Intelligent damper for synchronously self-monitoring of force and displacement
A damper, self-monitoring technology, applied in the testing of instruments, measuring devices, mechanical parts, etc., can solve the problem of less actual data of dampers, and achieve the effect of high accuracy and strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
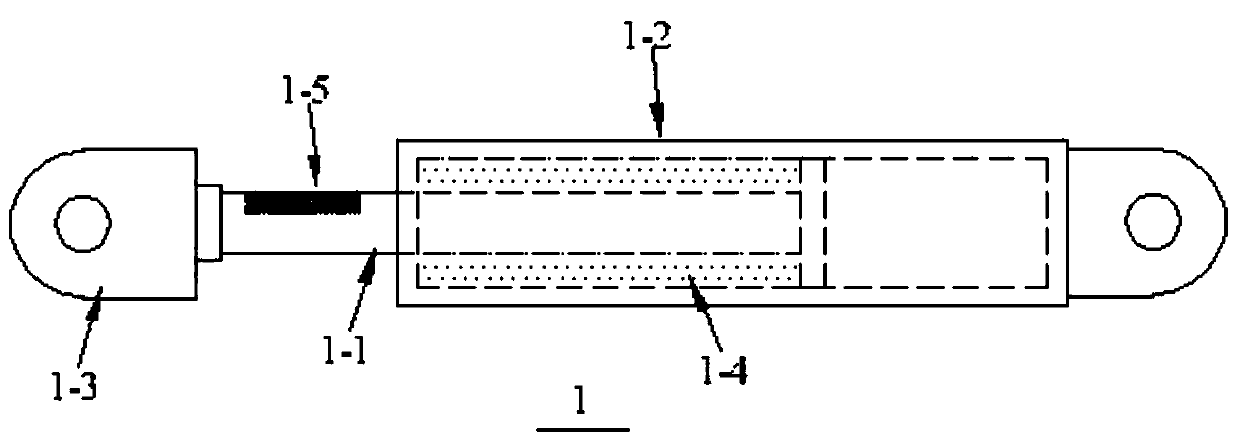
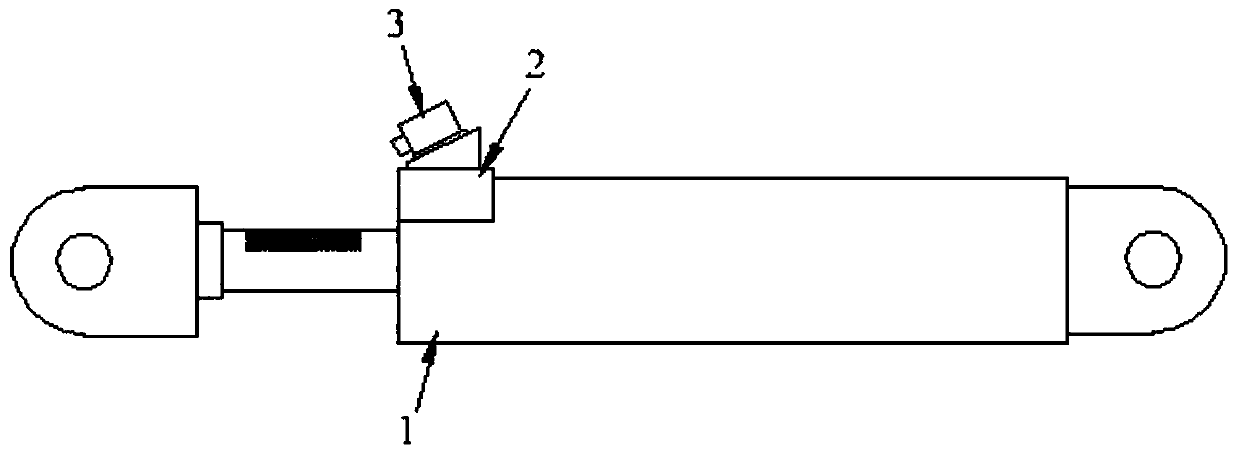
[0024] Such as Figure 1~2 Shown: a kind of intelligent damper of synchronous self-monitoring of force and displacement, comprises damper (1), displacement measuring frame (2), camera system (3), it is characterized in that: described damper (1) comprises piston ( 1-1), the cylinder (1-2), the connecting section at both ends (1-3), the damping medium (1-4) and the image speckle (1-5), the piston (1-1) is located in the cylinder ( 1-2) Inside, the damping medium (1-4) is in the cylinder (1-2), when the damper (1) is disturbed and works, the piston (1-1) forces the cylinder (1-2) The damping medium (1-4) moves, so that the damping medium (1-4) converts the external energy into heat energy and dissipates it. The connecting sections (1-3) at both ends connect one end of the piston (1-1) to the cylinder One end of (1-2), the minimum net cross-sectional size of the connecting section (1-3) at both ends must meet the requirements of the elastic state of the damper (1) in normal use,...
Embodiment 2
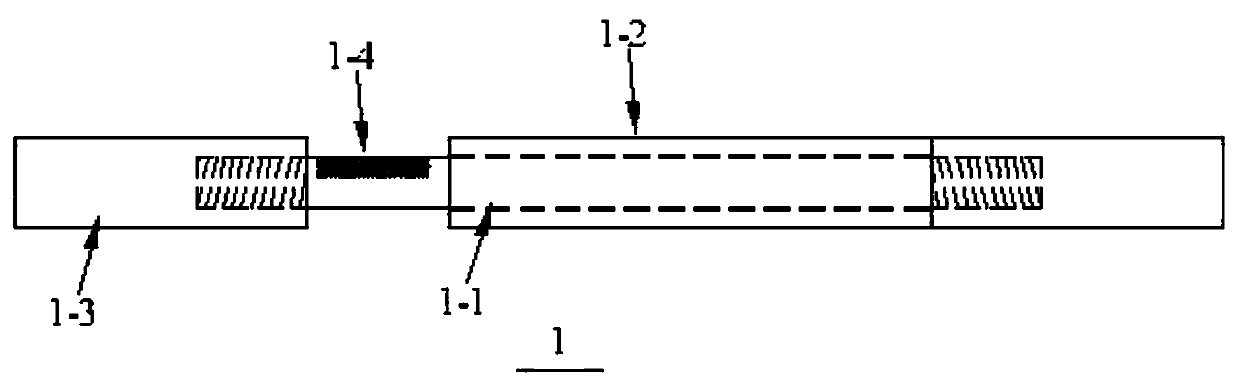
[0030] Such as Figure 3-4 Shown: this embodiment is the same as the rest of embodiment 1, the difference is that the damper (1) is an anti-buckling support damper, and the damper (1) includes a core component (1-1), an outer restraint Components (1-2), connecting segments at both ends (1-3) and image speckle (1-4), the core component (1-1) is located inside the outer constraint component (1-2), and the outer constraint component (1- 2) The length of the damper (1) is slightly shorter than that of the core component (1-1), and its inner dimension is slightly larger than the cross-sectional dimension of the core component (1-1). When the damper (1) works normally, its outer dimension needs to meet the requirements of the outer constraint component ( 1-1) Requirements of being in an elastic state, the cross-sectional size of the connecting section at both ends (1-3) is slightly larger than that of the core part (1-1), and the image speckle (1-4) is in the unconstrained part (1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com