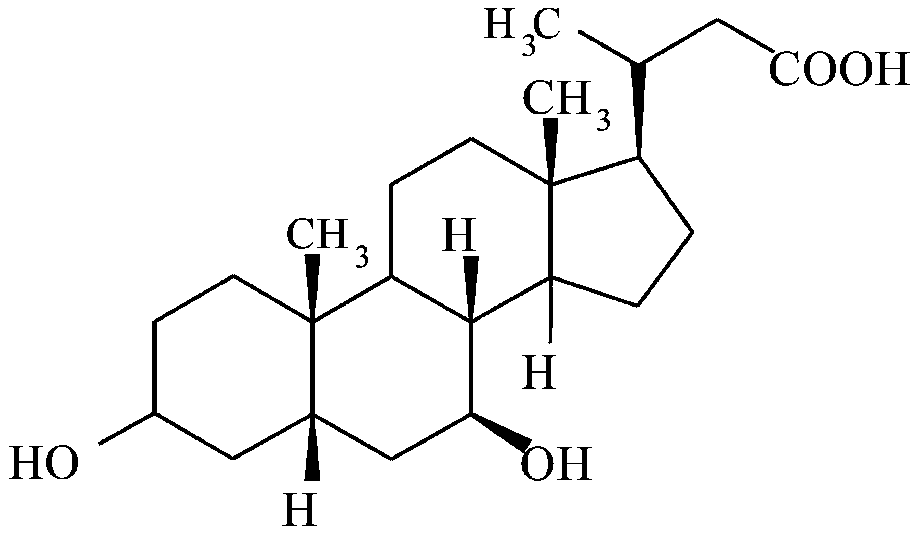
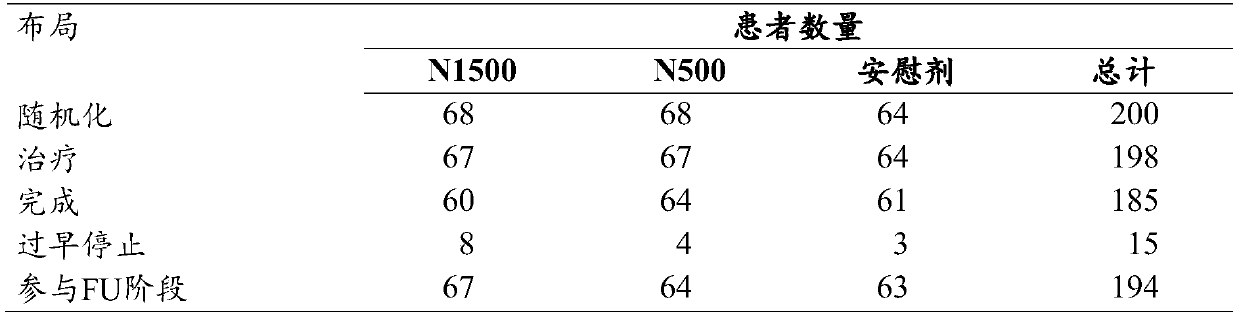
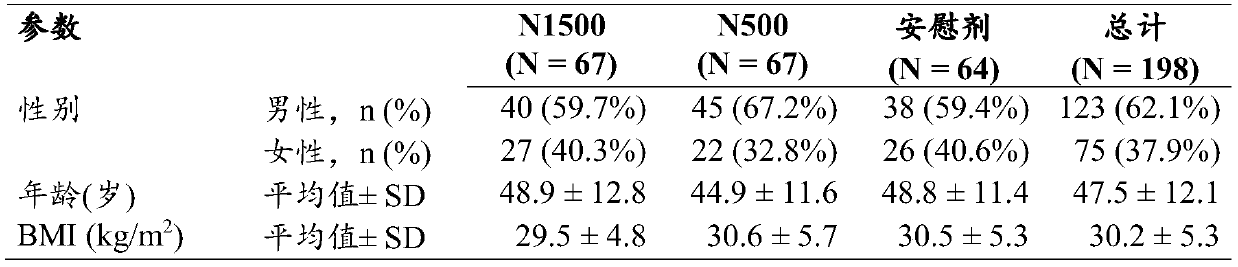
Use of nor-ursodeoxycholic acid for reducing liver fat
A technology for hepatic steatosis and use, applied in the field of use of demethylursodeoxycholic acid for reducing liver fat, can solve the problem of no safe and effective drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0184] Example 1: Ultrasound Examination of the Liver
[0185] method:
[0186] Ultrasonography is performed at V1 or within 4 weeks before V1 and within 1 week after V1 and at V6, specifically checking for the following:
[0187] Liver: size, echogenicity, overall findings (normal, abnormal - not clinically significant, abnormal - clinically significant.
[0188] Hepatic steatosis was assessed on a four-point scale according to the following grades:
[0189] ○ No / Minimal Steatosis: Normal echogenic properties of the liver were documented in the absence of steatosis, or: Minimal steatosis indicated by: slightly increased echogenicity of the liver relative to the right The echo is clearly visible.
[0190] o Mild steatosis: defined by moderately elevated echogenicity of the liver compared to the right kidney, slightly reduced visibility of intrahepatic vessel walls, and reduced reflectivity of the hemidiaphragm.
[0191] o Moderate steatosis: defined by moderately elevate...
Embodiment 2
[0199] Example 2: Liver stiffness measured according to Fibroscan or ARFI during the study
[0200] method:
[0201] A) If possible, perform Fibroscan at V1 or within 4 weeks before V1 and within 1 week after V1 and at V6. For measurement purposes, patients should fast.
[0202] Liver stiffness measurement / transient elastography
[0203] Fibroscan is a non-invasive device (Echosens, France) for the detection of steatosis hepatitis by vibration-controlled transient elastography. It consists of a vibrator device coupled to an ultrasound system. Signals from the device allow the stiffness of the tissue being scanned to be calculated, thereby assessing the extent of the disease. The results of liver elasticity should be expressed in hardness (kPa) and success rate (%).
[0204] During the measurement, an ultrafast pulse-echo sequence (pulse repetition frequency 6 kHz) is emitted during the propagation of a controlled shear wave. Acquisition lasts only 80 milliseconds, an...
Embodiment 3
[0226] Example 3: Liver Fat Fraction Measured by MRI and / or MRS
[0227] method:
[0228] Magnetic resonance imaging / spectroscopy (MRI / MRS) at V1 or within 4 weeks before V1 and 1 week after V1 and at V6, if available. Both MRI and MRS are MR-based methods to separate the liver signal into water and fat components. The resonance frequencies corresponding to the protons in water and the dominant protons in fat are different and can be quantified directly from the spectrogram trace.
[0229] The following formula was used to calculate liver fat fraction derived from chemical shift imaging (CSI) data:
[0230] CSI Liver Fat Score 未校正的 =SI 同相的 –SI 反相的 / 2x SI 同相的
[0231] To illustrate that differences in signal intensity are independent of fat content, in the spleen, a region of interest was also placed in the same image from which liver measurements were taken. To calculate the liver fat fraction corrected for signal intensity (measured using the spleen), the above form...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com