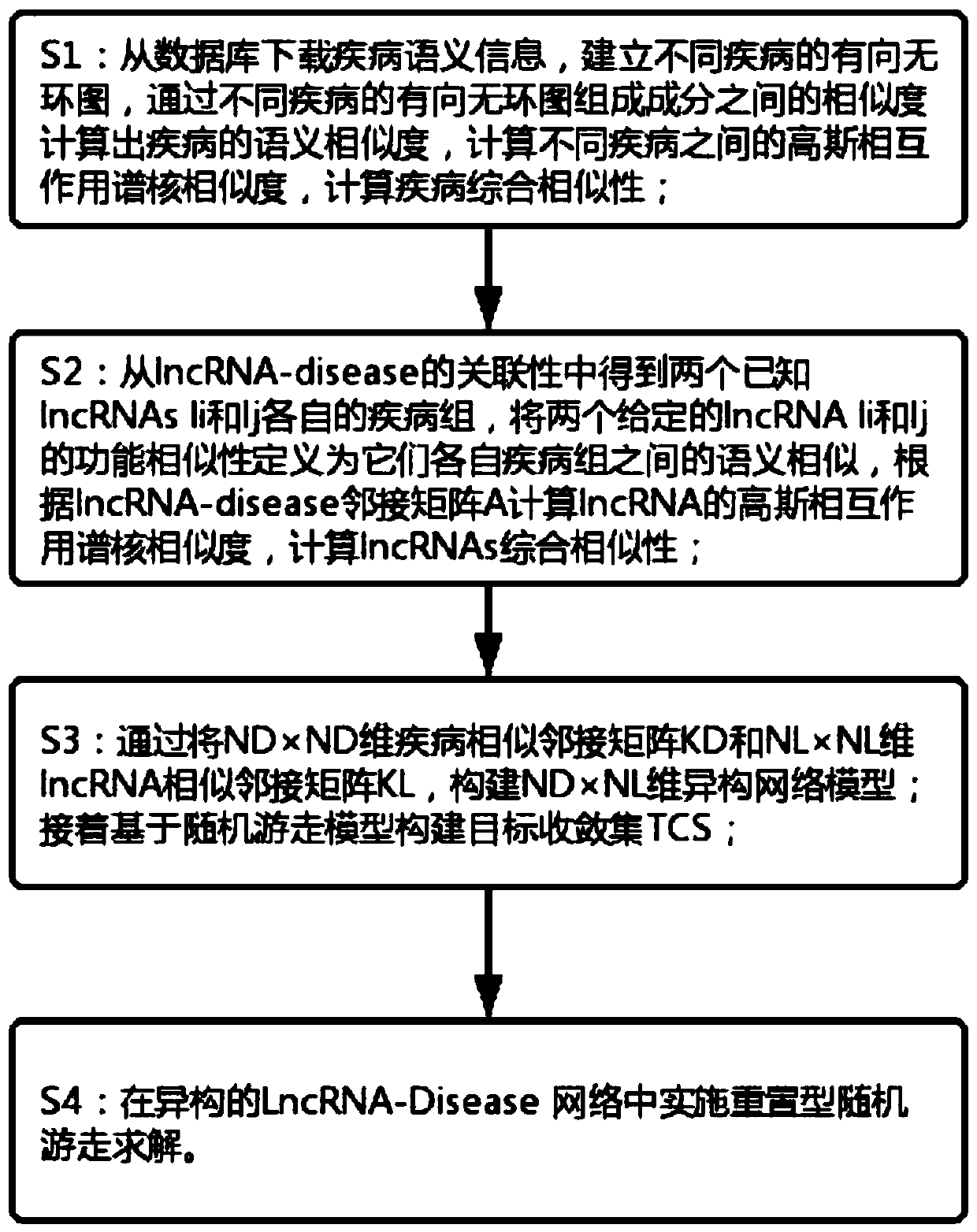
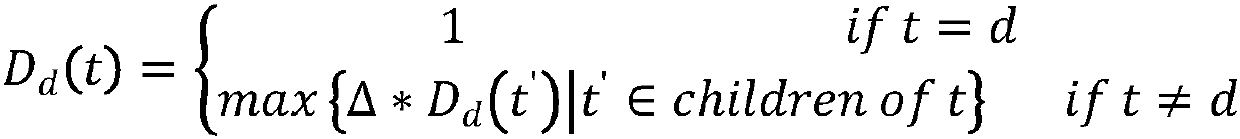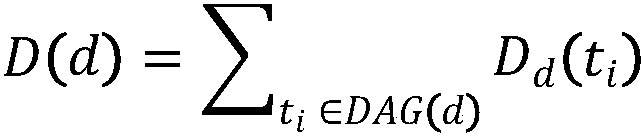Method for predicting potential lncRNA disease based on random walk target convergence set technology
A random walk and technology prediction technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as undiscovered correlation, time complexity, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] For many years, it was thought that an organism's genetic information was stored only in the genes used to code for proteins, and RNA had been considered an intermediary in the process by which DNA codes for proteins. However, recent studies have shown that protein-coding genes account for only a small portion of the human genome (less than 2%), and more than 98% of the human genome is not composed of gene-coded proteins and long non-coding RNAs. Furthermore, as the complexity of biological organisms increases, so does the importance of non-coding RNAs in biological processes. Generally speaking, according to the length of nucleotides in the transcription process, non-coding RNAs can be divided into two categories: short-chain non-coding RNAs and long-chain non-coding RNAs, in which short-chain non-coding RNAs consist of less than 200 nucleotides, Including microRNAs and transfer RNA, etc. However, long noncoding RNAs contain more than 200 nucleotides. In 1990, resear...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com