In situ gel-forming pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof for sinus diseases
A composition and drug technology, applied in the direction of drug combination, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as undeveloped drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
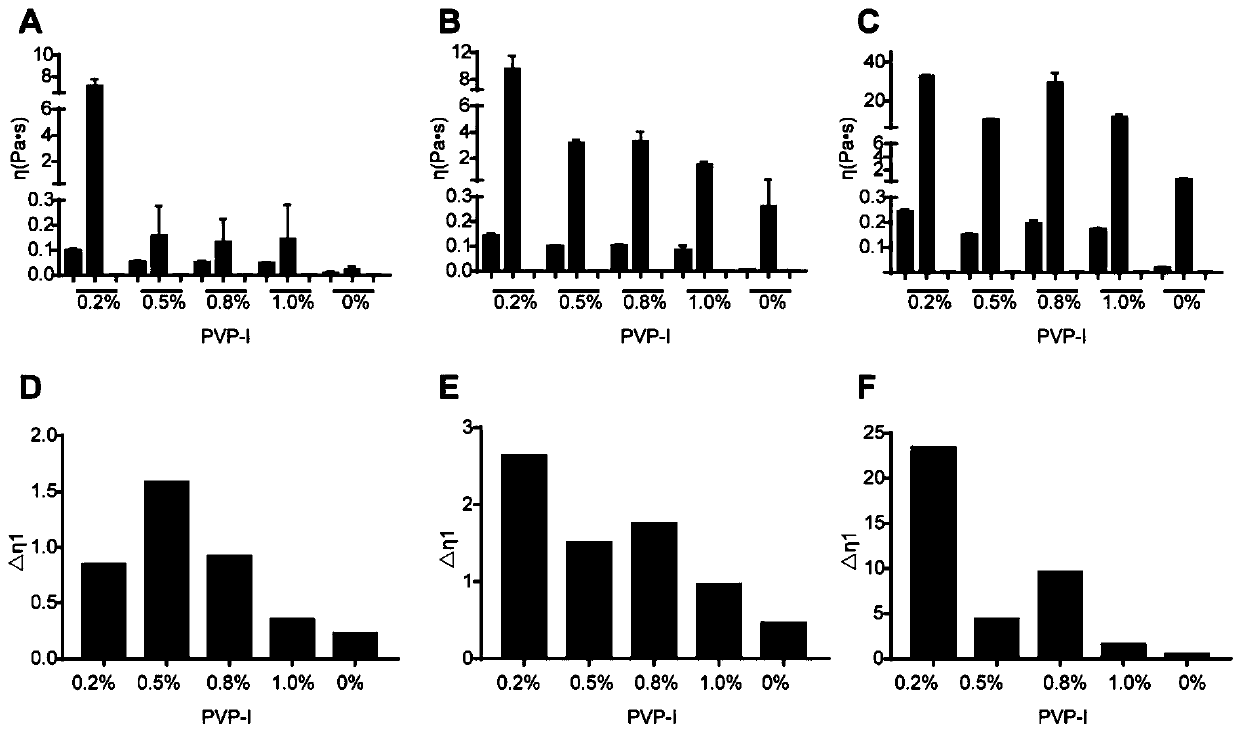
[0069] Example 1. Screening of PVP-I suitable concentration in the prescription
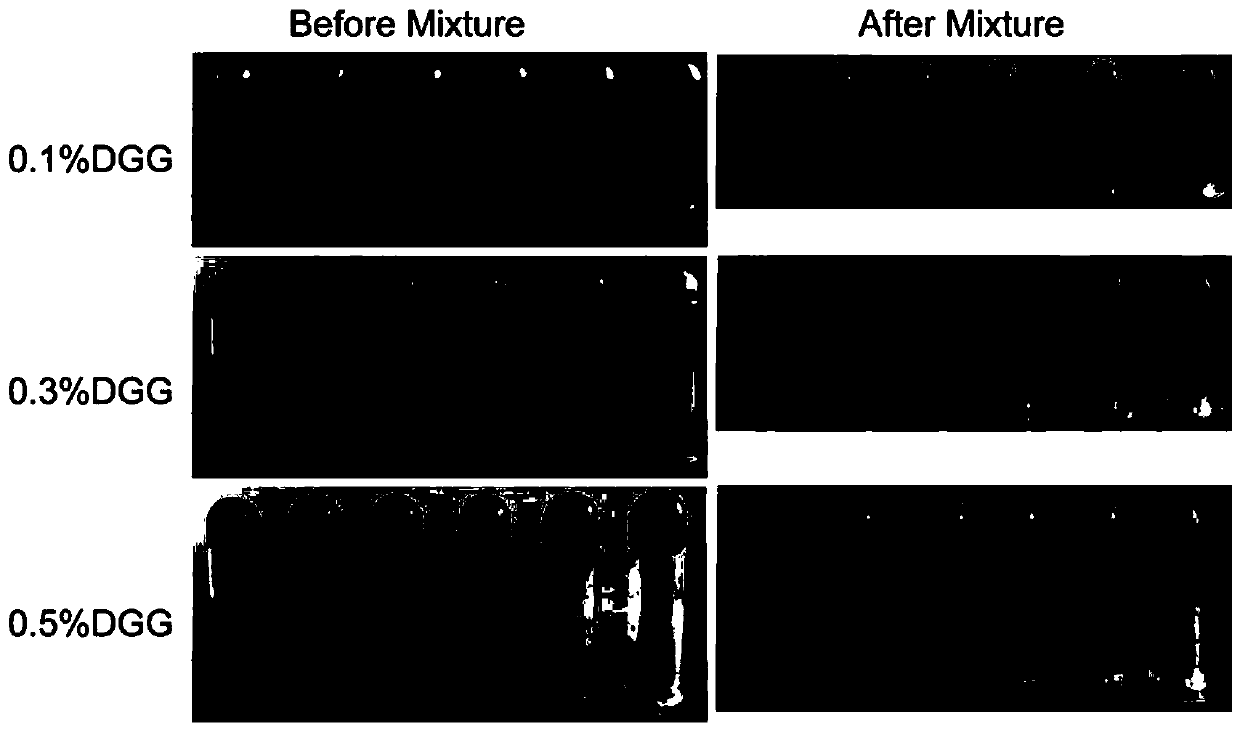
[0070] The composition contains 0.064% (w / w) budesonide and 0.25% (w / w) sodium chloride. Gellan gum concentrations were 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5% (w / w), and PVP-I concentrations were 0.2%, 0.5%, 0.8%, 1.0% (w / w). Mix different concentrations of gellan gum and PVP-I separately, and study the basic properties of their composition.
[0071] Table 1 prescription dosage
[0072]
[0073] The viscosity of the samples before and after mixing simulated nasal fluid (SNF) was tested under conditions of high shear rate (100 / s) at 25°C and low shear rate (0.1 / s) at 34°C. To simulate the viscosity change of the sample before and after spraying into the nasal cavity, and to simulate the contact of the drug with the simulated nasal fluid, so as to compare the spray ability of the sample and the gel-forming ability when mixed with the nasal cavity simulated fluid. The difference between the sample viscosity at low ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The prescription screening of embodiment 2.DGG and NaCl dosage
[0085] The weighed micronized budesonide and glycerin were thoroughly mixed, and when no gellan gum was added, 2% of the PVP-I solution and pure water were added to the total weight of the sample. Under stirring conditions, an addition of 1% gellan gum solution was added to the total weight of the sample. Adjust the pH to 4-5.5 with tromethamine and hydrochloric acid. Each group of mother liquors was prepared according to the ingredients shown in Table 5 (without NaCl). 50 μL of sodium chloride solutions of different concentrations were added to 2 mL of the mother liquor, so that the final concentration of sodium chloride was in the range of 0%-0.6%. The sample solutions containing different NaCl concentrations are shown in Table 6.
[0086] Table 5 Prescription Example
[0087]
[0088] Table 6 Prescription Example
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] The viscosity of the samples before and after mixi...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Embodiment 3. Prescription-viscosity curve research
[0110]
[0111]
[0112] The aim of this study was to investigate how different NaCl concentrations in the formulation changed the gel properties of the samples.
[0113] process
[0114] 1) Solution preparation
[0115] Solution 1 (1% DGG solution):
[0116] Add 29.7g of ultrapure water into a 50ml beaker; slowly disperse 0.3g of DGG into the beaker while stirring. Then put the solution into a 90°C water bath and stir for 1 hour to fully expand the gellan gum solution. After 1 hour, the stirring was stopped, the beaker was taken out from the water bath, the stirring was continued, the solution was allowed to cool at room temperature (25° C.), and then the stirring was stopped. This solution is labeled solution 1.
[0117] Solution 2 (2% povidone iodine in water):
[0118] When Solution 1 begins to cool, a 2% povidone-iodine solution in water needs to be prepared.
[0119] Put 39.2g of ultrapure water in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com