A Faraday Cup-Based Plasma Charging Current Monitoring Method on Satellite Surface
A surface plasmon and Faraday cup technology, applied in the field of space radiation, can solve problems such as the difficulty in determining the size relationship, the existence of deviations, and the inability to effectively judge and identify the risk of electrification on the surface of satellites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
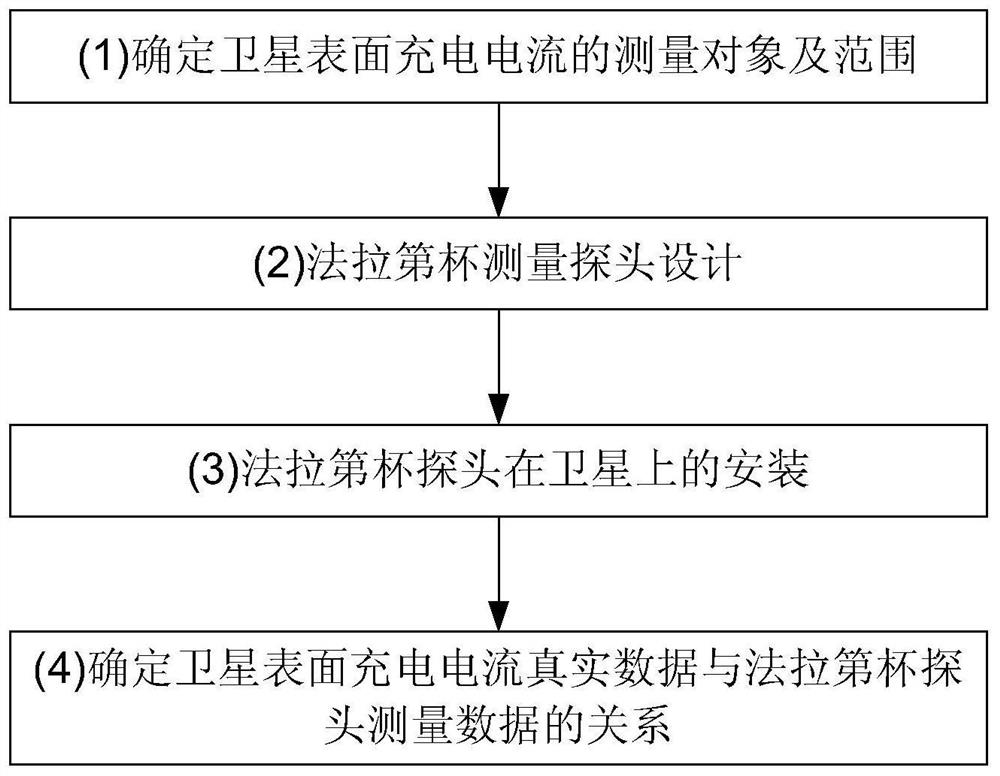
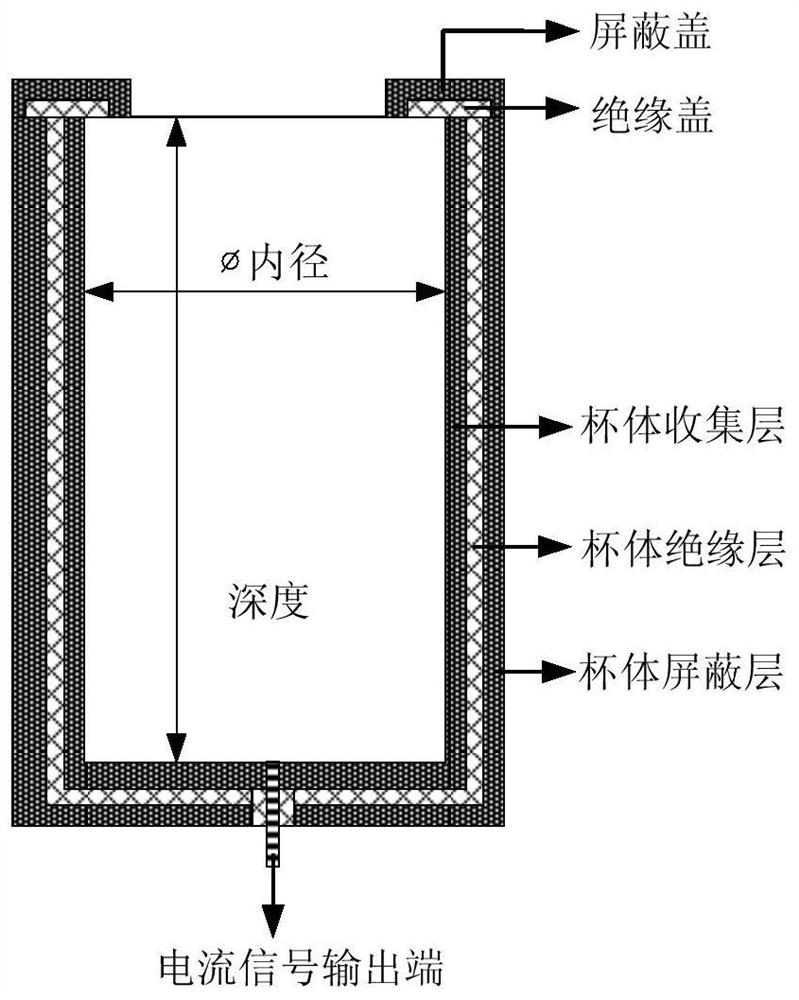
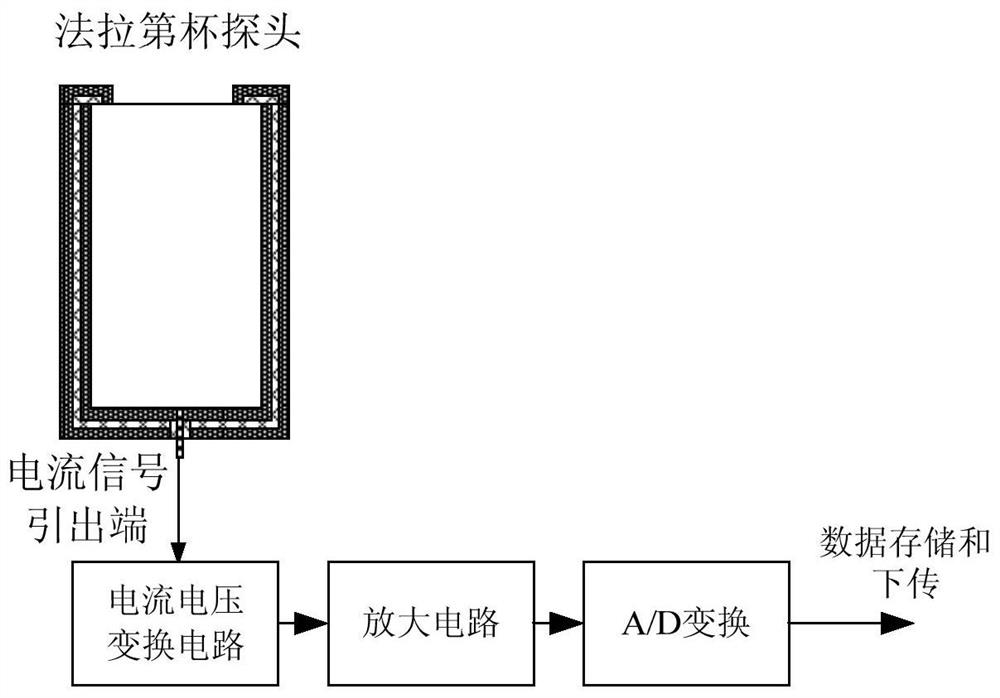
[0043] like figure 1 As shown, a method for monitoring the plasma charging current on the surface of a satellite based on a Faraday cup includes the following steps:
[0044] (1) Determine the measurement object and range of the charging current on the satellite surface
[0045] The charging current on the surface of the satellite is mainly formed by the electrons in the thermal plasma with an energy of 10eV to 100keV in space, so the measurement object is the charging current formed by the electrons, and the current density is greater than -0.01nA / cm 2 The probability of about 95% greater than -0.7nA / cm 2 The probability is about 0.1%, and the maximum charging current density actually measured on the track is -1.52nA / cm 2 , the design value of charging current density recommended by ESA is -10nA / cm 2. Considering the above factors comprehensively, the mea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com