Method for screening and identifying strains with high glucosinolate degradation capacity
A technology for strain screening and identification methods, used in microorganism-based methods, microbial assay/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
Inactive Publication Date: 2020-03-17
SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
View PDF2 Cites 1 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0010] 4. Traditional microbial identification methods
But studies have shown that there are many microorganisms that cannot be achieved using current culture techniques
Therefore the traditional method has its limitations, side illustration of the diversity of microorganisms
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
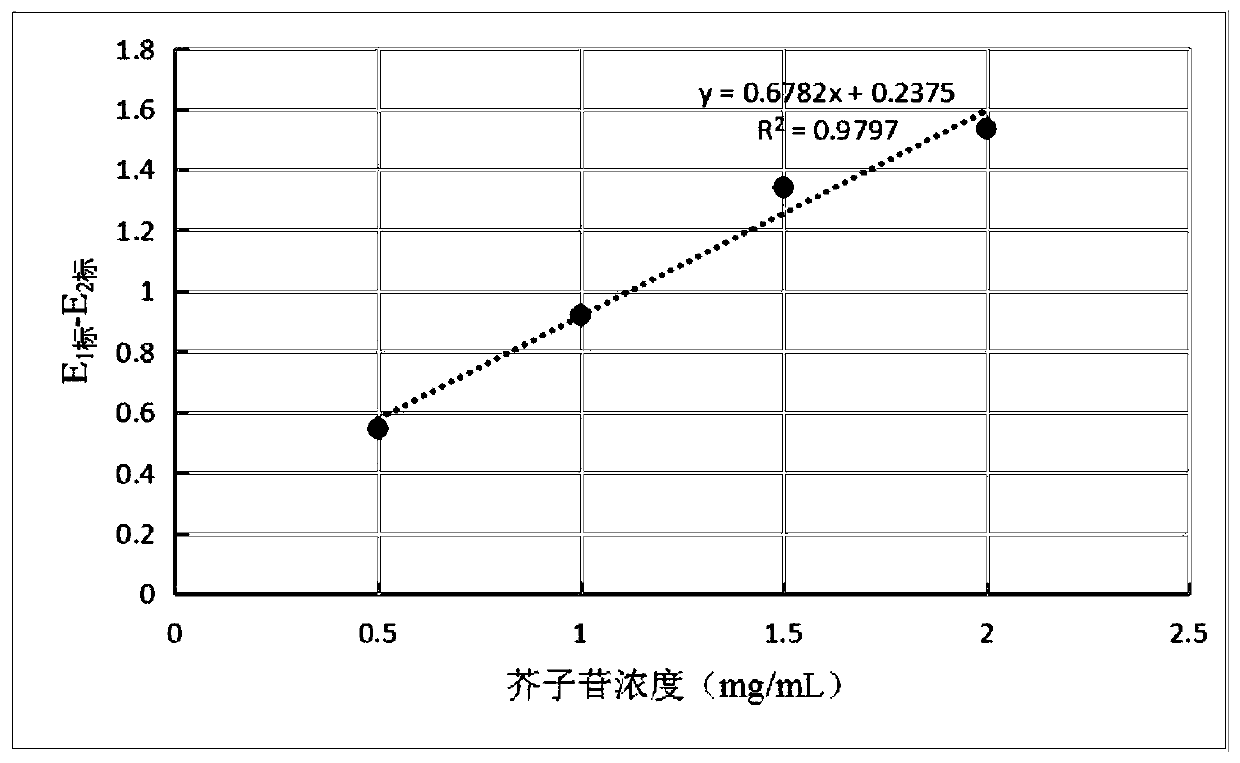
[0054] The experimental materials required for the bacterial strain screening and identification method with high sinapin degradability of the present embodiment are as follows:
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention discloses a method for screening and identifying strains with high glucosinolate degradation capacity. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting glucosinolate, determiningthe content of glucosinolate, and setting the concentration of a glucosinolate standard substance; S2, purifying the strain by using MRS and PDA as culture media, carrying out morphological observation, carrying out liquid culturing on a single bacterial colony, and then carrying out strain preservation and gram staining on the strain; S3, determining the glucosinolate degradation rate of the strain, carrying out first screening, carrying out tolerance experiment on the screened strain, and carrying out second screening; and S4, carrying out rapid molecular biological identification on the screened strain by using a 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis method.
Description
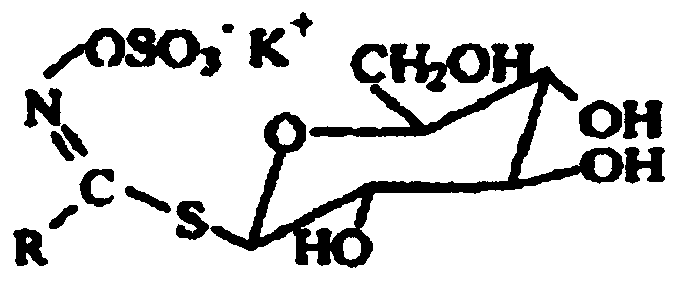
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial degradation measurement of sinapinin, in particular to a strain screening and identification method with high sinapinin degradation ability. Background technique [0002] 1. Brief introduction of sinaprin [0003] Sinoglucosinolate, also known as glucosinolate, is a glucoside formed by combining aglycone containing a sulfhydryl group (-SH) with glucose, and mainly exists in cruciferous plants. Simple structure such as figure 1 , where R is various aryls and alkanes. Myrosinin is an anti-nutritional factor, and myrosinin can be degraded by myrosinase or heat to generate isothiocyanate. [0004] 2. Study on the characteristics of isothiocyanate, the degradation product of sinaprin [0005] Isothiocyanates are a family of compounds characterized by sulfur containing N=C=S functional groups. It is an important and unique class II plant product. Isothiocyanates are widely used in food, medicine...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/04C12Q1/689C12R1/07C12R1/15C12R1/01
CPCC12Q1/04C12Q1/689
Inventor 杨吉霞
Owner SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com