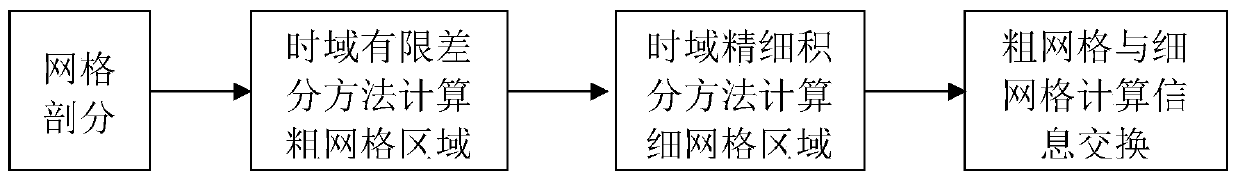
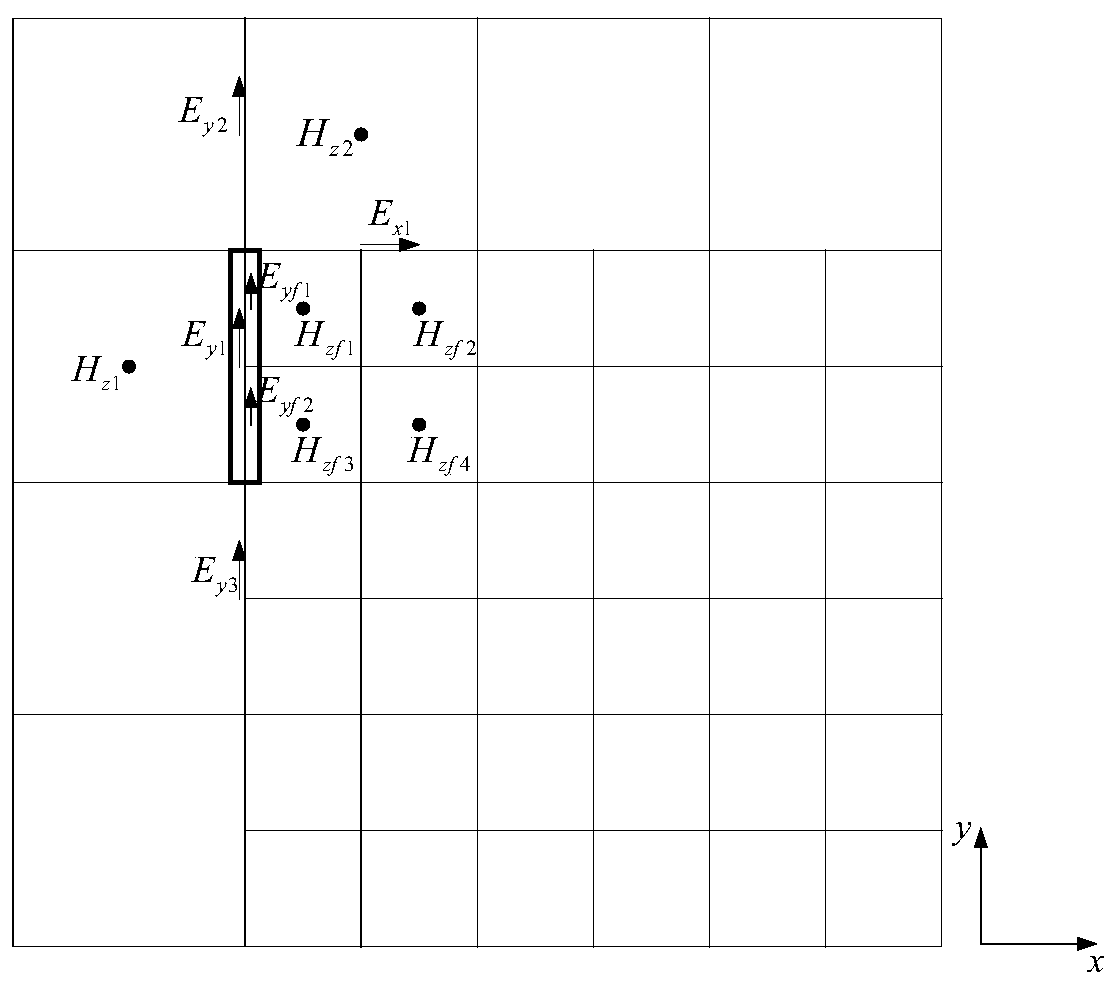
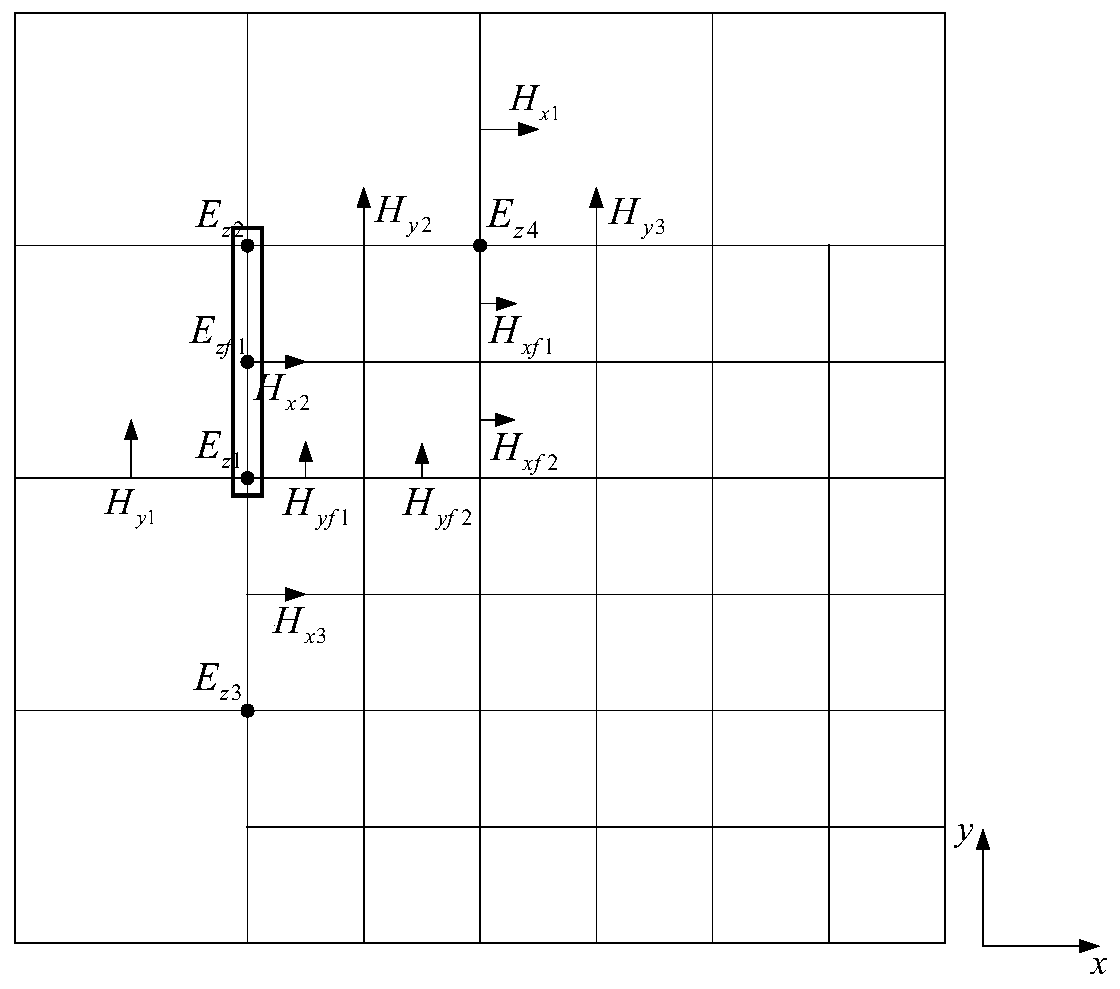
Electromagnetic wave time domain efficient numerical hybrid algorithm based on sub-grid technology
An electromagnetic wave and numerical technology, applied in the field of computational electromagnetics, can solve problems such as long CPU execution time and small time steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0172] Embodiment 1: In a 40×40 free space calculation area, the space step is Δx=Δy=0.001m. The 4 × 4 grids at the center of the calculation area are subdivided into fine grids according to the ratio of 1:2, and the absorption boundary conditions of perfectly matching layers are set around the calculation area, with a thickness of 10 layers.
[0173] Figure 6 Shown in the two-dimensional TE mode, the electric field intensity E y Graph over time.
[0174] Figure 7 It is shown that in the two-dimensional TM mode, the electric field intensity E y Graph over time.
Embodiment 2
[0175] Embodiment 2: Taking the TE mode as an example, in a 201×201 free space calculation area, the space step is Δx=Δy=0.001m. A grid at the center of the calculation area is subdivided into fine grids at a ratio of 1:10, and a perfectly matching layer absorbing boundary condition is set around the calculation area, with a thickness of 10 layers.
[0176] Figure 8 It is shown that the electric field intensity E y Graph over time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com