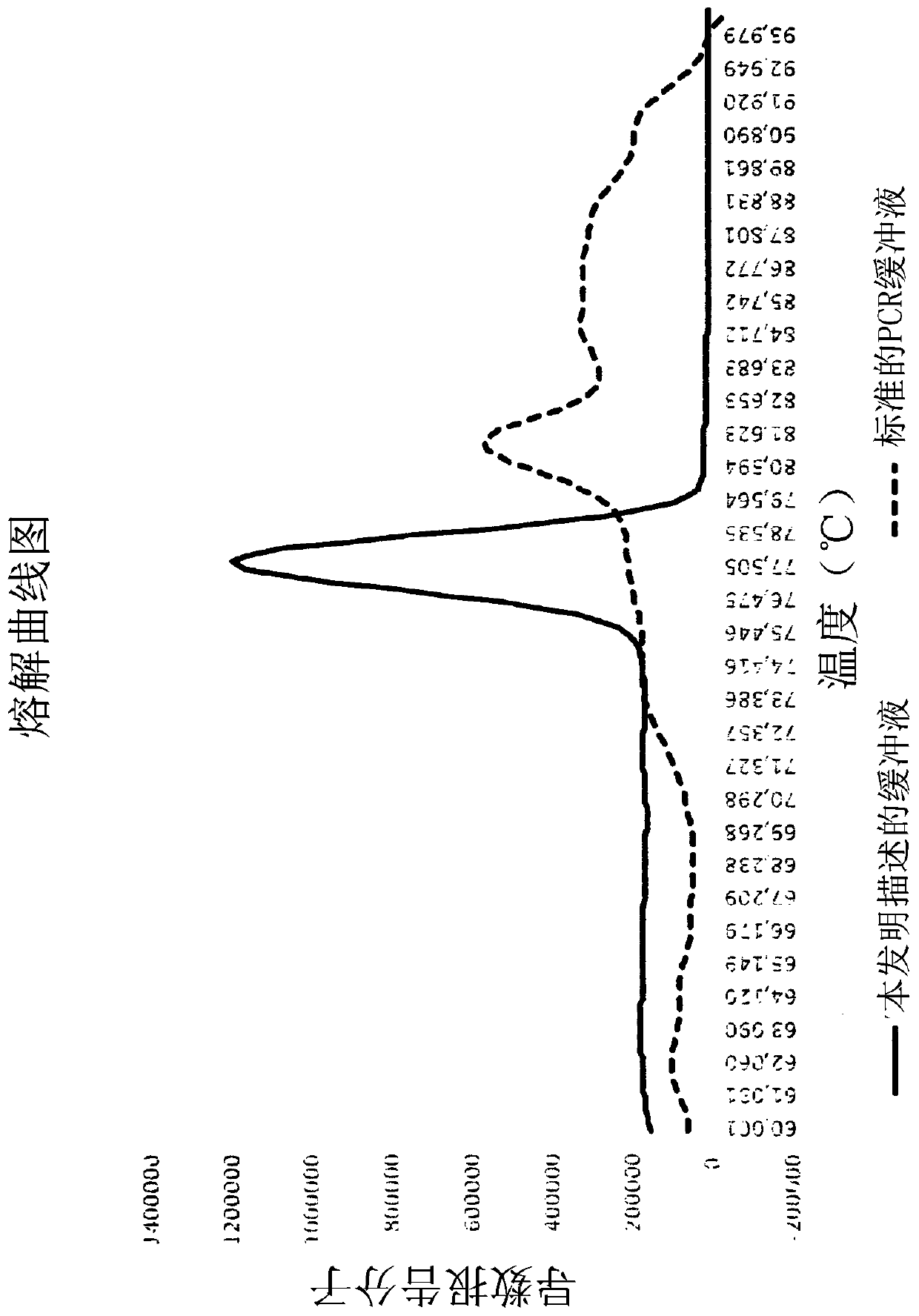
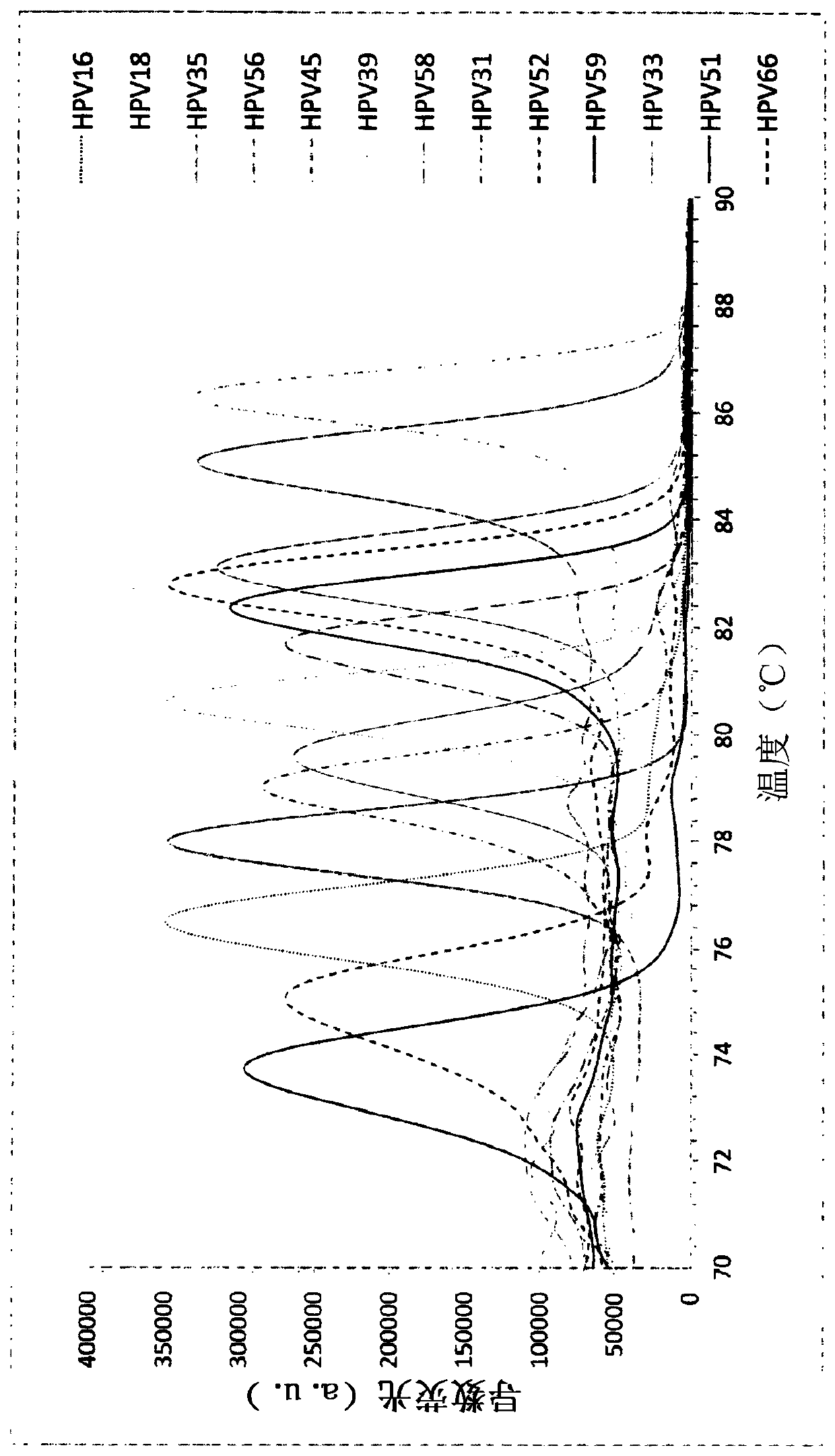
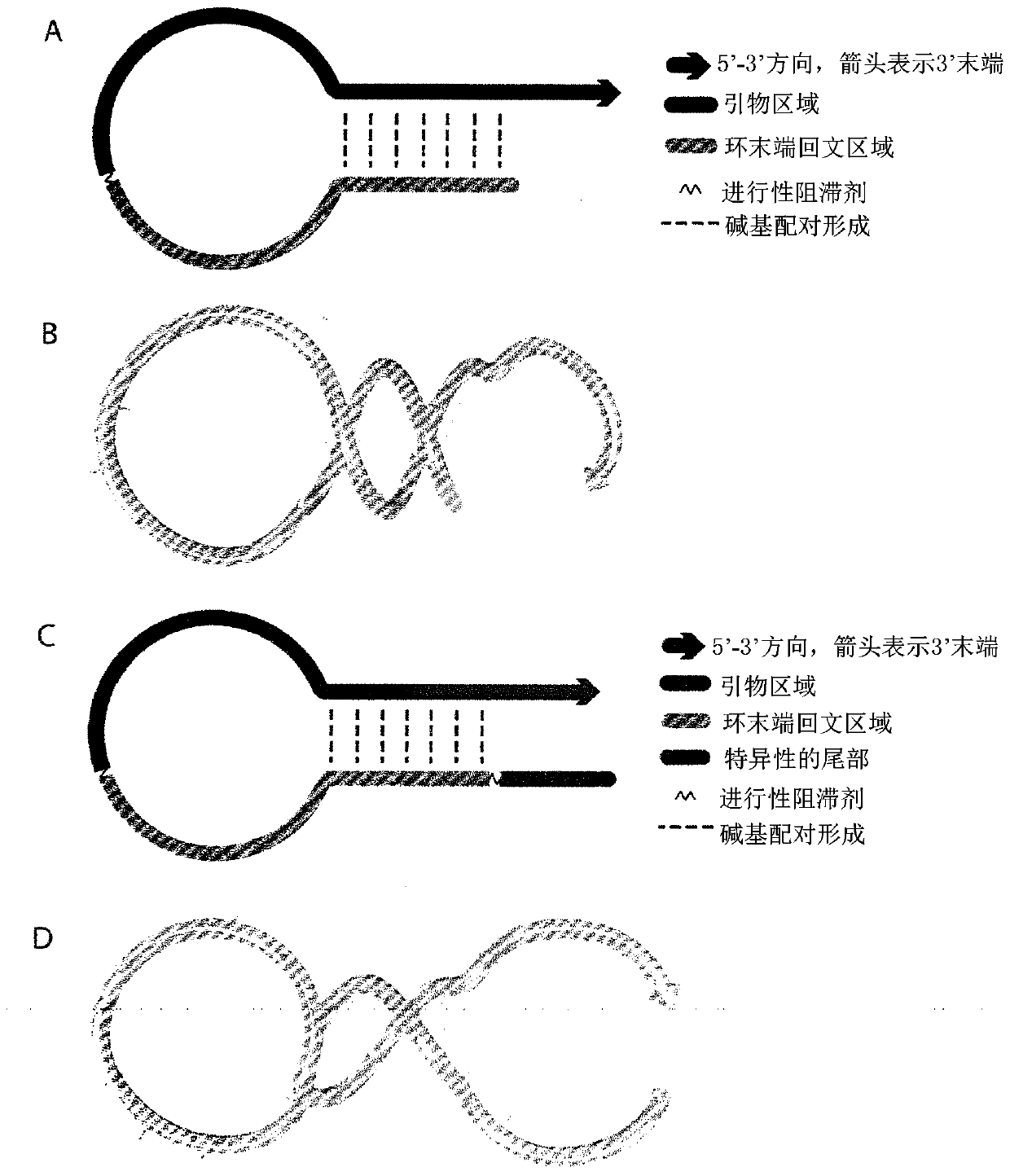
Molecular fingerprinting methods to detect and genotype dna targets through polymerase chain reaction
A chain reaction and genotyping technology, applied in the field of multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, can solve the problems of increasing the test cost and affecting the stability of the test, and achieves the effect of being cheap in implementation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0143] In one embodiment, possible first amplification buffers for diagnostic purposes comprise dNTPs, sources of monovalent or divalent cations, buffer solutions, BSA, hot-start DNA polymerases, intercalating molecules or compounds. For example, one embodiment of the first amplification buffer comprises:
[0144] a) dNTPs (final concentration range: 0.05 mM to 0.3 mM)
[0145] b) MgCl 2 (Final concentration range: 0.3 mM to 4 mM)
[0146] c) TrisHCl buffer solution (final concentration range: 10 mM to 50 mM; pH: 6.00 to 10.00)
[0147] d) KCl (final concentration range: 10 mM to 50 mM)
[0148] e) BSA (final concentration range: 0.005 to 0.05 mg / ml)
[0149] f) Hot start polymerase
[0150] g) SYTO-9 (final concentration range: 1 μM to 8 μM).
[0151] In another possible embodiment, a possible alternative second amplification buffer for diagnostic purposes is provided, comprising dNTPs, a source of monovalent or divalent cations, a buffer solution, BSA, a hot-start DNA ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com