Message passing method and device in distributed graph calculation process
A technology of message passing and graph computing, which is applied in the directions of multi-program device, computing, and inter-program communication, and can solve the problems of large storage cost and huge communication cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
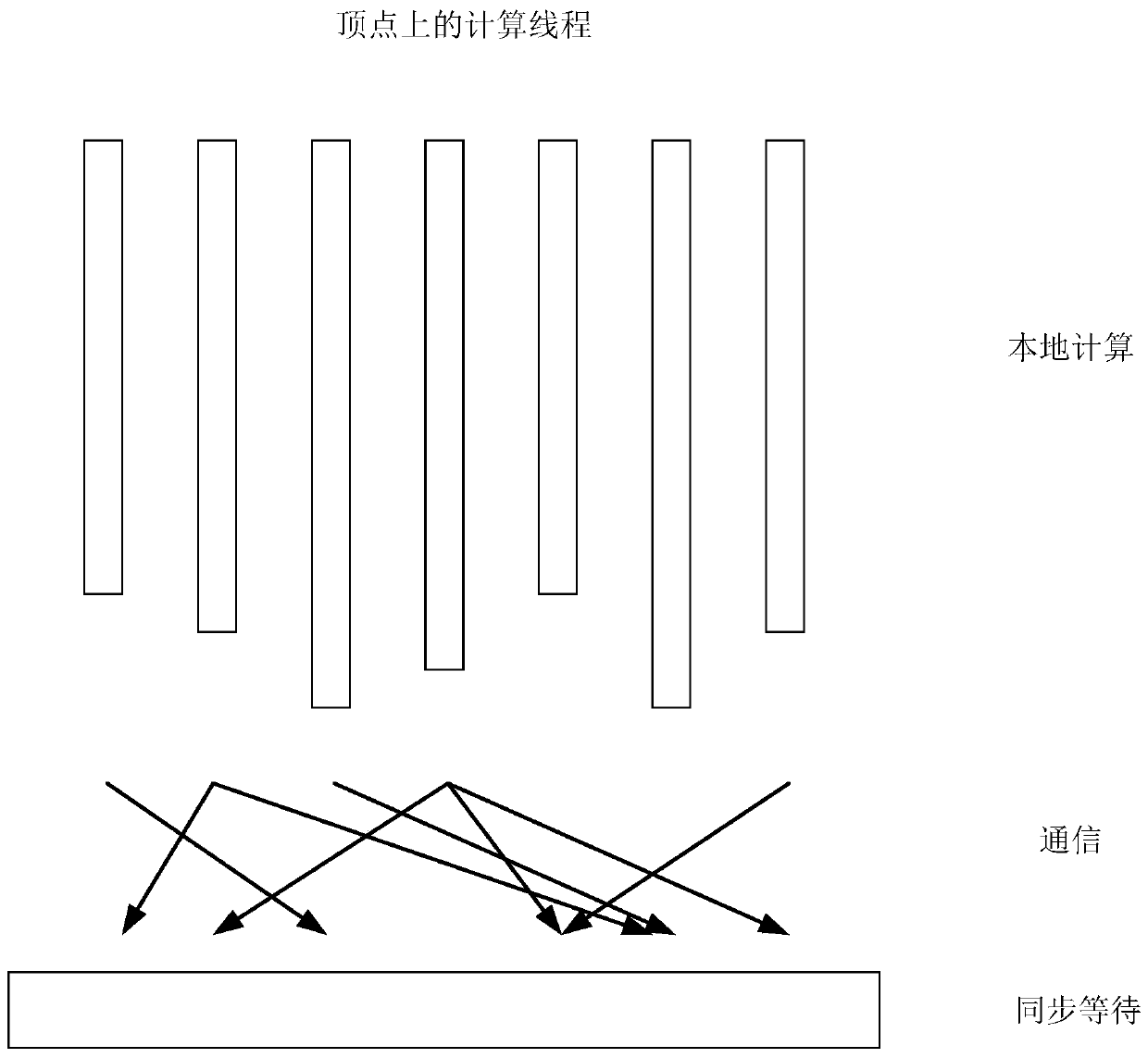
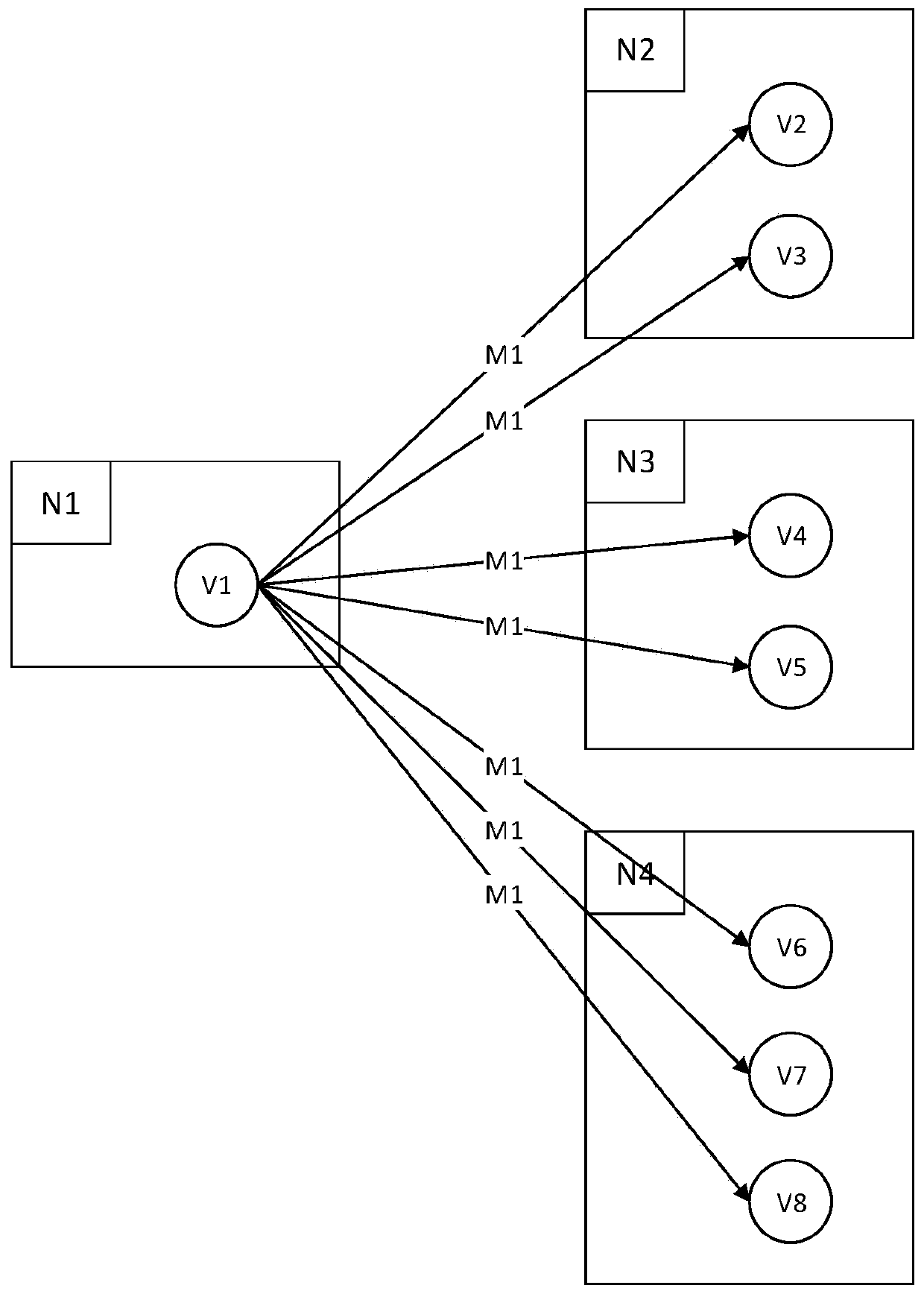
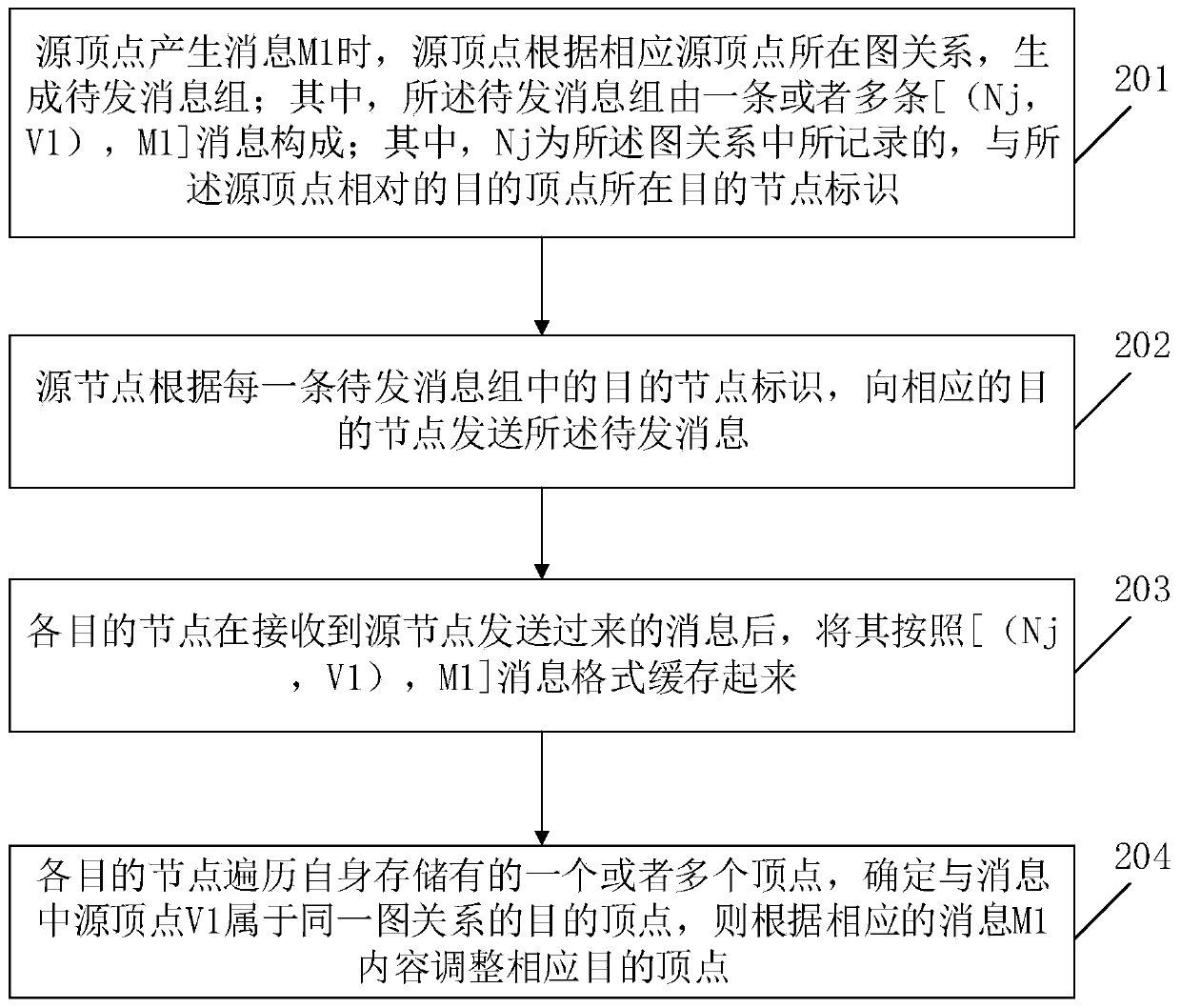
[0061] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a message delivery method in the process of distributed graph calculation. The vertices of the graph are distributed and stored on different computer nodes. It is characterized in that the identifier Nj of the sending destination node and the identifier number of the source vertex Vi, combined as the primary key (Nj, Vi) of the message record; wherein, the message record generated by the corresponding source vertex is: [(Nj, Vi), Mi]; where j is the number identification number of the corresponding destination node, i is The numbered identification number of the corresponding source vertex, such as image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, delivery methods include:
[0062] In step 201, when the source vertex generates a message M1, the source vertex generates a message group to be sent according to the graph relationship where the source vertex is located; wherein, the message group to be sent consists of one or more [(Nj, V1), M1...
Embodiment 2
[0086] An embodiment of the present invention provides a graph data access method based on a group association table, which is used to support the message passing method in the distributed graph computing process described in Embodiment 1, such as Image 6 , including the following steps:
[0087] Step 301, using the attribute table to store the attribute data of the graph, and using the group association table to store the topology data of the graph; wherein, the topology data includes adjacent vertices and associated edge information of each vertex in the graph.
[0088] Graph data can be divided into attribute data and topological data. The attribute data and the topological data are stored separately using different data storage structures. Among them, the attribute data of points and edges in the graph are stored in the attribute table, which can be stored through the Key - Value can be stored in the form of a link or linked list. The topology data of the graph is stored...
Embodiment 3
[0118] like Figure 11 As shown in FIG. 2 , it is a schematic structural diagram of a message passing device in a distributed graph computing process according to an embodiment of the present invention. The message passing device in the distributed graph calculation process of this embodiment includes one or more processors 21 and memory 22 . in, Figure 11 A processor 21 is taken as an example.
[0119] Processor 21 and memory 22 can be connected by bus or other means, Figure 11 Take connection via bus as an example.
[0120] The memory 22, as a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, can be used to store non-volatile software programs and non-volatile computer-executable programs, such as the message passing method in the distributed graph computing process in Embodiment 1 . The processor 21 executes the message passing method in the distributed graph computing process by running the non-volatile software programs and instructions stored in the memory 22 .
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com