An Optimal Method for the Two-Stage Site Selection-Route Problem in Urban Logistics
An optimization method and route technology, applied in logistics, data processing applications, forecasting, etc., can solve problems such as restricting the promotion and application of two-layer logistics network systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
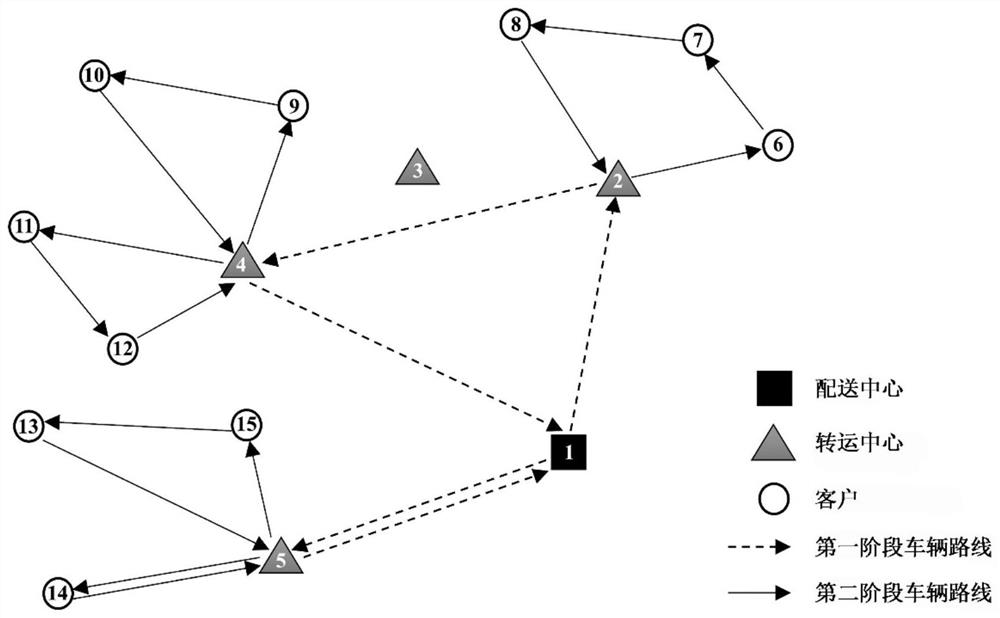
[0079] Embodiment 1, the optimization method of the small-scale two-stage site selection-route problem (5 alternative transshipment centers / 25 clients);
[0080] (1) Site selection for the transshipment center. The initial concentration of pheromone assigned to each candidate transshipment center was 1, and the first group of ant colony consisting of 4 ants was arranged to be responsible for site selection. The number of transshipment centers selected by each ant is given by the following formula:
[0081]
[0082] Wherein, U(0, u) represents any integer between 0 and u (take u=3). The probability of each alternative transshipment center being selected is determined by the following formula:
[0083]
[0084] Among them, α represents the importance coefficient of relevant heuristic information relative to the concentration of pheromone in the transit center (take α=1).
[0085] The selection of n transshipment centers is carried out according to the rule of pseudo-pro...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Embodiment 2. An optimization method for a large-scale two-stage site selection-route problem (10 alternative transshipment centers / 200 customers).
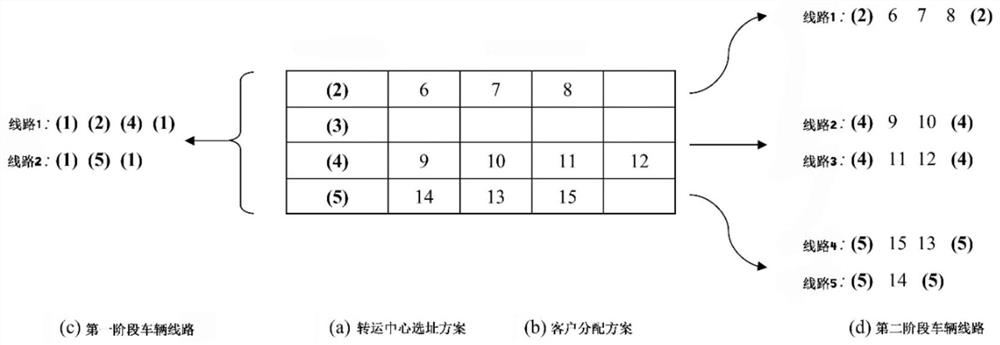
[0108] (1) Transshipment center site selection - customer allocation. Simplify the two-stage location-routing problem into a classic facility location problem, and use the IBM ILOG CPLEX optimization software package to solve it directly to obtain the location selection plan of the transshipment center and the customer allocation plan.
[0109] (2) Vehicle route arrangement in the first stage. The vehicle route of the first stage is constructed using the saving method. The vehicle starts from the distribution center or the transshipment center, and selects the next visiting node according to the principle of maximum saving, that is, using The transshipment center j with the largest value; where, is the cost savings from transit center i to transit center j, c io is the route cost between transshipment center i and dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com