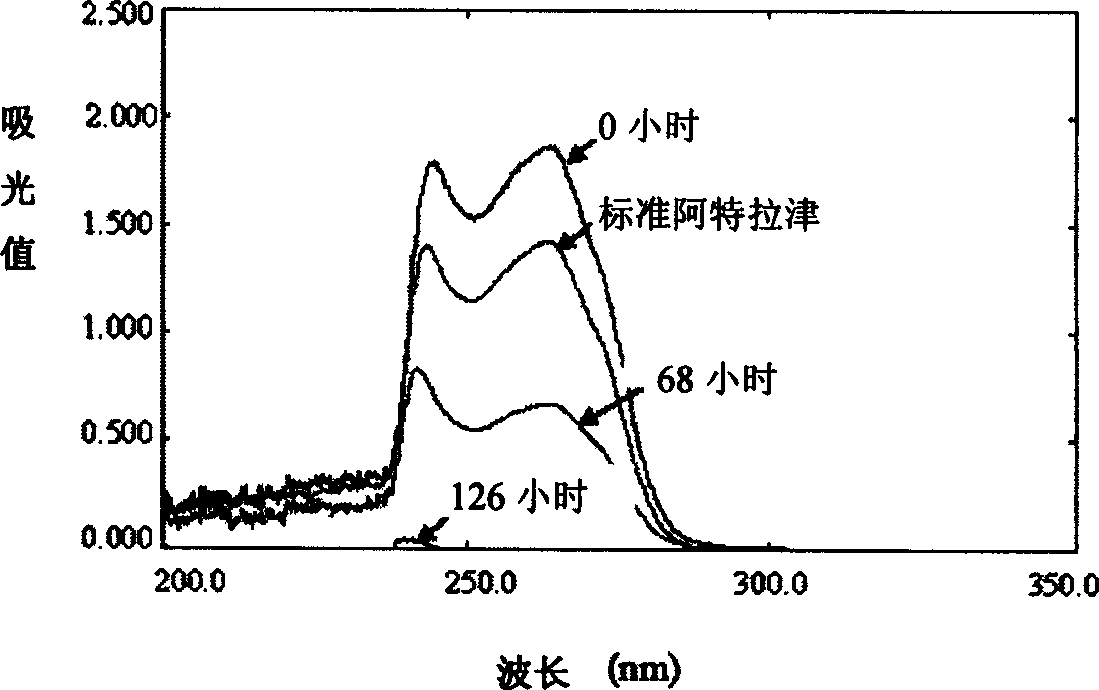
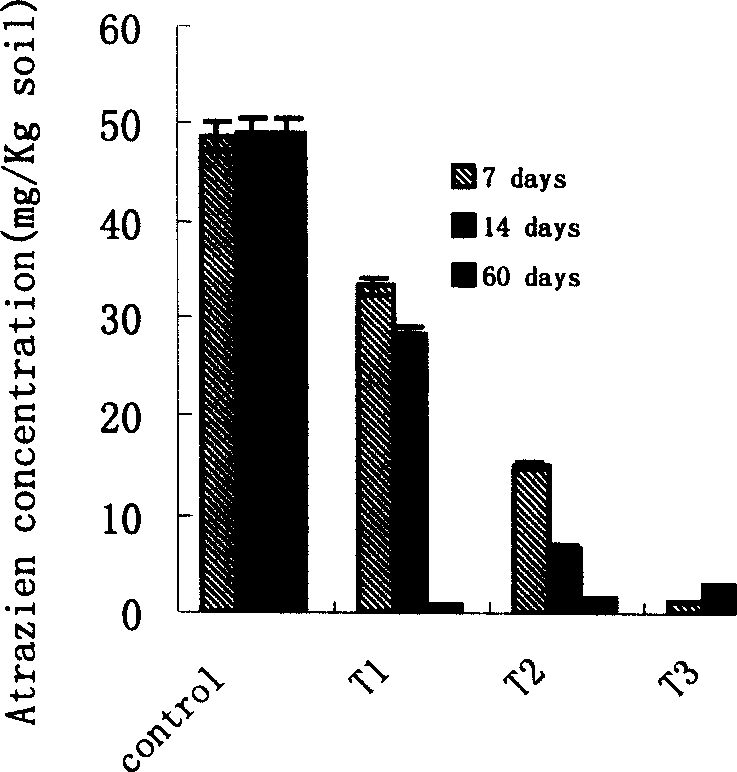
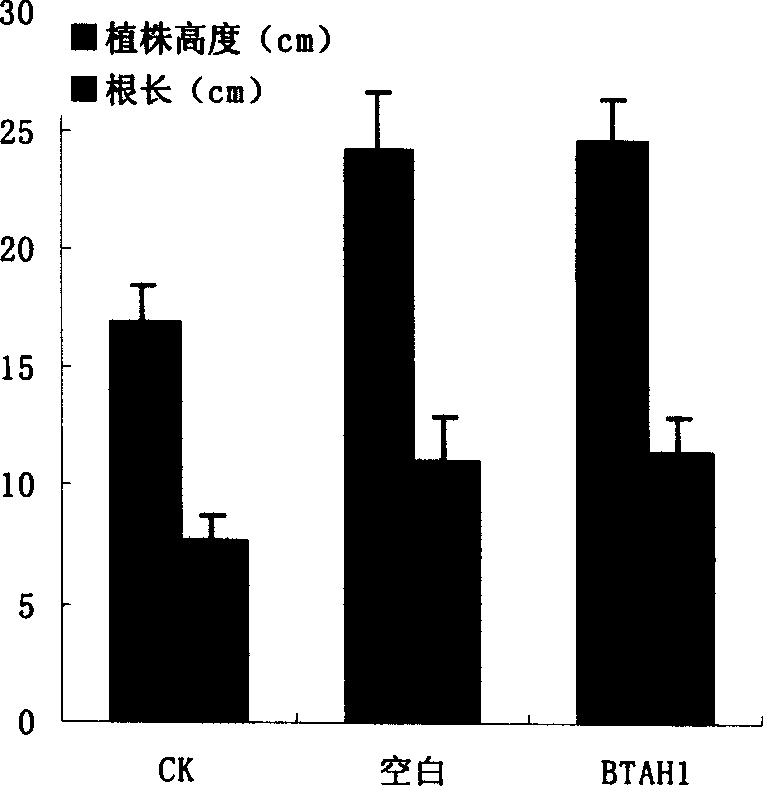
Triazine herbicide residual degrading strain and strain therefrom
A technology for the degradation of pesticide residues and inoculants, which is applied in the field of high biology, can solve the problems of narrow degradation spectrum of strains and limited use, and achieve the effects of low production and use cost, increased added value, and good removal effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Examples of the present invention are described below.
[0019] Activate the original seed of the microbial organophosphorus pesticide residue-degrading bacteria BTAH1 of the present invention on a petri dish, measure its degradation performance, and inoculate it on the inclined surface of a test tube for later use. The test tube seeds were inoculated into 1000ml shake flasks containing 200ml broth medium, cultured with constant temperature shaking until logarithmic phase, and prepared to inoculate seed tanks. 500 liters of seed tanks, 400 liters of feeding capacity, the medium formula is: glucose 0.8%, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1%, K 2 HPO 4 0.2%, MgSO 4 0.05%, NaCl 0.01%, CaCO 3 0.3%, yeast extract 0.02%, pH 7.2-7.5. After the feeding is completed, sterilize under high pressure at 121°C, cool to 33°C, inoculate the above cultured shake flask strains into a 500-liter seed tank at an inoculum size of 10%, and cultivate until the logarithmic growth phase, with a stirring ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com