Metallic wall section cooling method
A cooling method and metal wall technology, which can be used in cooling devices, pipeline heating/cooling, nuclear power generation, etc., can solve problems such as reduced operating efficiency, and achieve the effects of prolonging creep life and preventing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
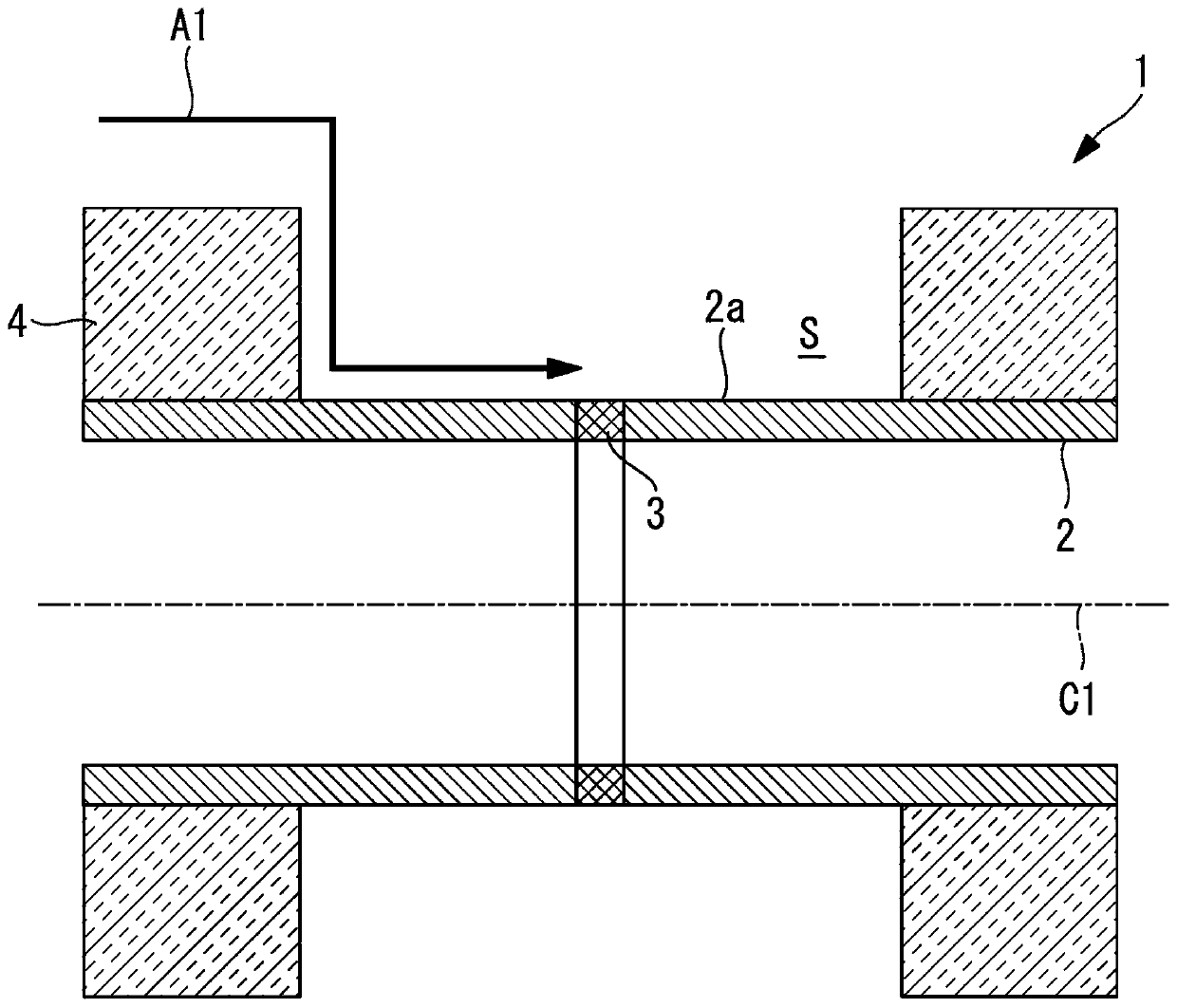
[0043] exist figure 1 The pipe cooling structure 1 which locally cools the pipe (metal wall part) used as a cooling object is shown in FIG. The heat insulating material 4 is arranged on the outer periphery of the pipe 2 . In the pipe 2 , a welded portion 3 is formed in the circumferential direction (pipe circumferential direction), and a space S is formed by removing a part of the heat insulating material 4 in a region including the welded portion 3 . Through the space S, the outer surface 2a of the pipe 2 is exposed to the outside (atmosphere). In addition, when the welded part is formed in the pipe axial direction, the thermal insulation material 4 is partially removed so that the region along the welded part formed in the pipe axial direction is exposed.
[0044] The piping 2 is a circular pipe having a central axis C1, and low alloy steel (1.25Cr-Mo steel or 2.25Cr-Mo steel, etc.), high Cr steel (9Cr steel), austenitic steel (SUS316 ), Ni-based alloy steel (HR6W) and ot...
no. 2 approach
[0095] Next, a second embodiment will be described.
[0096] This embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that the temperature distribution in the pipe axis direction of the pipe 2 is considered, but the other points are the same. Therefore, differences from the first embodiment will be described below.
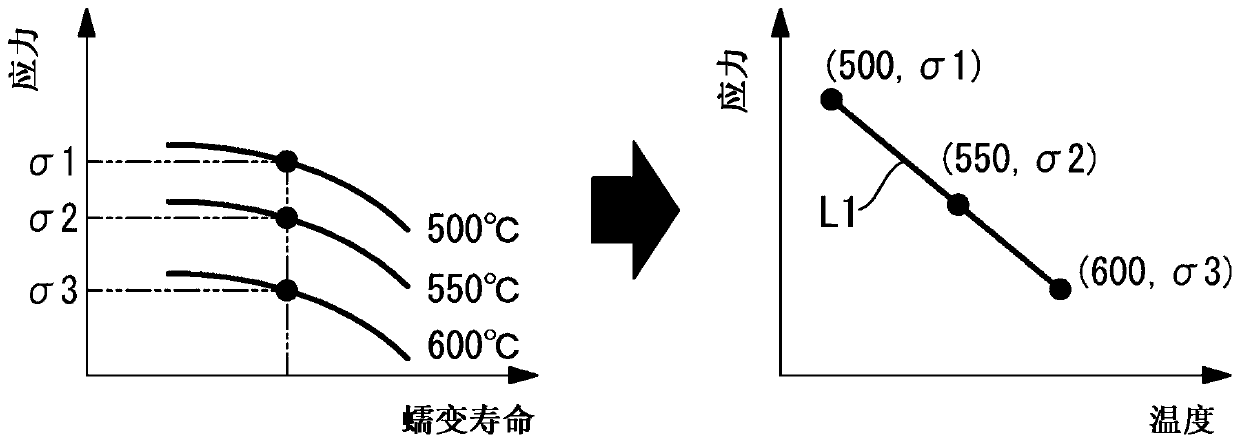
[0097] Ruo Ru figure 1 Removing only a part of the thermal insulation material 4 in the pipe axis direction of the pipe 2 as shown will generate a temperature distribution in the pipe axis direction. If temperature distribution occurs in the tube axis direction, thermal stress will further occur due to the temperature distribution.
[0098] Expressing this in a coordinate diagram becomes Figure 8 like that. As shown in the figure, according to the overlapping of the thermal stress due to the temperature distribution in the tube axis direction, the stress becomes higher as in the curve L6 compared to the curve L4 which does not consider the thermal stress. T...
no. 3 approach
[0102] Next, a third embodiment will be described.
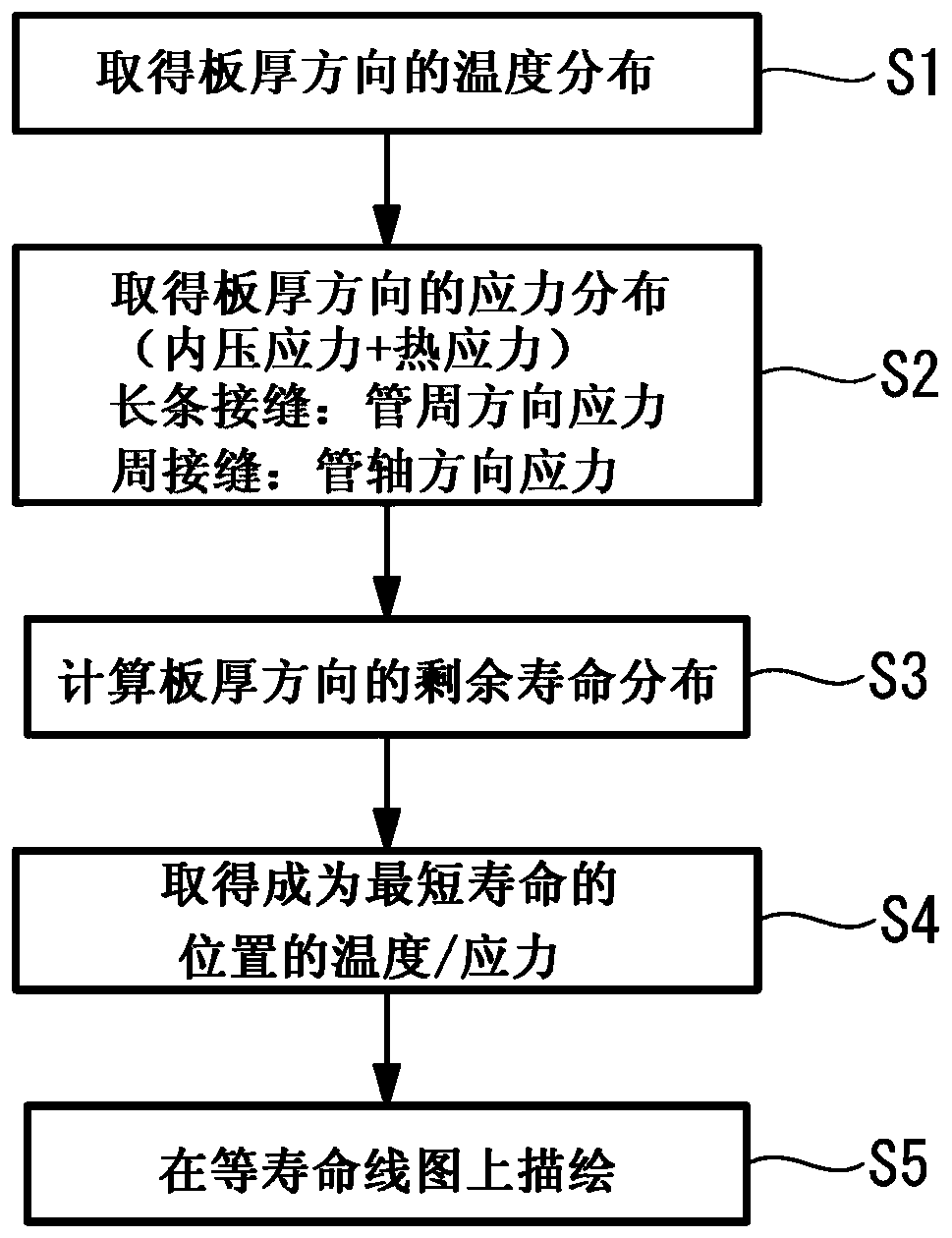
[0103] In the second embodiment, the target post-cooling temperature is corrected based on the temperature distribution in the tube axis direction and the tube circumference direction, but it is necessary to grasp the temperature distribution in the tube axis direction and the tube circumference direction generated in the pipe 2 . On the other hand, this embodiment provides a simpler cooling method by limiting the temperature distribution in the tube axial direction and the tube peripheral direction to a predetermined range.
[0104] Such as Figure 9 As shown, in step S11, the temperature decrease amount is set. The amount of temperature reduction means that from Figure 8 The temperature difference from plot point P1 to the target post-cooling temperature is shown. Therefore, it is the amount of temperature drop exceeding the temperature range ΔT1' from the plot point P1, and the target after-cooling temperature determi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com