Patents
Literature
38 results about "Echogenicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
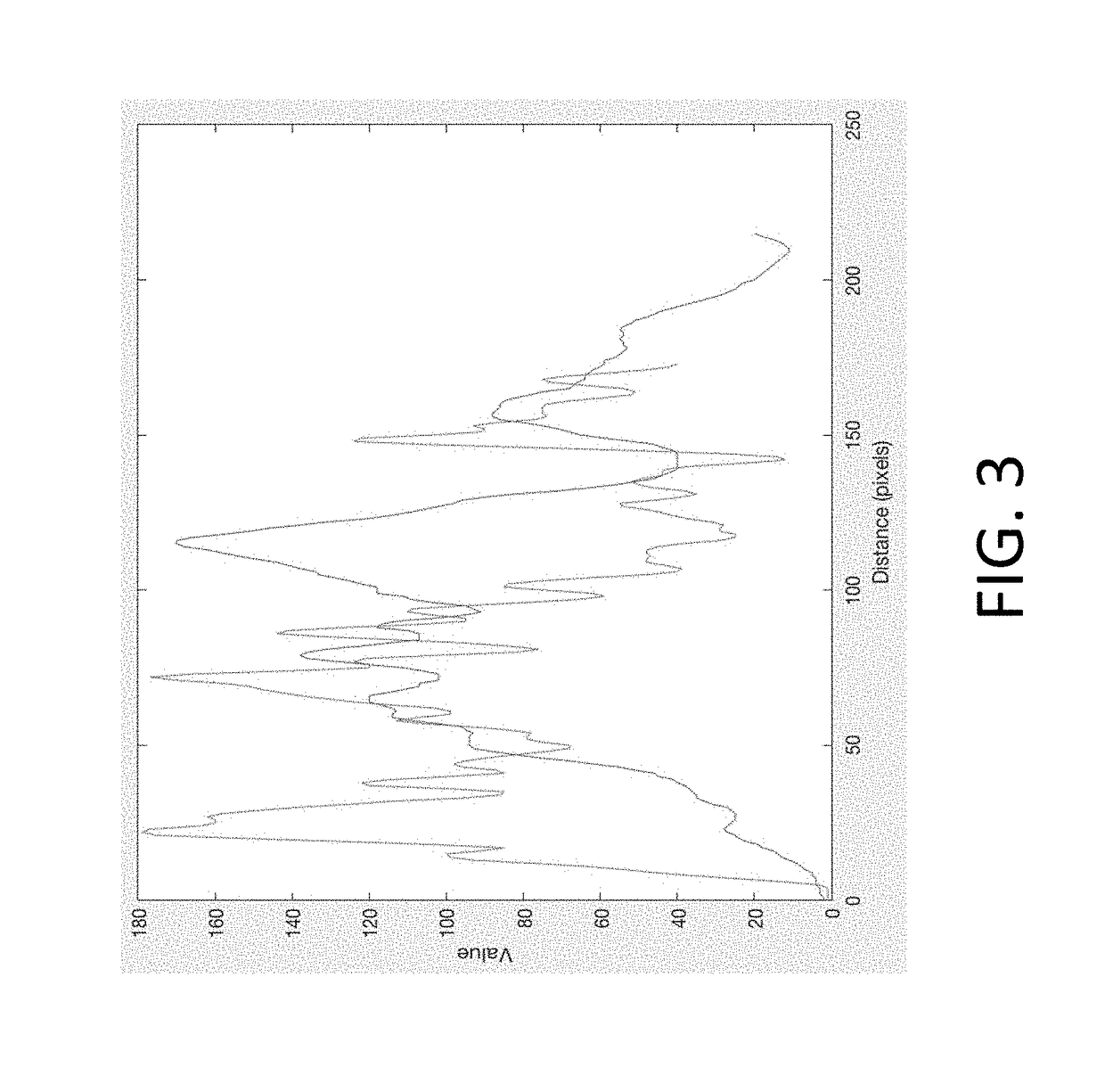
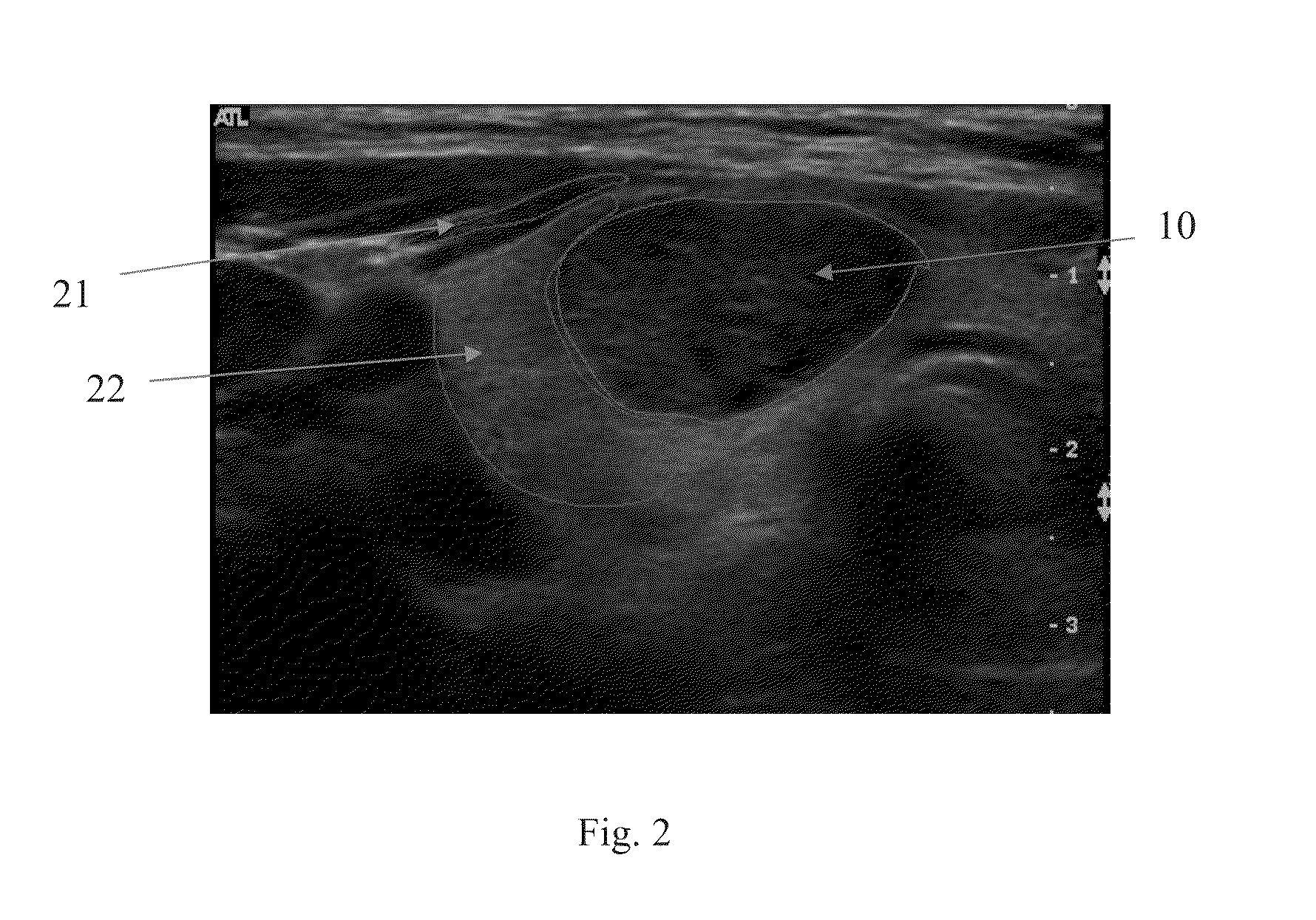
Echogenicity (misspelled sometimes as echogenecity) or echogeneity is the ability to bounce an echo, e.g. return the signal in ultrasound examinations. In other words, echogenicity is higher when the surface bouncing the sound echo reflects increased sound waves. Tissues that have higher echogenicity are called "hyperechogenic" and are usually represented with lighter colors on images in medical ultrasonography. In contrast, tissues with lower echogenicity are called "hypoechogenic" and are usually represented with darker colors. Areas that lack echogenicity are called "anechogenic" and are usually displayed as completely dark.
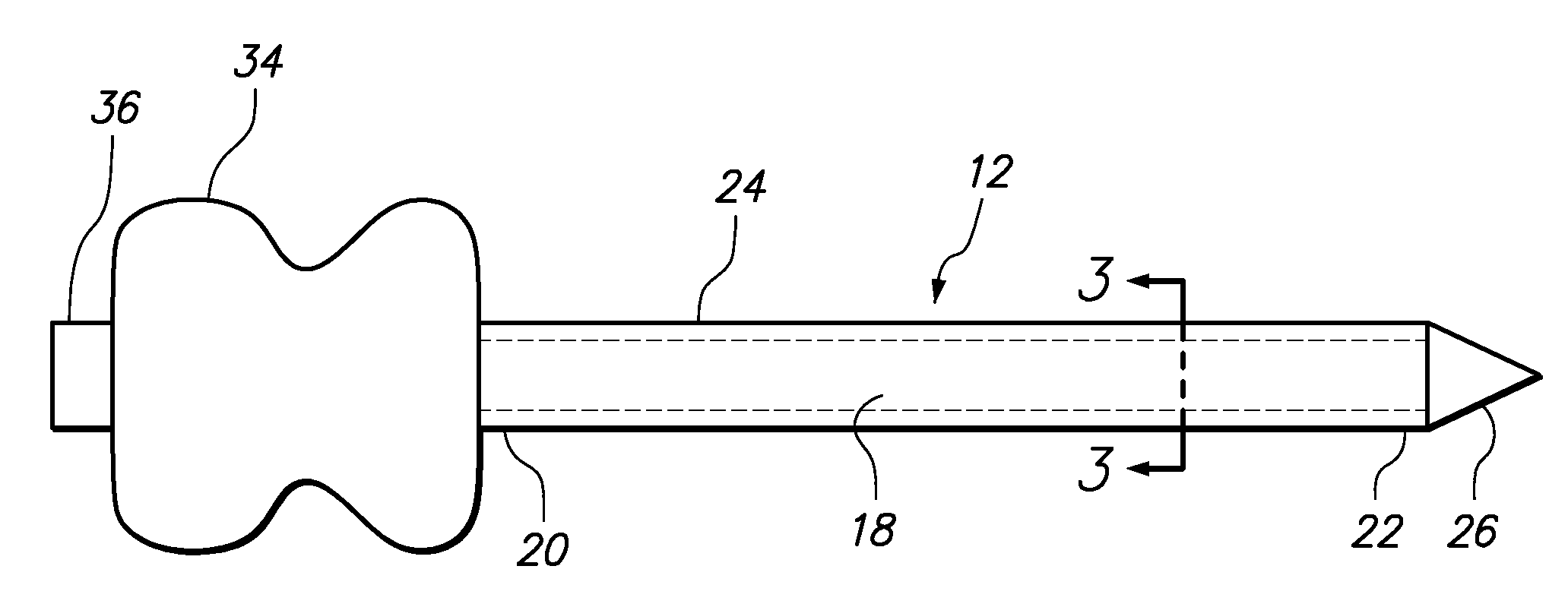
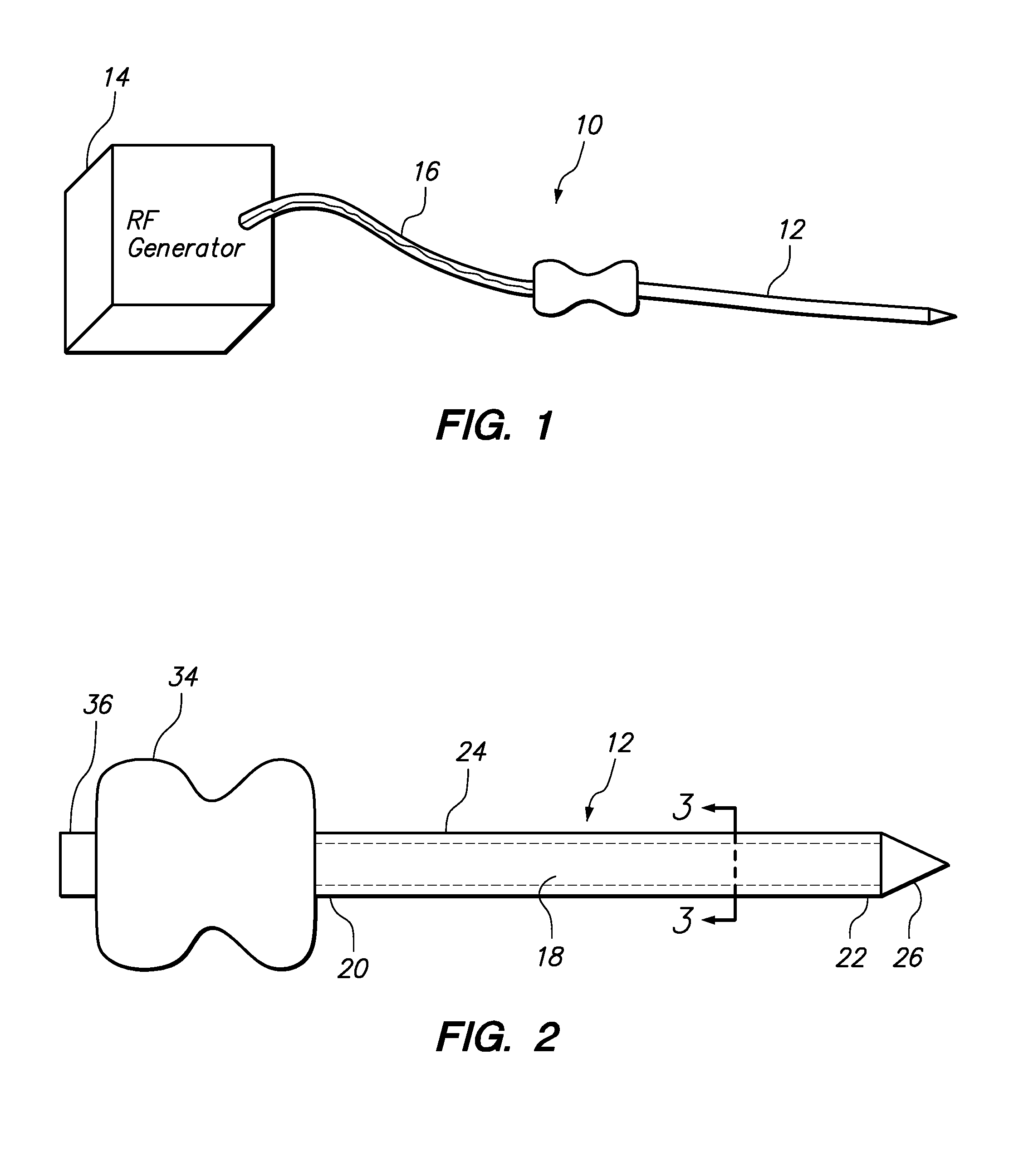
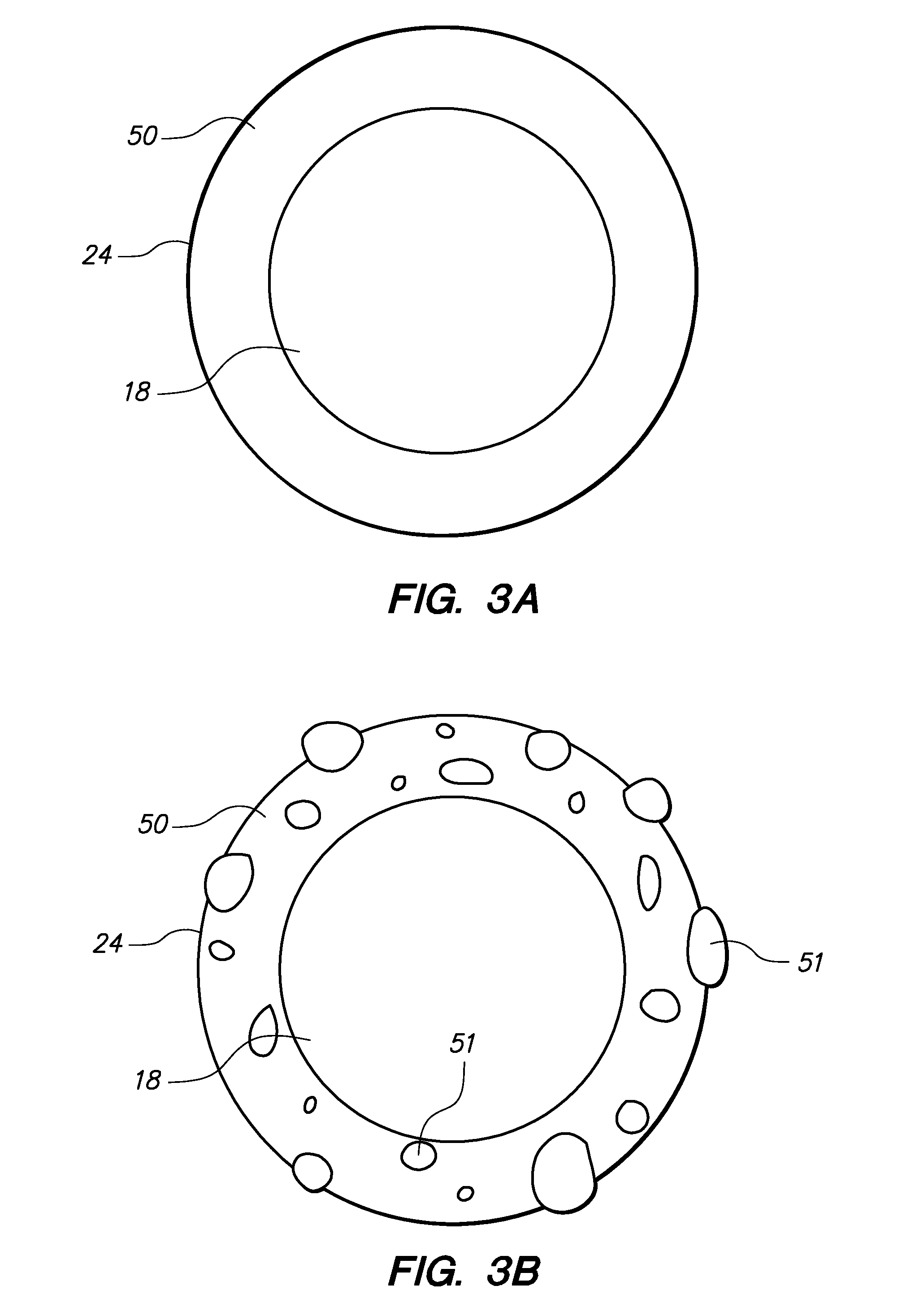
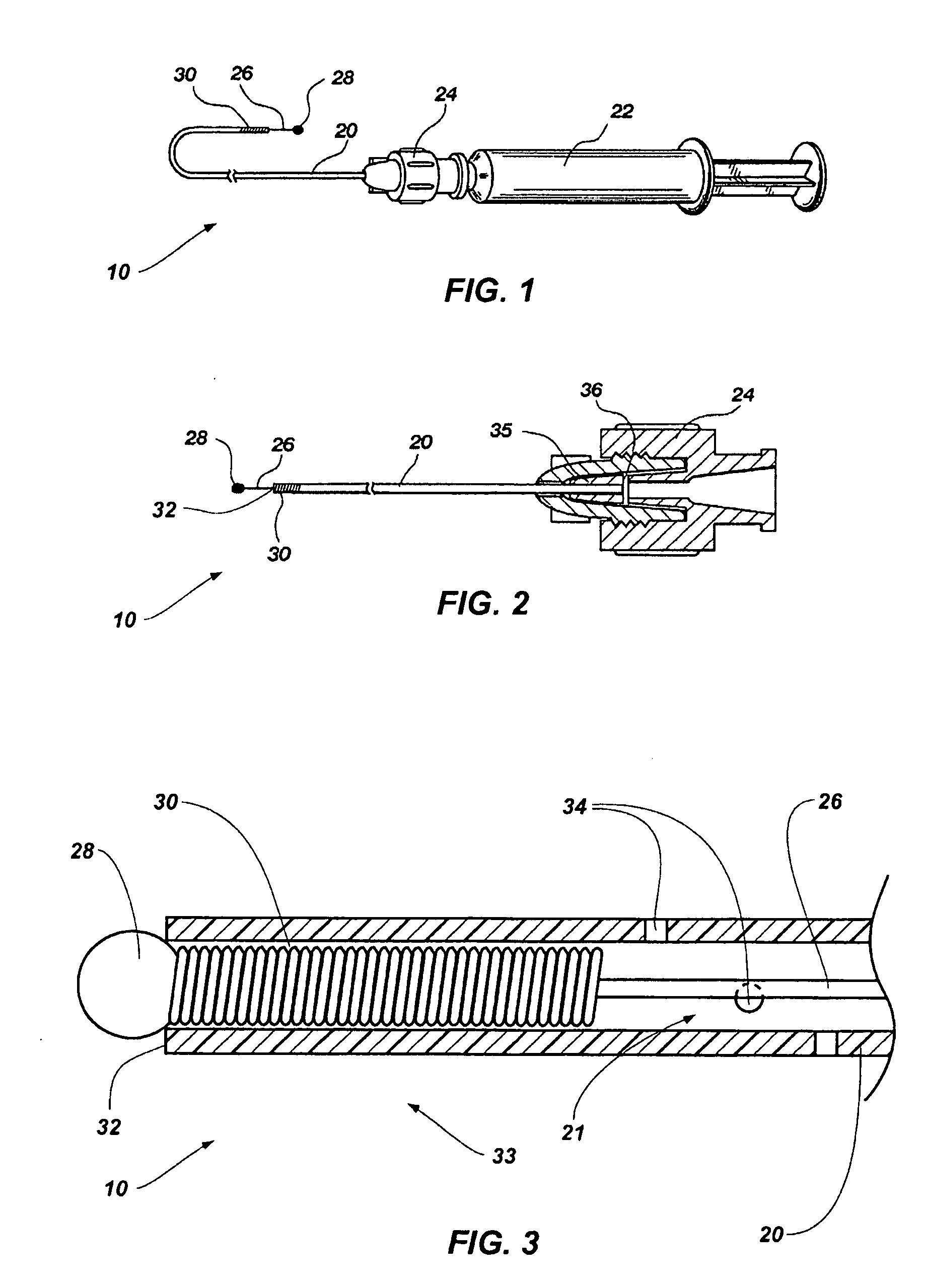
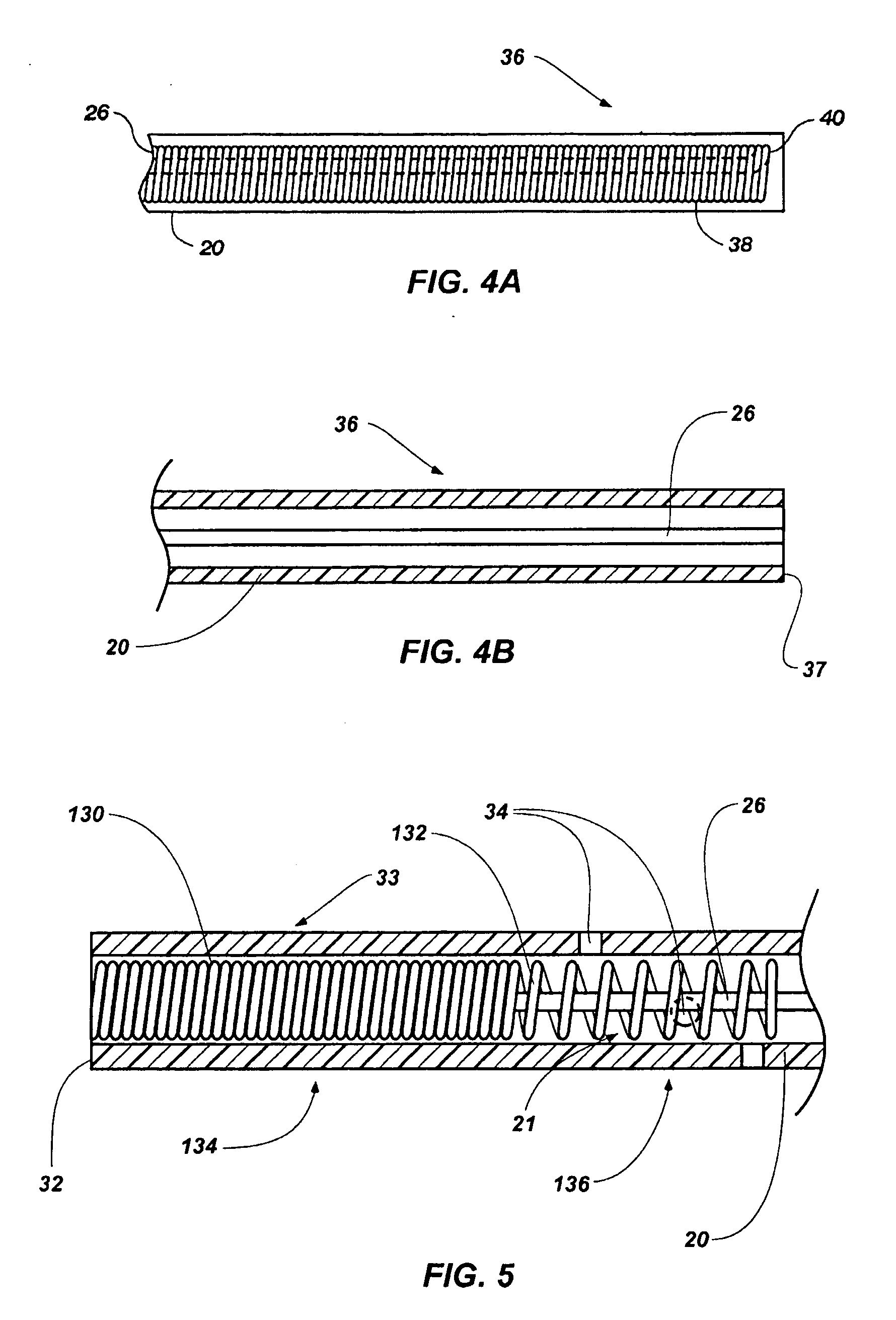
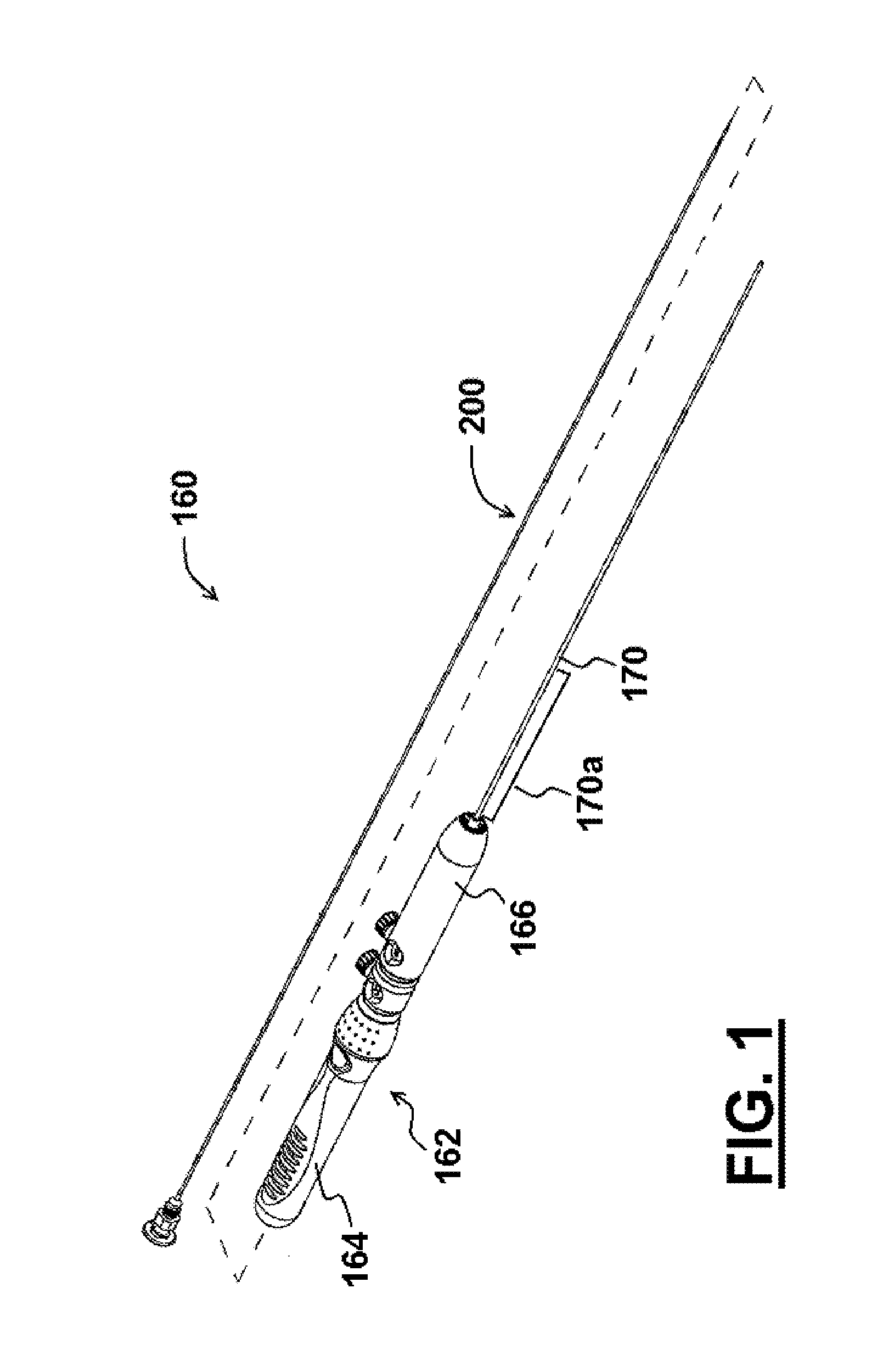
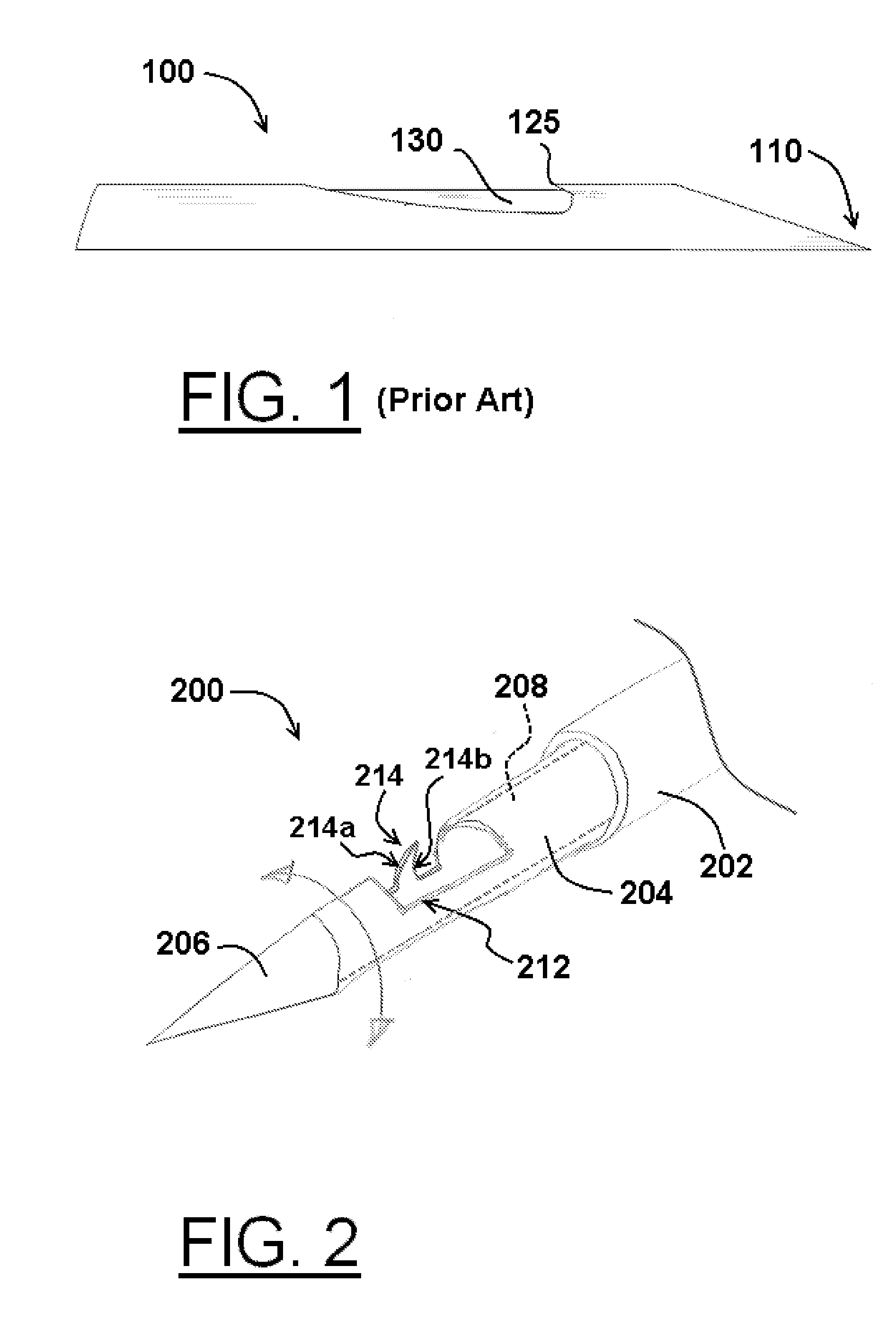
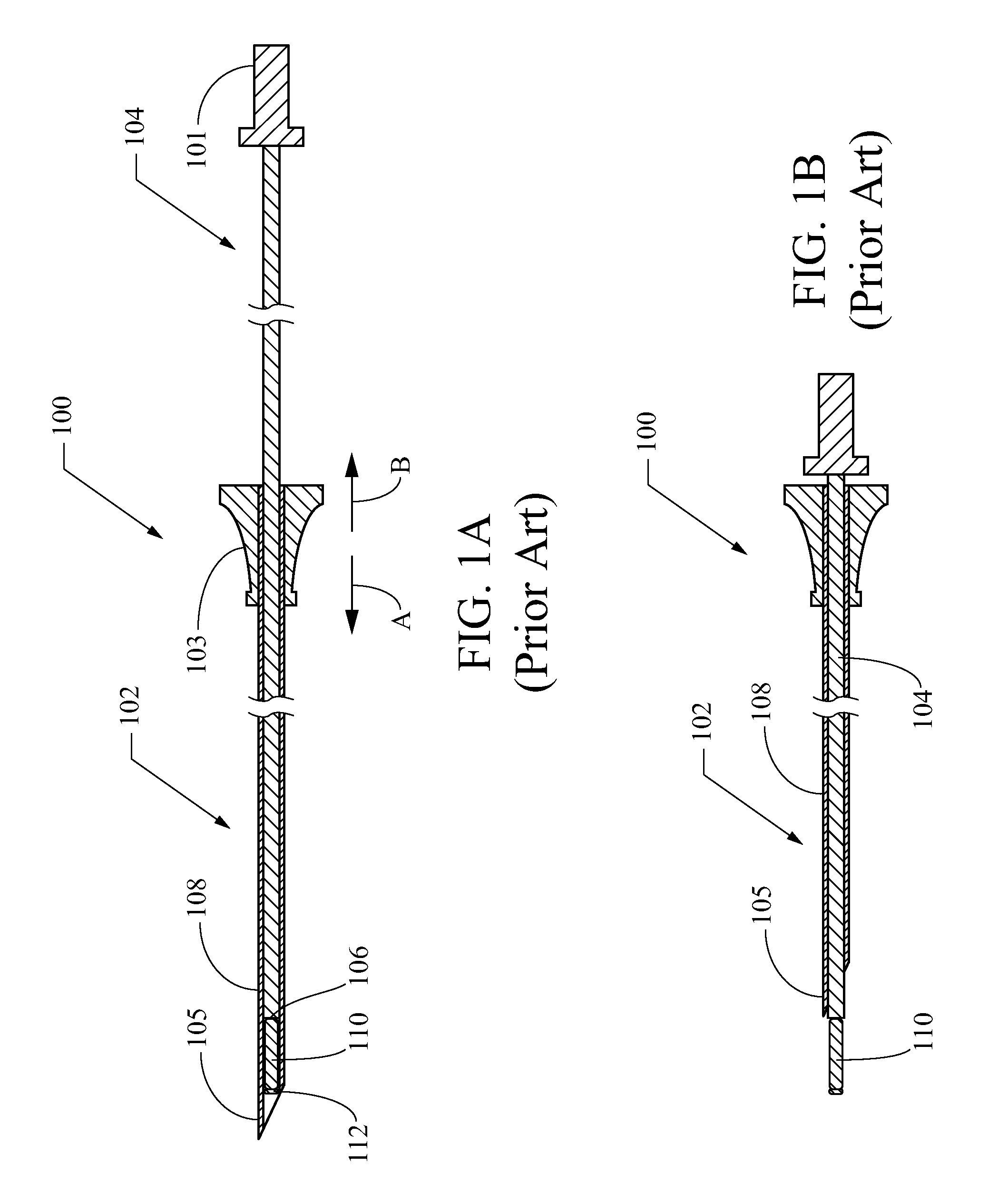
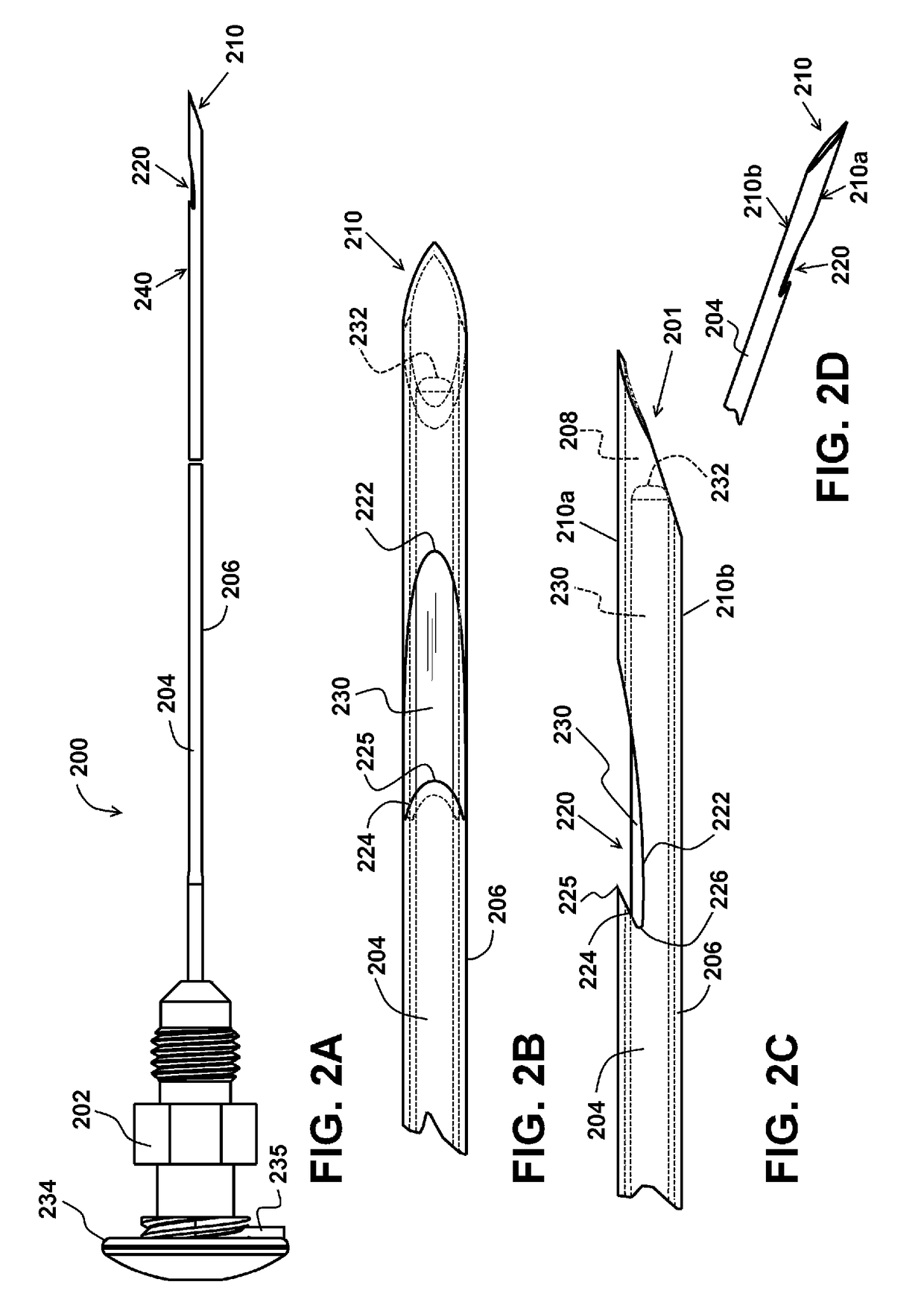
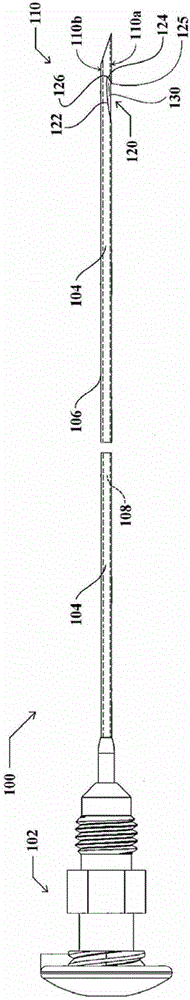
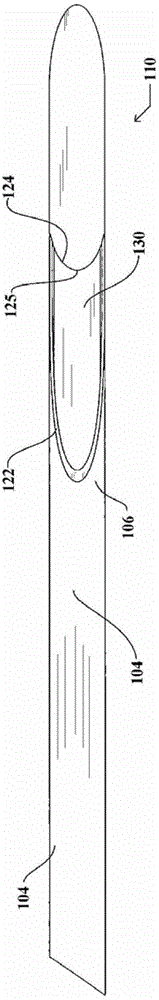
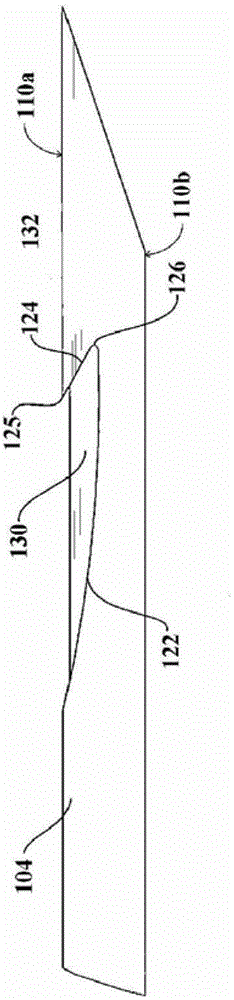
Grooved brachytherapy sources
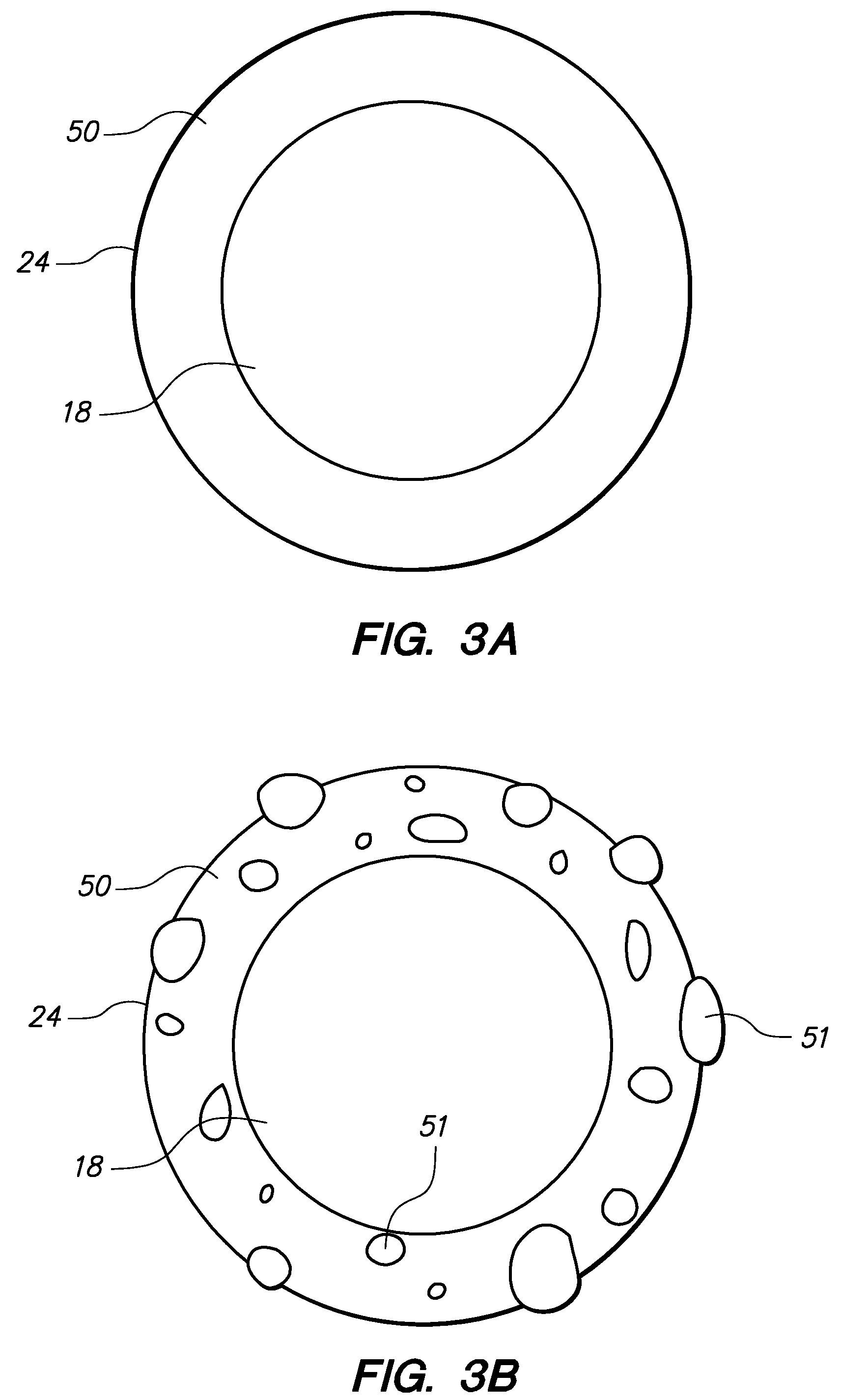
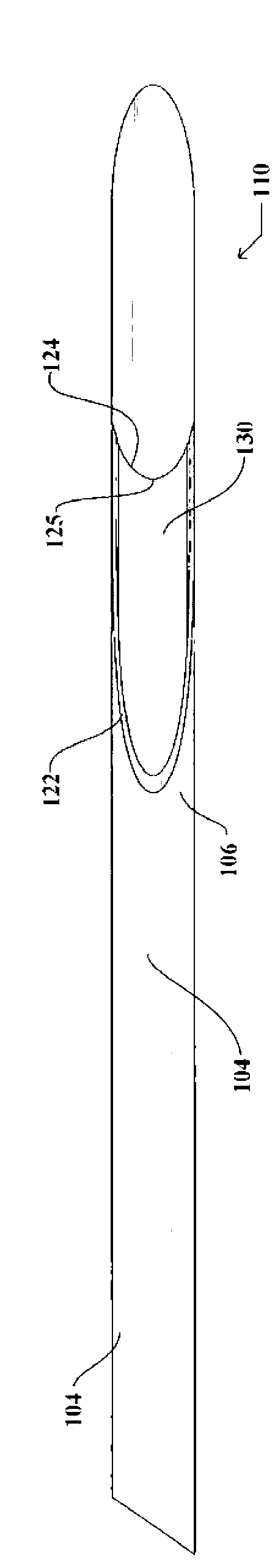
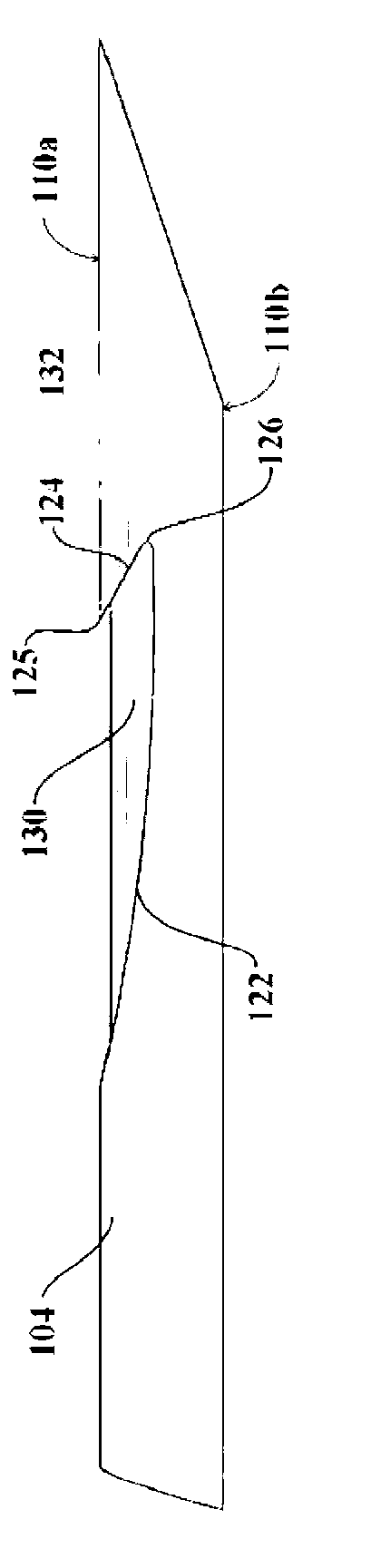
InactiveUS7083566B2Increase ultrasound visibilityIncrease reflectionDiagnosticsSurgeryVisibilityBrachytherapy source
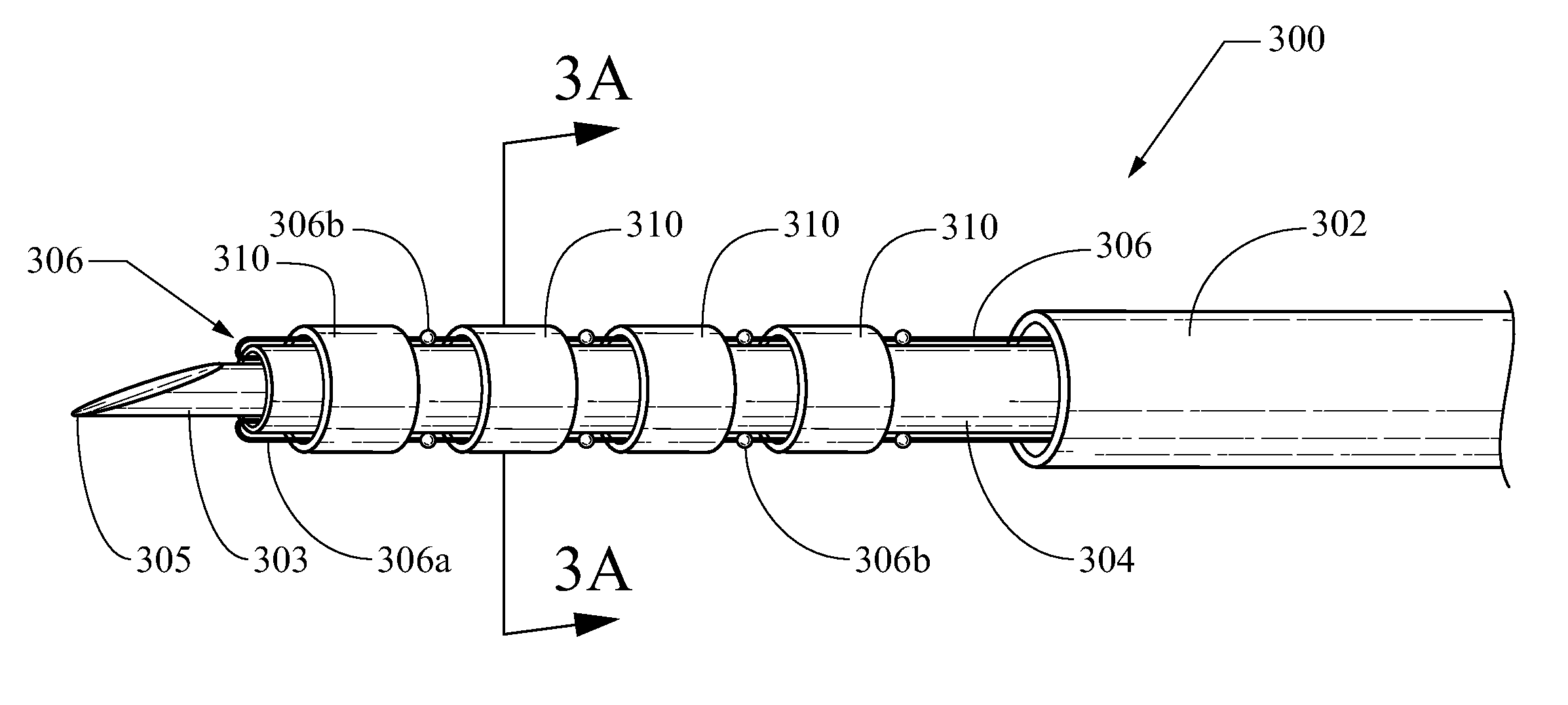
Radioactive sources, preferably radioactive seeds, for use in brachytherapy comprising a radioisotope within a sealed biocompatible container, wherein at least one part of the outer surface of the container is grooved, preferably with a curved groove. The grooved outer surface is preferably substantially free from angularities. Such grooves enhance the echogenicity of the source using medical ultrasound at a greater range of angles to the ultrasound probe, thus enhancing the ultrasound visibility of the source. Preferred radioisotopes are palladium-103 and iodine-125.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
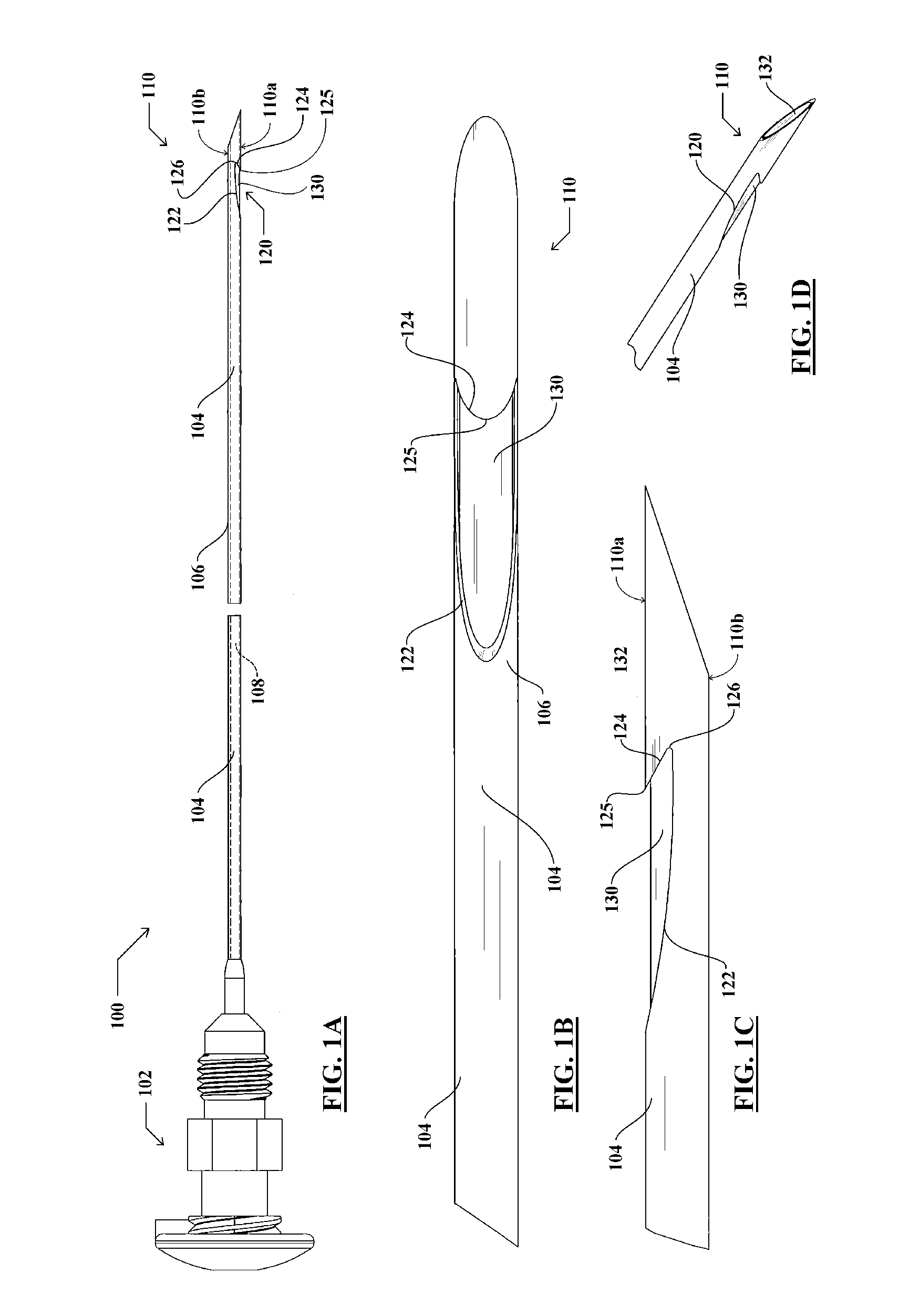
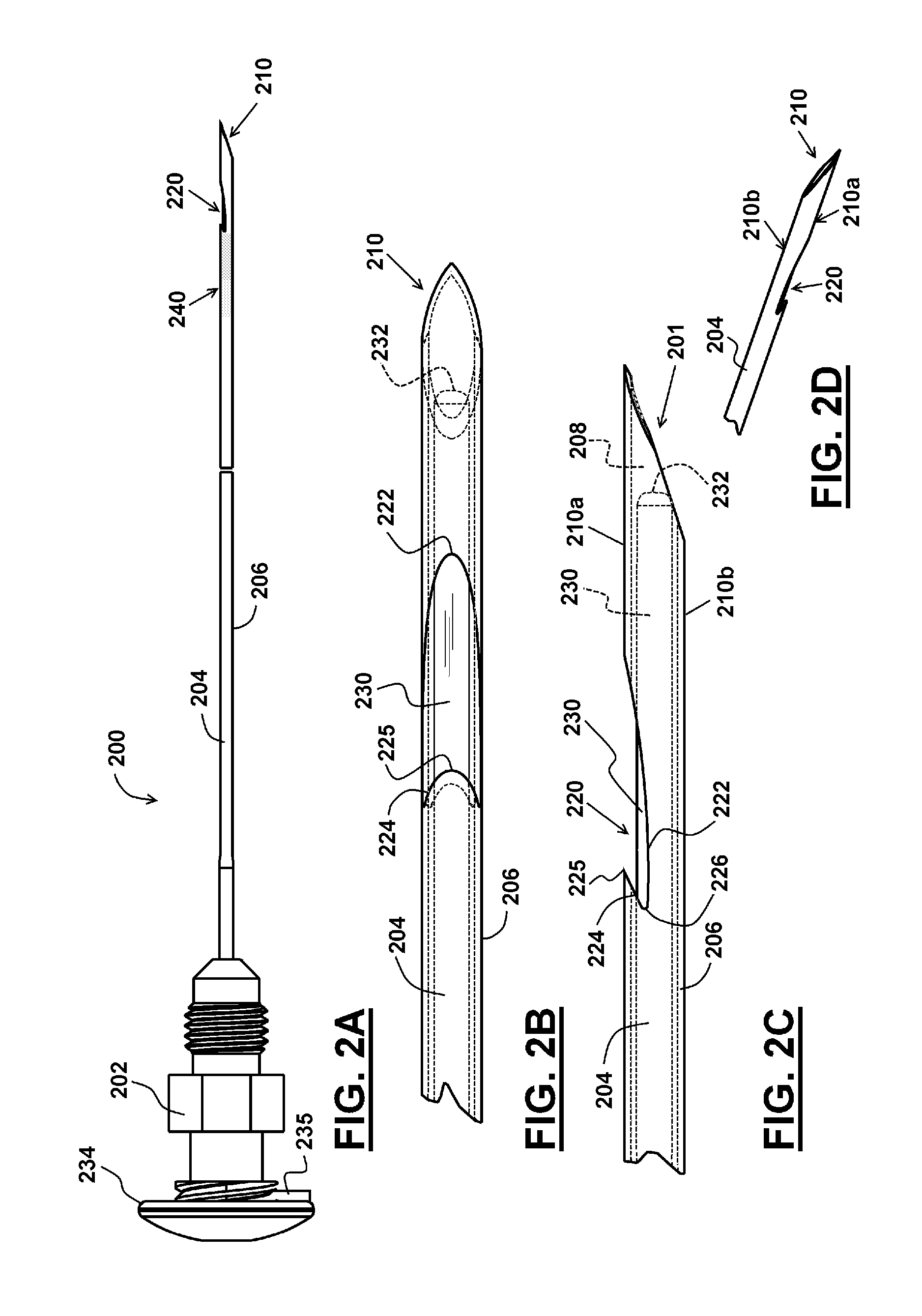
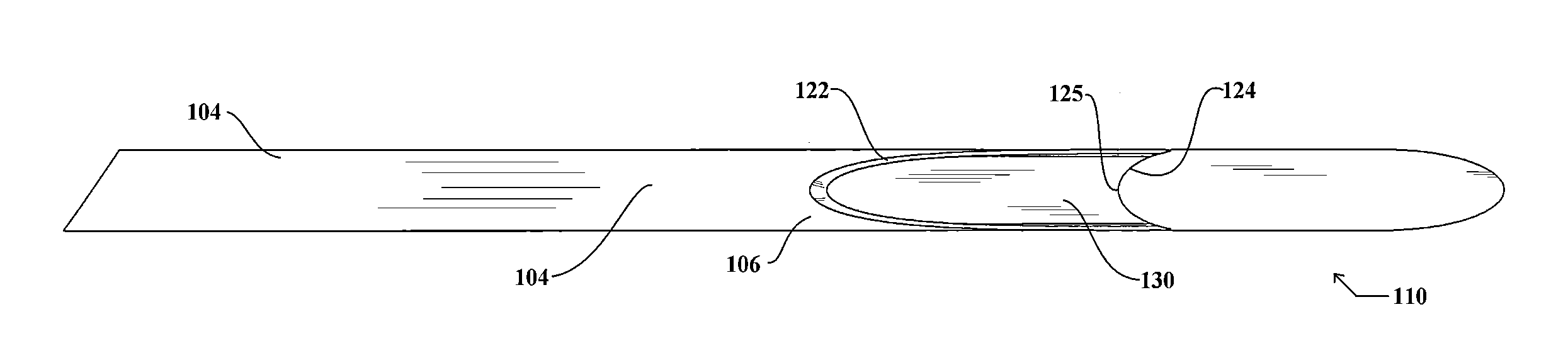
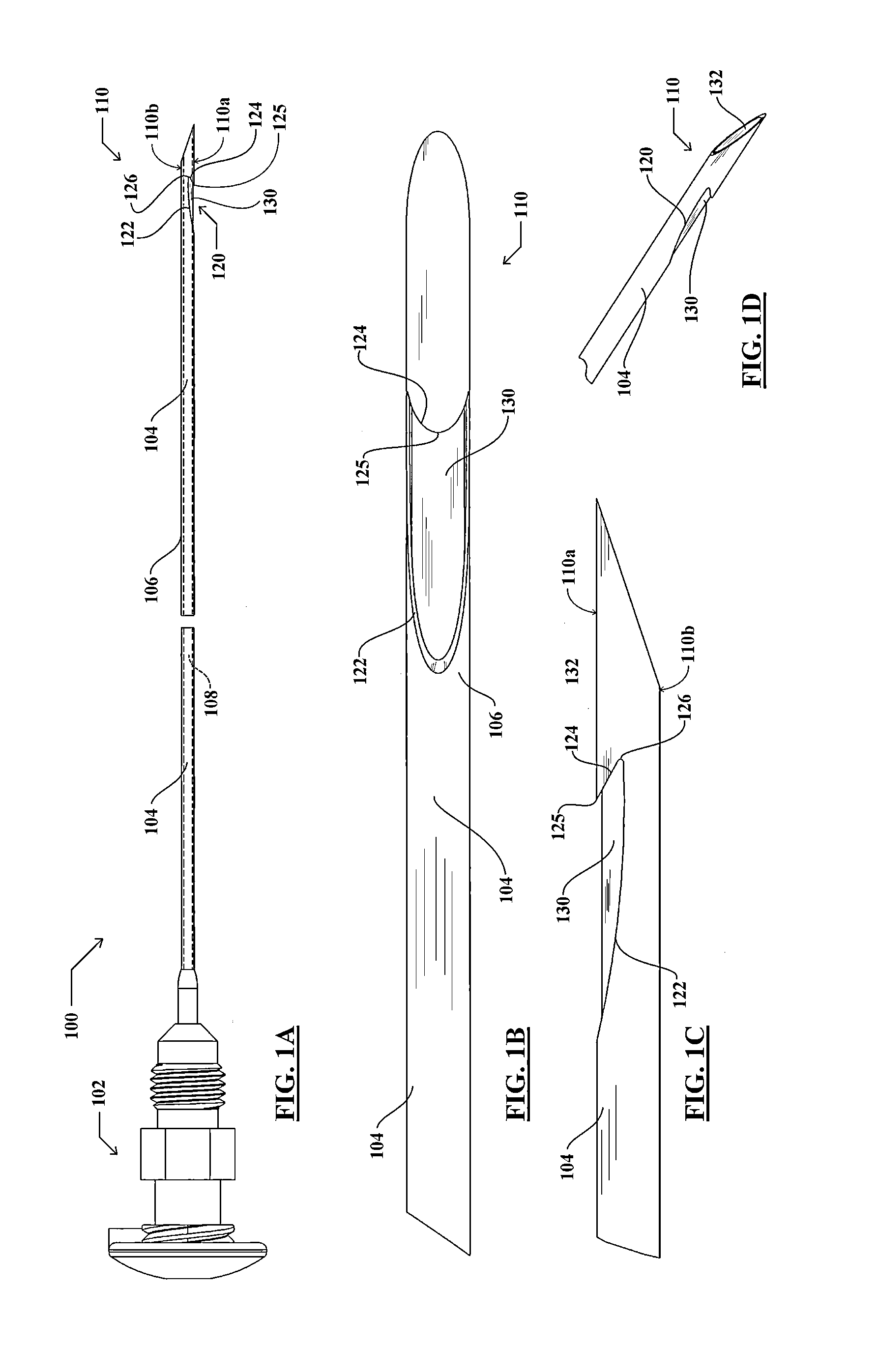
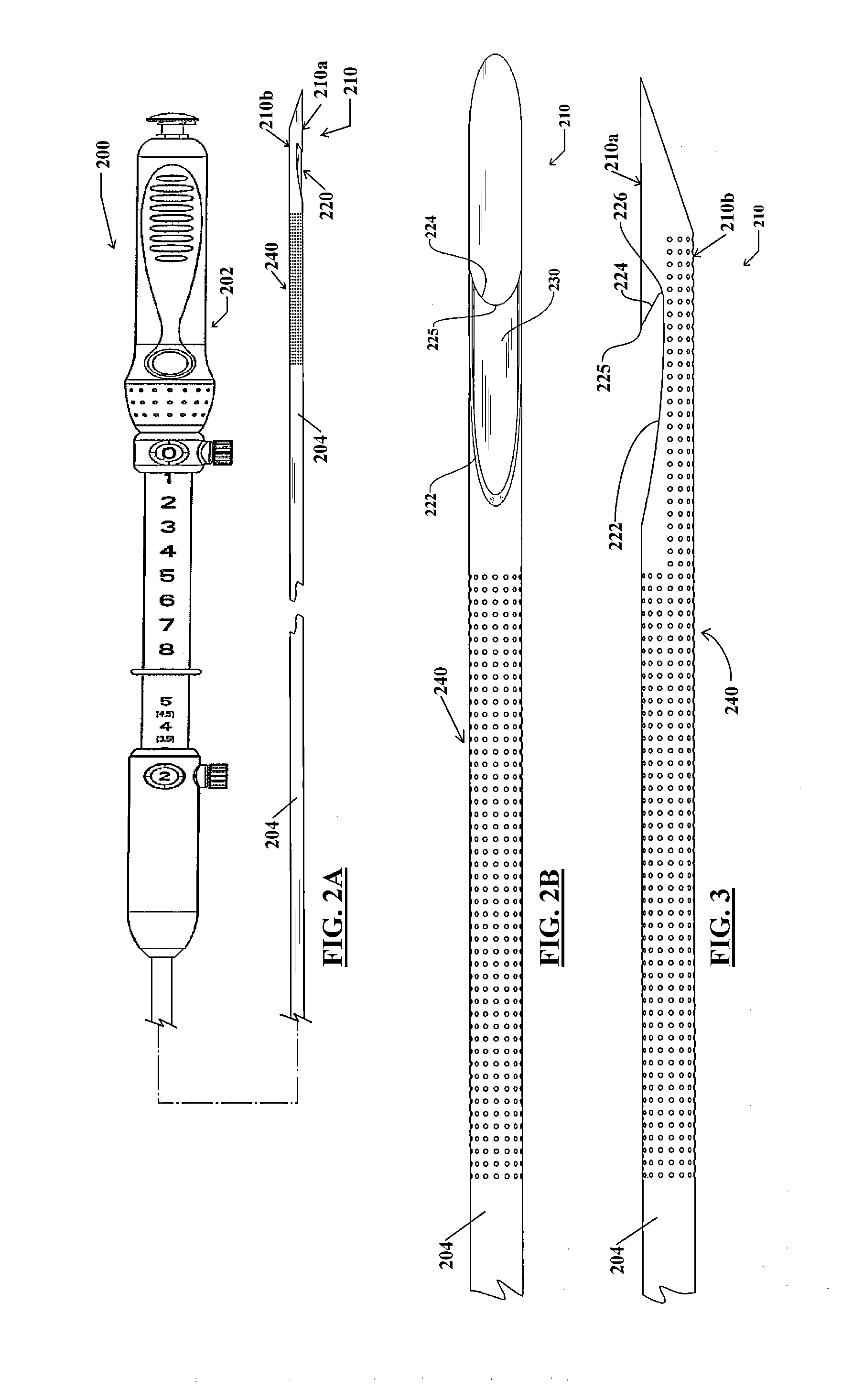
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy needle
ActiveUS20120253228A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesTissue CollectionEndoscope
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Automatic volume measurements: an application for 3D ultrasound
InactiveUS6939301B2Accurate and reliable processThe method is accurate and reliableOrgan movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionMagnificationCalipers
A method for determining the volume of an irregularly shaped body part or body such as a fetus using a 3D ultrasonic image composed of light and dark pixels. A caliper is placed on a portion whose volume is to be determined and a computer having the image, automatically counts every pixel with the same echogenicity in every direction as long as it is continuous with the spot the caliper is in, and wherein the computer means stops counting in any direction where the pixels become significantly more echogenic (dark). The volume of the portion, is determined, based on the counted number of pixels and the magnification of the image; and the calculated volume is used to determine physiological characteristics based on known values such as fetal gestation age.
Owner:ABDELHAK YAAKOV
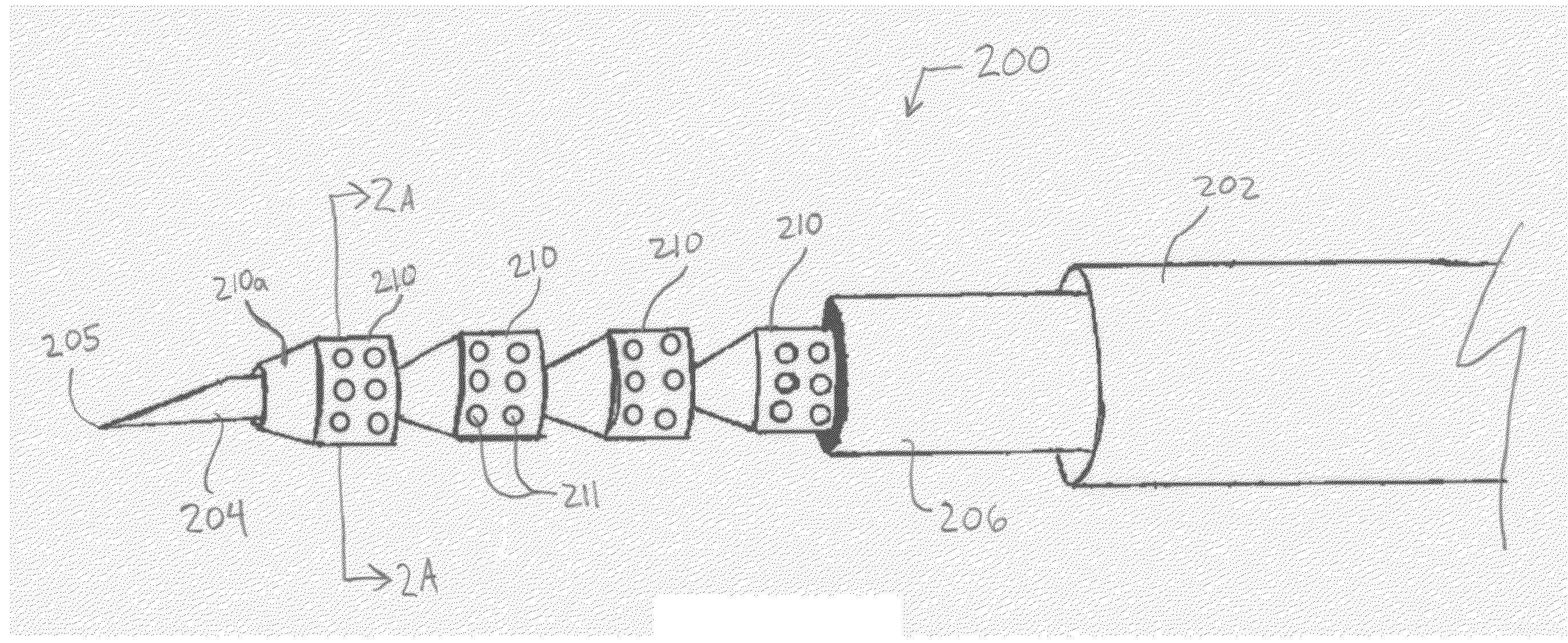
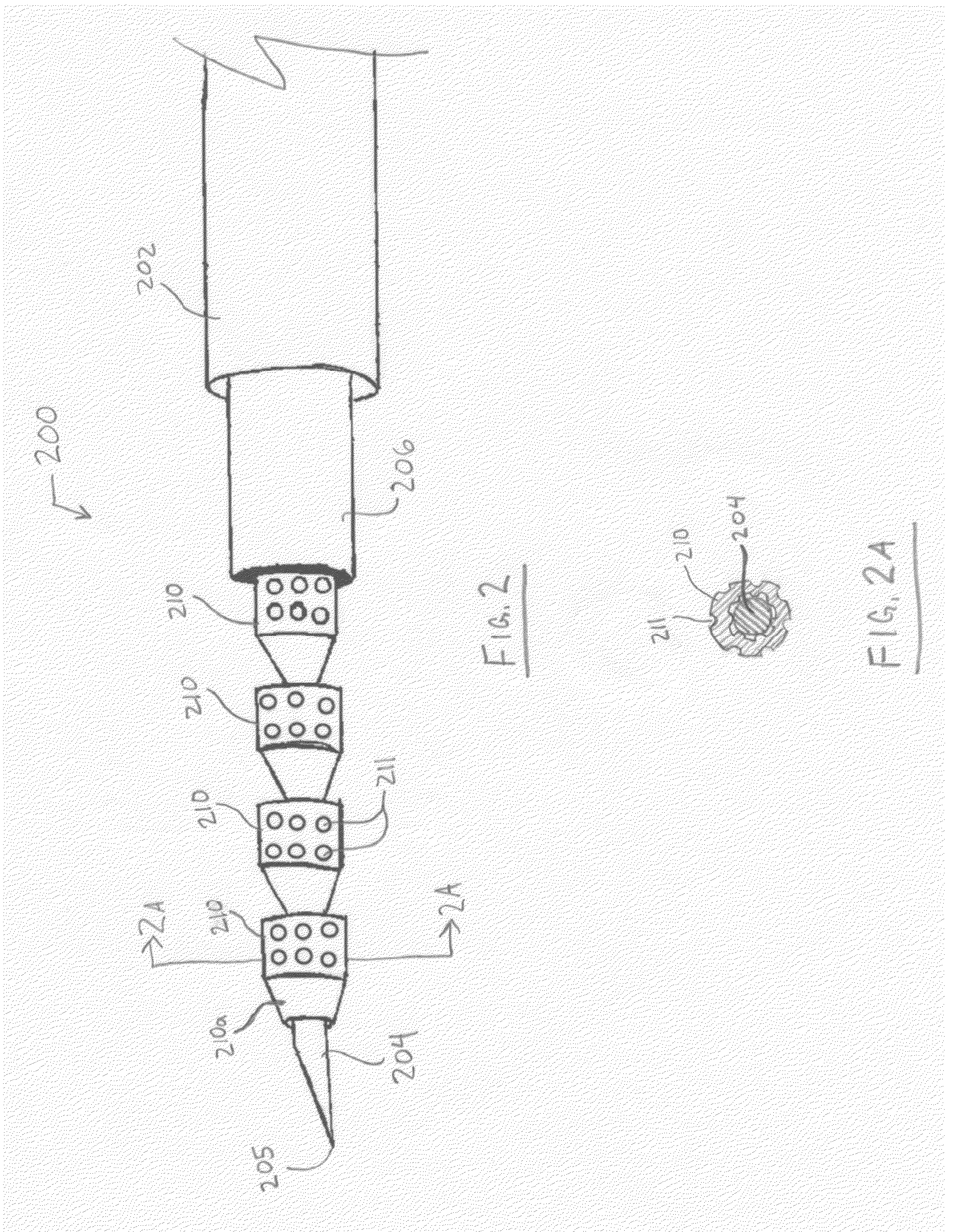
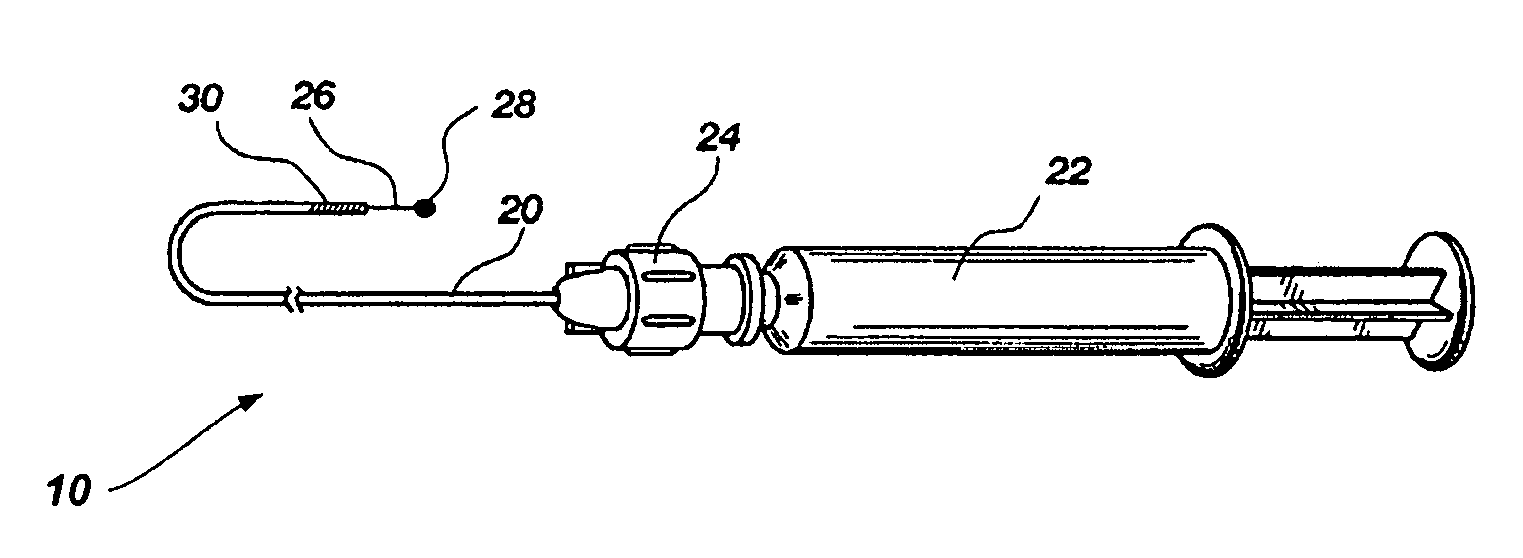
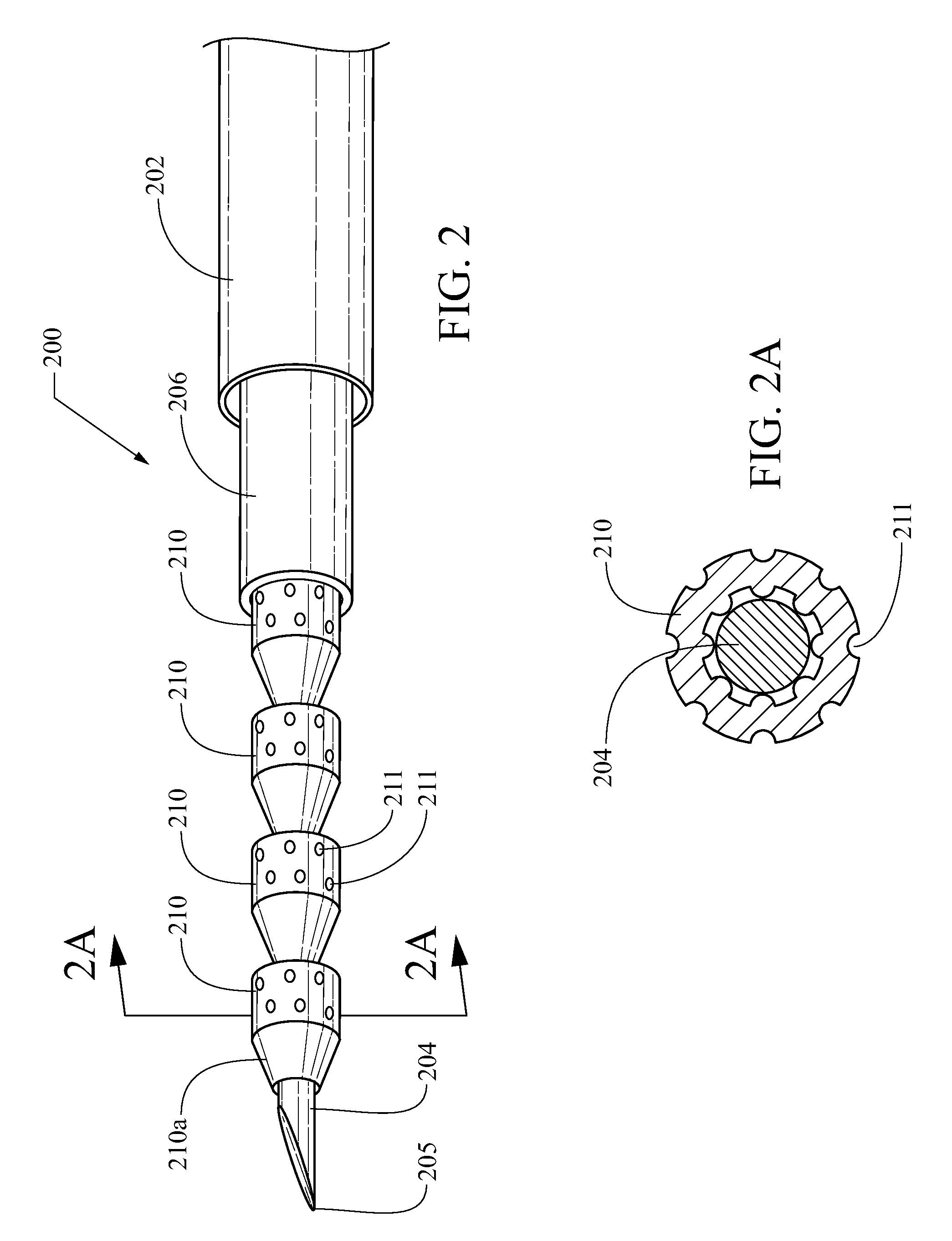
Fiducial deployment needle system
Embodiments include a fiducial deployment system. A fiducial may include dimples to enhance echogenicity and / or to provide for engagement with a delivery cannula or stylet. The needle system may be configured to deliver a plurality of fiducials to a target location in serial fashion, one at a time, when the fiducials are coaxially disposed around a central deployment member that may be embodied as a delivery cannula or stylet. In certain embodiments, echogenic placement of fiducials may present certain advantages. An elongate structure may be included that is configured to distally advance fiducials along the deployment member.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
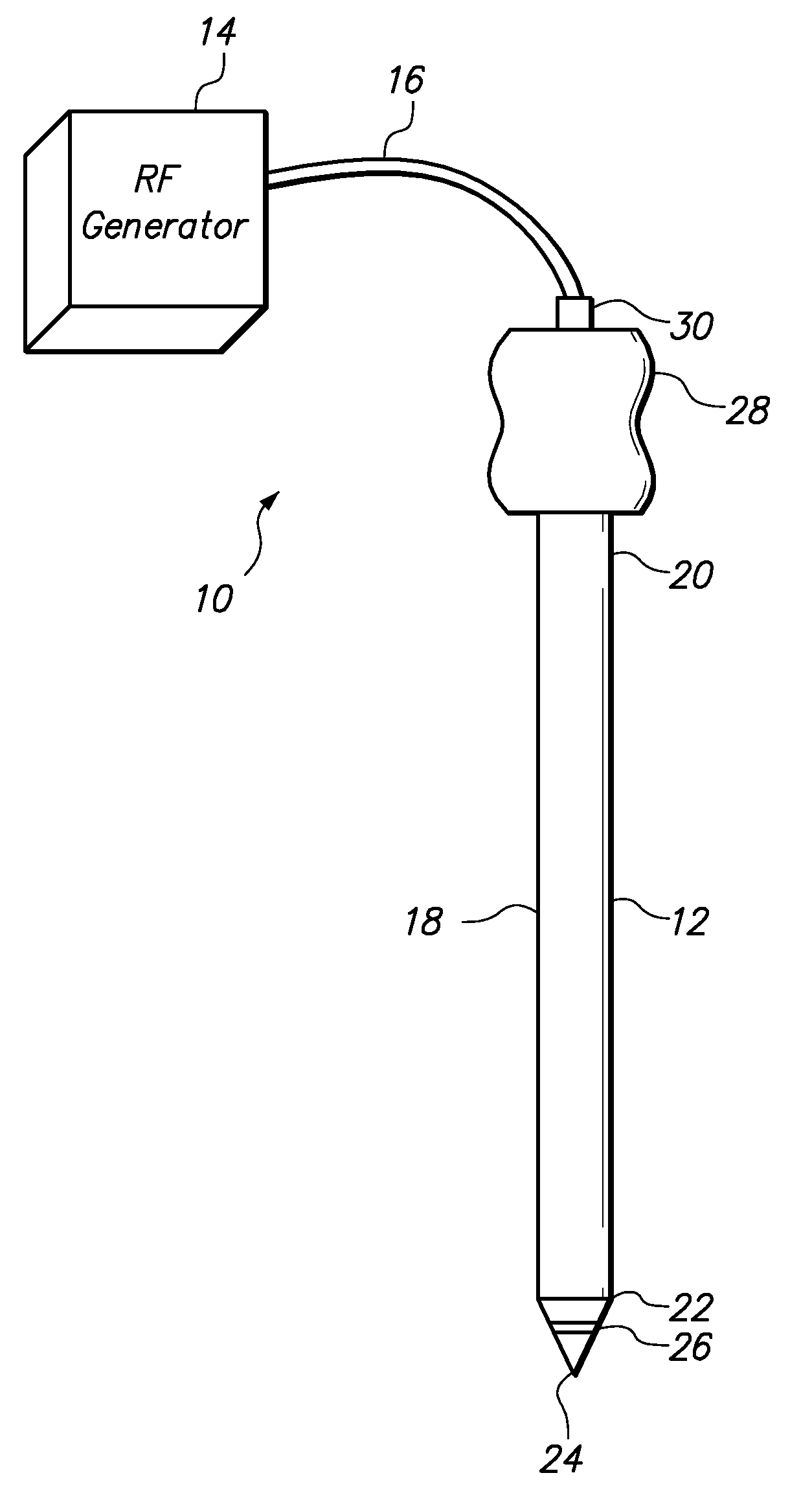
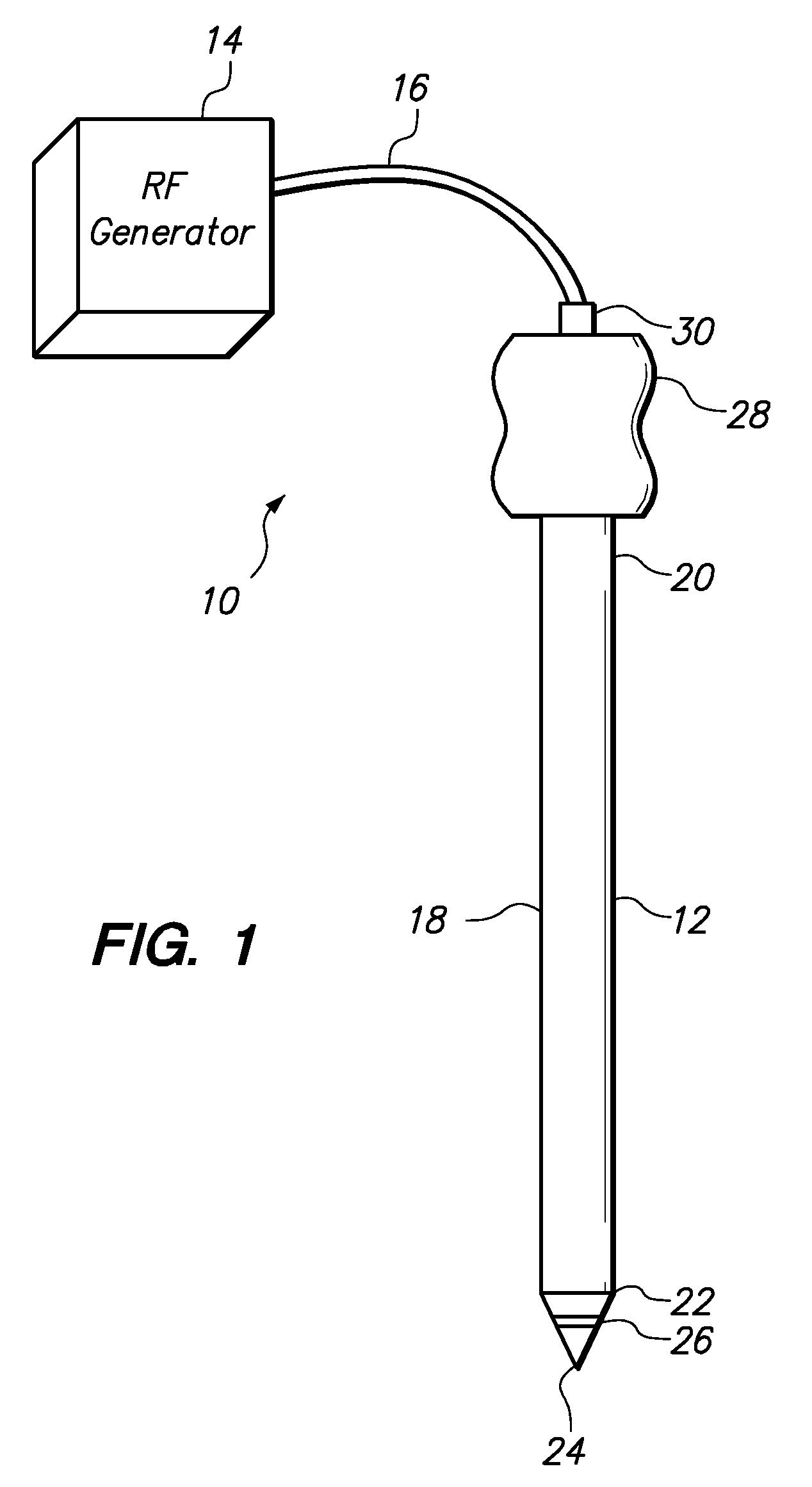
Medical probe with echogenic and insulative properties
Tissue ablation probes and methods of using tissue ablation probes are provided. Each tissue ablation probe comprises an electrically conductive probe shaft, at least one tissue ablation electrode carried by a distal end of the probe shaft, and one or both of an insulative element and an echogenic element. The insulative element and / or the echogenic element may, e.g., be affixed to, or selectively removable from, the probe shaft to increase the insulative capability and echogenicity of the probe. An echogenic sheath having the insulative element and / or the echogenic element may be slidably disposed over the probe shaft to impart insulative and echogenic properties to the probe shaft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
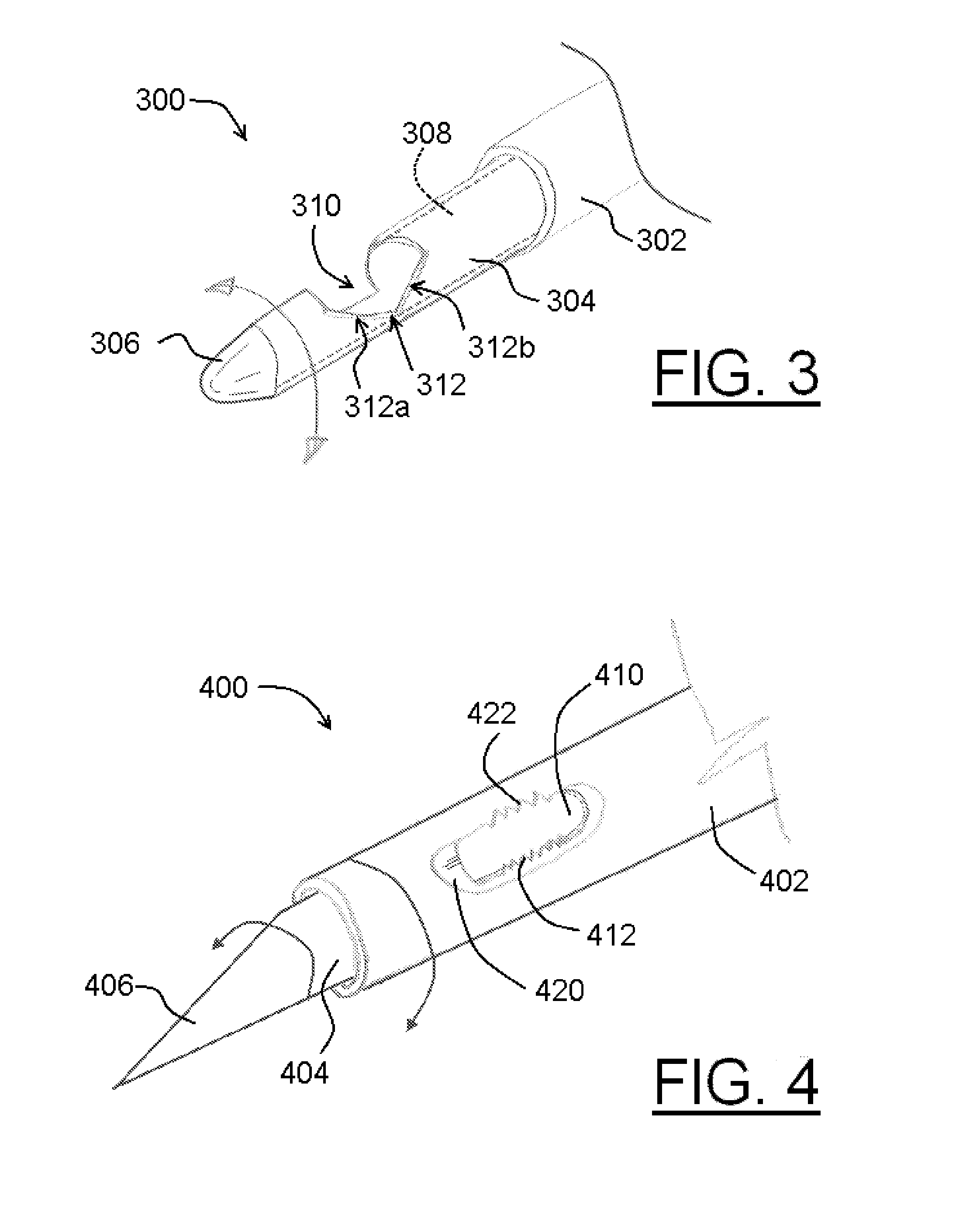
Ablation with echogenic insulative sheath
InactiveUS20080009852A1Diameter minimizationIncrease echogenicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesPolyether ether ketoneTissue ablation
Tissue ablation probes are provided. Each tissue ablation probe comprises an electrically conductive probe shaft, at least one tissue ablation electrode carried by a distal end of the probe shaft, and an electrically insulative outer sheath disposed on the probe shaft. The sheath is at least partially composed of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and another material comprising condensed-phase particles interspersed throughout the PEEK to increase the echogenicity of the outer sheath. The durability of the PEEK allows the sheath to be formed as thinly as possible, thereby minimizing the diameter of the ablation probe, while the inclusion of condensed-phase particles within the PEEK does not significantly degrade the durability of the sheath.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
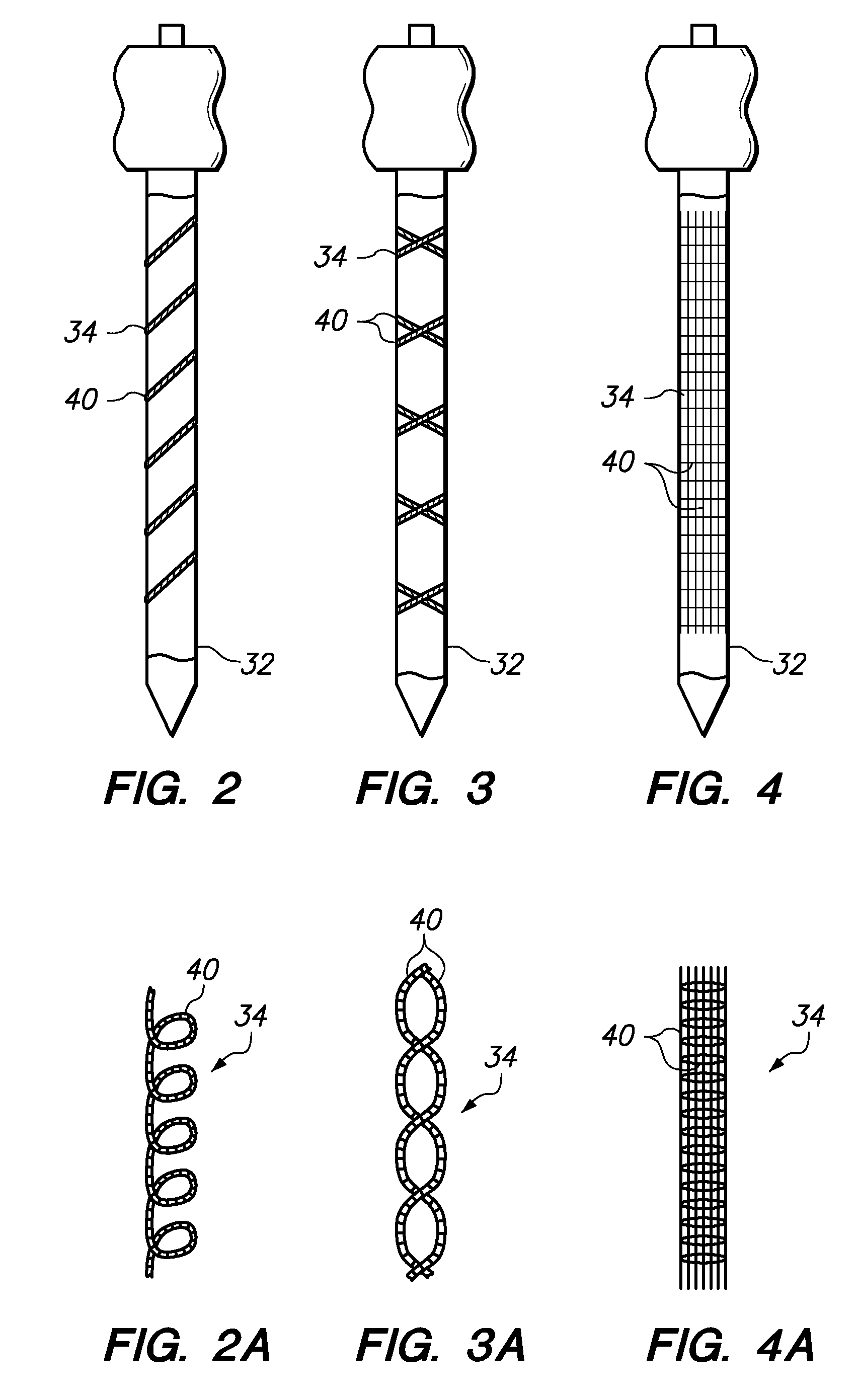
Ultrasound guided echogenic catheter and related methods
InactiveUS20110172542A1Increase echogenicityImproved ultrasound guidanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDistal portionCatheter
Described are methods and apparatus for ultrasound guidance of a tool for a clinical procedure performed upon a subject, wherein the improvement includes a catheter having an echogenic structure disposed in a distal portion of the catheter, which increases the echogenicity of the catheter.
Owner:CUSTOM MEDICAL APPL
Systems and methods for automated image recognition of implants and compositions with long-lasting echogenicity
InactiveUS20190053790A1Increase awarenessComputationally efficientImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityUltrasound contrast media
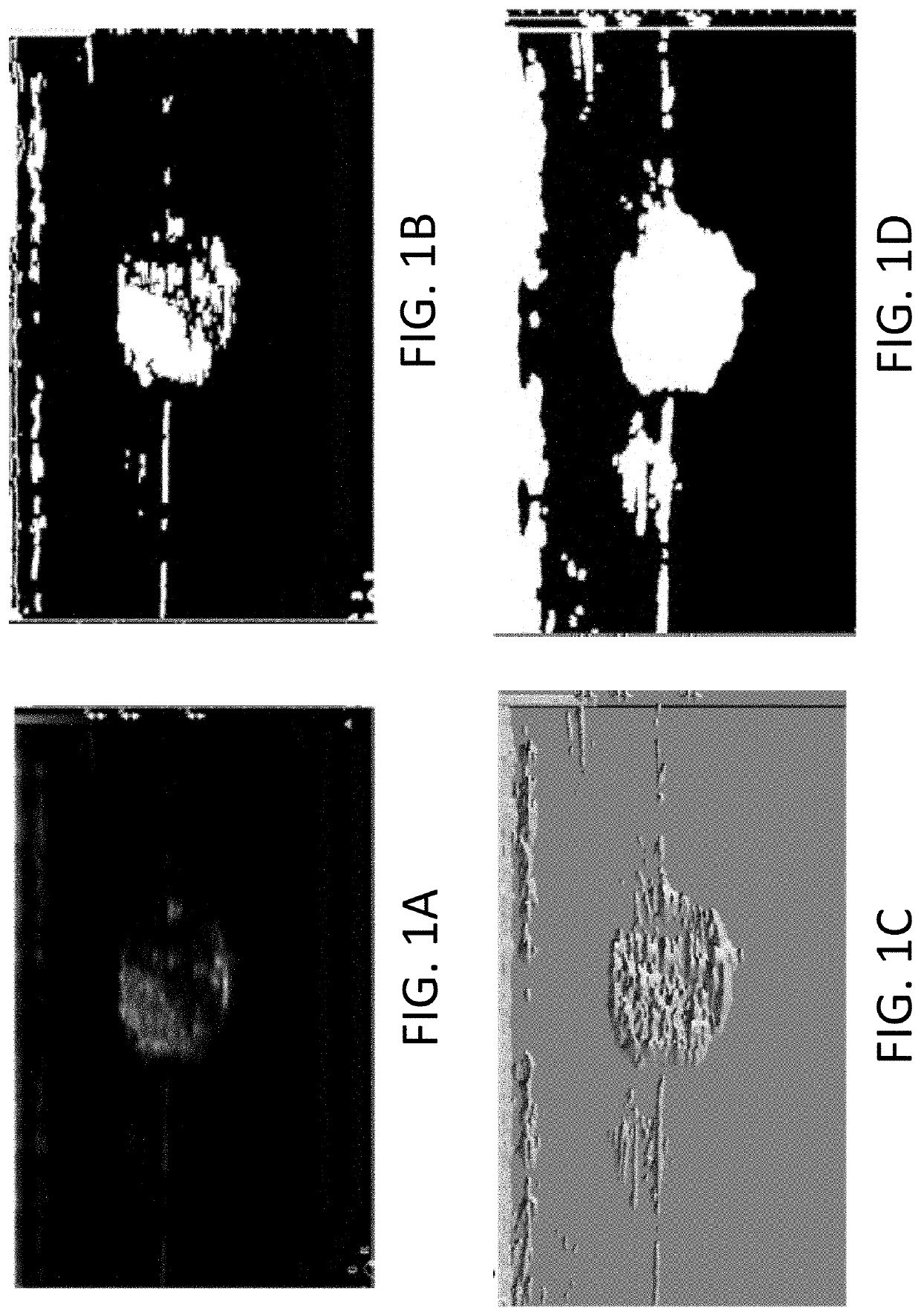
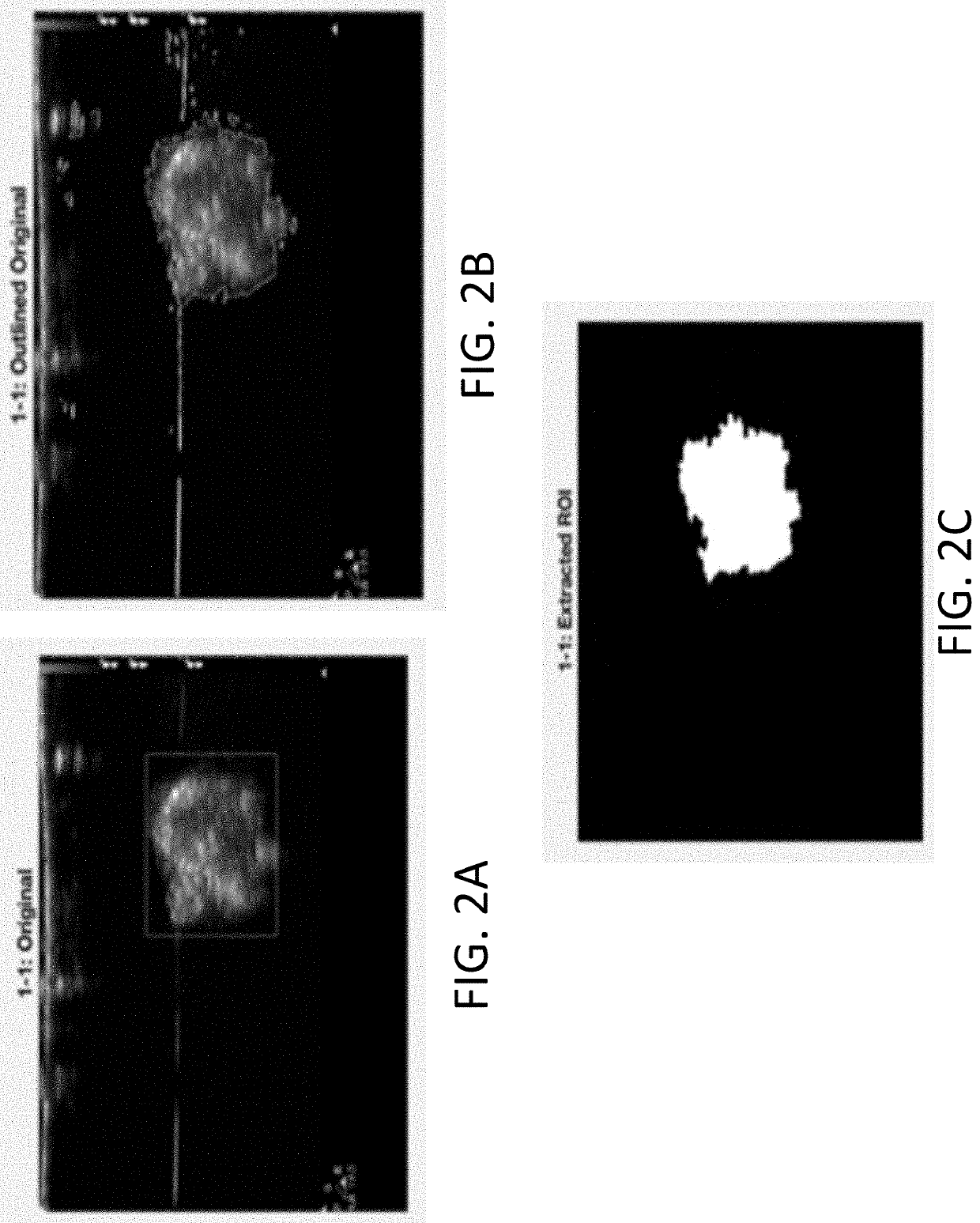
Systems and methods for imaging an object that are capable of capturing an image or images of the object using an imaging modality, automatically detecting and analyzing the image or images by way of converting the image or images to at least one binary image, and analyzing the at least one binary image to extract and / or segment regions-of-interest (ROIs) from the at least one binary image. The object can be or include an implantation, occlusion, medical device, body lumen, tissue, organ, duct, and / or vessel. The imaging modality can be or include X-ray, CT, MRI, PET, and / or ultrasound, or any combination thereof. Also included are compositions of soft, implantable materials with one or more carbon-based material, nanomaterial, and / or allotrope present in an amount sufficient as an ultrasound contrast agent effective for days, months, or years and which compositions are useful in the automated imaging methods of the invention.
Owner:CONTRALINE INC
Apparatus with an echogenic coating and echogenic layer
InactiveUS20100239505A1Produced economicallyFine cleaning and activationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsBiomedical engineeringEchogenicity
An apparatus having an echogenic coating of a polymer with hollow spaces present in the polymer. In order to achieve an echogenicity that supplies largely isotropic ultrasonic echo images, the hollow spaces should be microhollow spheres embedded in the polymer.
Owner:RM TEMENA
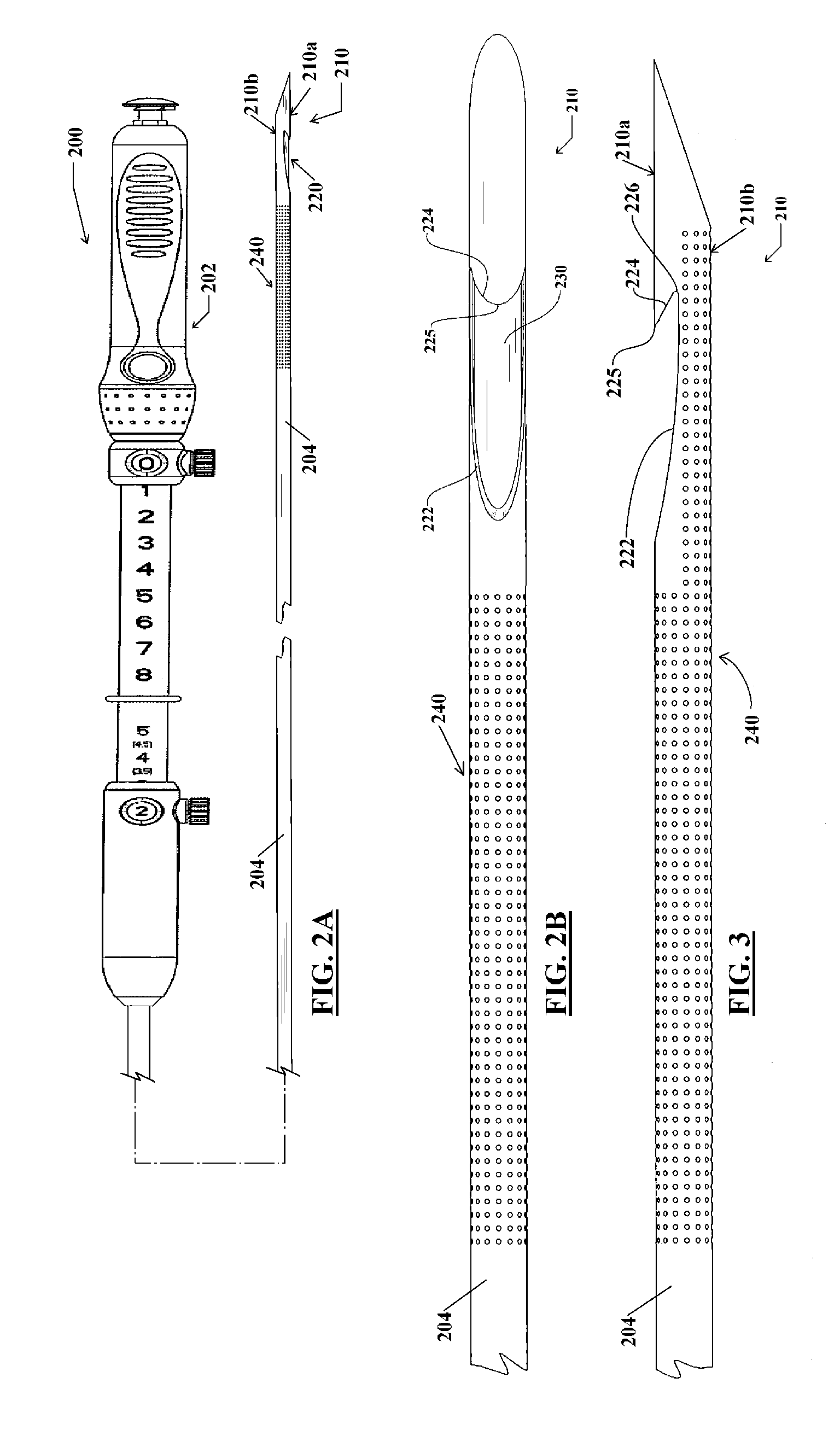
Endoscopic biopsy needle with coil sheath
ActiveUS20140257136A1Large outer diameterHigh strengthSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue CollectionEndoscope
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features. A coated-wire sheath through which the needle is slidably disposed includes an overcoating that is thicker along a distal length and thinner along a proximal length.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
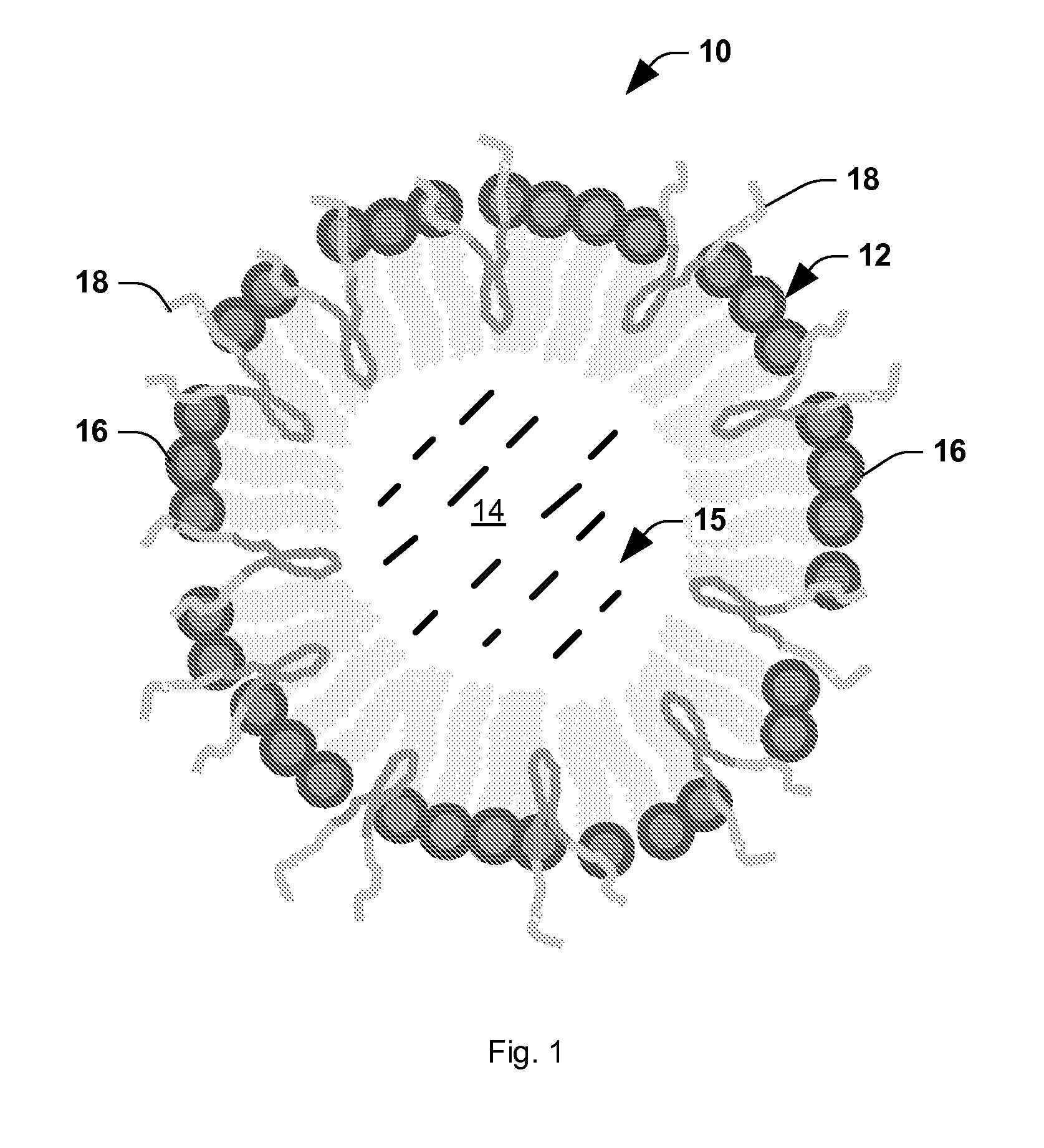
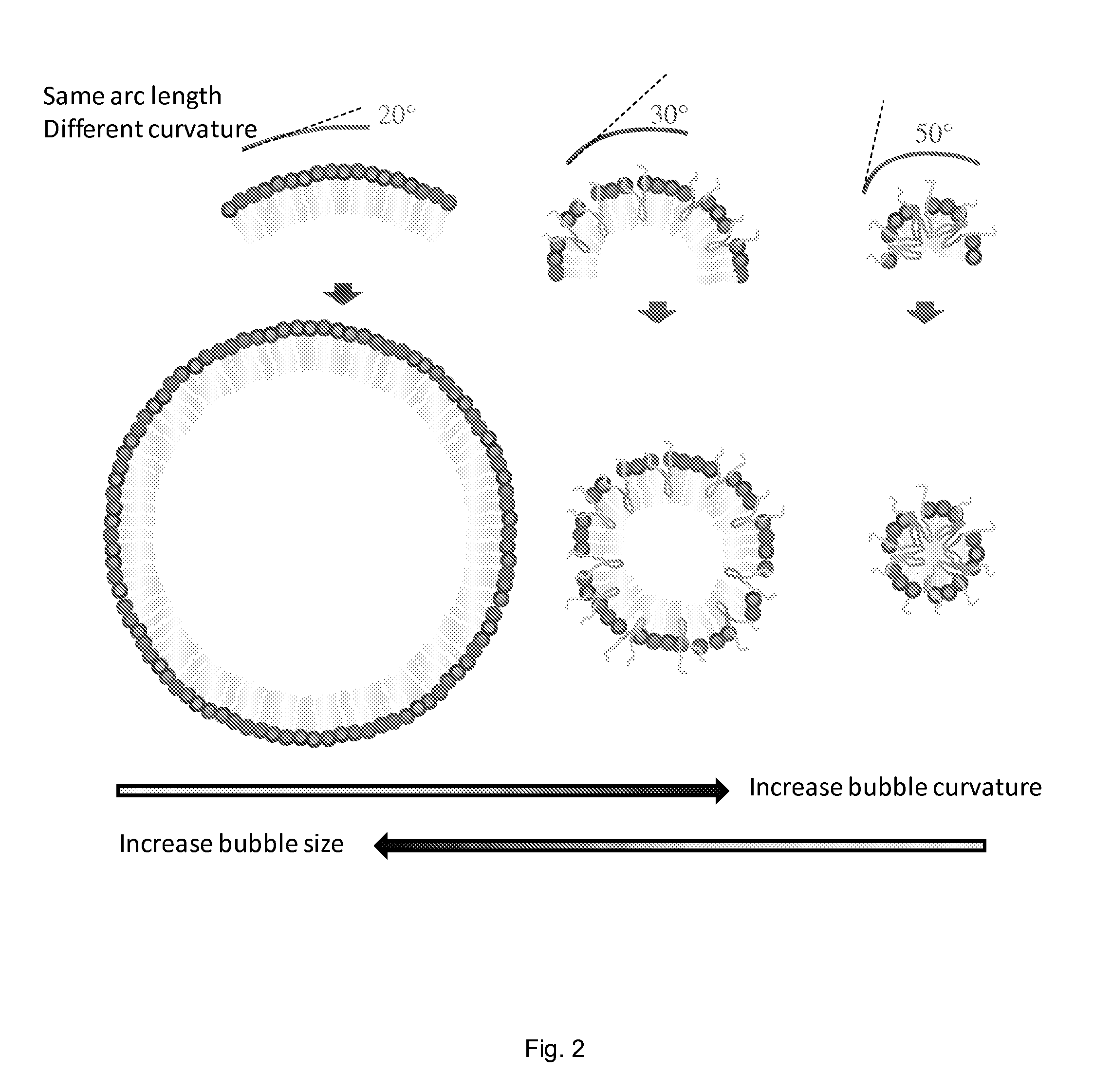
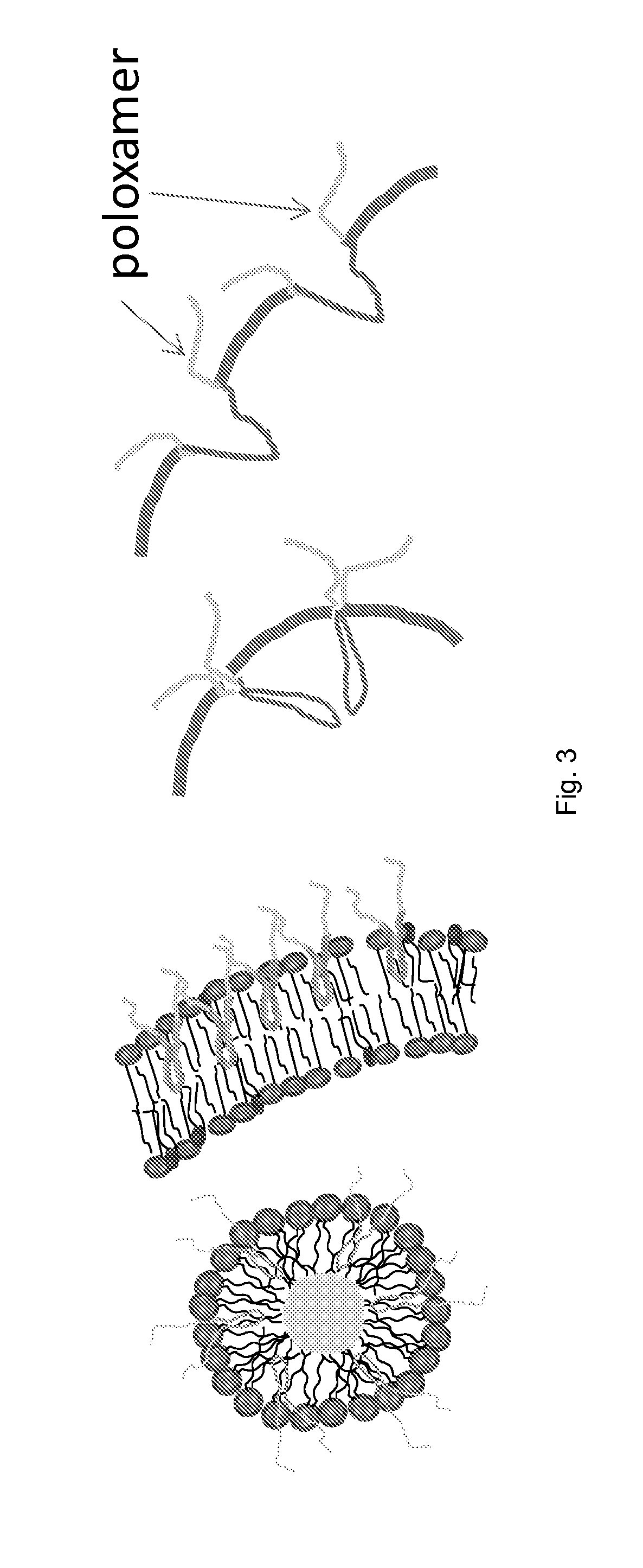
Stabilized nanobubbles for diagnostic and therapeutic applications
ActiveUS20140147390A1Effective controlPromote extravasationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsIn vivoCopolymer
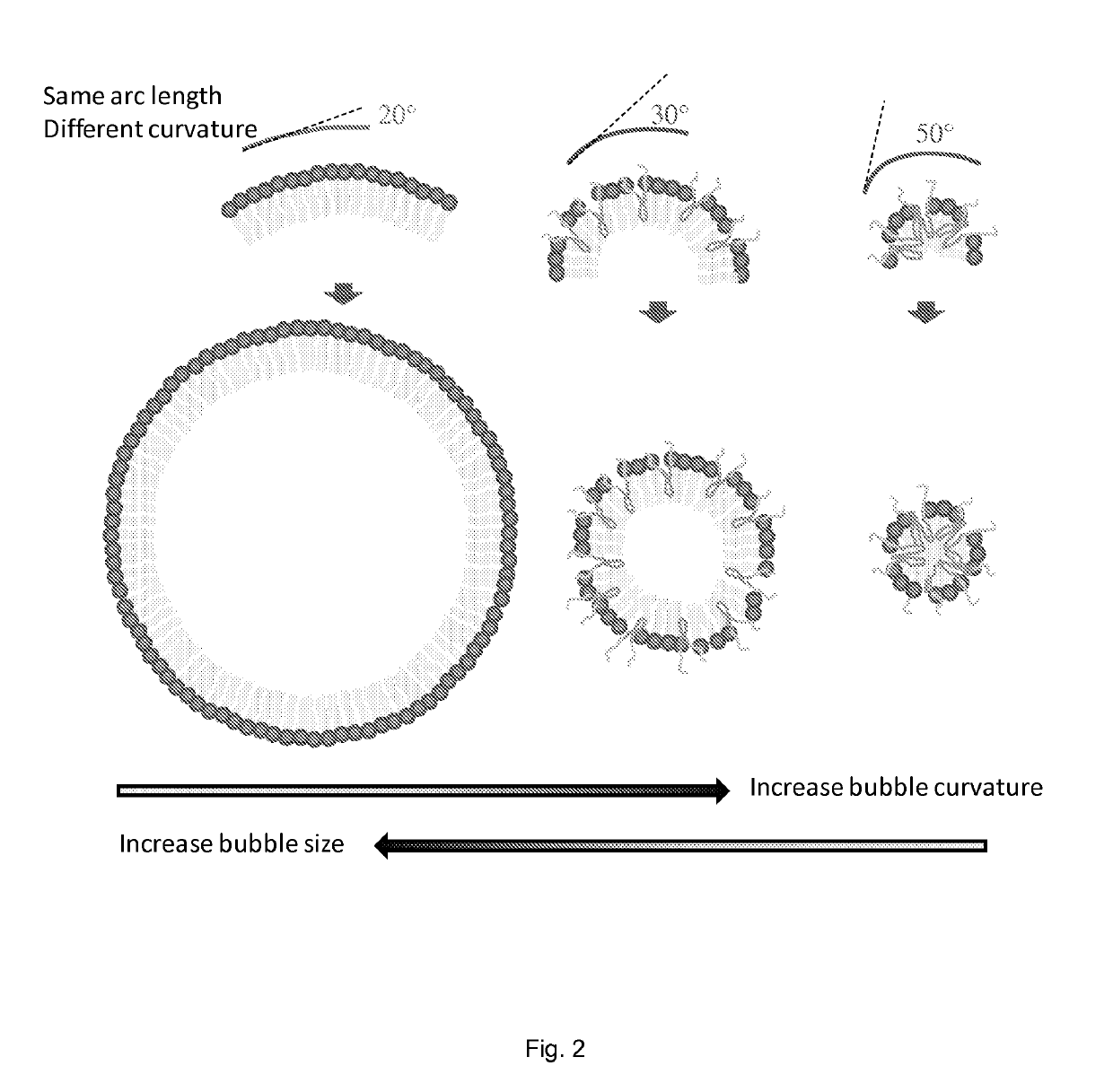
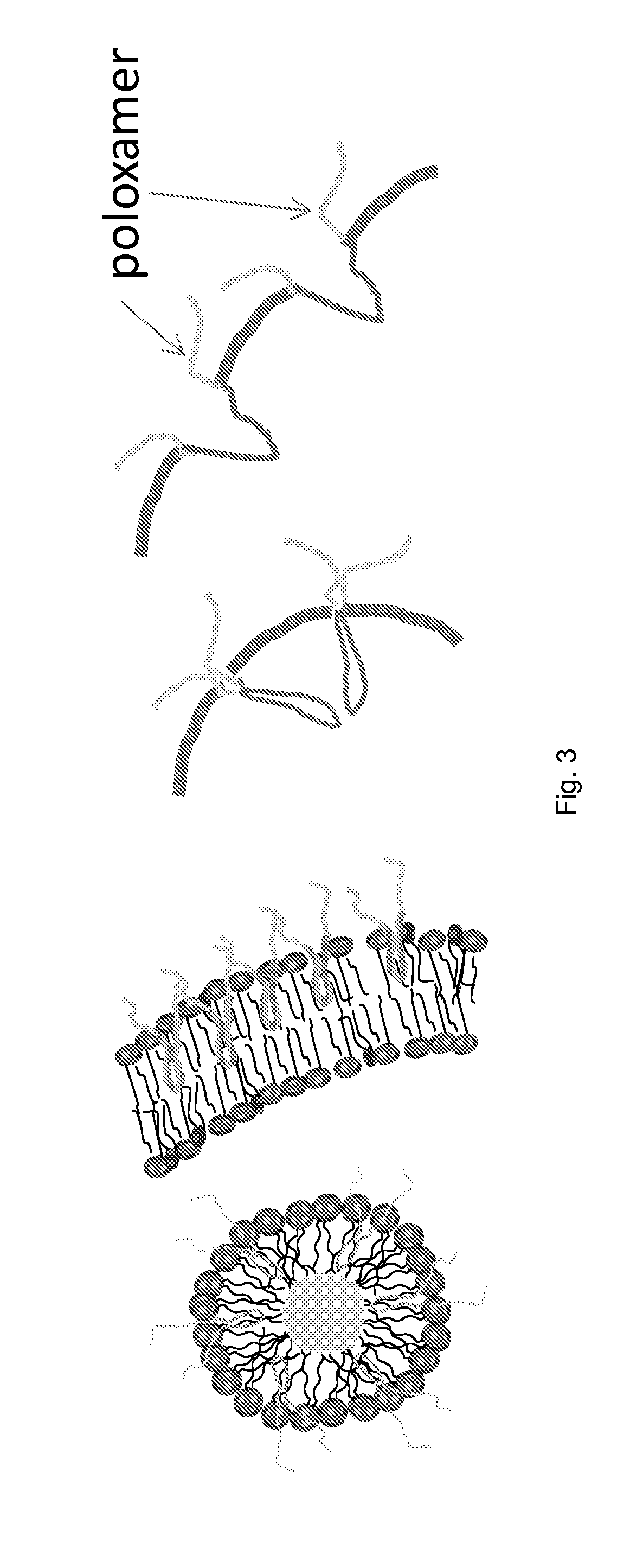
A stabilized nanobubble can include a membrane that defines at least one internal void, which includes at least one gas. The membrane can include at least one lipid and at least one nonionic triblock copolymer that is effective to control the size of the nanobubble without compromising in vitro and in vivo echogenicity of the nanobubble.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method and apparatus of echogenic catheter systems
PendingUS20180360424A1Easy to useComfortable procedureBalloon catheterOrgan movement/changes detectionMedicineCatheter
Methods and apparatuses for utilizing an integrated, automated aerating device for echogenicity are described. The aeration device can have a pressurized vessel to provide echogenic air bubbles independently of fluid delivered for sonohsyterosalpingography. The aeration device can selectively supply a gas in liquid during ultrasound and radiographic procedures for enhanced visualization of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
Owner:CROSS BAY MEDICAL INC
Acoustic streaming for fluid pool detection and identification
ActiveUS20170273658A1Inexpensive and fast and safe and convenient modalityReduce fieldImage enhancementImage analysisRelative displacementUltrasound attenuation
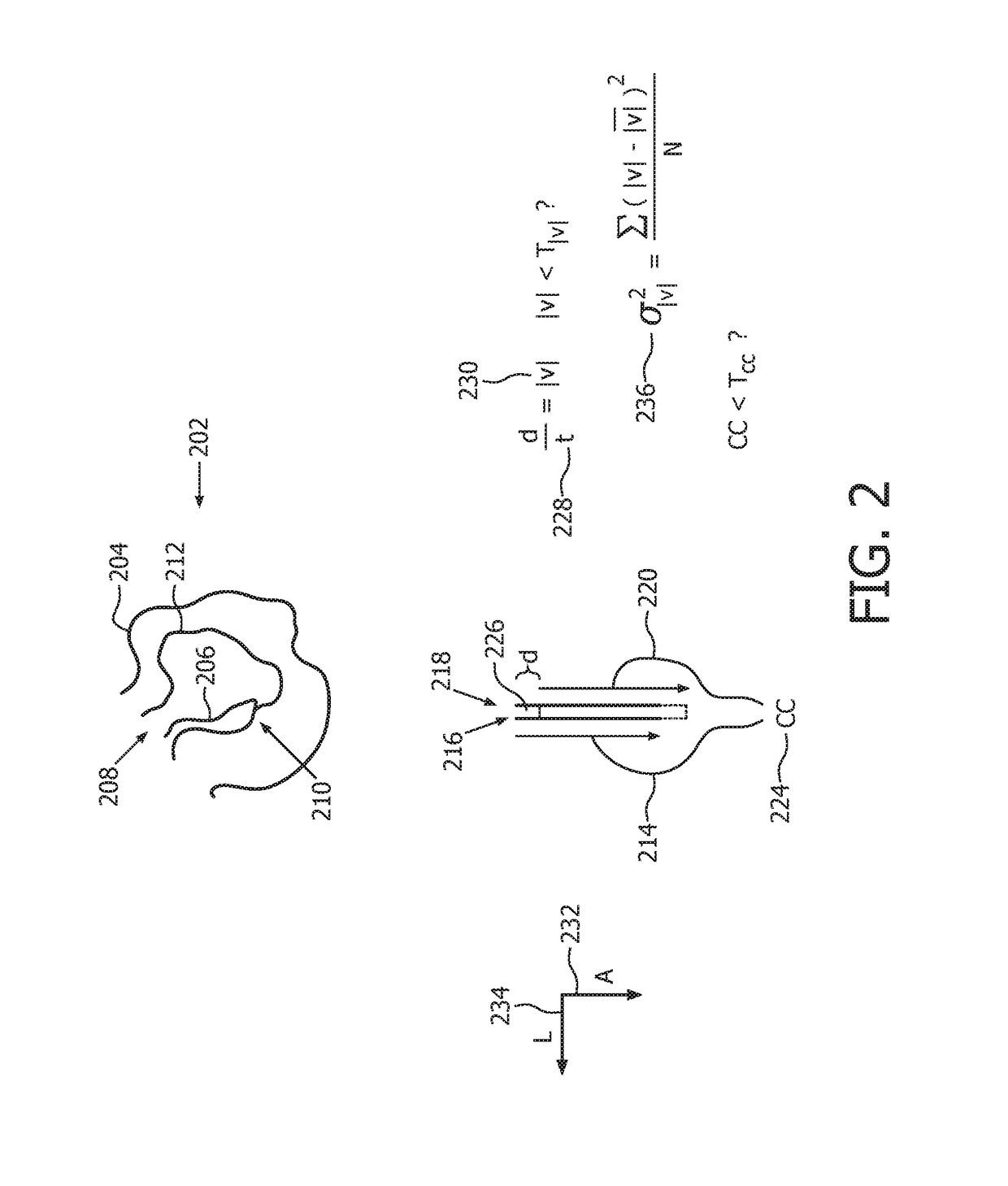
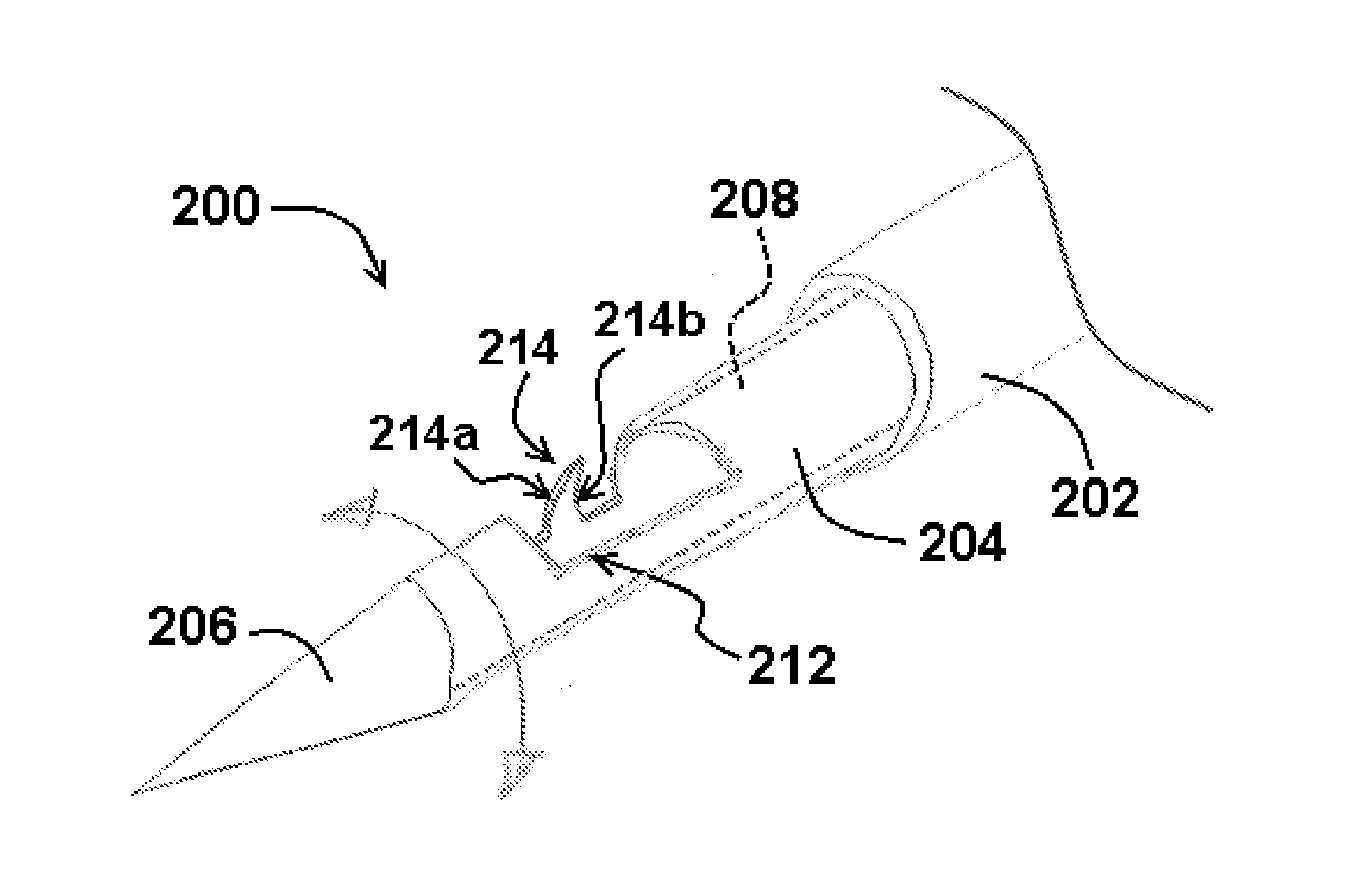
Ultrasound-based acoustic streaming for deciding whether material is fluid is dependent upon any one or more of a variety of criteria. Examples are displacement, speed (230), temporal or spatial flow variance, progressive decorrelation, slope or straightness of accumulated signal to background comparisons over time, and relative displacement to adjacent soft tissue. Echogenicity-based area identification is combinable with the above movement characteristic detection in the deciding. Fluid pool identification is performable from the area-limited acoustic streaming testing and ultrasound attenuation readings. Candidates from among the areas (210) are screenable based on specific shapes or bodily organs detected. Natural flow can be excluded from streaming detection by identification of blood vessels (206). Processing for each FAST ultrasound view (202), or for the entire procedure, is performable automatically, without need for user intervention or with user intervention to identify suspected areas.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Rotary sample-collection needle
InactiveUS20140100448A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesTissue CollectionEchogenicity
A rotary tissue-collection needle configured is provided with a closed distal tip and a distal aperture including a generally longitudinal cutting edge configured to excise tissue into the aperture for collection by rotation of the needle. The needle may be provided as part of a system including an outer sheath within which the needle may be rotated. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Ablation with echogenic insulative sheath
InactiveUS7799022B2Diameter minimizationIncrease echogenicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesPolyether ether ketoneTissue ablation
Tissue ablation probes are provided. Each tissue ablation probe comprises an electrically conductive probe shaft, at least one tissue ablation electrode carried by a distal end of the probe shaft, and an electrically insulative outer sheath disposed on the probe shaft. The sheath is at least partially composed of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and another material comprising condensed-phase particles interspersed throughout the PEEK to increase the echogenicity of the outer sheath. The durability of the PEEK allows the sheath to be formed as thinly as possible, thereby minimizing the diameter of the ablation probe, while the inclusion of condensed-phase particles within the PEEK does not significantly degrade the durability of the sheath.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided notched biopsy needle
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Medical devices with non-uniform coatings for enhanced echogenicity
The invention provides medical devices comprising improved non-uniform coatings for ultrasound detection, which provide optimal ultrasound images. Methods for preparing such devices are also provided.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy needle
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine- needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
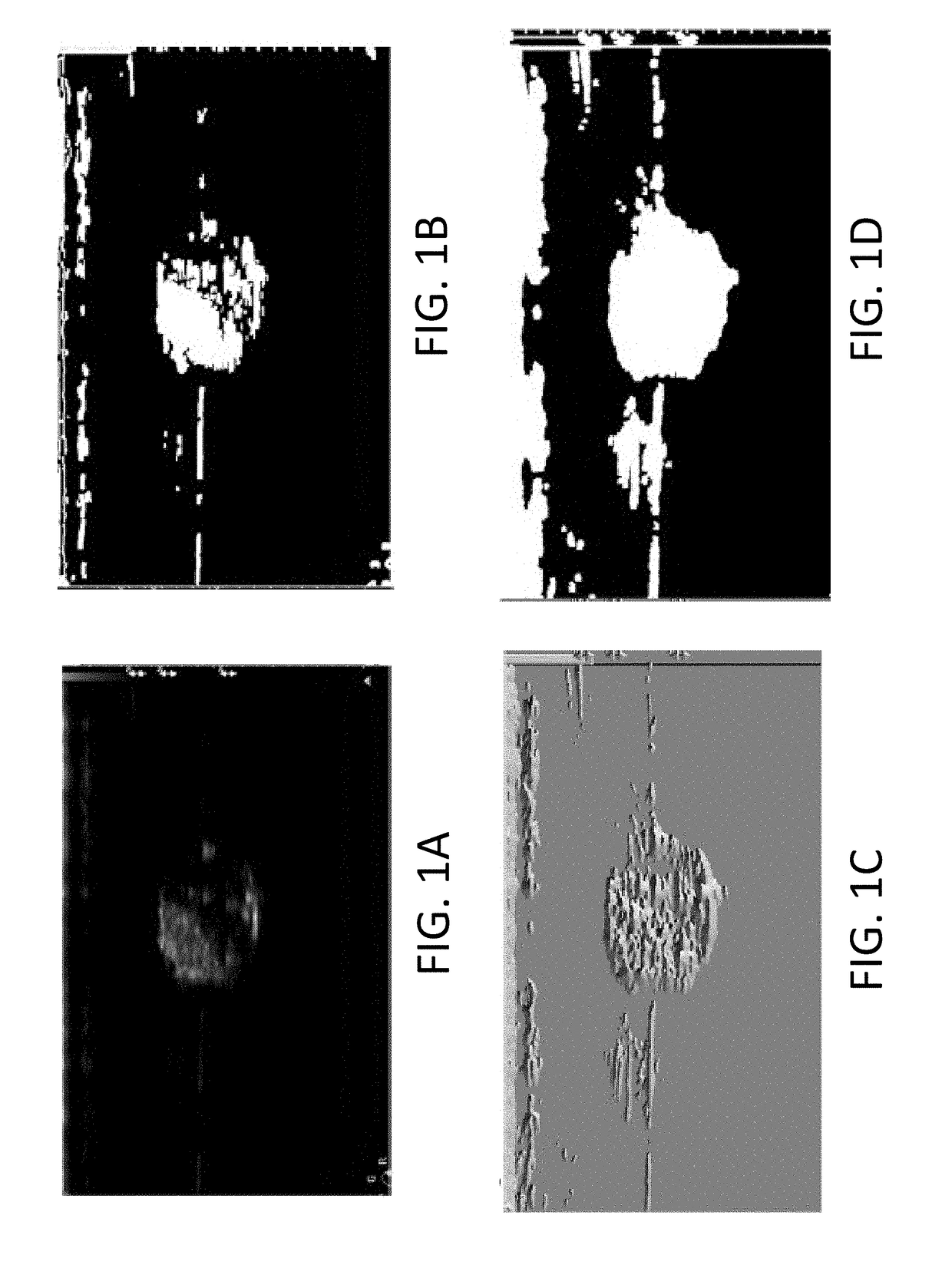
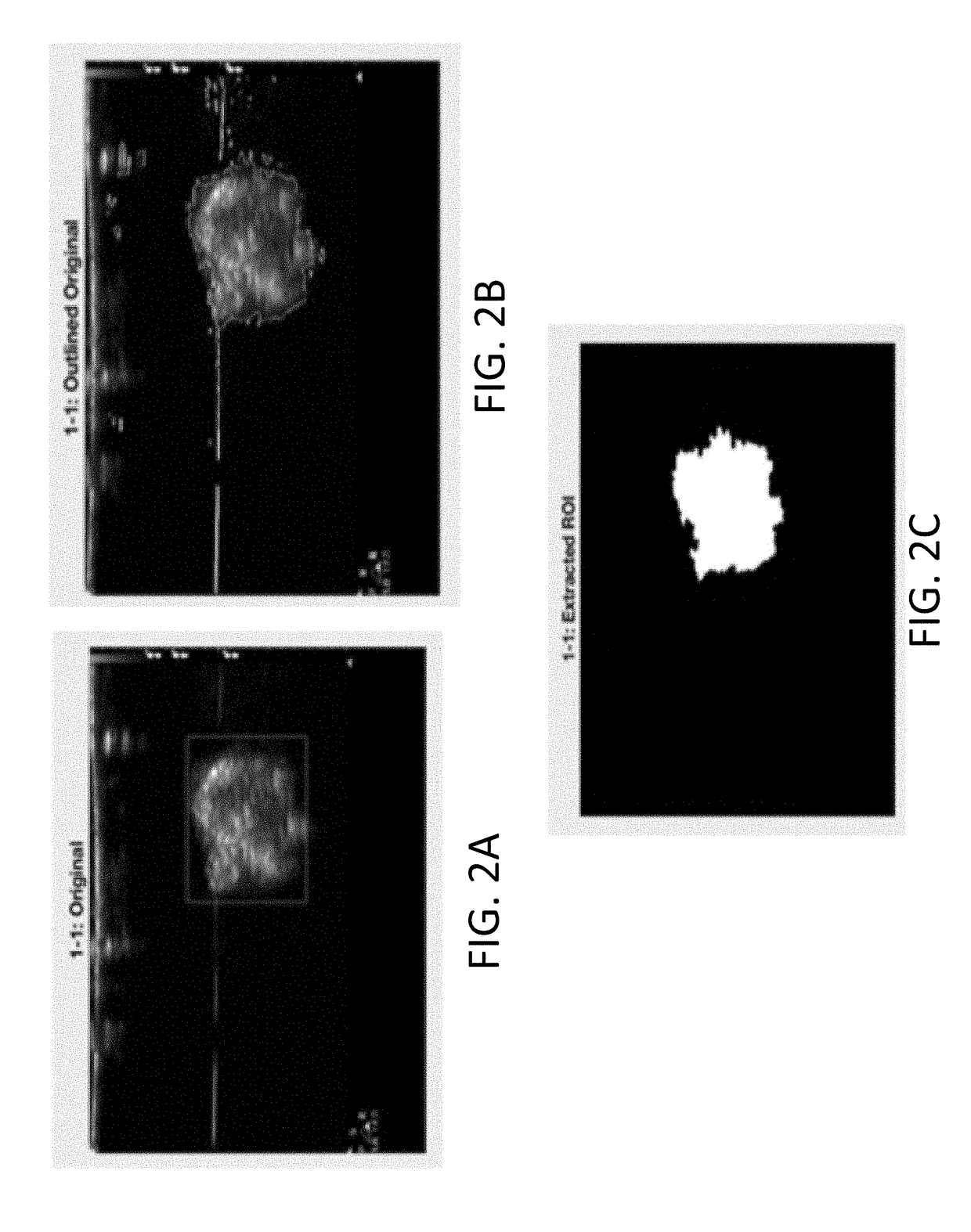
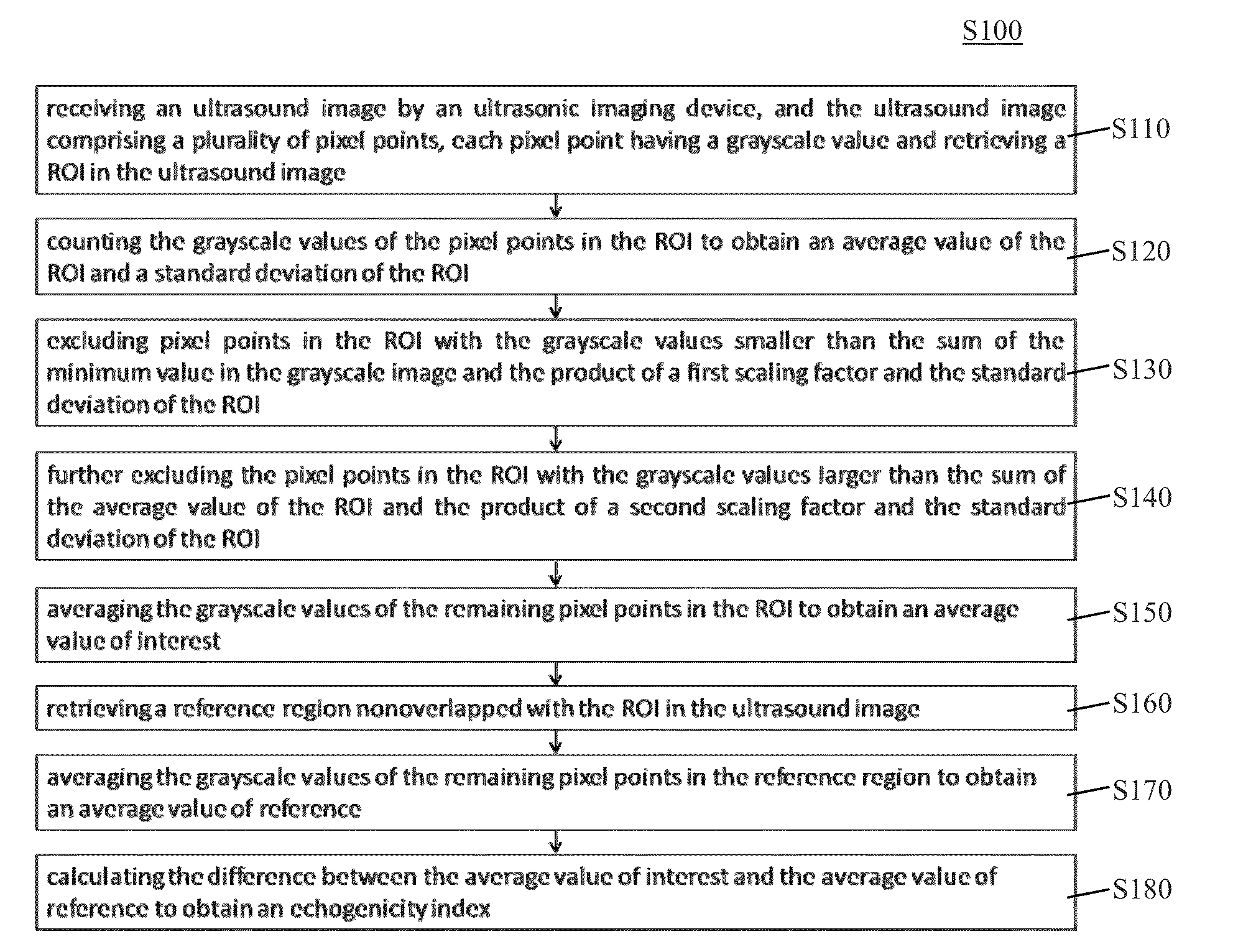
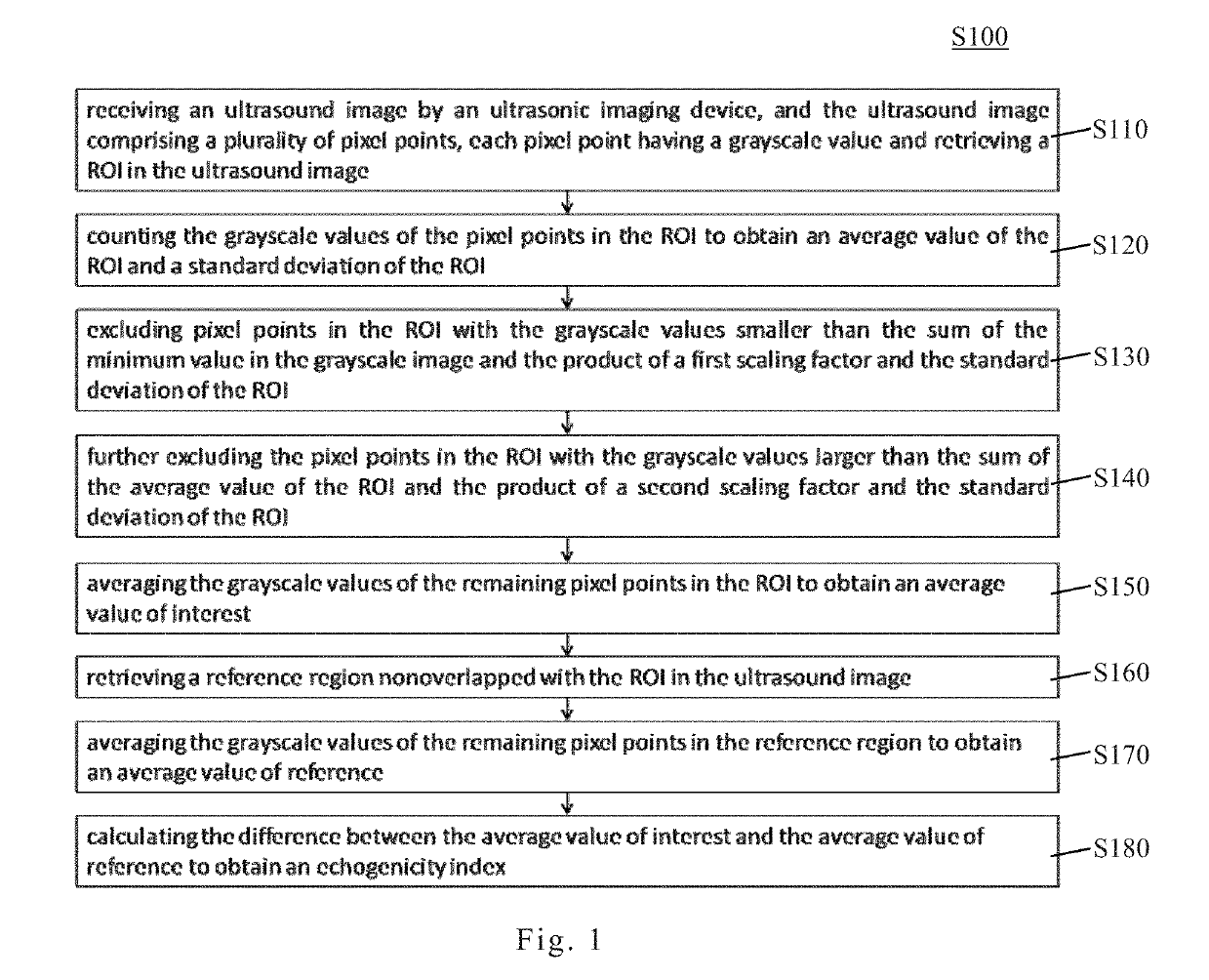
Echogenicity quantification method and calibration method for ultrasonic device using echogenicity index
ActiveUS20150086094A1Improve accuracyStrong specificityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSonification
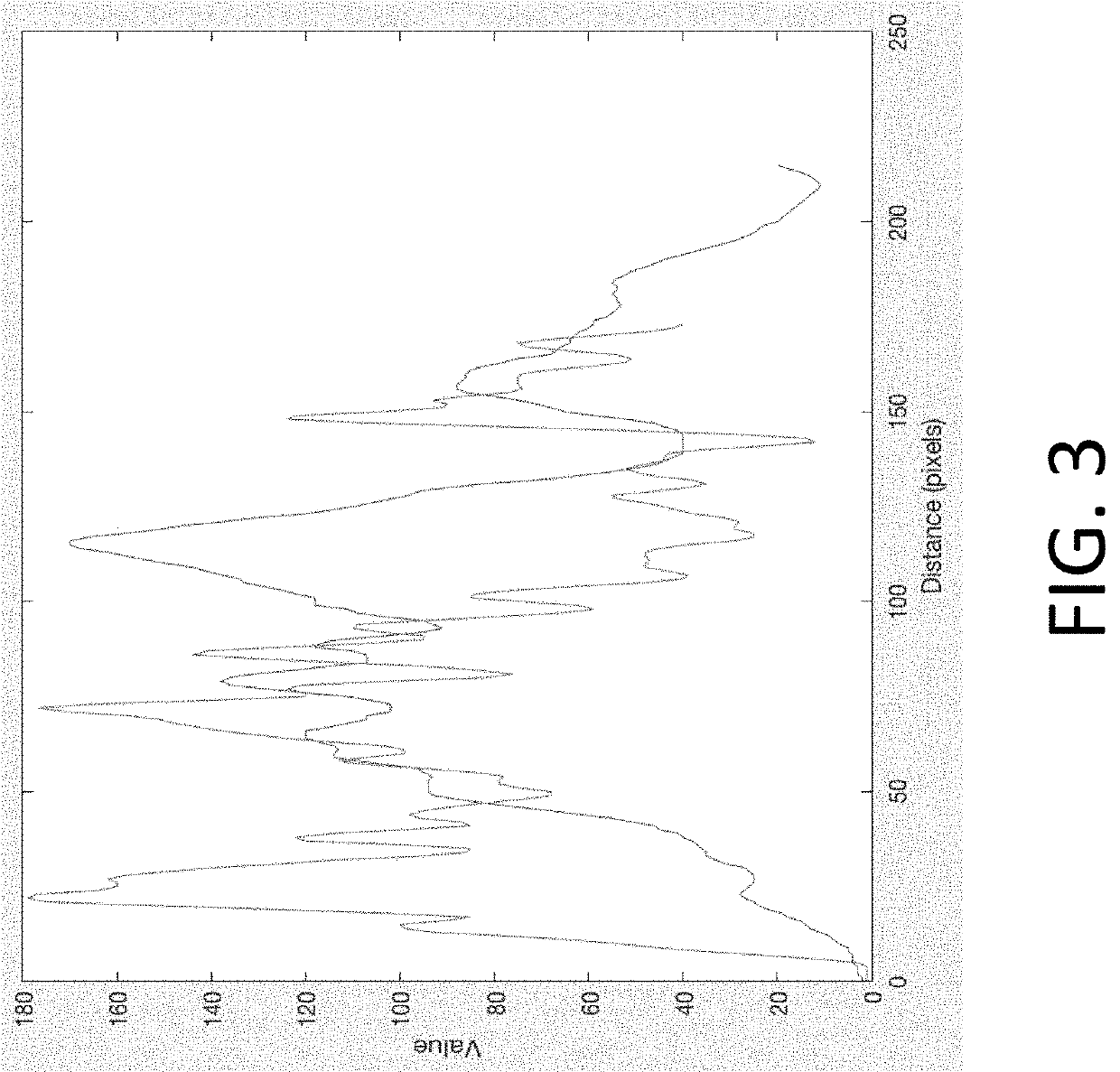
An echogenicity quantification method and a calibration method for ultrasonic device using echogenicity index are disclosed. The method includes: receiving an ultrasound image which comprises a plurality of grayscale pixels; choosing a region of interest (ROI); calculating the values of the grayscale pixels in ROI to obtain average value and standard deviation; excluding pixels in ROI with the grayscale value smaller than the sum of the minimum value in the grayscale image and the product of a first scaling factor and the standard deviation, and larger than the sum of the average value and the product of a second scaling factor and the standard deviation; averaging the values of the remaining grayscale pixels in ROI to obtain an average value of interest; choosing a reference region; averaging the values of the remaining grayscale pixels in the reference region to obtain an average value of reference; and calculating the difference between the average value of interest and the average value of reference to obtain an echogenicity index.
Owner:AMCAD BIOMED CORP
Medical probe with echogenic and insulative properties
Tissue ablation probes and methods of using tissue ablation probes are provided. Each tissue ablation probe comprises an electrically conductive probe shaft, at least one tissue ablation electrode carried by a distal end of the probe shaft, and one or both of an insulative element and an echogenic element. The insulative element and / or the echogenic element may, e.g., be affixed to, or selectively removable from, the probe shaft to increase the insulative capability and echogenicity of the probe. An echogenic sheath having the insulative element and / or the echogenic element may be slidably disposed over the probe shaft to impart insulative and echogenic properties to the probe shaft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and methods for automated image recognition of implants and compositions with long-lasting echogenicity
PendingUS20220015742A1Increase awarenessComputationally efficientImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound contrast mediaImage conversion
Owner:CONTRALINE INC
Fiducial deployment needle system
Embodiments include a fiducial deployment system. A fiducial may include dimples to enhance echogenicity and / or to provide for engagement with a delivery cannula or stylet. The needle system may be configured to deliver a plurality of fiducials to a target location in serial fashion, one at a time, when the fiducials are coaxially disposed around a central deployment member that may be embodied as a delivery cannula or stylet. In certain embodiments, echogenic placement of fiducials may present certain advantages. An elongate structure may be included that is configured to distally advance fiducials along the deployment member.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method for enhancing echogenicity and decreasing attenuation of microencapsulated gases
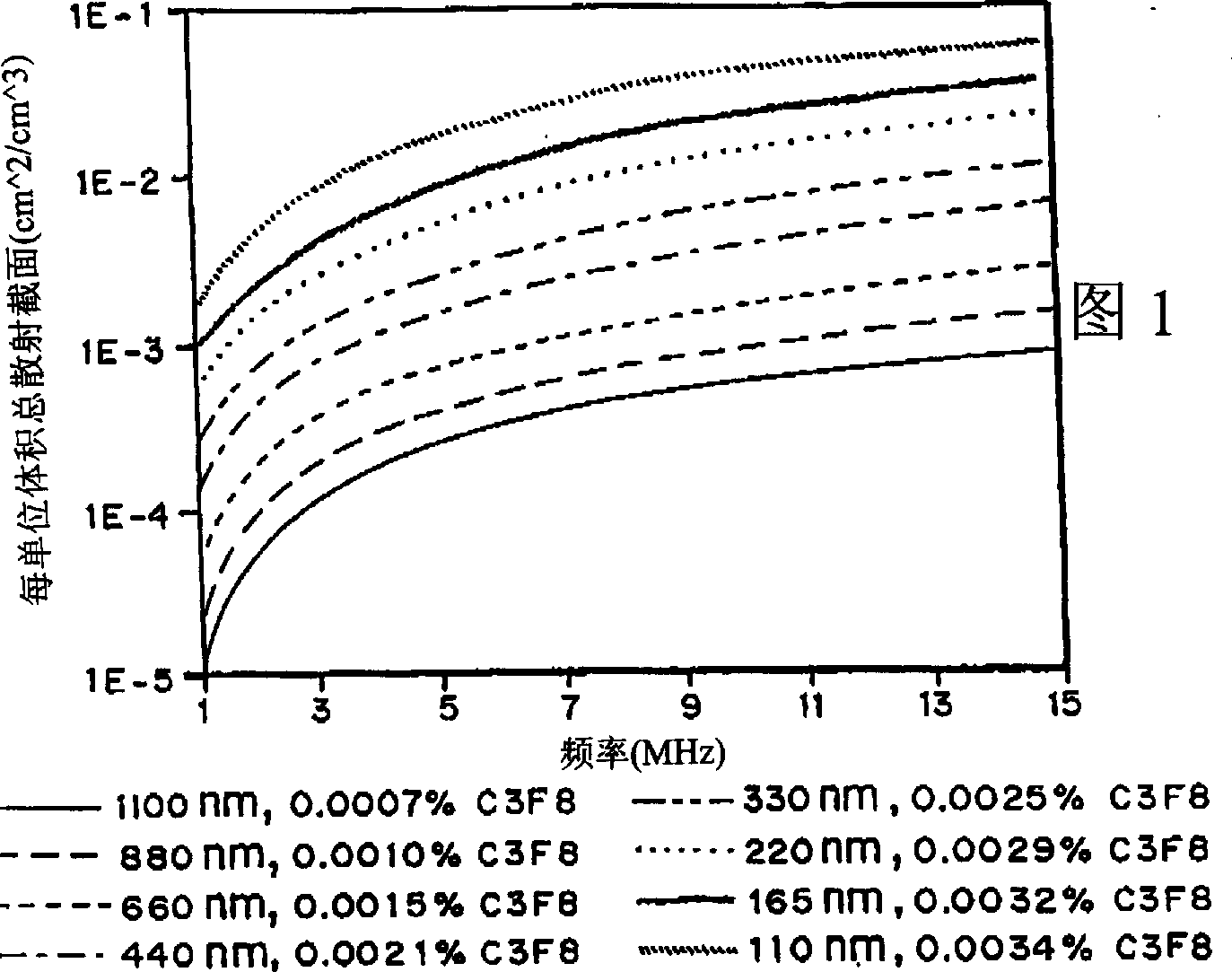
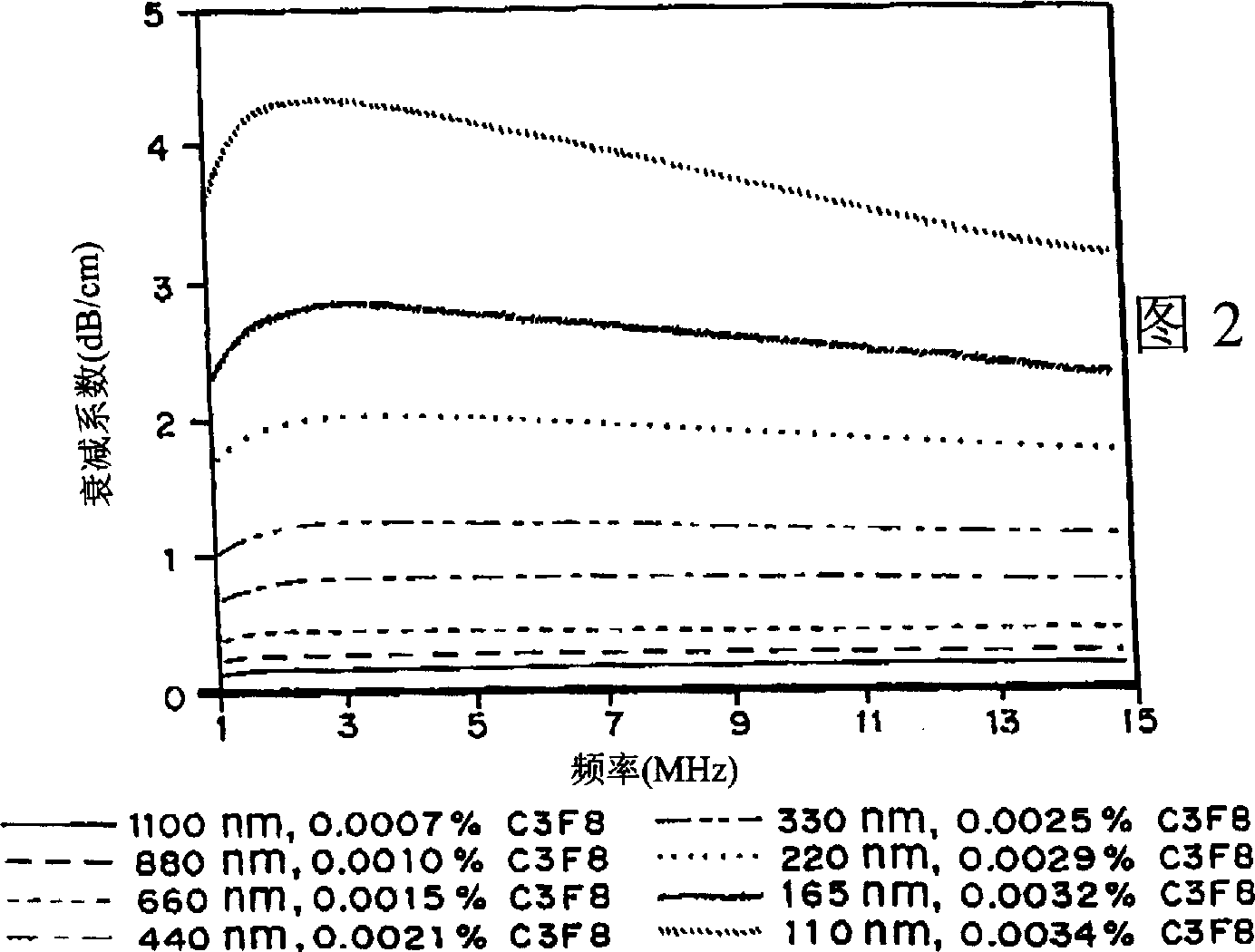
InactiveCN1261809AEnhanced echoSmall attenuationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsMicrospherePolyethylene glycol
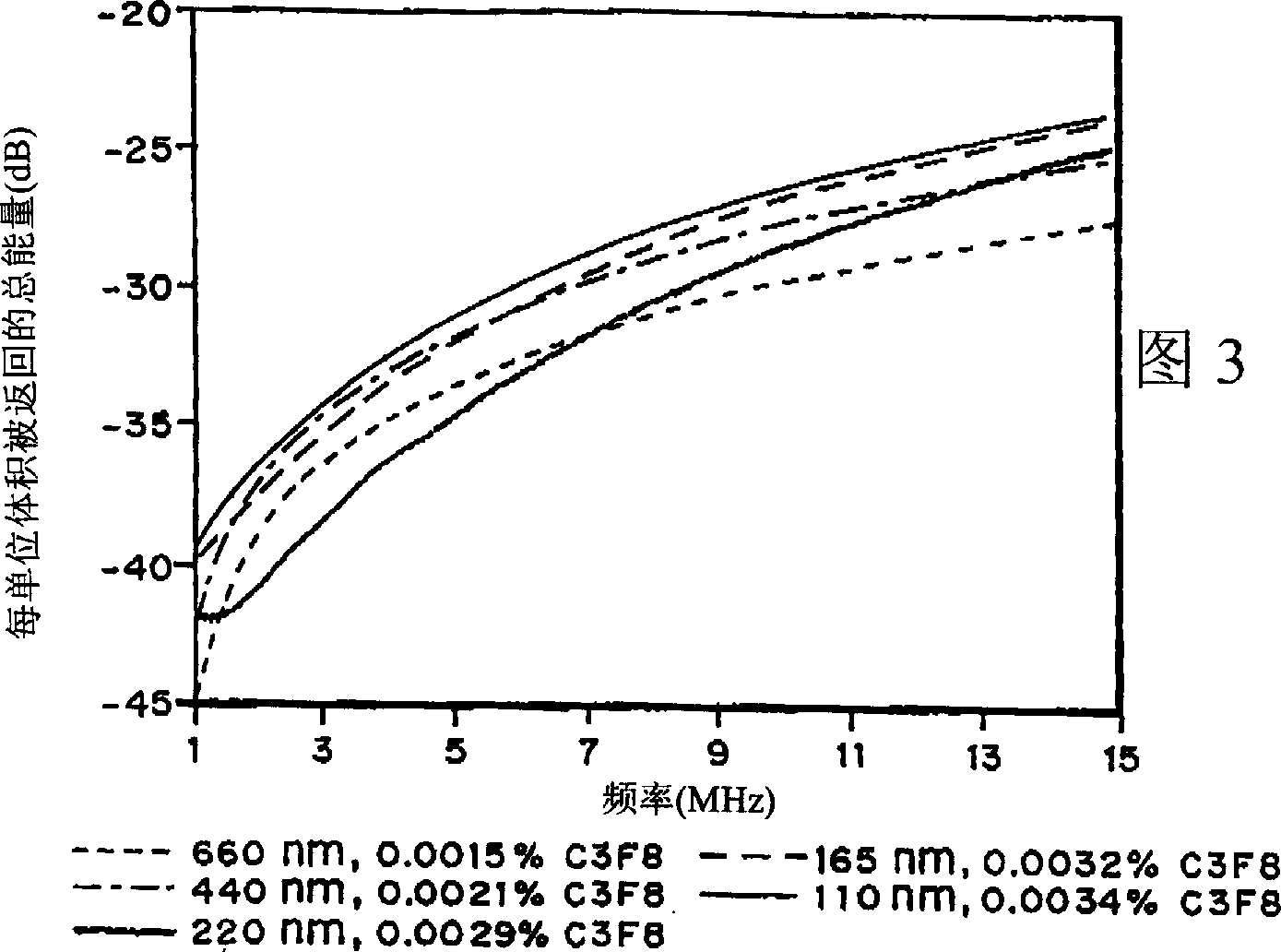
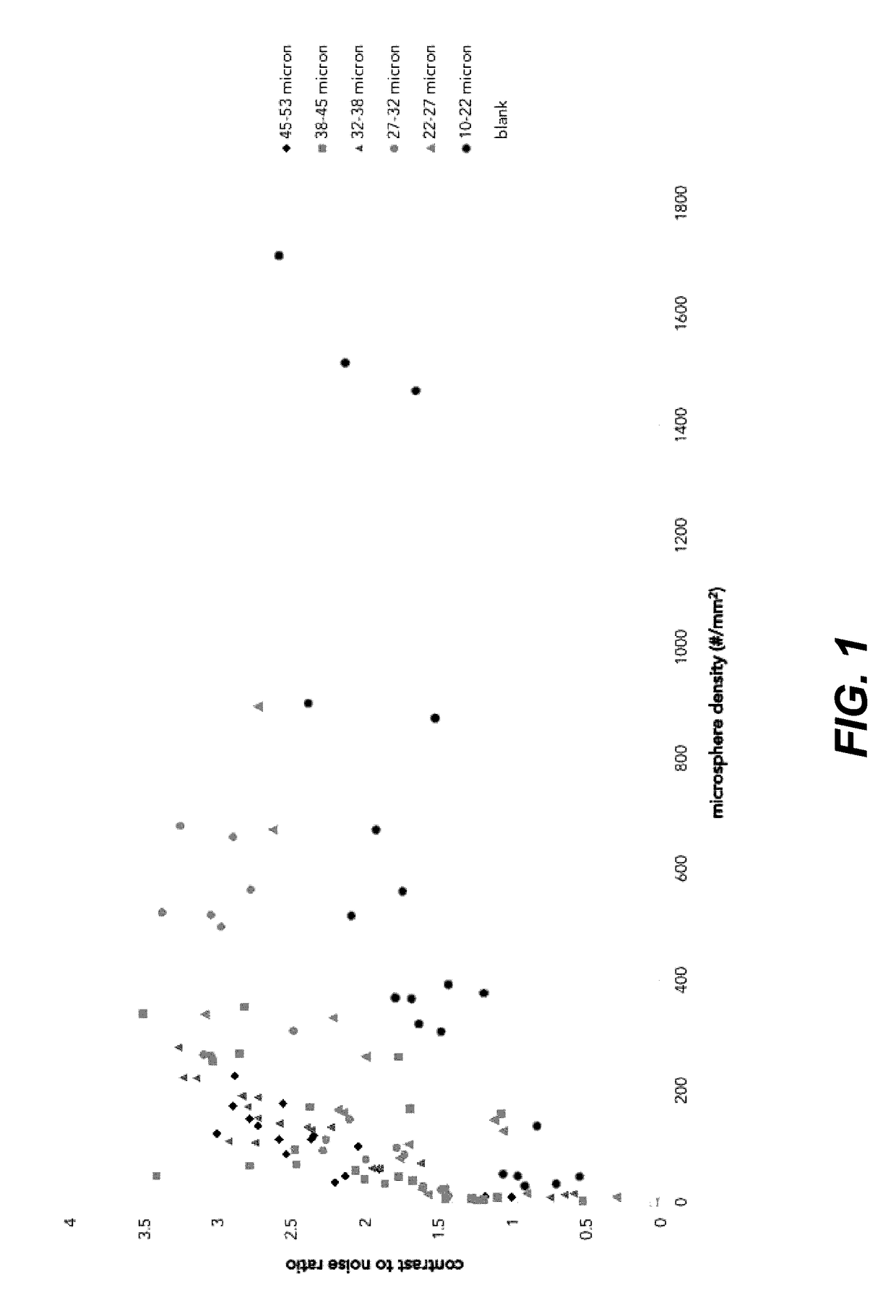
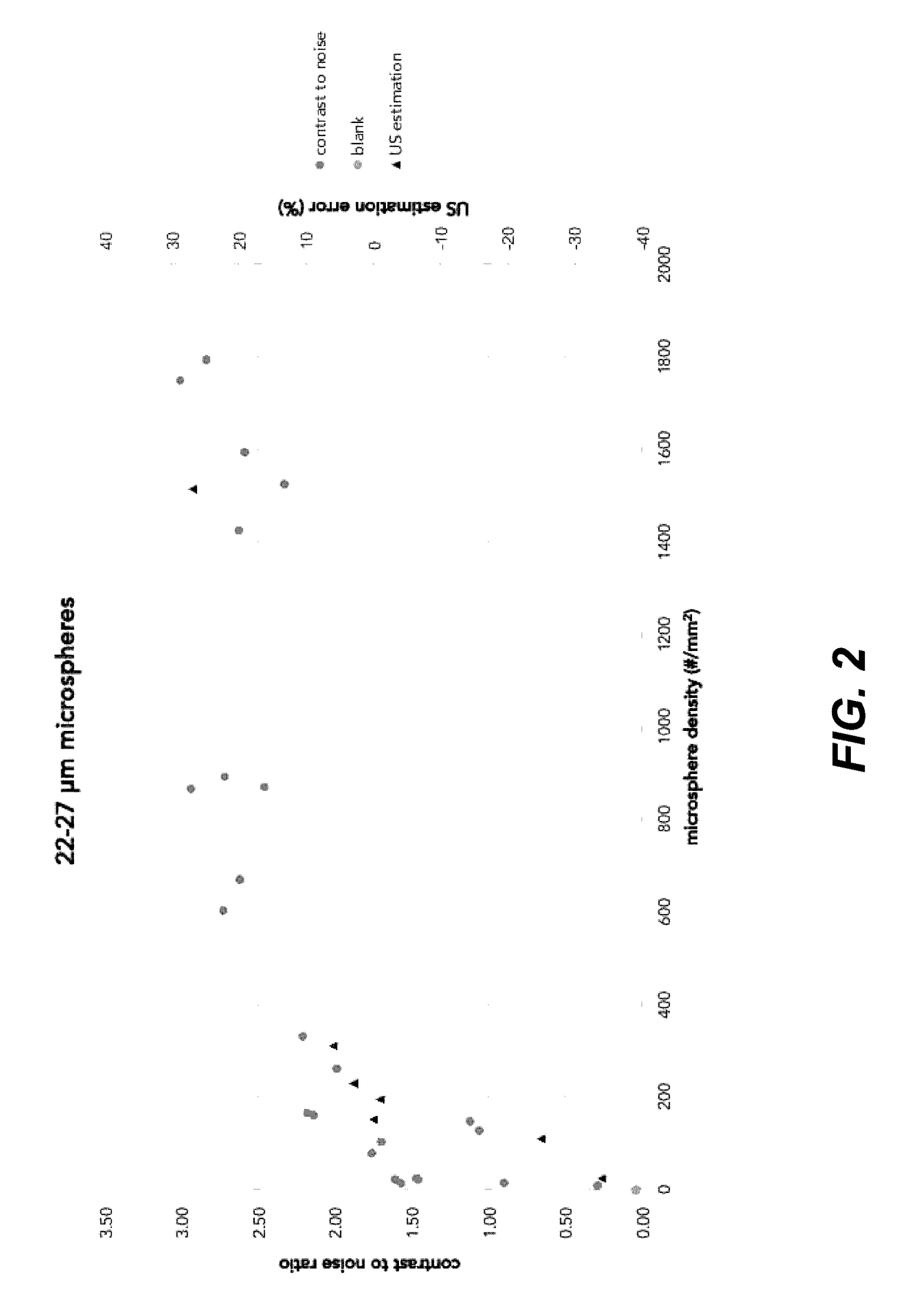
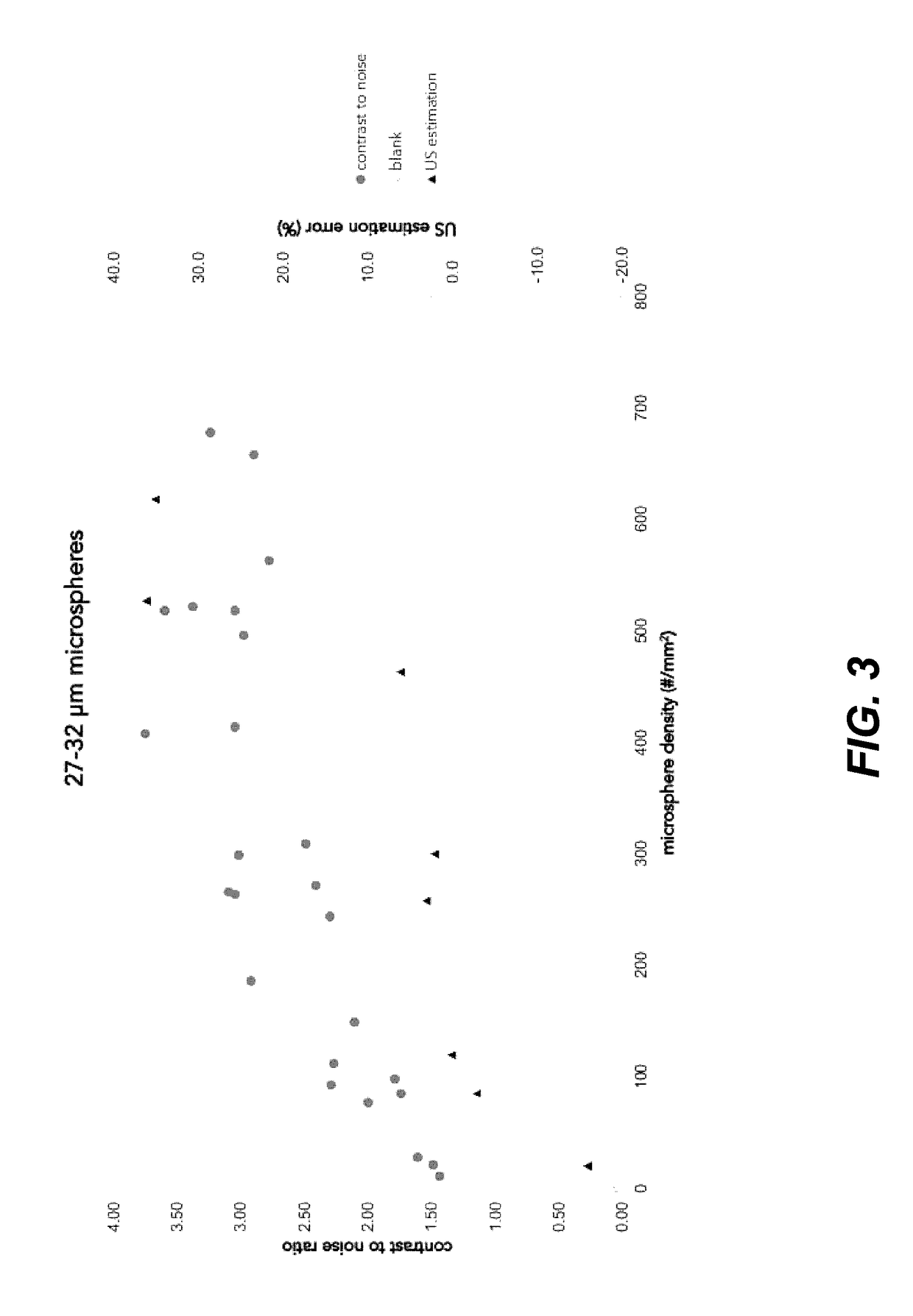
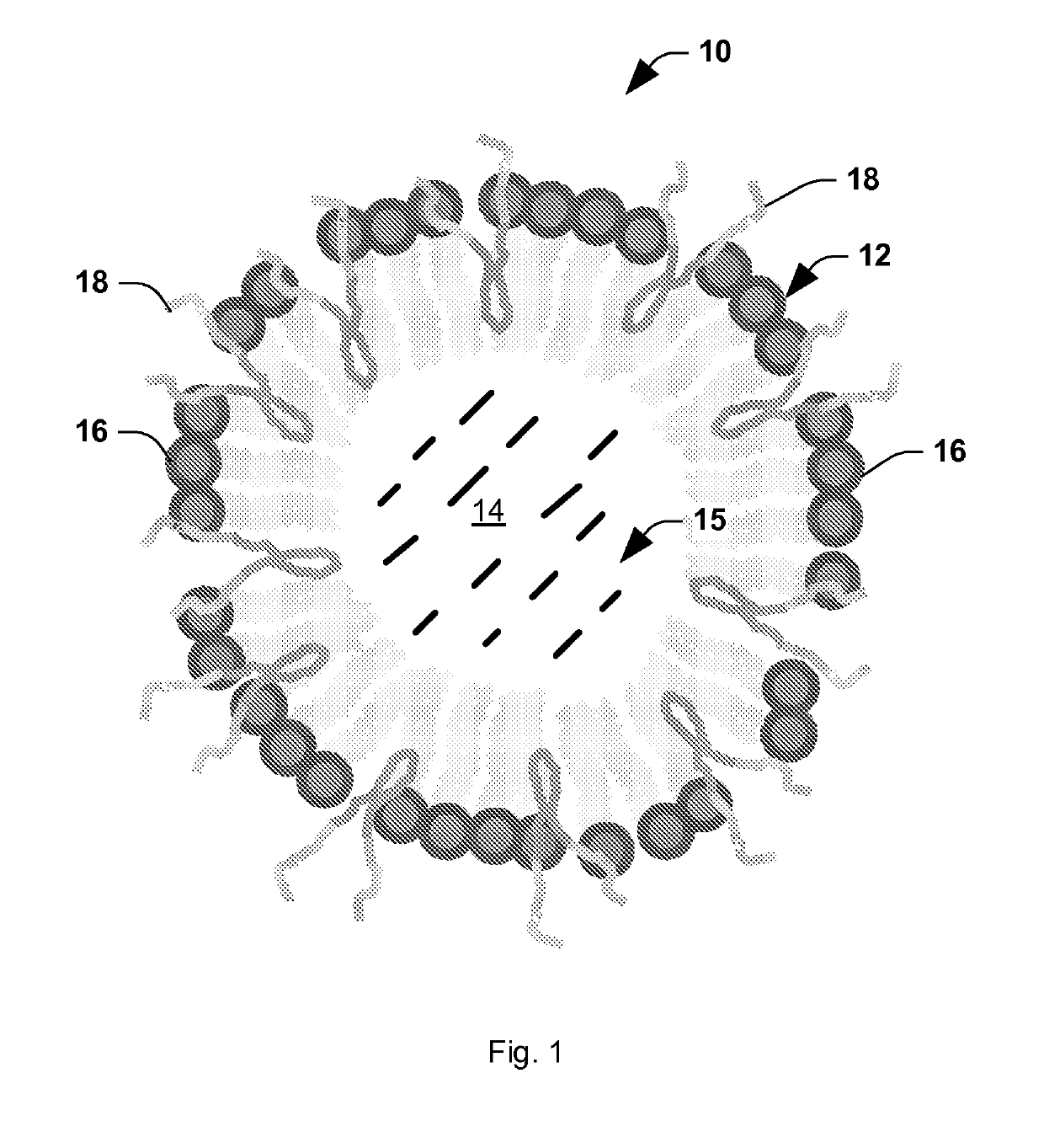
It has been discovered that microparticles formed from natural or synthetic polymer with thicker walls have significantly enhanced echogenicity as compared with microparticles having thinner walls. The effect of wall thickness has been determined experimentally as well as inserted into a formula for use in predicting the optimum conditions. In the preferred embodiment, the polymers are synthetic biodegradable polymers and the wall thickness is between about 100 and 660 nm, although wall thicknesses from about 20 nm to in excess to 500 nm can be used. The microparticles are manufactured with a diameter suitable for the targeted tissue to be imaged, for example, with a diameter for between 0.5 and 8 microns for intravascular administration, and a diameter of between 0.5 and 5 mm for oral administration for imaging of the gastrointestinal tract or other lumens. Preferred polymers are polyhydroxy acids such as polylactic acid-co-glycolic acid, polylactide or polyglycolide, most preferably conjugated to polyethylene glycol or other materials inhibiting uptake by the reticuloendothelial system (RES). The microspheres may be used in a variety of ultrasound imaging applications including cardiology applications, blood perfusion applications as well as for organ and peripheral vein imaging.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Medical devices with coatings for enhanced echogenicity
ActiveUS20150351721A1Improve visibilityBetter the user can locate the objectSurgical needlesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The disclosure provides medical devices comprising improved coatings for ultrasound detection, which provide optimal ultrasound images. Methods for preparing such devices are also provided.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Medical devices with coatings for enhanced echogenicity
ActiveUS9681852B2Improve visibilityBetter the user can locate the objectSurgical needlesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismRadiologyUltrasonic testing
The disclosure provides medical devices comprising improved coatings for ultrasound detection, which provide optimal ultrasound images. Methods for preparing such devices are also provided.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Stabilized nanobubbles for diagnostic and therapeutic applications
ActiveUS10357575B2Promote extravasationInhibit expressionEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsLiposomal deliveryIn vivoCopolymer
A stabilized nanobubble can include a membrane that defines at least one internal void, which includes at least one gas. The membrane can include at least one lipid and at least one nonionic triblock copolymer that is effective to control the size of the nanobubble without compromising in vitro and in vivo echogenicity of the nanobubble.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Endoscopic biopsy needle with coil sheath
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features. A coated-wire sheath through which the needle is slidably disposed includes an overcoating that is thicker along a distal length and thinner along a proximal length.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
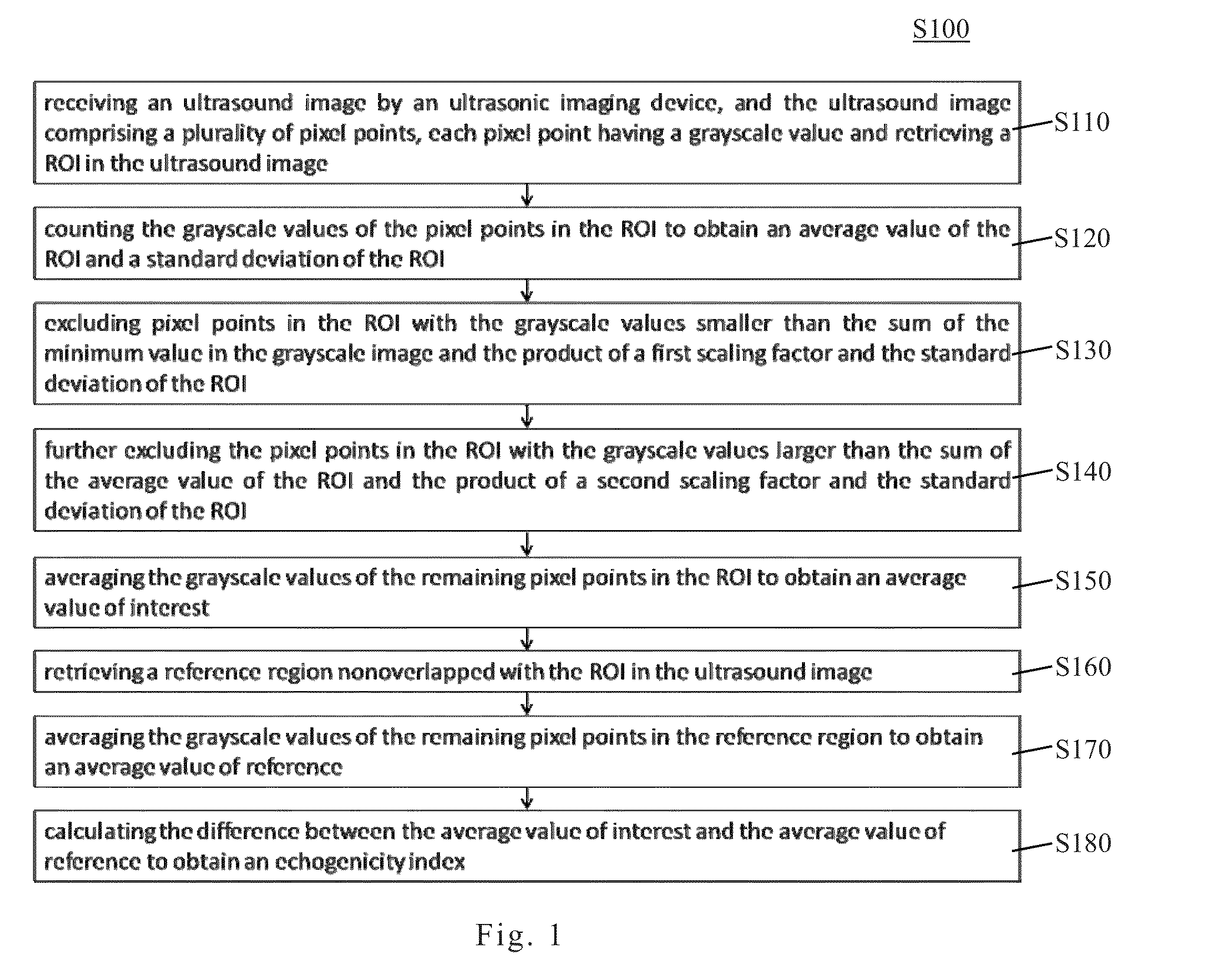
Echogenicity quantification method and calibration method for ultrasonic device using echogenicity index
ActiveUS10249037B2Improve accuracyStrong specificityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSonification
An echogenicity quantification method and a calibration method for ultrasonic device using echogenicity index are disclosed. The method includes: receiving an ultrasound image which comprises a plurality of grayscale pixels; choosing a region of interest (ROI); calculating the values of the grayscale pixels in ROI to obtain average value and standard deviation; excluding pixels in ROI with the grayscale value smaller than the sum of the minimum value in the grayscale image and the product of a first scaling factor and the standard deviation, and larger than the sum of the average value and the product of a second scaling factor and the standard deviation; averaging the values of the remaining grayscale pixels in ROI to obtain an average value of interest; choosing a reference region; averaging the values of the remaining grayscale pixels in the reference region to obtain an average value of reference; and calculating the difference between the average value of interest and the average value of reference to obtain an echogenicity index.
Owner:AMCAD BIOMED CORP
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy needle
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine- needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus of echogenic catheter systems
Methods and apparatuses for utilizing an integrated, automated aerating device for echogenicity are described. The aeration device can have a pressurized vessel to provide echogenic air bubbles independently of fluid delivered for sonohsyterosalpingography. The aeration device can selectively supply a gas in liquid during ultrasound and radiographic procedures for enhanced visualization of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
Owner:CROSS BAY MEDICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com