Patents
Literature
172 results about "Gram staining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gram stain or Gram staining, also called Gram's method, is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial species into two large groups (Gram-positive and Gram-negative). The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique.
Bacillus adhaerens and its use in preparing health food having thrombolysis property
InactiveCN1464046AHigh activityStrong thrombolytic effectBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
Bacilliis natto NLSSc with the preservation number CGMCC No. 0724 is Gram staining positive, non-acid fast, straight or near straight, (0.6-0.8)x(1.5-2.0) micron sized and aerobic; has mesial and un-swelled spore with the spore number inside one sporange cell not more than one, meso diamino heptane diacid and glycin contained in the cell wall, no characteristic saccharum and peripheral flagellum; and can be grown well in five kinds of natural organic culture medium and can form relatively thick mycoderm and butter fat colored colony with smooth edge in soybean cake powder culture medium. Bacilliis natto can be cultured in culture medium with nitrogen source to obtain thrombus dissolving matter natto kinase and the cultured matter may be extracted to obtain powdered matter as the additive for thrombolytic health food.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus vallismortis and application thereof
The present invention provides Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4, which has the preservation number of CGMCC No.8273. According to the present invention, the strain grows on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium in a single cell reproduction growth manner to form bacterial colonies, and the bacterial colonies have characteristics of round shape, milk white color, slightly elevated center, and moist and transparent surface; microscopic examination results show that the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 has a rod shape, has flagella, has a size of 0.7-0.82*1.6-2.2 mum, presents the positive Gram staining effect, has spores, and can grow on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium containing 2-5% of NaCl, wherein the beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium comprises: 3.0 g of a beef extract, 10.0 g of peptone, 5.0 g of NaCl, 17 g of agar and 1000 ml of water, and the pH value is 6.8-7.2; and the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 provides significant antagonism effects for pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng root rot, blight, sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis cinerea. The present invention further provides an application of the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 in prevention and control of plant fungal diseases or preparation of microorganism preparations for prevention and control of plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
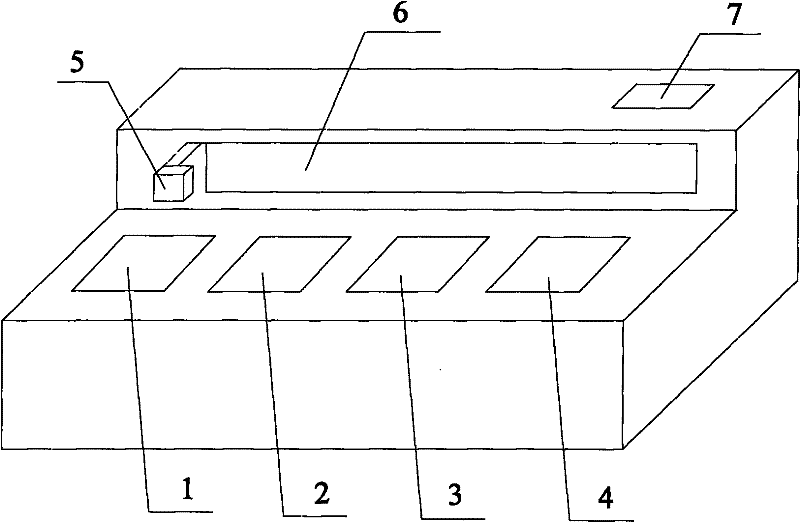
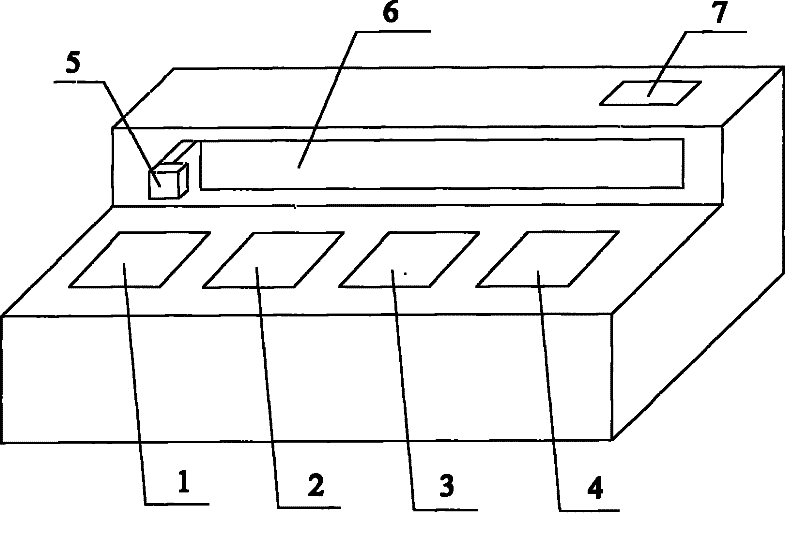
Multifunctional fully-automatic Gram staining instrument
ActiveCN104777027AImprove dyeing efficiencyAvoid false positivesPreparing sample for investigationStainingResource saving
The invention relates to a multifunctional fully-automatic Gram staining instrument. The instrument comprises a glass slide lateral movement device, a microbe automatic staining device, a glass slide entering and departing device, a push rod device and a liquid path control device, the push rod device pushes a coated glass slide positioned on the glass slide entering and departing device into the glass slide lateral movement device, the glass slide moves with a first glass slide rack on a reciprocating movement mechanism to the automatic staining device, is stained, cleaned and blow-dried, the liquid path control device cooperates a computer program in order to control a staining solution in a Gram staining solution bottle to carry out staining, water spraying, gas spraying, drying and other fully-automatic activities on the coated glass slide according to preset steps and time, and the push rod device moves the processed glass slide into the glass slide entering and departing device in order to carry out subsequent operation. The instrument has the advantages of fully-automatic realization of the whole Gram staining process, accurate delivery, cross infection avoiding, staining solution waste avoiding and manpower resource saving.
Owner:JIANGSU BIOPERFECTUS TECH CO LTD
Pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof
ActiveCN103540545AImprove acid resistanceGood resistance to bile saltsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyStaining
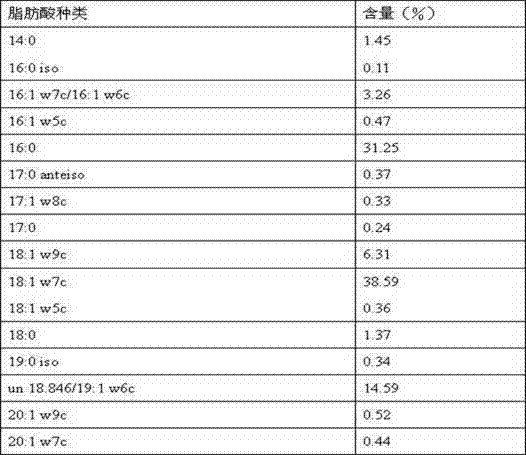
The invention discloses pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof. The Latin name of the pediococcus pentosaceus is Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05, and the pediococcus pentosaceus is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7049. The pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention has the morphological characteristics that the thallus is rod-shaped, dose not generate spores, does not have motility, and has masculine Gram staining. The whole-cell fatty acid of the pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention comprises the following main components in percentage by weight: about 1.45% of 14:0, about 3.26% of 16:1w7c / 16:1w6c, about 31.25% of 16:0, about 6.31% of 18:1w9c, about 38.59% of 18:1w7c, about 1.37% of 18:0 and about 14.59% of un18.846 / 19:1w6c. The invention also discloses a complete sequence of 16S ribosome DNA (16SrDNA) of the pediococcus pentosaceus. The pediococcus pentosaceus and a preparation thereof disclosed by the invention can be used for adjusting the micro-ecological balance of intestinal tracts of human or animals, promoting digestive absorption and slowing down the happening and development of liver failure of experimental animals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacillus cereus producing keratinase and application thereof
PendingCN107868762APromote degradationStable enzyme productionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganismBacillus cereus
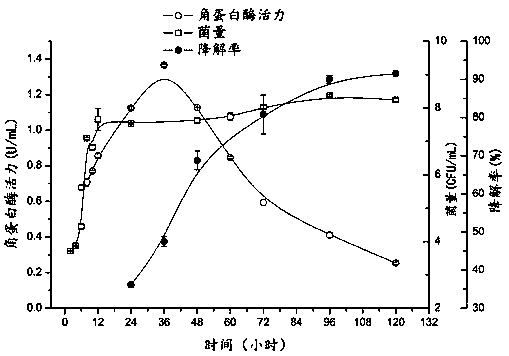
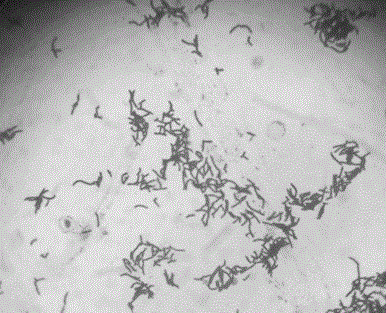
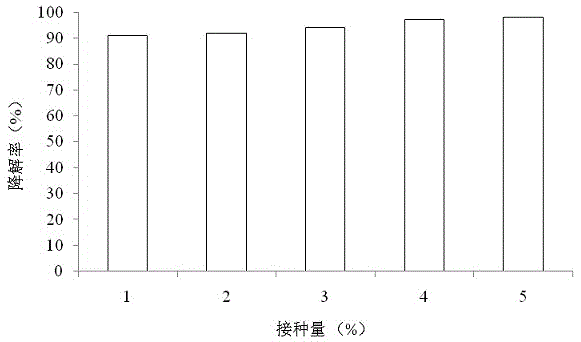
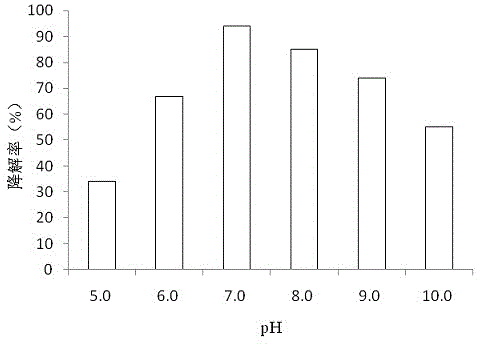
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, particularly relates to ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 for efficiently degrading feather keratin, and further relates to application of the ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15. The ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in June 6, 2017, with the culture preservation number being CGMCCNO. 14221; the colonial morphology on a milk screening plate is as follows: bacterial colony is white and circular, the waxiness on the surface is non-transparent, and the edge is wavelike; gram staining shows a positive result, and the thallus is bacilliform. The ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 screened and cultured has excellent degradation effect on keratin.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof
ActiveCN106591168AResidue reductionReduce production and use costsBacteriaWater contaminantsAntibiotic YBiology
The invention discloses rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof. The invention provides a strain namely rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading residual nicosulfuron in wastewater, and the identification shows that the strain belongs to Rhodococcus. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC in February 9th, 2015; and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 10542. The main biological characteristics are as follows: the Gram staining reaction is negative; the bacterial colony is in an orange yellow color, is in a round shape, and is opaque, the surface of the bacterial colony is rough and dry; the cell is in a sphere shape or short bar shape, does not have any flagellum, is motionless, and does not generate any spore; the strain is aerobic and chemoheterotrophic and cannot liquefy gelatin and hydrolyze starch; the enzyme contact reaction is positive, the V.P. reaction is positive, the methyl red reaction is negative; the strain cannot degrade casein, cannot reduce nitrates; and the strain can produce acids from glucose, can utilize glucose, fructose, and citrates, cannot utilize mannose, arabinose, and raffinose, and can reduce more than 90% of antibiotics in water through direct application.
Owner:JIANGSU NANZI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Chlorotoluron pesticide residue degradation strain agent prepared by the strain
InactiveCN101338286AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStandard problemPesticide residue
The invention provides a pesticide-degrading bacterium for removing the residue of a herbicide of chlorotoluron; the bacterium that is used is gram staining reaction negative bacilli YBL3 which is identified to be Sphingobium sp. The bacterium is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in May 23rd, 2008 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CCTCC M208076. The technique for producing the bacterium includes: slant seed-shake flask seed-seed pot-production pot-product (the packaging formulation is liquid bacterium or solid absorption bacterium). The product of the degrading bacterium can be directly applied to reduce the pesticide residue in the crops by more than 90 percent, thus solving the over standard problem of the pesticide residue in agricultural production and being capable of producing green agricultural products with no poison and social effects of pollution.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Automatic staining instrument with Gram staining two-step method
InactiveCN102220236AInput NoneProduce noneBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingGram
The invention relates to an automatic staining instrument with a Gram staining two-step method. The staining instrument comprises two staining pools, a cleaning pool, a hot air flow drying pool, a manipulator, a rail and a display screen, wherein the first staining pool, the second staining pool, the cleaning pool and the hot air flow drying pool are sequentially arranged at the front part of the staining instrument, the manipulator is arranged at the upper part of the staining instrument, slices to be stained or quality control slices can be placed in the front end of the manipulator, the back end of the manipulator is connected with the rail, and the display screen is arranged at one side of the top of the staining instrument. Compared with the prior art, the instrument has the advantages that the protective technology and the operation flow are simple, special requirements to water quality are free, no harmful organisms are introduced and produced during the production and detection processes, more quick and easily-standardized experiment results can be provided, the result is easy to observe and judge, and the safety and reliability are provided.
Owner:叶元康
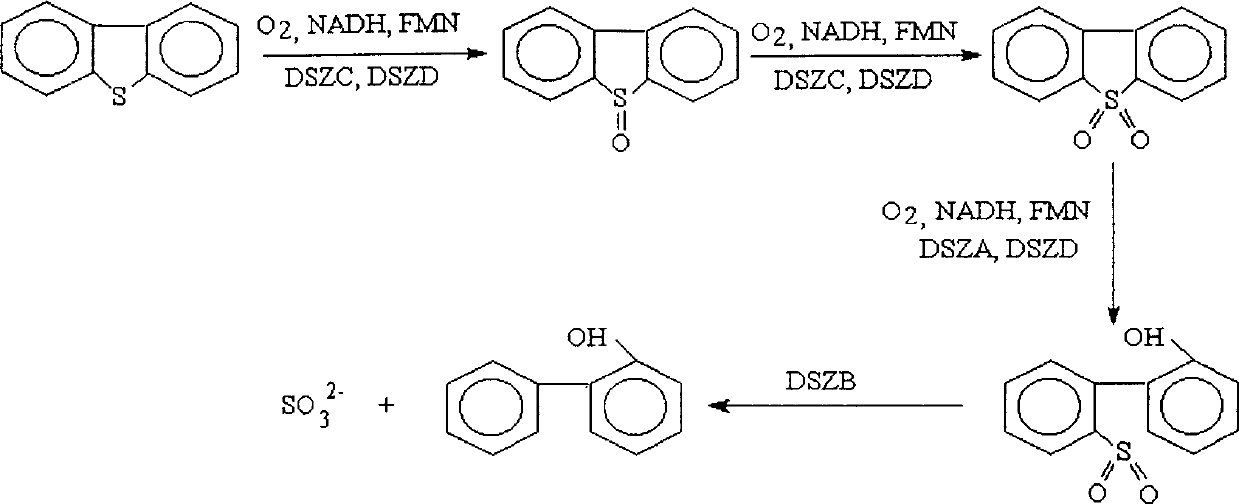
Gordona nitida and application of removing sulfur element from sulfur compound
A Gordona nitida LSSEJ-1 (CGMCC No.0700) and its application in removing sulfur from the S-contained organic compound are disclosed. Said rod-shaped Gordona nitida LSSEJ-1 has 2-3 microns in length, shows positive to Gram staining, and contains meso diaminopimelic acid, characteristic arabinose and galactose, nocardomycolic acid and MK-9 (H2).
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of bacillus pumilus and its application in killing nematodes
The invention relates to a Bacillus pumilus and an application thereof on killing eelworms. The morphological characteristics of the Bacillus pumilus strain with the function of killing eelworms are as follows: the strain is short rhabditiform, the size of the thallus is 0.58*2.1 microns, and the strain has endogenous spores and is positive by Gram staining. A bacterial colony protrudes on a beef extract-peptone solid culture medium, the edge is smooth and fine, the bacterial colony is milk white and the size is 1.1-1.8 mm; the bacterial colony is smaller on a DSMZ88 improved solid culture medium, the bacterial colony is white, the surface of the bacterial colony is more dry, the edge is rough and irregular and the diameter is 1.5-2.0 mm. The Bacillus pumilus is prepared by a regular method. The Bacillus pumilus is intermediately cultured and the insect-killing effects on Panagrellus redivivus, Meloidogyne incognita and ovum of the Meloidogyne incognita are detected. The Bacillus pumilus provided by the invention has better killing effects on the P.redivivus, the Meloidogyne incognita and the ovum of the Meloidogyne incognita and can be developed as an eelworm anti-biological inoculant.
Owner:HONGYUN HONGHE TOBACCO (GRP) CO LTD +1
Triazine herbicide residual degrading strain and strain therefrom
InactiveCN1584018AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaTriazine herbicideBiological property
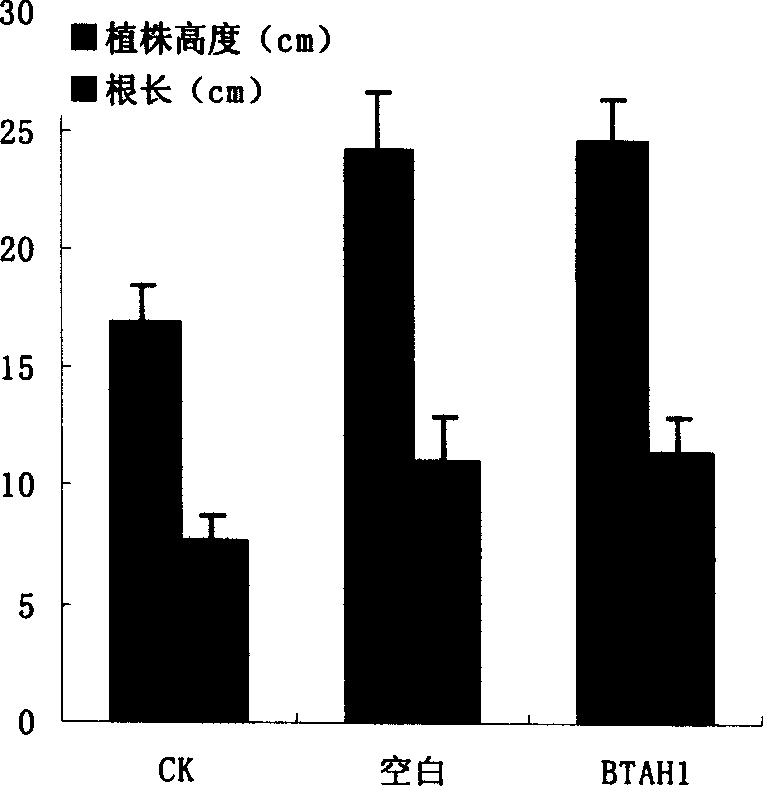
A method for preparing degrading bacteria for eliminating residual triazine herbicide is disclosed. The strain is Gram's chromatic reacting positive strain BTAH1, which belongs to exiguobacterium sp. Its characteristics are G+, irregular nemaline, 0.7-1.2X2.0-4.0mum, contact enzyme is positive, and it can hydrolyze starch. Genbank landing number of the strain 16S rDNA is AY205564. Its advantages include decrement of pesticide residual amount, atoxic and innoxious green agricultural product.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacterium for degrading chlorpyrifos pesticide residue and produced bacterium formulation
The invention provides a prodegradant which can dispel the organic phosphorus pesticide residue of chlorpyrifos. The used strain is Gram's stain reaction hysteroptosis Dsp-2 which is Sphingomonas sp. The main biology characteristic is G-; the thaliana is the rod type of asporous whose size is 1.0-1.5um; the scavenger enzyme is male and the oxidative enzyme is female which can not be hydrolysed starched and be gelatin liquidated; the methyl red reaction is female and not to produce the indole with the aquolysis temperature 80 deg. The Genbank landing number of the strain 16S rDNA is AY994060.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
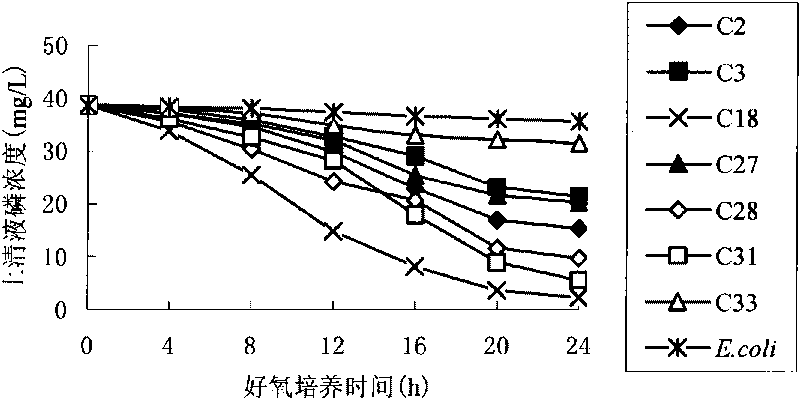
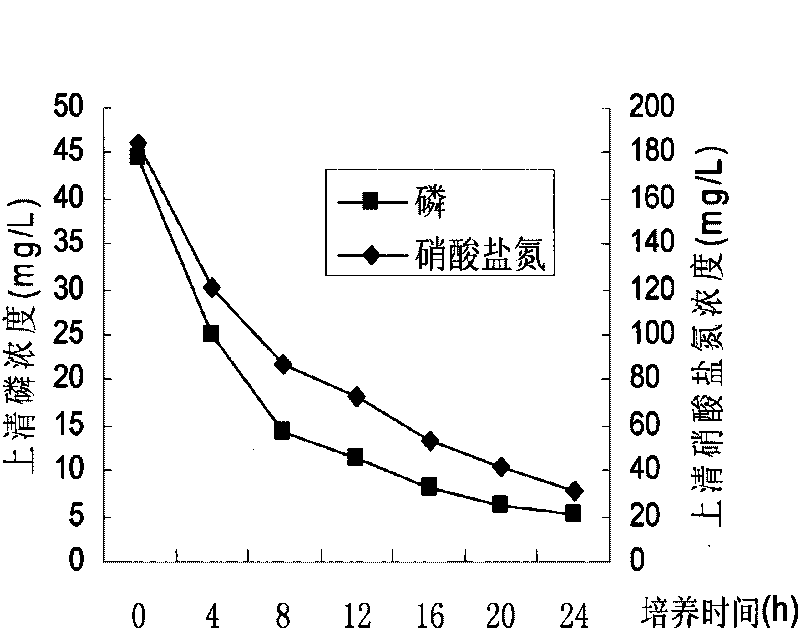
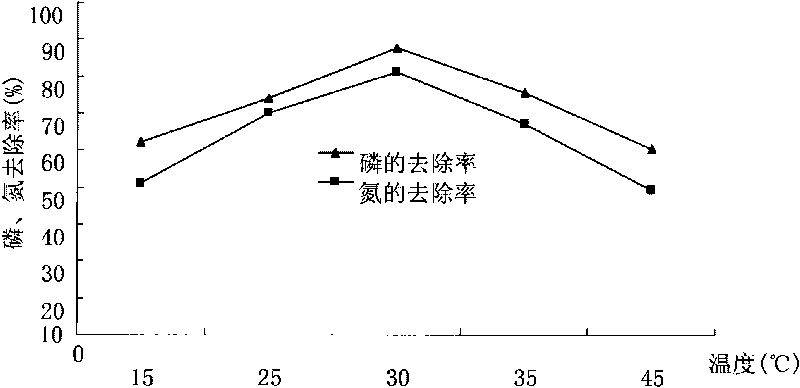
High-efficiency denitrification and dephosphorization bacterial strain C18
InactiveCN101735973AGood nitrogen and phosphorus removal capacityReduce processing costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological propertyIndole test
The invention provides a high-efficiency denitrification and dephosphorization bacteria strain C18, which belongs to the technical field of waste water biochemical treatment process. The bacterial strain C18 is gram-negative bacteria, which is identified as a pseudomonas (pseudomonas grimontii). The main biological characteristic of the bacterial strain is G-; thalli is of short rod shape; the size is about 0.9*0.6 mu m; a flagellum is grown on a partial side; V-P test is positive; indole test is positive; and the bacterial strain can hydrolyze starch. After 24 hours anaerobic cultivation, the bacterial strain C18 has a dephophorization rate of 88.3 percent and a denitrogenation rate of 83.4 percent, and can be used in the waste water biochemical treatment process so as to reduce the content of the nitrogen and the phosphorus in the waste water greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly identifying bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria
InactiveCN102453752ARapid determinationEfficient determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesKlebsiella oxytoca
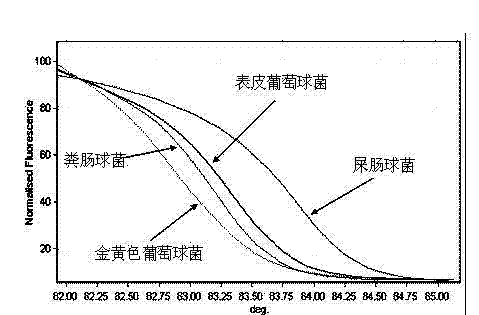
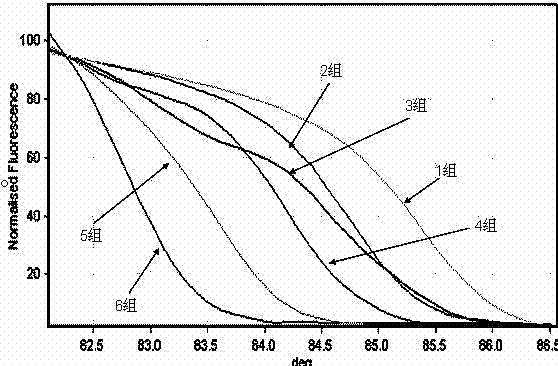
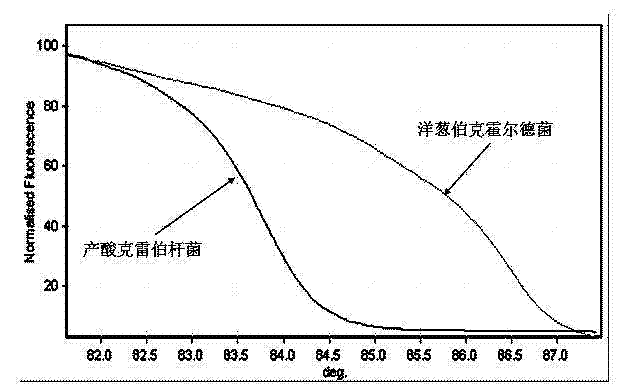
The invention belongs to the field of examination of microorganisms, and relates to a method for quickly identifying bloodstream infection bacteria by a high-resolution fusion curve method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing smear gram staining on a blood culture positive culture flask to distinguish negative bacteria and positive bacteria; selectively amplifying different 16S fragments for the negative bacteria and the positive bacteria; and analyzing by the high-resolution fusion curve method. Common bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria comprise staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, acinetobacter baumannii, pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella oxytoca, acinetobacter lwoffii, enterobacter aerogenes, stenotrophomonas maltophilia and burkholderia cepacia. By the method, the common bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria can be measured quickly, efficiently and accurately, so that strong evidences are provided and precious time is striven for subsequent treatment.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
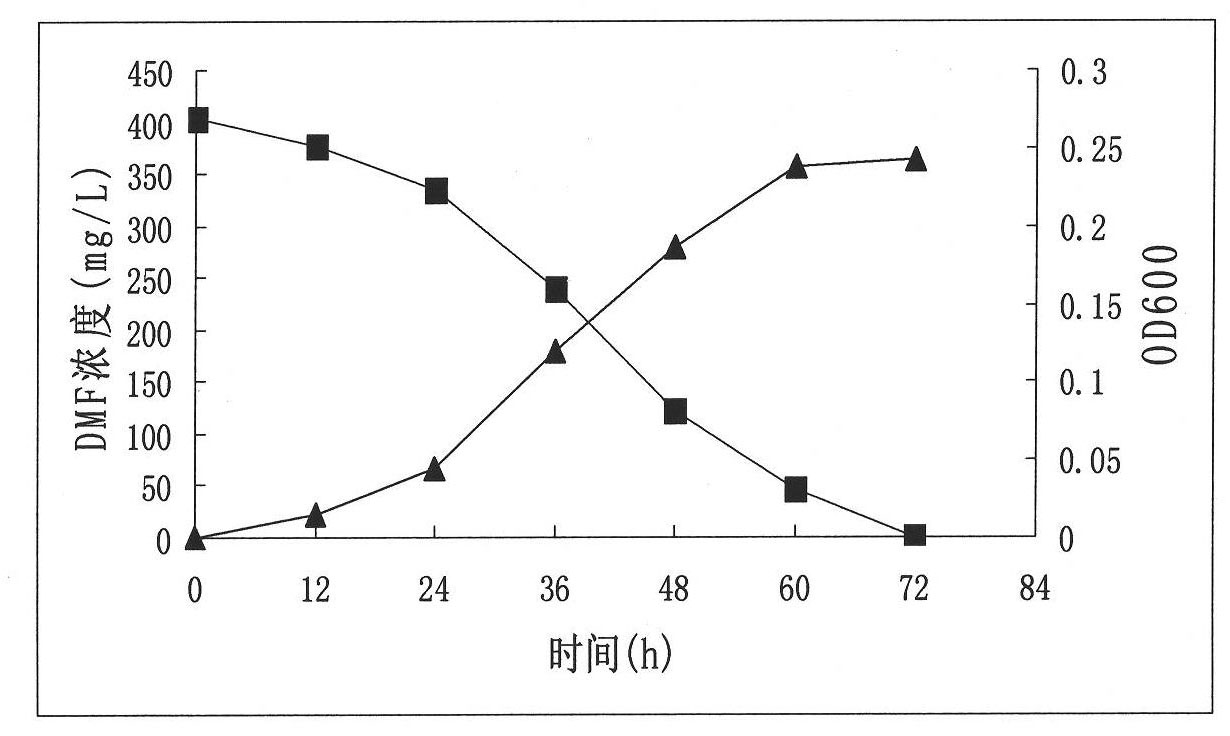
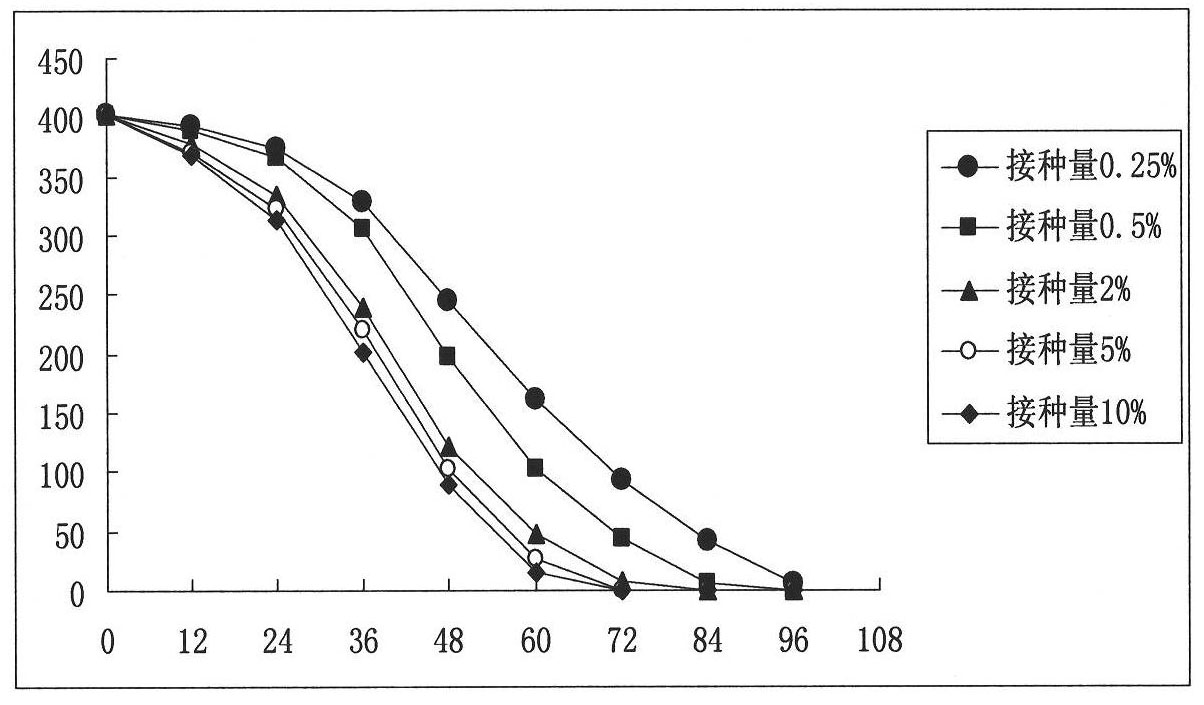
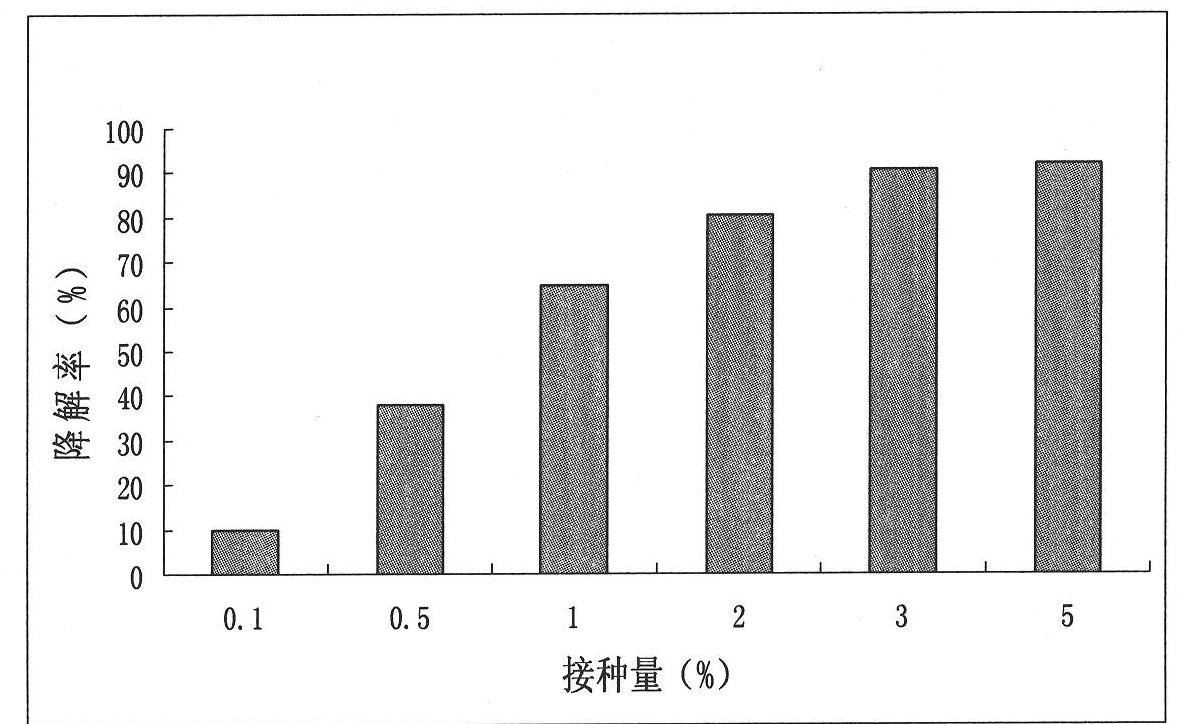
Dimethylformamide degrading bacteria and bacterial agent produced from same
ActiveCN101935626AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaWater contaminantsChemical oxygen demandBiology
The invention provides dimethylformamide (DMF) degrading bacteria and a bacterial agent produced from the same, which belong to the field of biological high technology. The strain is a Gram staining reaction negative bacteria strain DMF3 and is identified as pseudomonasplecoglossicida. The strain has the main biological characteristic of G<->, an irregular rod-shaped strain body, the size of about 0.5-1.0*1.5-5.0 mu m and no stipe or mycoclena, does not produce spore, is aerobic, undergoes strict respiratory metabolism and can grow by taking DMF as a unique carbon source and nitrogen source so as to be completely mineralized for releasing ammonia nitrogen. The strain can reduce the residual quantity of the DMF with certain concentration in waste water by over 95 percent at the temperature of 30 DEG C under the pH value of 7.0 within 3 days, so that the problem of difficult treatment of the DMF in chemical production waste water is solved, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) of the DMF waste water reaches the standard and the waste water can be discharged.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Triethylamine degrading bacterium and microbial agent produced therefrom
ActiveCN101935625AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobial agentEthylamine
The invention provides a degrading bacterium eliminating the pollution of triethylamine and a degrading microbial agent and belongs to the high-technical field of biology. The used strain is a gram staining reaction positive bacterium R4, is determined as arthrobacter protophormiae, and has a biological characteristic of G+. The logarithmic phase thallus is bacilliform, sporeless and aerobic to grow, and can grow by taking the triethylamine as the only carbon source or nitrogen source and thoroughly mineralize the triethylamine to generate ammonia nitrogen. In a flask experiment in a laboratory, the strain can completely degrade 100mg / L triethylamine and solve the problem of the difficult biodegradation of the triethylamine in wastewater treatment.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Paracoccus MXX-04 for bromoxynil degradation and application thereof
ActiveCN103243056AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSynechococcusMotility
The invention provides a degradation strain for eliminating residual bromoxynil, belonging to the field of biological high technology. The adopted bacterial strain is a gram staining reaction negative strain MXX-04 which is identified to be paracoccussp. The main biological properties are G-, short rod shape, no spores, no motility and positive oxidase and catalase. The strain provided by the invention can grow by taking bromoxynil as a unique nitrogen source and mineralize the bromoxynil. Under the condition of a shake flask in a laboratory, the strain can degrade 95.3% of 100mg / L bromoxynil within 24 hours, thus the problem that bromoxynil is hard to degrade biologically in the environment is solved.
Owner:JIANGSU NANZI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Enterococcus faecium producing bacteriocin and application thereof
ActiveCN105779346AImprove toleranceImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaFood preservationSynechococcusAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to an Enterococcus faecium strain producing bacteriocin. The strain was preserved as a name Enterococcus faecium R1 by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 20, 2016, with preservation number CGMCC No.12085. A source of the strain is farm traditional fermented soybean paste and is presented as a circular or elliptic white smooth nontransparent colony smaller than 1mm in an MRS agar culture medium; uniform turbid growth is presented in an MRS liquid culture medium; thalli are spherical under an electron microscope and are arranged in pairs or in a chain, and gram staining is positive. The strain provided by the invention is sensitive to antibiotics, does not contain virulence genes and is a safe strain. The bacteriocin produced by the strain is enterococcin P, is stable under acidic conditions, has a very good thermal stability and has a good bacteriostatic effect on common enteropathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Identification method of bacillus subtilis with high protease output
InactiveCN103882097AHigh selectivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAMicroscopic exam
The invention discloses an identification method of bacillus subtilis with a high protease output. The method includes: inoculating a bacterial strain to be identified onto a skim milk powder plate culture medium, culturing at 35 DEG C for 24 h, performing Gram staining, performing microscopic examination, separately extracting a DNA template from 1.0 mL of the bacterial strain to be identified by adoption of a genome DNA extraction solvent kit, designing and synthesizing PCR amplification primers, with the upstream primer P1 being 5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3' and the downstream primer P2 being 5'-AGTAAGGAGGTGATCCAACCGCA-3', and performing PCR amplification of 16SrDNA. The method is high in bacterial strain selectivity, scientific in identification method, short in time and period and high in efficiency.
Owner:QINGDAO ZHONGREN PHARMA
Strain of petroleum aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium and applications thereof
ActiveCN107893047AEfficient degradation abilityWide temperatureBacteriaWater contaminantsBioremediationOil concentration
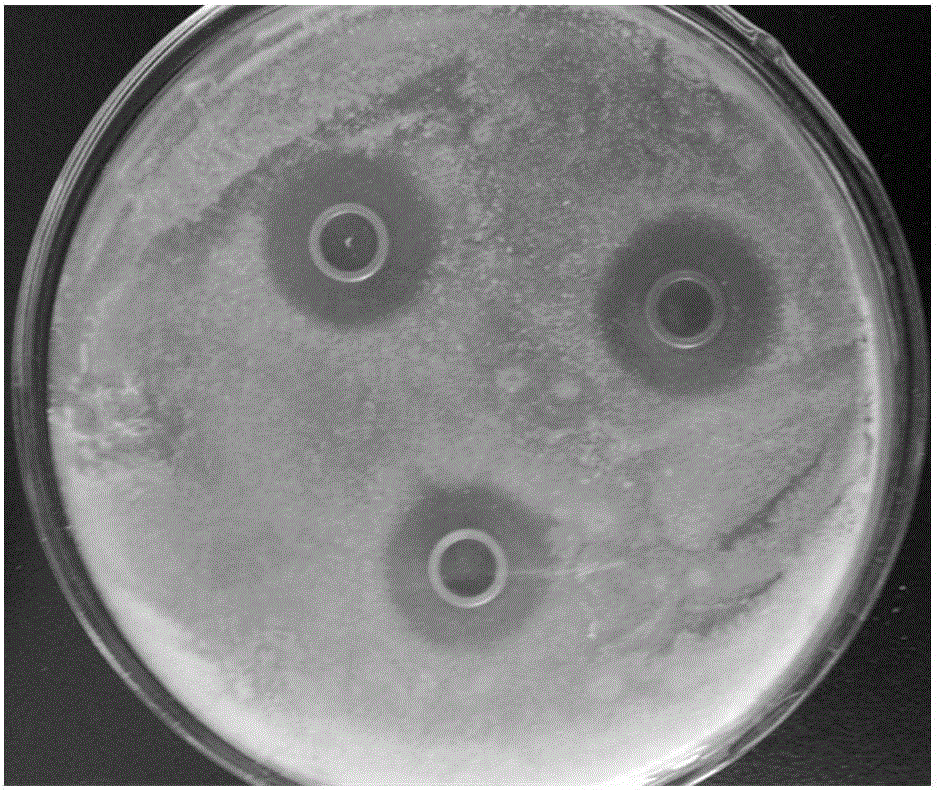
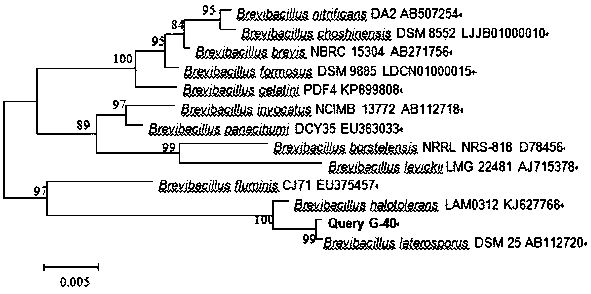
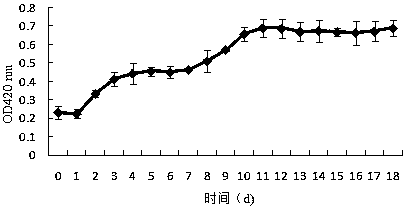
The invention discloses a petroleum aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium (G-40), which is named as brevibacillus laterosporus G-40 and belongs to brevibacillus. The strain has been saved in ChinaCenter for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), Wuhan university, China in June 30, 2017. The preservation number is CCTCC No. M2017400. The strain is screened from petroleum polluted soil in the oil producing region of Guanghua oil field in Qianjiang city. The strain (G-40) has an ellipsoidal shape. The result of gram staining is positive. The strain (G-40) can degrade 53.02% of petroleum aromatic hydrocarbons after the strain is cultured for 30 days under following conditions: temperature: 35 DEG C; pH value: 7.3; oil concentration: 0.6%; salt concentration: 0.5%; inoculation amount: 10%; nitrogen source: (NH4)2SO4; and phosphor source: Na2HPO4. The strain (G-40) can adapt with wide ranges of temperature, pH value, and salinity, and has a good prospect and economic value in fields such as petroleum pollutant elimination, biological restoration of petroleum aromatic hydrocarbon polluted soil and water, and the like.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Kit for separating and identifying campylobacter rectus as well as preparation and application for kit
InactiveCN102816831AValid identificationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesCulture mediumsCampylobacter jejuni
The invention relates to a kit for separating and identifying campylobacter rectus as well as a preparation and an application for the kit, and mainly solves technical problems of high omission factor, complex identifying steps, higher cost and insufficiently visualized screened results in the existing method for separating the campylobacter rectus, such as campylobacter jejuni and non campylobacter jejuni. The kit for separating and identifying the campylobacter rectus has the technical scheme that: the kit comprises a selective enrichment broth I, a selective enrichment broth II, an improved Karmali agar plate, a Columbia blood plate, a microaerophilic gas generation bag, a gram staining solution, an oxidase reagent, a hippuric acid paper sheet and a hippuric acid enzyme reaction reagent. The campylobacter jejuni or non campylobacter jejuni is identified through a reaction combination test of a substrate and a typical colonial morphologic, simple biochemical and specific enzyme of the campylobacter rectus correspondingly grown in a culture medium for selective separation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Bromoxynil octanoate degrading bacteria and bacterial agent prepared from same
ActiveCN101935627AEasy to useReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBromoxynil octanoateCatalase
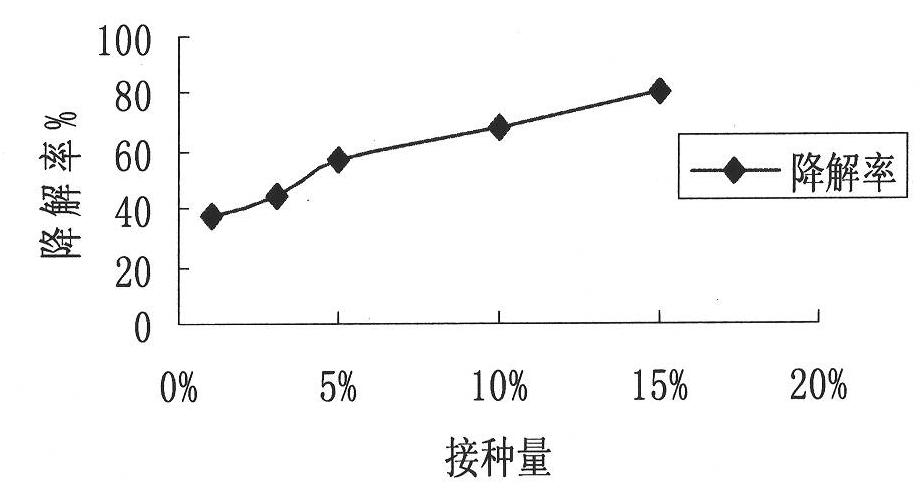
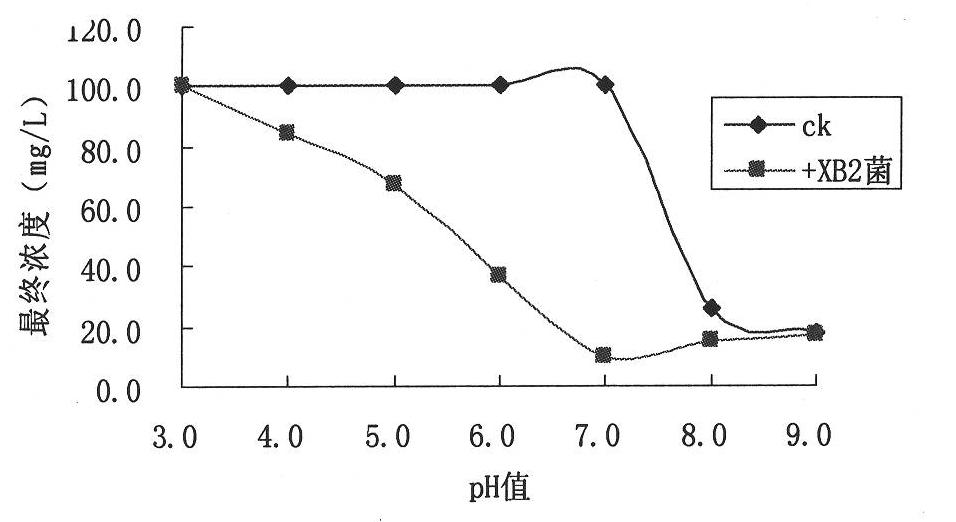
The invention provides degrading bacteria for eliminating residue of pesticide, namely bromoxynil octanoate, and a degrading bacterial agent thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology high-technology. The strain is Gram staining reaction negative bacteria XB2 and is identified as Acinetobacter baumannii. The strain has main biological characteristics that: the strain is G-; the thallus has a short-rod shape with the size of 0.9-1.6*1.5-2.5 mu m, has no spores and is strictly aerobic; and the strain is negative for oxidase and positive for catalase and can grow by taking the bromoxynil octanoate as a unique carbon source. The degrading bacteria is directly applied to make bromoxynil octanoate residue in crops reduced by over 90 percent, solves the problem that the bromoxynil octanoate residue in agricultural production is overproof, and can produce non-toxic and nuisanceless green agricultural products.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
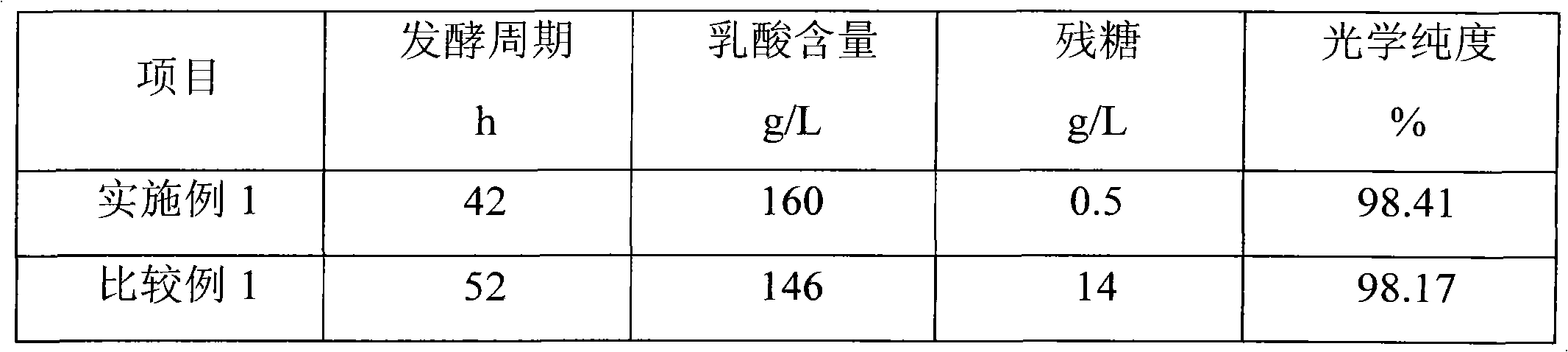
Lactobacillus casei and application of lactobacillus casei in ferment production of L-lactic acid
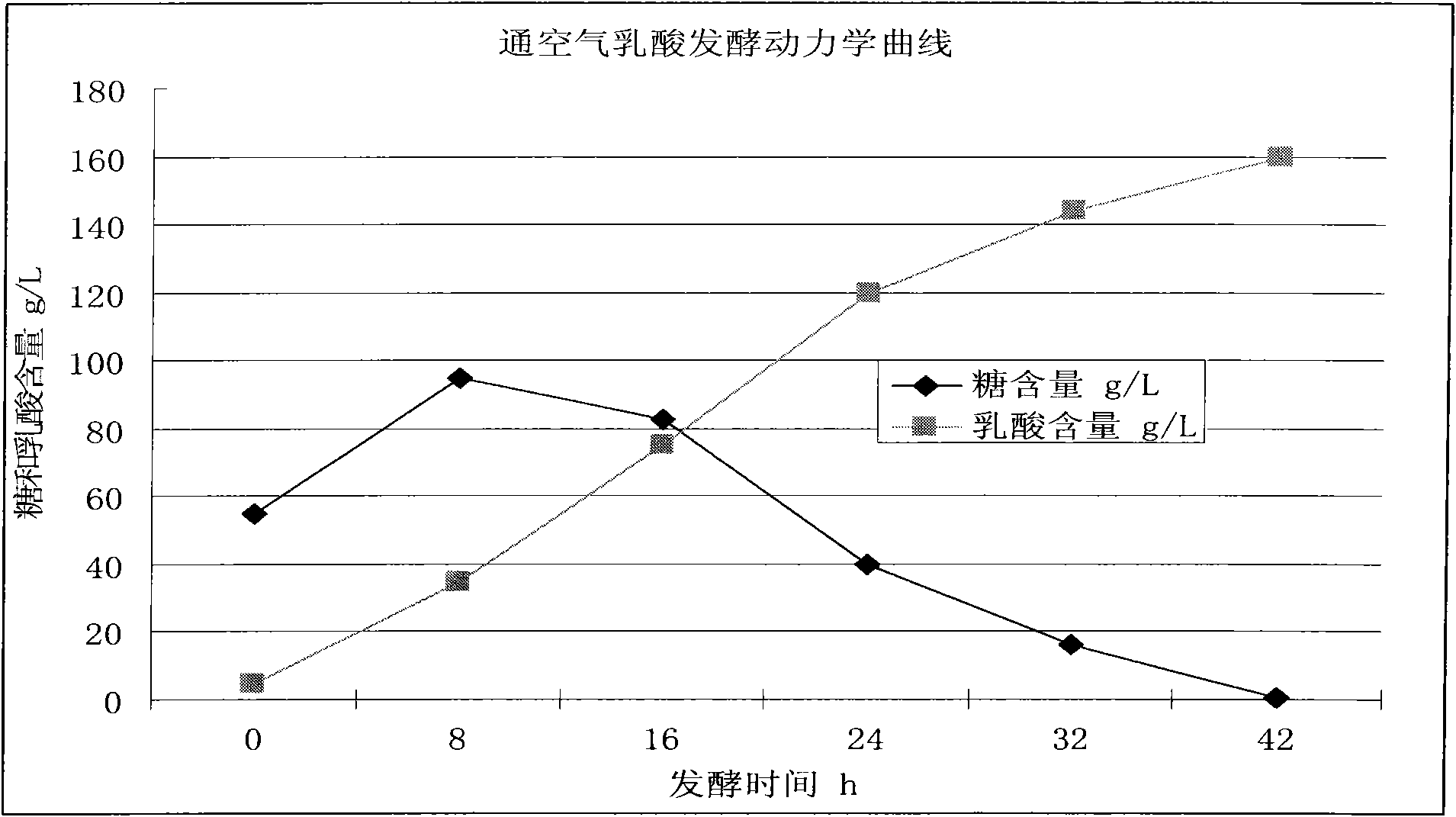
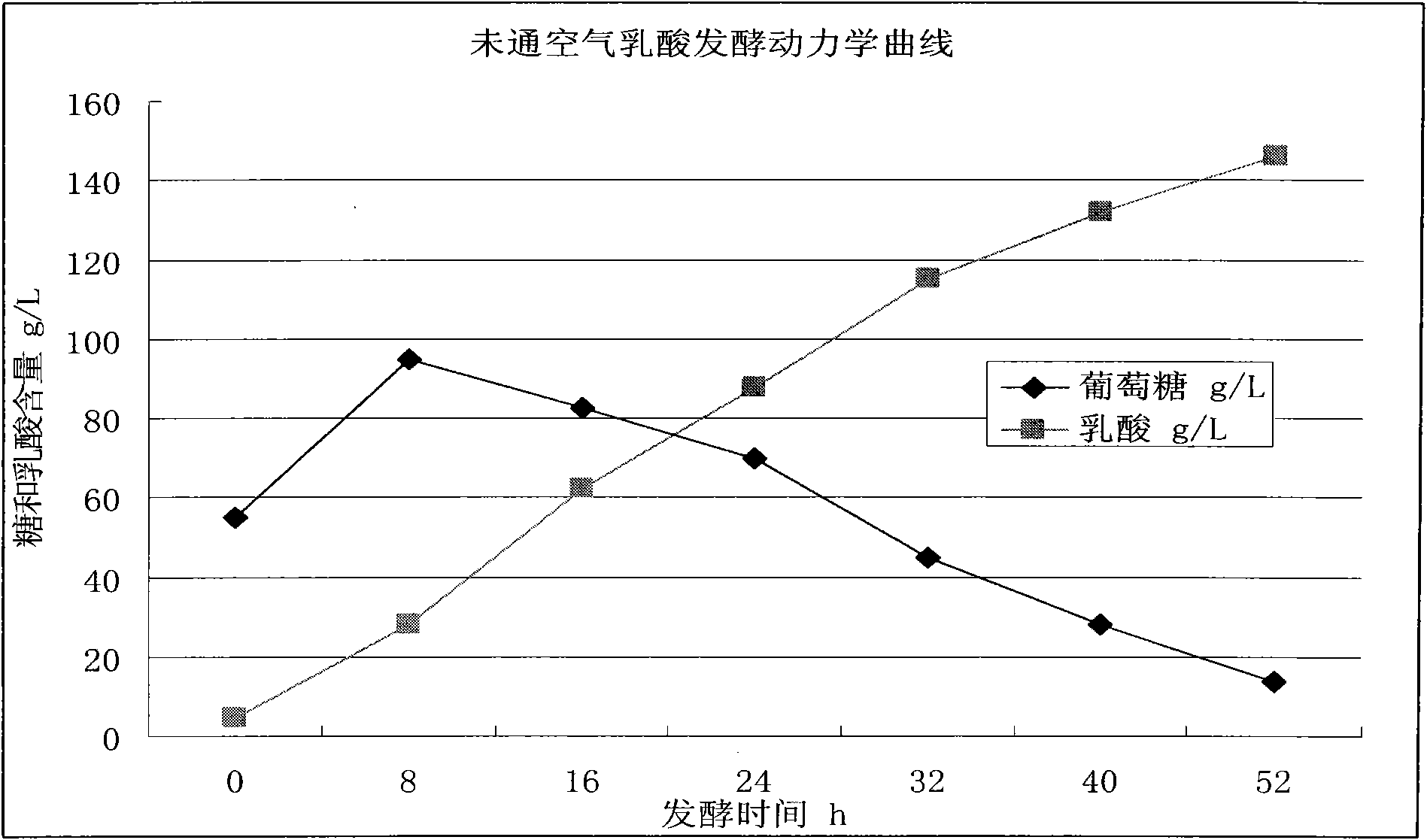
ActiveCN102051336AHigh optical purityMeet the needs of productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFacultativeMicrobiology
The invention relates to lactobacillus casei for producing L-lactic acid and application thereof. A strain is lactobacillus casei FY-04 and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on September 11th, 2009, and the collection number is CGMCC No.3269. The strain is negative in Gram staining, and is facultative and aerobic. When the strain is used for fermenting starch for producing the L-lactic acid, air is introduced in the process of fermentation, a trace amount of oxygen can promote thalli to proliferate, and by introducing oxygen, carbon dioxide can be carried out of a fermentation system, which ensures that the pH value in the fermentation system is stable and the fermentation system is favorable for the growth of the strain. Compared with the anaerobic strain fermentation process, the fermentation process has stable pH value and high acid producing efficiency.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Screening of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus and application of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus to improvement on greenhouse vegetable soil hardening
The invention relates to screening of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus JJMSH1 and application of the phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus to improvement on greenhouse vegetable soil hardening. The strain has a good phosphorus and potassium decomposing function. The strain is screened from rhizosphere soil of a plant in a vegetable greenhouse; the soil is enriched through an organic phosphorus culture medium and then subjected to screening through an inorganic phosphorus culture medium and a silicate culture medium successively, and a molybdenum and antimony resistant colorimetric method and a flame photometry are used for detecting the contents of effective phosphorus and rapidly available potassium in sequence, thus finally selecting the JJMSH1 as an ideal strain. The JJMSH1 is authenticated by gram staining and spore staining to be gram-positive bacillus. When the strain disclosed by the invention is used for treating hardened soil in the greenhouse, the contents of the effective phosphorus and the rapidly available potassium in the soil are relatively obviously increased, and the OD600 reaches 1.5; after being diluted 100 times, a microbial inoculum is applied to the soil, so that the content of the effective phosphorus is increased by 35.7 percent, and the content of the rapidly available potassium is increased by 26.1 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pig origin saliva lactobacillus viable bacteria preparation and application
InactiveCN106906166AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides a pig origin saliva lactobacillus viable bacteria preparation and an application and relates to the technical field of creatures. The preparation has a probiotic function on pigs, the colonization of the preparation in the enteric canal is guaranteed, wherein bacterial strains are gram staining positive and identified as Lactobacillus salivarius, the major biological characteristic is G+, and thalluses are of short rod shape; the preparation is facultative anaerobic, not capable of high temperature resistance, and has a certain inhibiting effect on escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus; according to the production process, the preparation comprises slant strains, shake flask seed solution, a fermentation tank, suspending agents and products, and animal experiments demonstrate that the diarrhea rate of pigs is reduced, the growth rate of pigs is improved, the feed conversion rate is reduced through the use, and the usage amount of antibiotics in the pig-feeding process is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI TECH BANK BIO TECH
Sporolactobacillaceae and produced preparation of living fungus thereof
InactiveCN1687400AReduce diarrhea rateAdd lessBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention provides a kind of bacterium and its procreation of living bacterium reagent, which can reduce the rate of piglet diarrhea. The used of bacterium is gelanshi pigmentation feedback electropositive bacterium S1, according to appraisal, it is Sporolactobacillus sp..Its main biological character is G+, the shape of bacterium is slim, divided burl, elliptical sporangium, after malachite pigmentation pigmentation is obvious, concurrently, exclude oxygen development, endure lower pH(pH2.5) and higher saline chroma(0.2%), not sensetive to pepsin, endure high temperature, it can restrain coliform and golden ball bacterium well. It indicated from the track of molecule biological technology, this bacterium can propagated in alvine of piglet. The flow chart is bevel bacterium--- rocky bottle seed liquid--- ferment jar---freez dryness--- production. The animal test indicates, this bacterium can be used directly and widely in reduce alvine of piglet, enhance the growth rate of piglet, reduce the use of antibiotics in piglet feedstuff.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Paracoccus versutus strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a paracoccus versutus (Paracoccus versutus) strain 2#CGMCC No. 13321 and application thereof for oxidizing nitrate serving as an electron acceptor to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in biogas under anoxic conditions. The strain is subjected to Gram staining to be negative, and the strain cells are in a shape of short rods and are small; the bacterial colony is white and bulged, the edge is neat and smooth, and the surface is wet; the strain is not salt-tolerant, and citrate cannot be utilized; and in the presence of nitrate, nitrite or nitrogen oxide, anaerobic growth of the strain can be promoted by taking nitrate, nitrite and nitrogen oxide as electron acceptors. After the paracoccus versutus strain CGMCC No.13321 is inoculated to a desulfurization reactor, the H2S can be subjected to biological oxidation in the reactor by taking the nitrate as the electron receptor and then is subjected to growth and propagation, the aim of removing the H2S in the biogas is achieved, the potential safety hazard brought by mixing of the introduced methane and oxygen in the traditional method for removing the H2S in the biogas by taking the oxygen as the electron acceptor is effectively avoided, and the removal rate of the H2S in the biogas is up to 93.8%.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S +1
Rapid detection method of coliform groups
InactiveCN101914609AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementLarge intestineColor changes
The invention relates to a rapid detection method of coliform groups. In the method, the situation that coliform group cells can generate gas and ferment lactose to generate acid in a short-time culture process is utilized to combine the coliform group cells with eosin methylene blue to ensure that a mixed eosin methylene blue culture solution generates atropurpureus or purplish red precipitation, and the image number of negative bacteria is obtained after carrying out gram stain on the atropurpureus or purplish red precipitation through a biological microscope lens so as to count the number of the coliform groups, or the mixed eosin methylene blue culture solution changes colors because of the atropurpureus or purplish red precipitation generated by the mixed eosin methylene blue culture solution, and the cell number of the coliform groups is recognized by utilizing the characteristics that the color change degree of the mixed eosin methylene blue culture solution is related to the cell number of the coliform groups. The method is suitable to rapid detection of the coliform groups in the fields of biology, medicines, foods and various articles.
Owner:殷涌光
Lactobacillus salivarius capable of inhibiting Candida albicans growth, and separation method thereof
ActiveCN103555604AShort fermentation cycleGood antibacterial effectAntimycoticsBacteriaBiotechnologySporeling
The present invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus salivarius capable of inhibiting Candida albicans growth, and a separation method thereof, wherein the Latin name is Lactobacillus salivarius LI01, the Lactobacillus salivarius LI01 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7045. The present invention discloses morphological characteristics of the Lactobacillus salivarius LI01, wherein the morphological characteristics comprise rod-shaped bacteria, no spore production, no motility, and positive Gram staining. The present invention discloses main components of the whole-cell fatty acid of the Lactobacillus salivarius LI01, wherein the main components comprise: about 38.48% of 16:0, about 8.29% of 18:1w9c, about 14.68% of 19:0cyclow10c / 19w6, about 5.94% of 18:0, about 12.75% of 19:0cyclow10c / 19w6, about 11.55% of 19:0cyclow8c, about 12.75% of 19:1w6c, and about 14.68% of 18:1w7c. The invention further discloses the whole sequence of 16S ribosomal DNA (16SrDNA) of the Lactobacillus salivarius LI01. The separation screening method of the present invention comprises three steps: carrying out enrichment culture with a MRS nutrient culture medium, adopting a Candida albicans covering layer to carry out primary screening, and adopting liquid co-culture to carry out re-screening. According to the present invention, the method is rapid and efficient, and the obtained Lactobacillus salivarius LI01 has strong Candida albicans resistance ability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
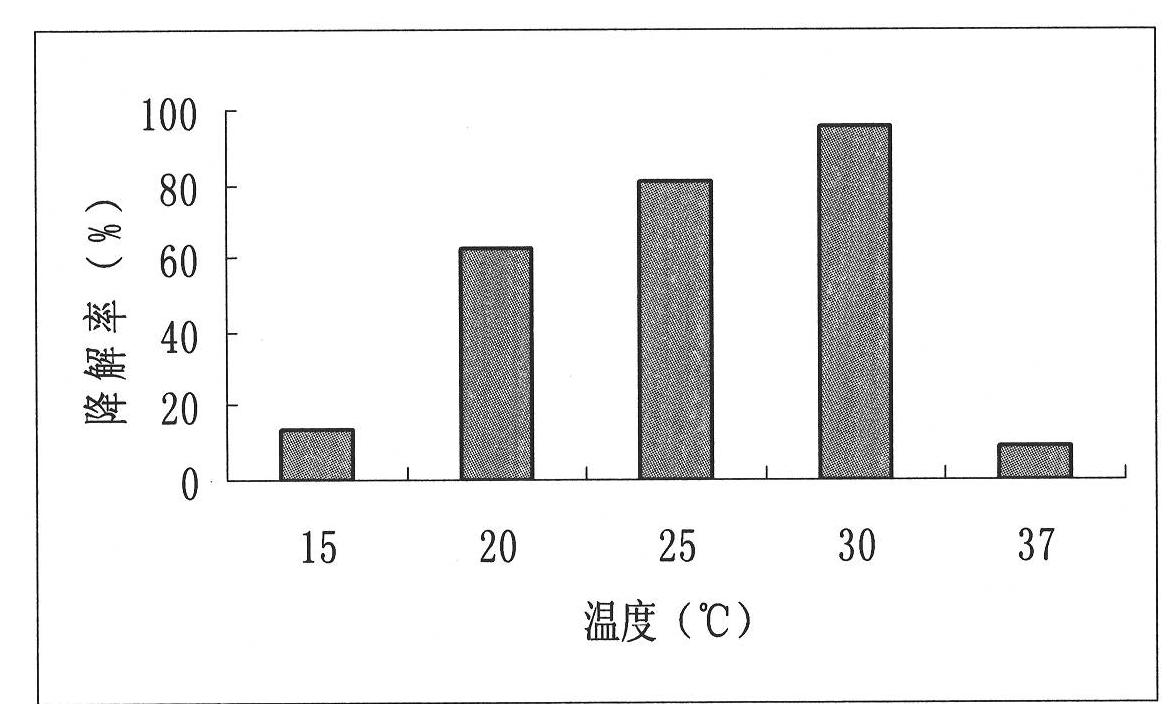
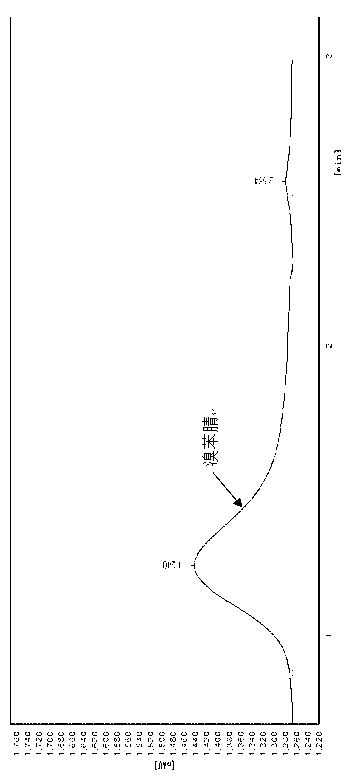
Ethinyl estradiol high-efficiency degrading strain and preparation method thereof
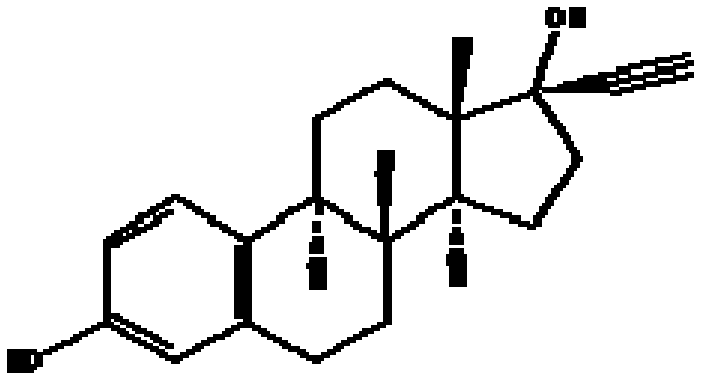
InactiveCN102352336AProvenance is easy to getThe separation and purification method is simple and fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPurification methodsEcological safety
The invention relates to an ethinyl estradiol high-efficiency degrading strain and a preparation method thereof. The thallus length of the strain is 0.4-0.8um; and the bacterial colony has a diameter of 1-2.5mm, is round in shape, has regular edges and a low convex surface, is golden yellow in color with no luster and no transparency, and appears as negative through Gram staining. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out directional domestication and culture on active sludge, enriching, separating, and purifying to obtain the ethinyl estradiol high-efficiency degrading strain. The ethinyl estradiol high-efficiency degrading strain can effectively degrade ethinyl estradiol, has an ethinyl estradiol degradation rate up to 80% or above, has no resistance to common antibiotics, and can be inactivated easily, thereby ensuring the ecological safety in use. Besides, the ethinyl estradiol high-efficiency degrading strain has the advantages of easy acquisition of sources and convenient separation and purification method.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com