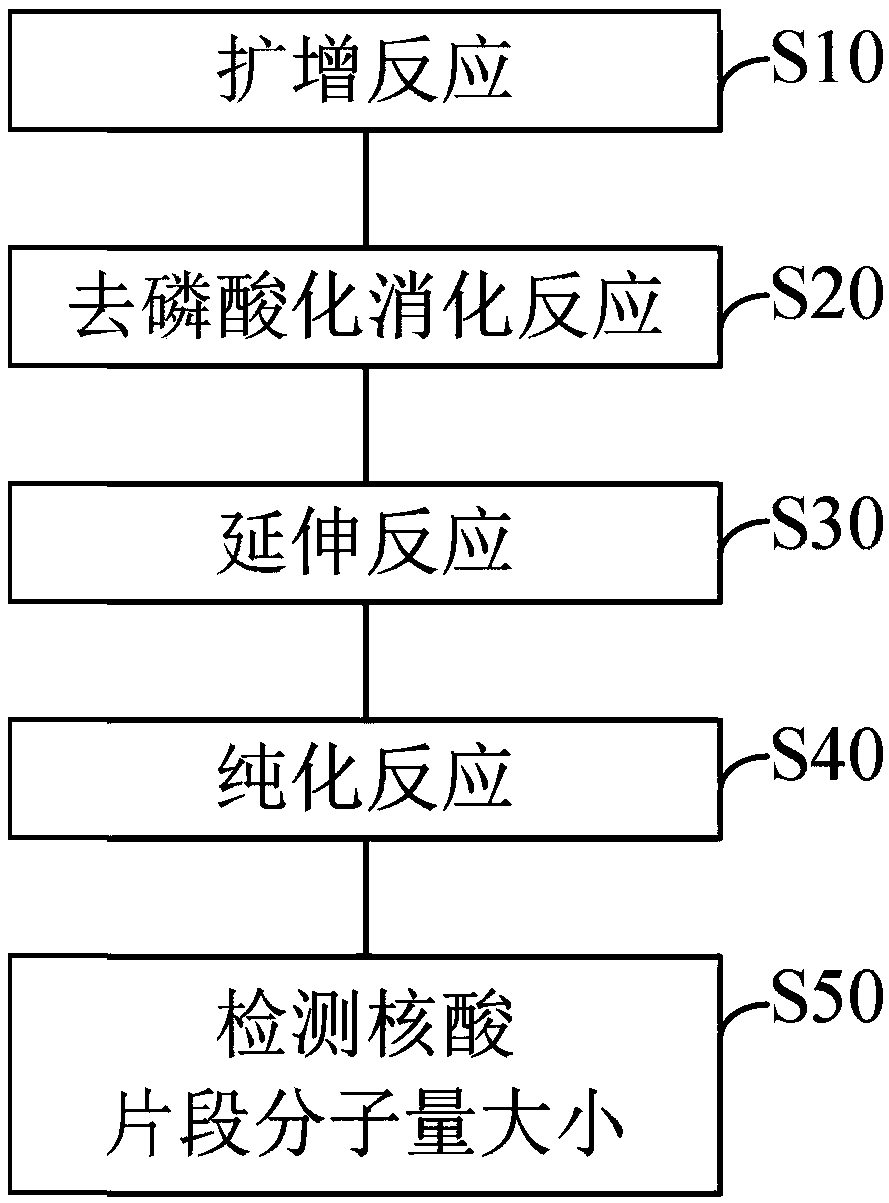
Embodiment Construction
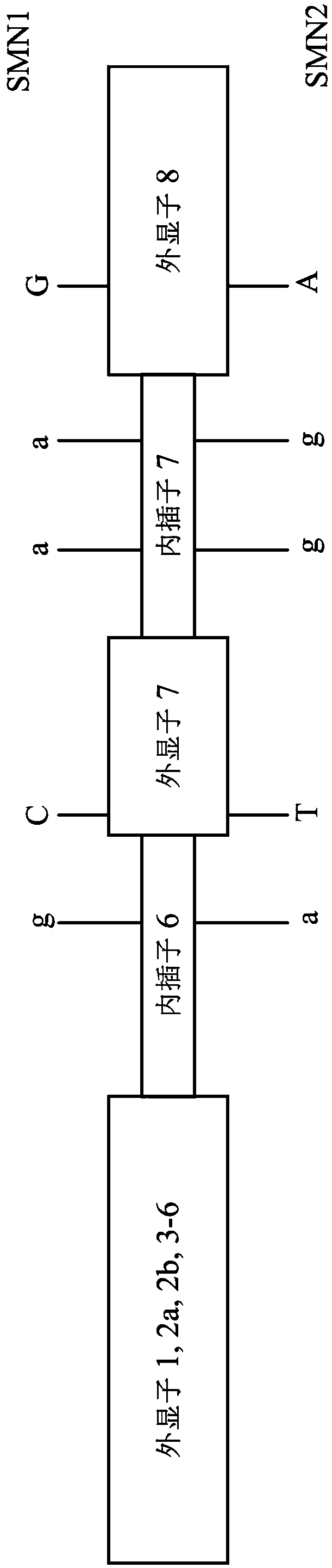
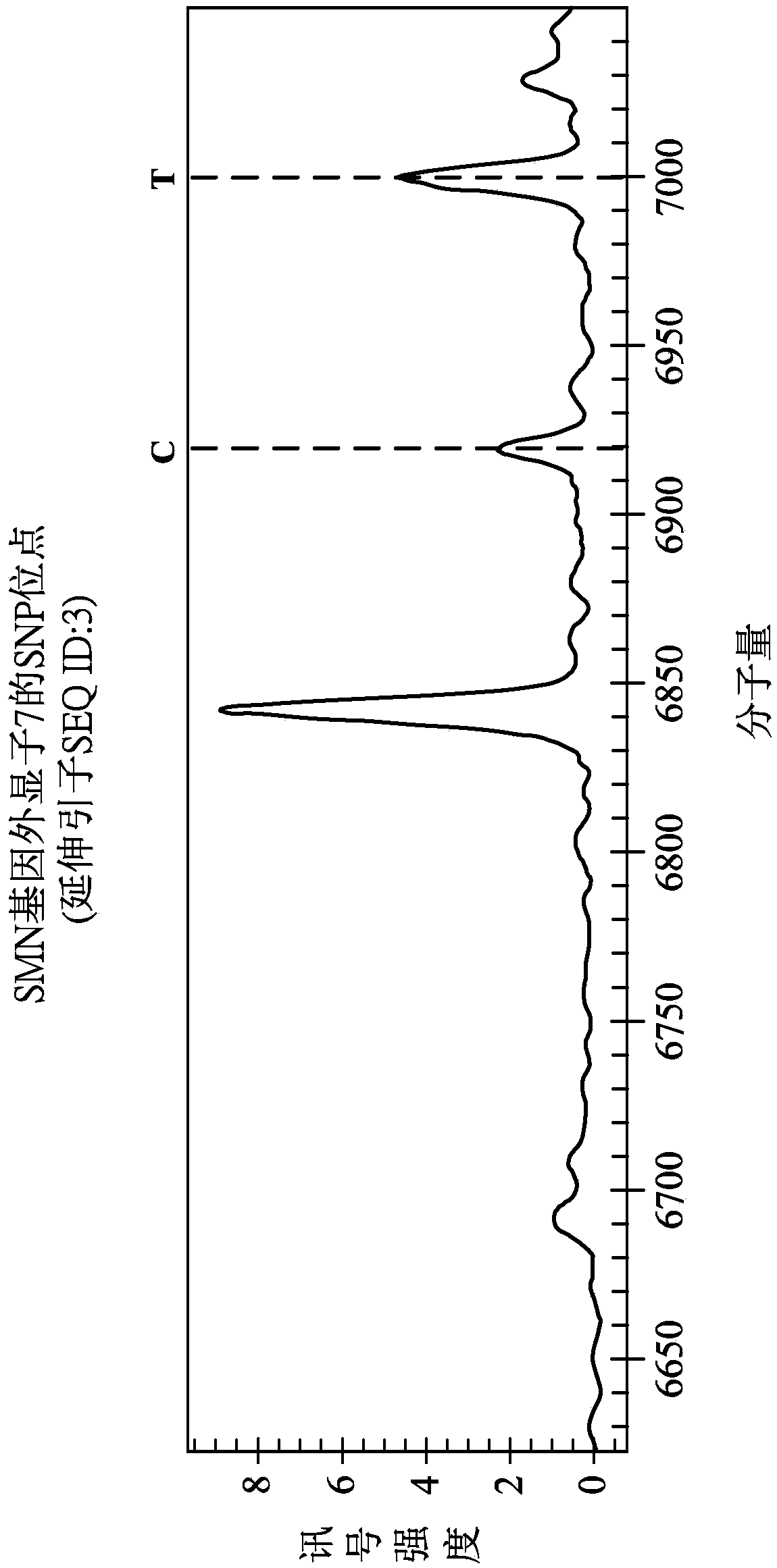
[0042] Please refer to figure 1 , which is a schematic diagram of the SNP (Singlenucleotide polymorphisms, single nucleotide polymorphisms) site of the SMA gene (Spinal Muscular Atrophy gene). The SMA gene consists of two genes, the SMN1 gene and the SMN2 gene (Survival Motor Neuron Gene), both of which encode the SMN protein. However, there are five nucleotide sequence differences between the SMN1 gene and the SMN2 gene. Glycine sequence differences are called SNP sites, as in figure 1 As shown in , they are respectively located in intron 6, exon 7, intron 7 and exon 8.
[0043] In interpolation 6, the base of the SNP site of the SMN1 gene is G, and the base of the SNP site of the SMN2 gene is A; in exon 7, the base of the SNP site of the SMN1 gene is C, and the base of the SNP site of the SMN2 gene is C. The base of the SNP site of the gene is T; in interpolation 7, the base of the first SNP site of the SMN1 gene is A, the base of the second SNP site is A, and the base of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com