Method for efficient inhibition of sewage plant effluent microalgae with submerged plants
A technology for submerged plants and sewage plants, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as low concentration of algae, expensive treatment costs, secondary pollution, etc. , to achieve good ecological and aesthetic benefits, significant effects, and strong nitrogen and phosphorus removal effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
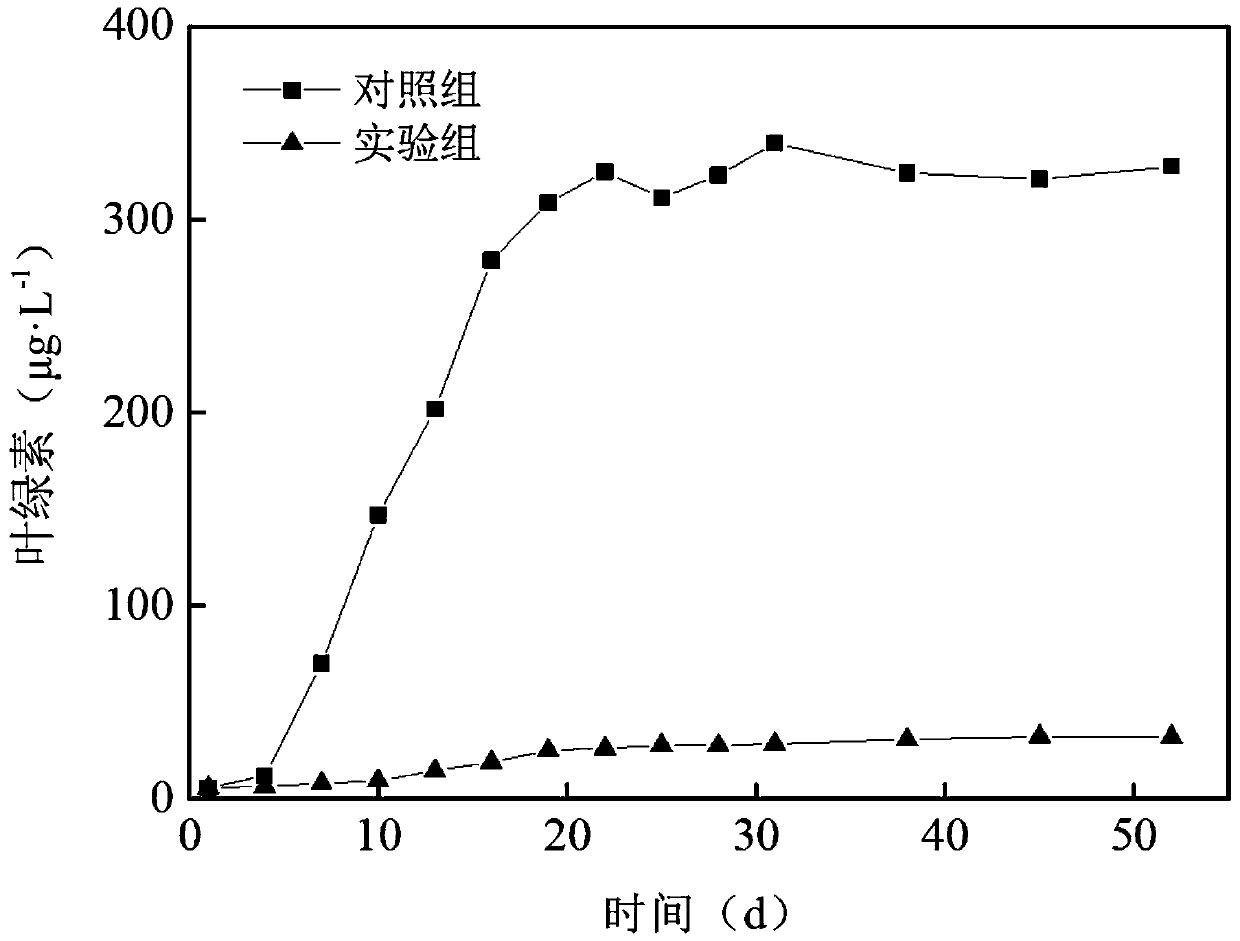
[0034] This embodiment is used to investigate the inhibitory effect of the present invention on the effluent microalgae of a certain water purification plant in Beijing, specifically comprising the following steps:
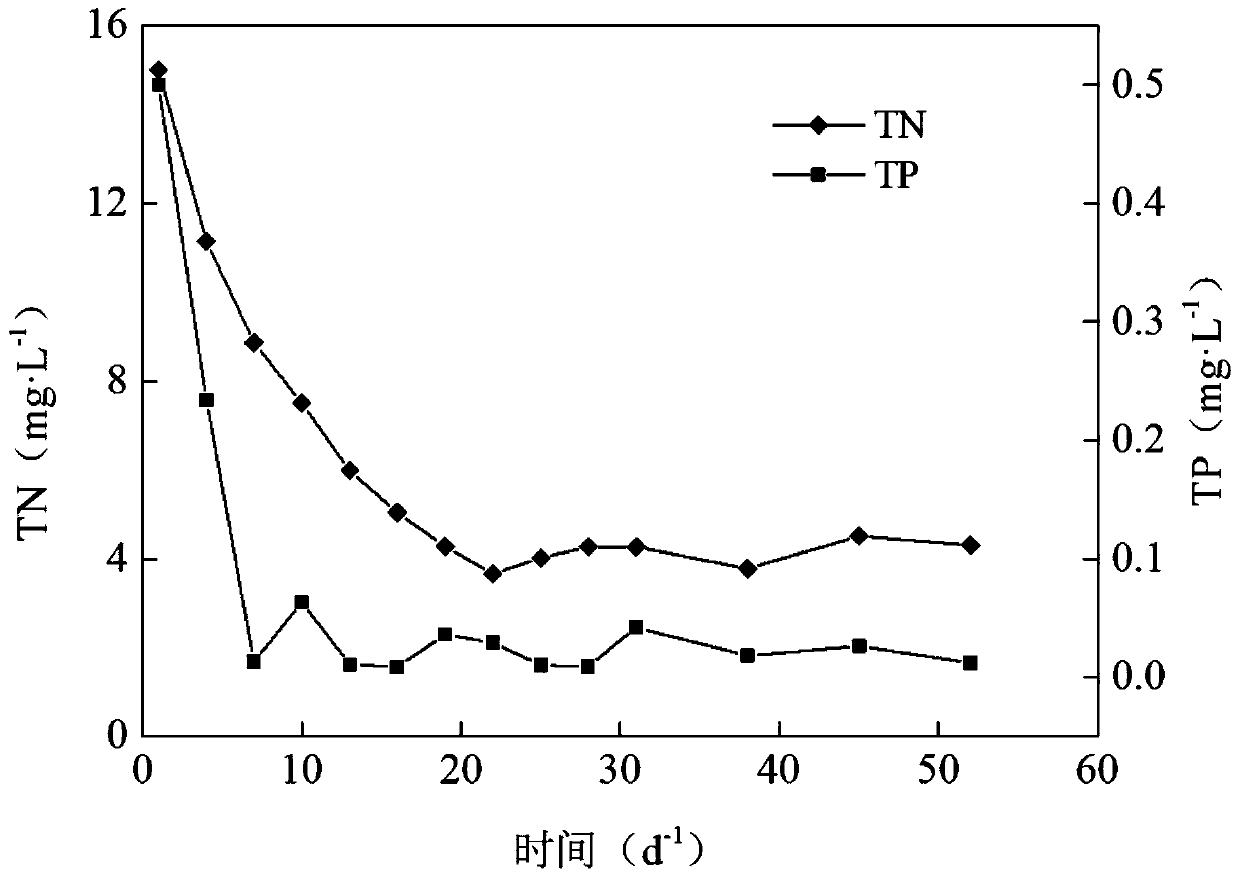
[0035] (1) Select the first-class A-marked water of a certain sewage plant, and measure its related indicators: the total nitrogen content TN is 15mg / L, the total phosphorus content TP is 0.5mg / L, and the chlorophyll concentration is 5.86μg / L;
[0036] (2) Select the submerged plants that control algae, such as black algae and P. spicanus, first rinse with tap water to remove the attached phytoplankton, and then plant them in a 20L glass tank with test water samples. Cultivate the bottom of the cup and pebbles to fix the submerged plants, and place them in the greenhouse for at least 2 weeks to adapt to the experimental conditions. Before the experiment, select plants that grow robustly and have the same size and condition, wash them with tap water to fully remove ...
Embodiment 2
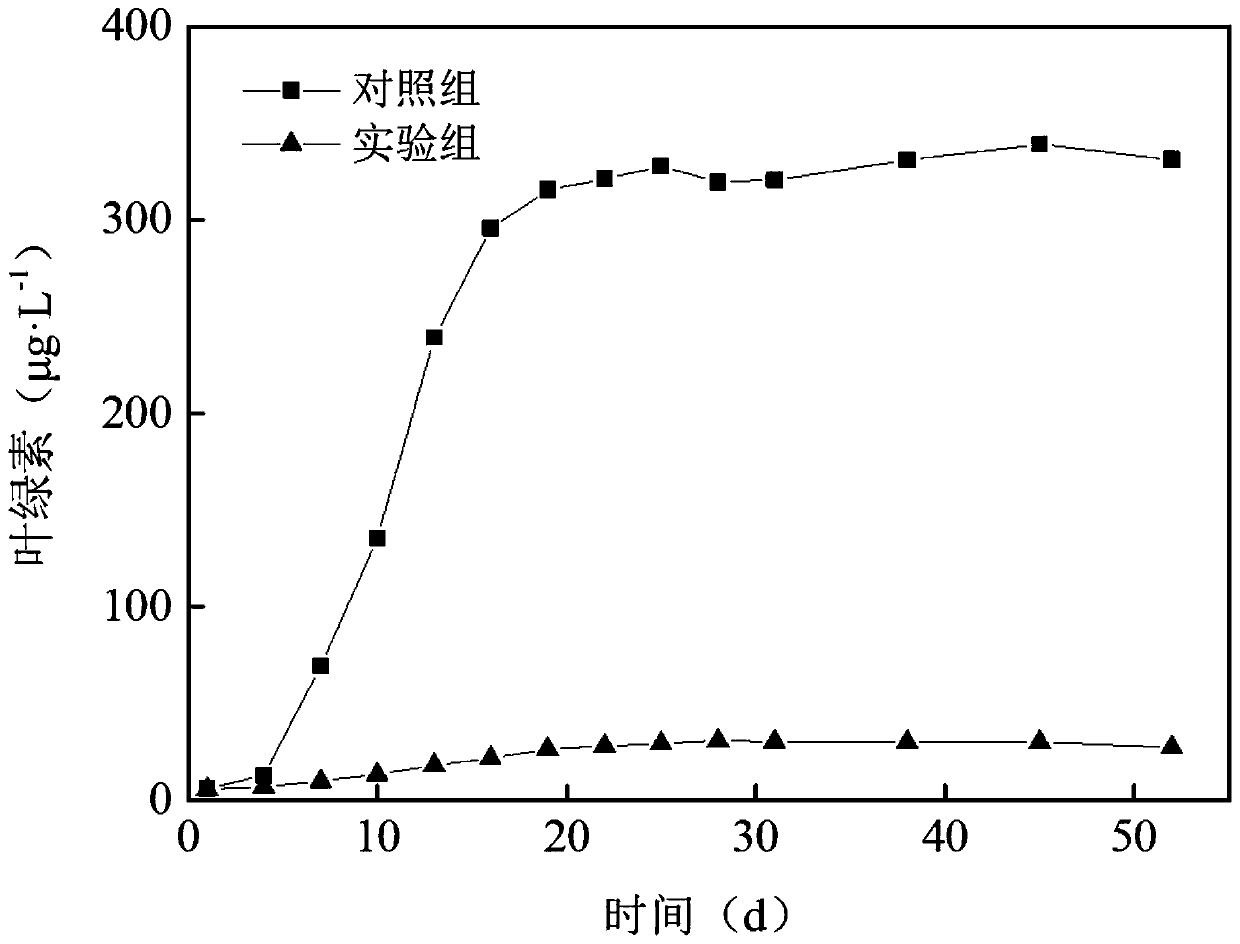
[0043] This embodiment is used to investigate the inhibitory effect of the present invention on the effluent microalgae of a certain water purification plant in Kunming City, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0044] (1) Select the first-class A-labeled water of a water purification plant in Kunming City, and measure its related indicators: the total nitrogen content TN is 14.3mg / L, the total phosphorus content TP is 0.42mg / L, and the chlorophyll concentration is 5.79μg / L ;
[0045] (2) Select the submerged plants that control algae, such as black algae and P. spicanus, first rinse with tap water to remove the attached phytoplankton, and then plant them in a 20L glass tank with test water samples. Cultivate the bottom of the cup and pebbles to fix the submerged plants, and place them in the greenhouse for at least 2 weeks to adapt to the experimental conditions. Before the experiment, select plants that grow robustly and have the same size and condition, wash them ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com