Circulating RNA signatures specific to preeclampsia
A pre-eclampsia, C-RNA technology, applied in the field of circulating RNA identification specific to pre-eclampsia, can solve the problem of lack of discrimination and prediction ability of patients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0204] Pregnancy-specific C-RNA markers
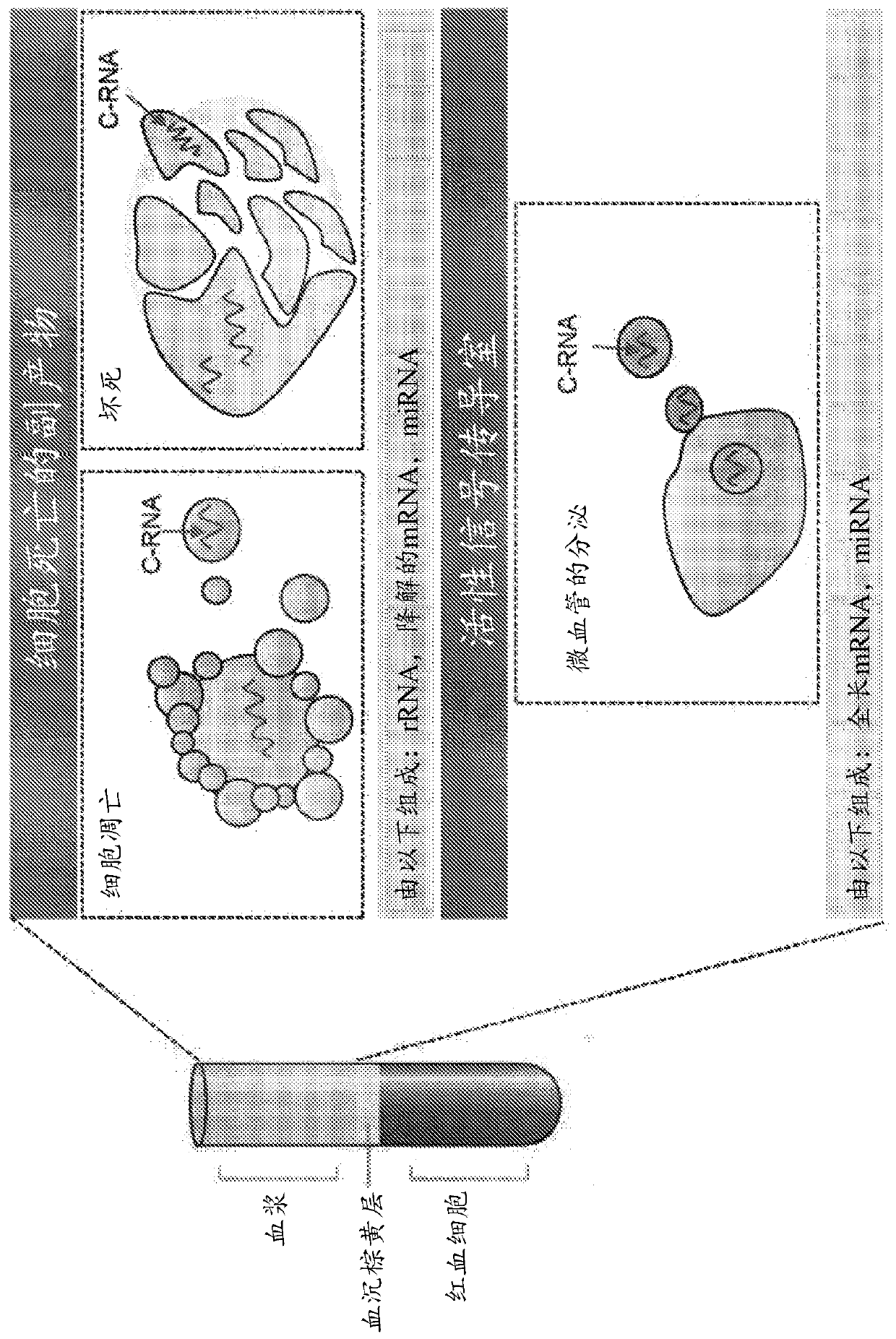
[0205] The presence of circulating nucleic acids in maternal plasma provides a window into fetal and placental progression and health ( figure 1 ). Circulating RNA (C-RNA) is detected in the maternal circulation and originates from two main sources. A large fraction of C-RNA originates from apoptotic cells that release C-RNA-containing vesicles into the bloodstream. C-RNA also enters the maternal circulation through the shedding of active signaling vesicles (eg, exosomes and microvesicles) from various cell types. Such as figure 2 As shown, C-RNA thus consists of by-products of cell death as well as active signaling products. Characteristics of C-RNA include being produced by common processes, being released from cells throughout the body, and being stable and contained in vesicles. It represents the circulating transcriptome, which reflects tissue-specific changes in gene expression, signaling, and cell death.
[0206] C-RNA ma...
example 2
[0212] C-RNA labeling across gestational ages
[0213] This example characterizes C-RNA signatures across different gestational ages throughout pregnancy. It is expected that the changes in C-RNA signatures at different time points throughout pregnancy will be more subtle than the differences noted in Example 1 between C-RNA signatures of pregnant and non-pregnant samples. Such as Figure 5 As shown, as the pregnancy progressed, the C-RNA profile of the marker genes was observed to change significantly over time, with a clear set of genes upregulated in the early period and a clear set of genes increased in the late period.
[0214] These genes include CGB8, CGB5, ZSCAN23, HSPA1A, PMAIP1, C8orf4, ITM2B, IFIT2, CD74, HSPA6, TFAP2A, TRPV6, EXPH5, CAPN6, ALDH3B2, RAB3B, MUC15, GSTA3, GRHL2, and CSHL1, as Figure 5 listed.
[0215] These genes may also include CSHL1, CSH2, KISS1, CGA, PLAC4, PSG1, GH2, PSG3, PSG4, PSG7, PSG11, CSH1, PSG2, HSD3B1, GRHL2, LGALS14, FCGR1C, PSG5,...
example 3
[0218] C-RNA signature of preeclampsia
[0219] In the case of this example, a C-RNA signature unique to preeclampsia was identified. Will be diagnosed with aura in two studies (the RGH14 study (registered with clinical trials.gov as NCT0208494) and the Pearl study (also referred to herein as the Pearl Biobank; registered with clinical trials.gov as NCT02379832)) C-RNA identification was determined in the collected samples of pregnant women with eclampsia and analyzed ( Figure 6 ). Two tubes of blood were collected at the time of diagnosis of preeclampsia. Eighty gestational age-matched control samples were collected to minimize transcriptional variability independent of preeclamptic disease status and to control for gestational age differences in C-RNA signatures. Samples from the RGH14 study were used to identify a panel of biologically relevant genes, and the predictive value of these biomarkers was validated in an independent cohort of samples from the Pearl Biobank. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com