Patents
Literature
41 results about "Brachytherapy source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Invasive microwave antenna array for hyperthermia and brachytherapy
ActiveUS20040243200A1Increase oxygenationEnhance tumor blood flowMicrowave therapySurgical instruments using microwavesElectrical conductorEngineering
A microwave hyperthermia apparatus that can be inserted into the body which includes a hollow central tube for the insertion of radioactive therapy sources. The use of a coaxial transmission line impedance transformation along the insertable portion of the coaxial cable enables a reduction in the characteristic impedance by increasing the outer diameter of the inner coaxial conductor so that the center conductor can be a metal tube. If the ratio of the outer coaxial conductor diameter vs. the inner coaxial conductor is decreased, the characteristic impedance of the transmission line is lowered. This enables the inner conductor diameter to increase sufficiently to make the central hollow opening large enough to receive standard radioactive sources therein. This provides for a good impedance match that improves microwave energy efficiency while at the same time permitting a large hollow center opening. The combination of the microwave antenna device and brachytherapy sources provides for enhanced effectiveness when the two treatments are delivered simultaneously or in close time proximity to each other.
Owner:PYREXAR MEDICAL
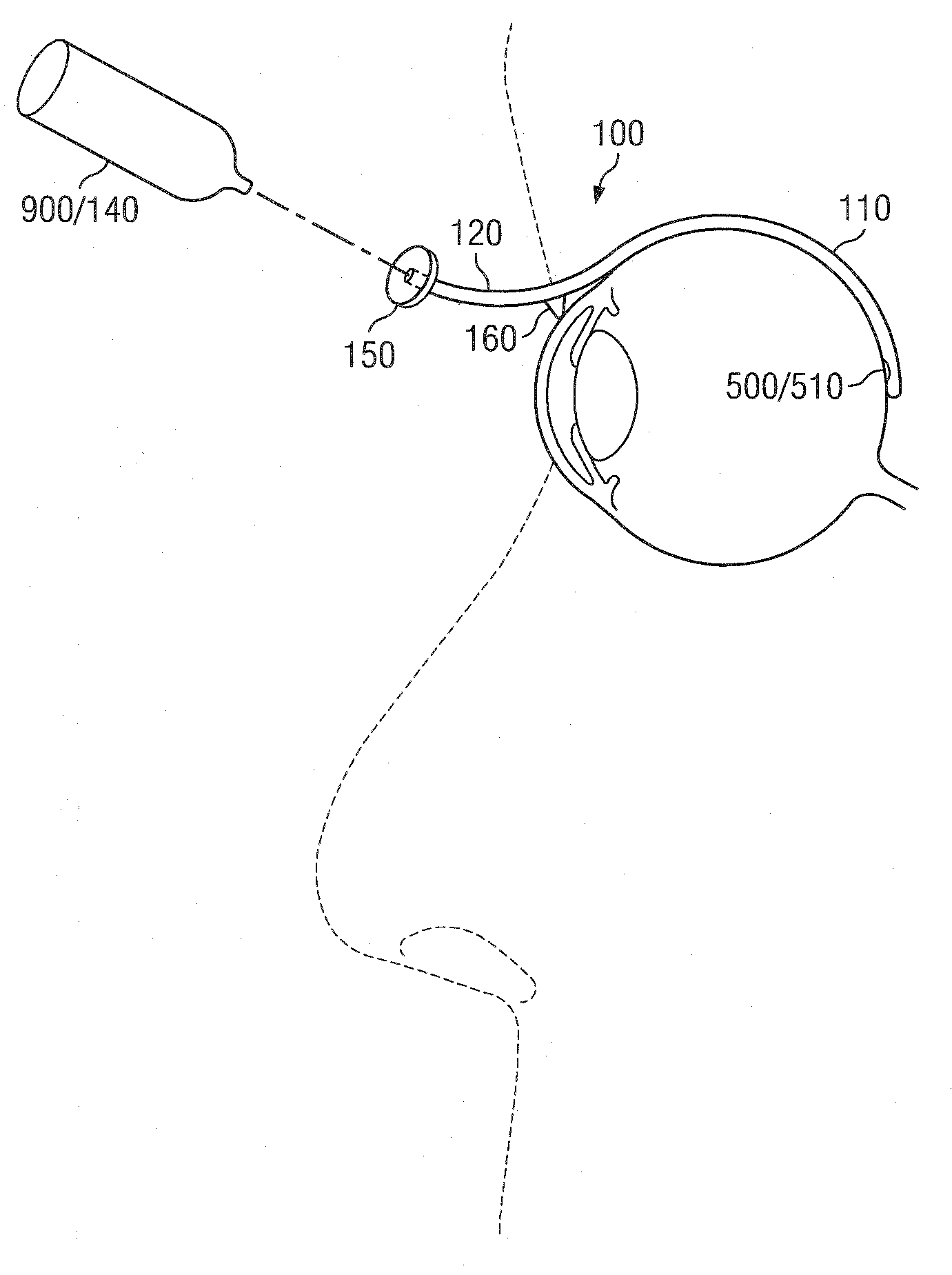
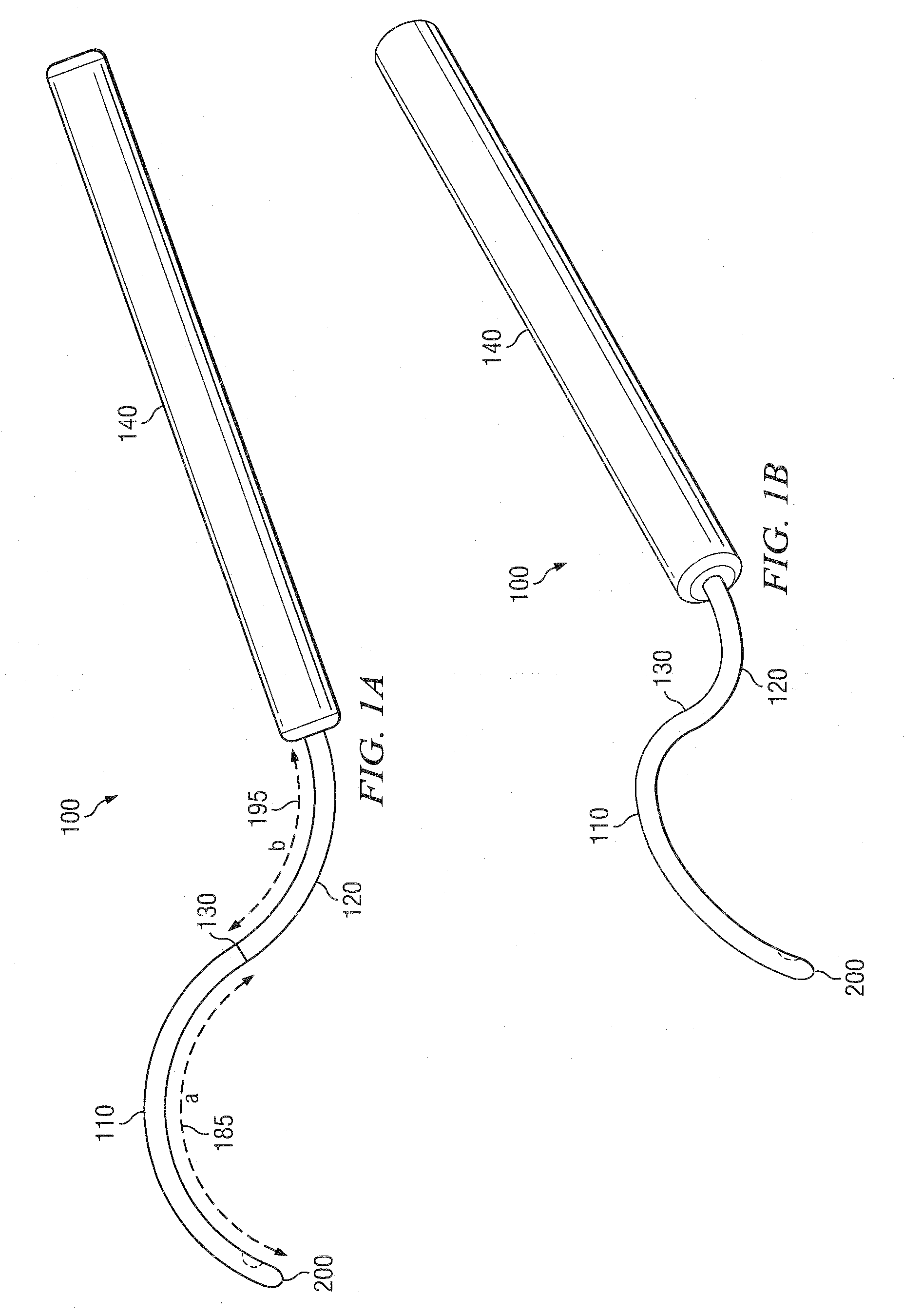
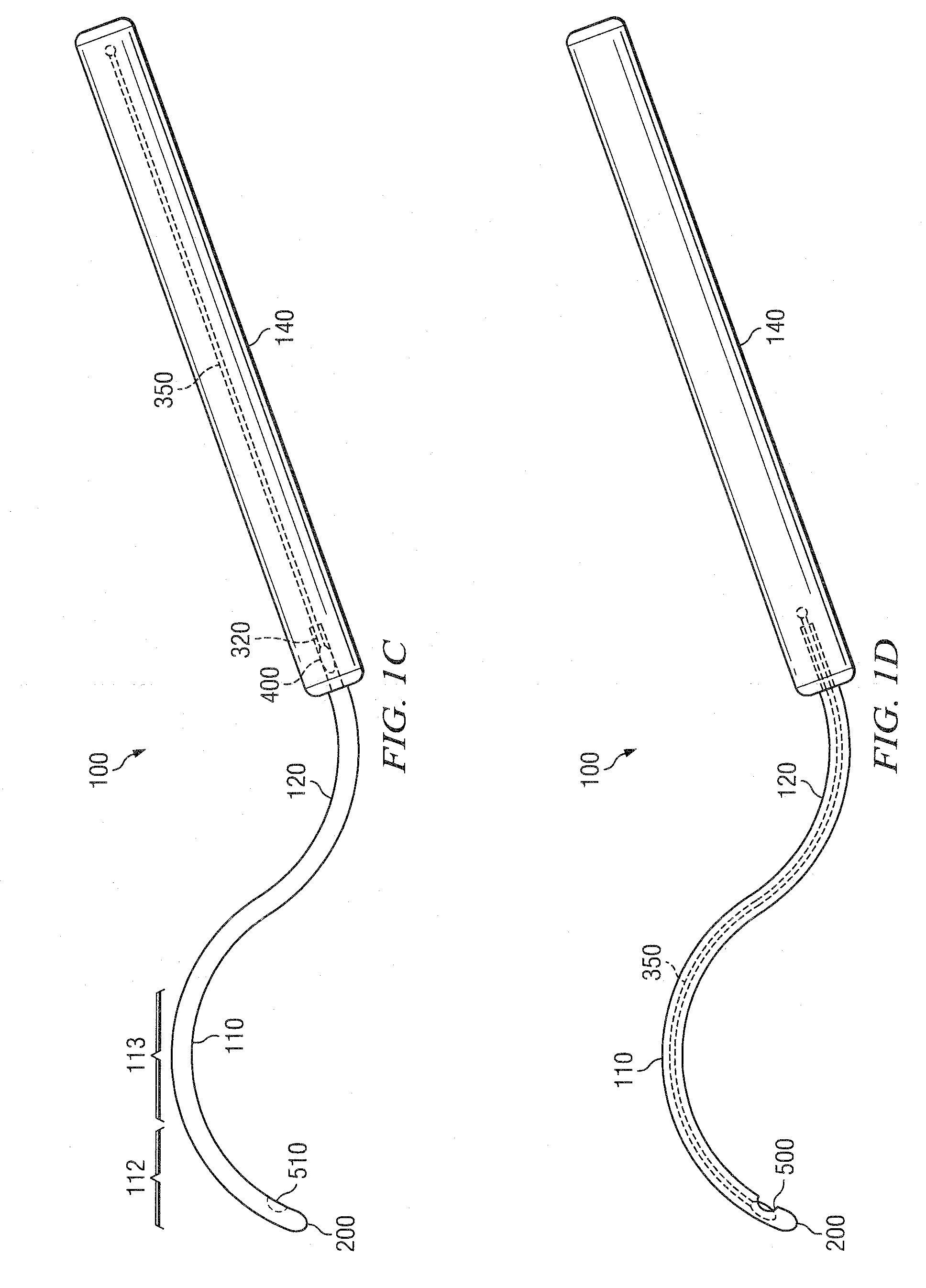
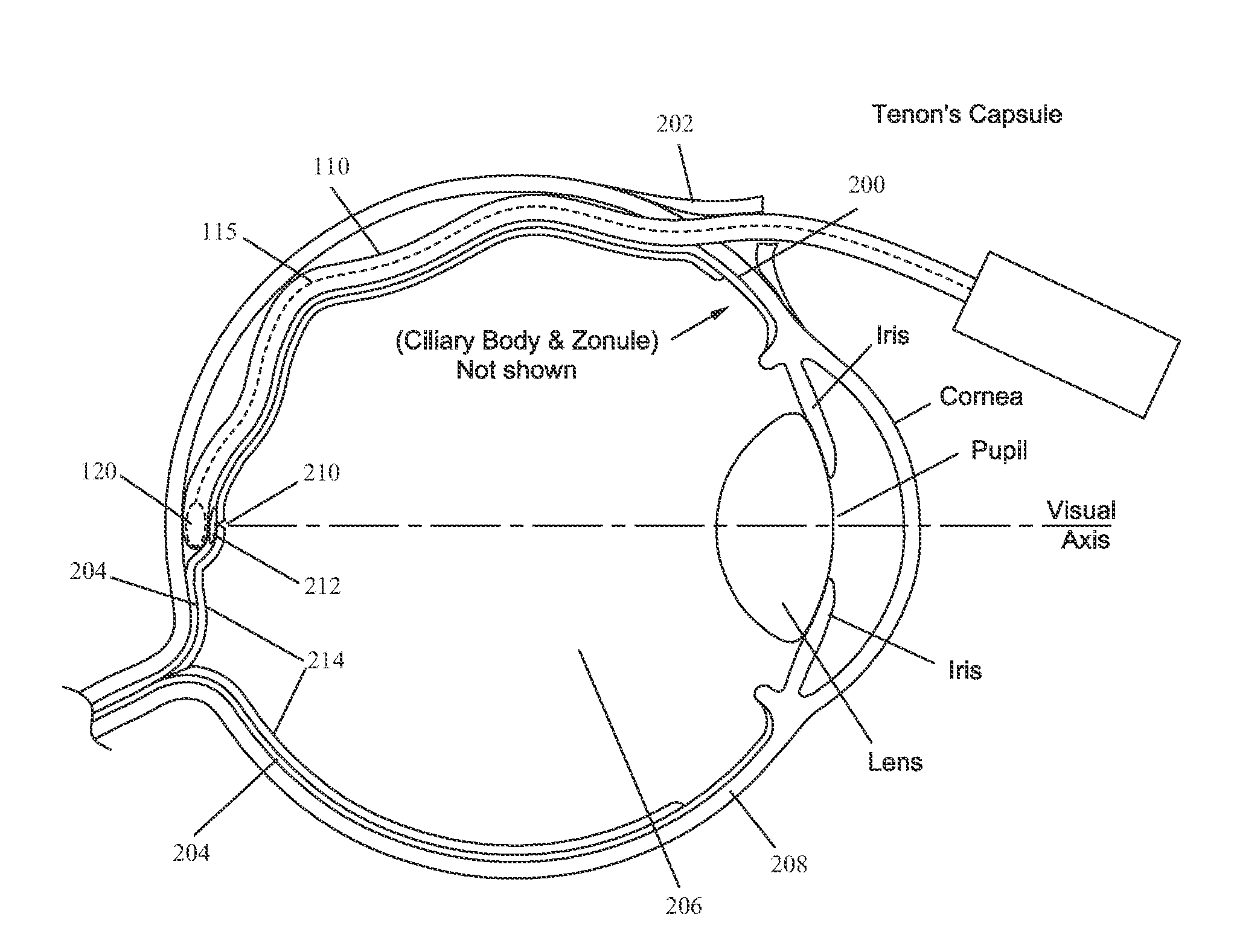
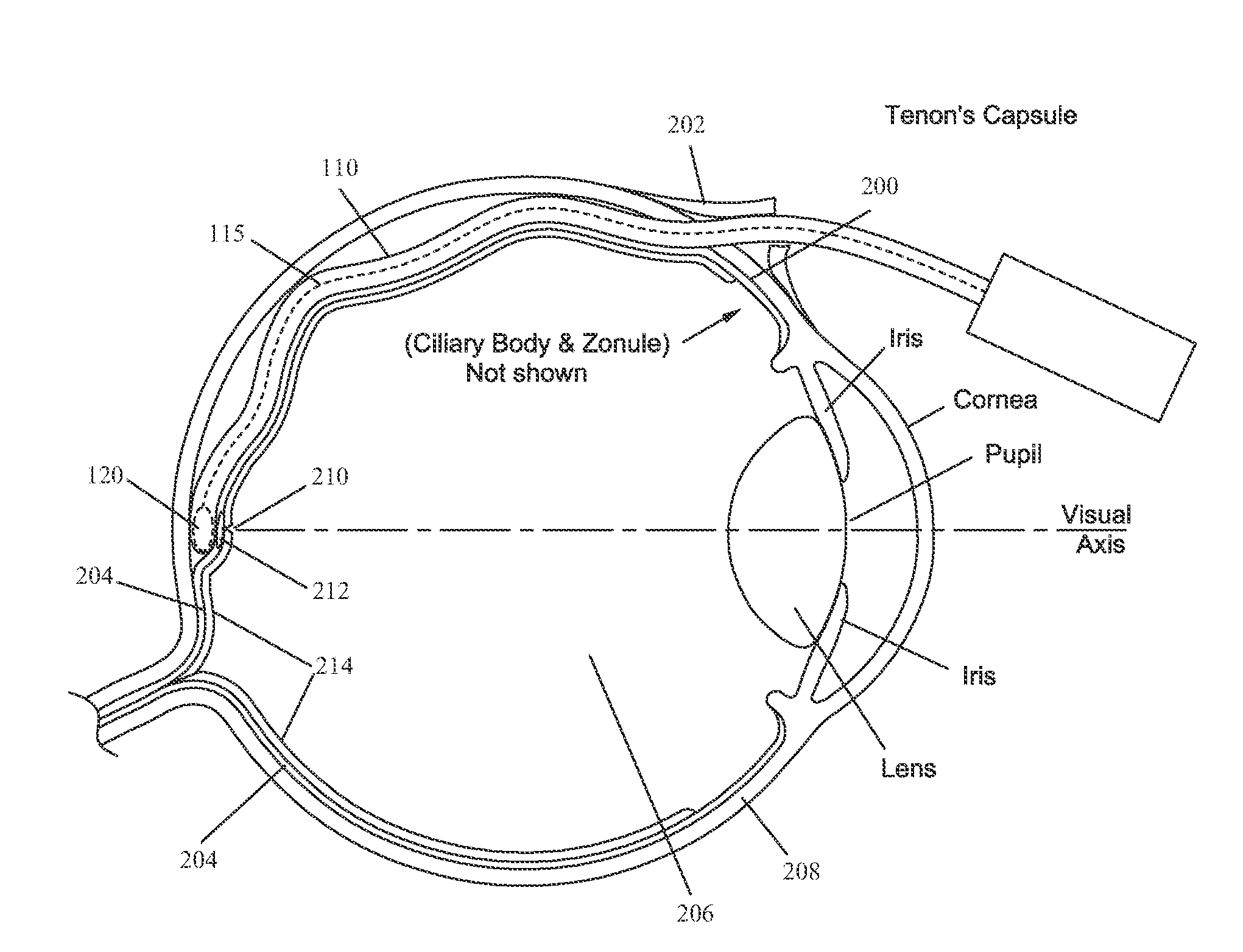
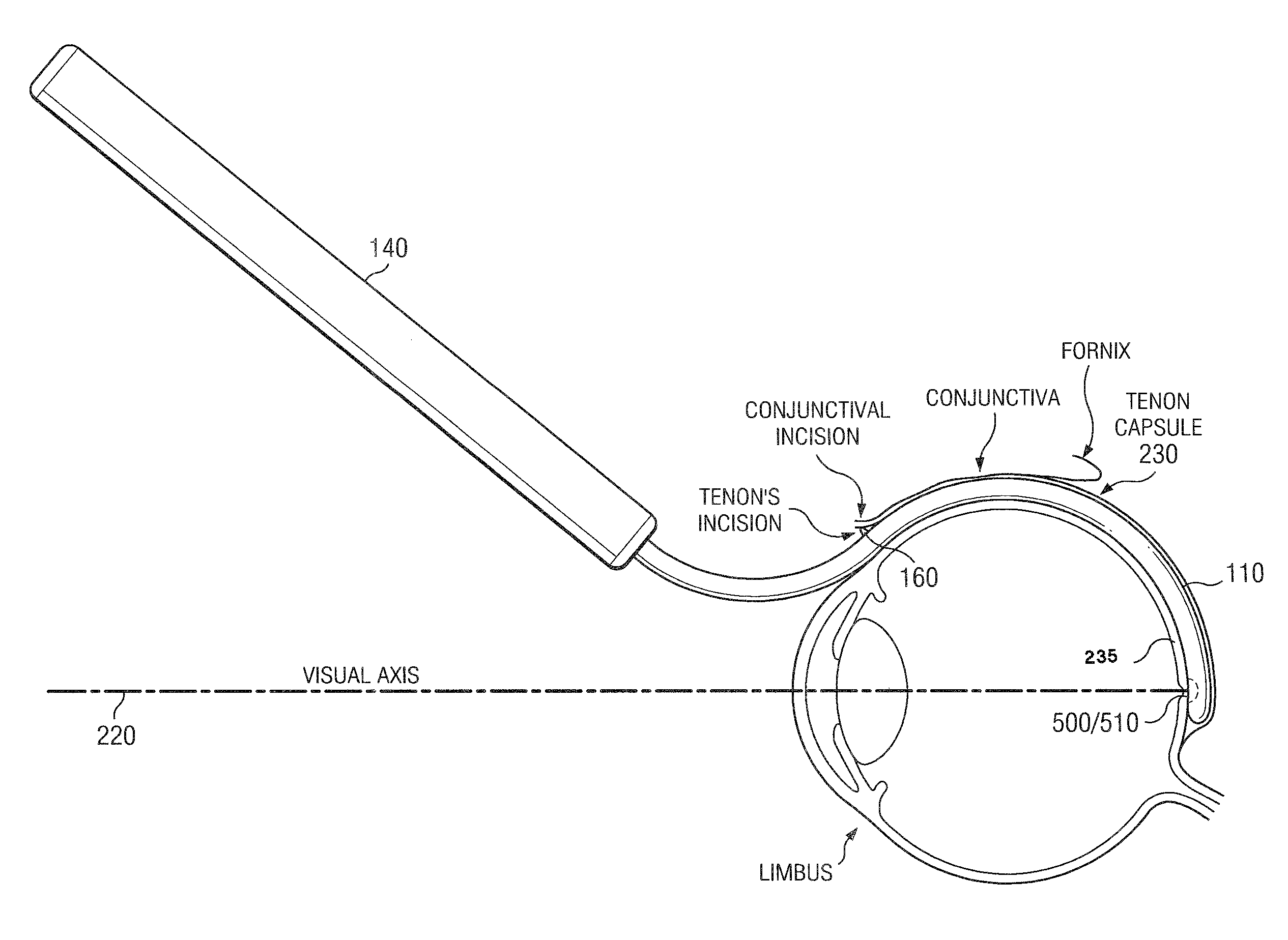
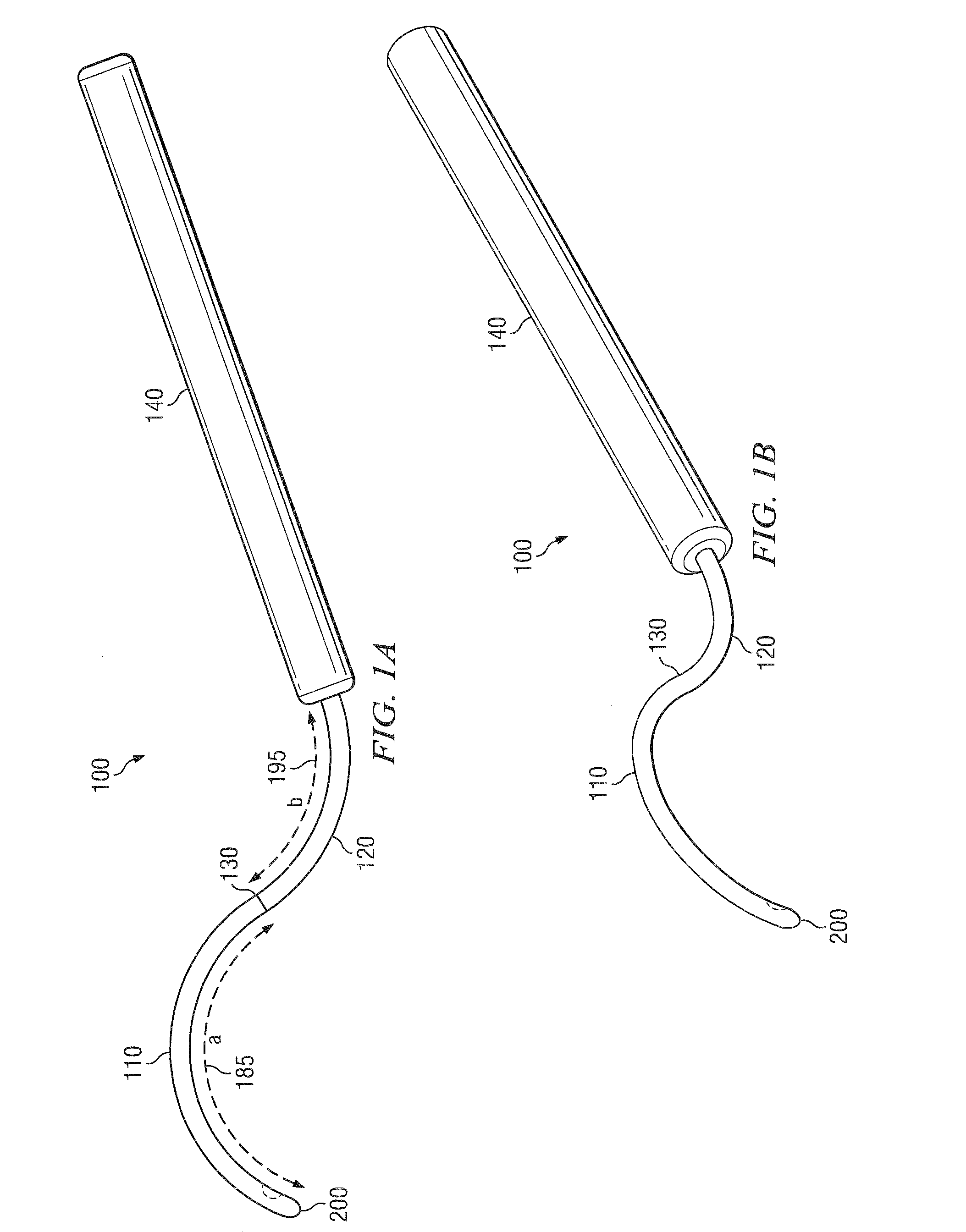
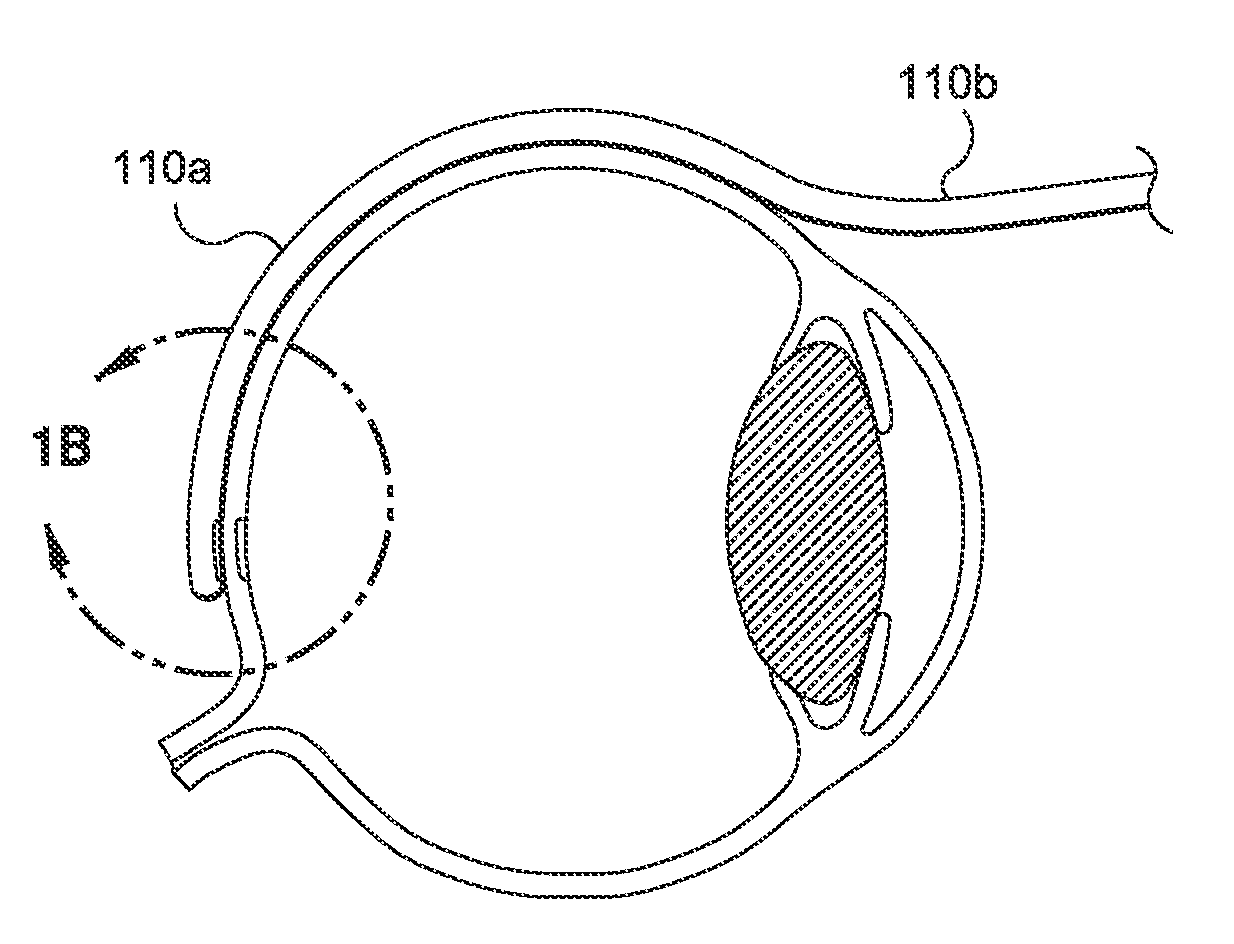
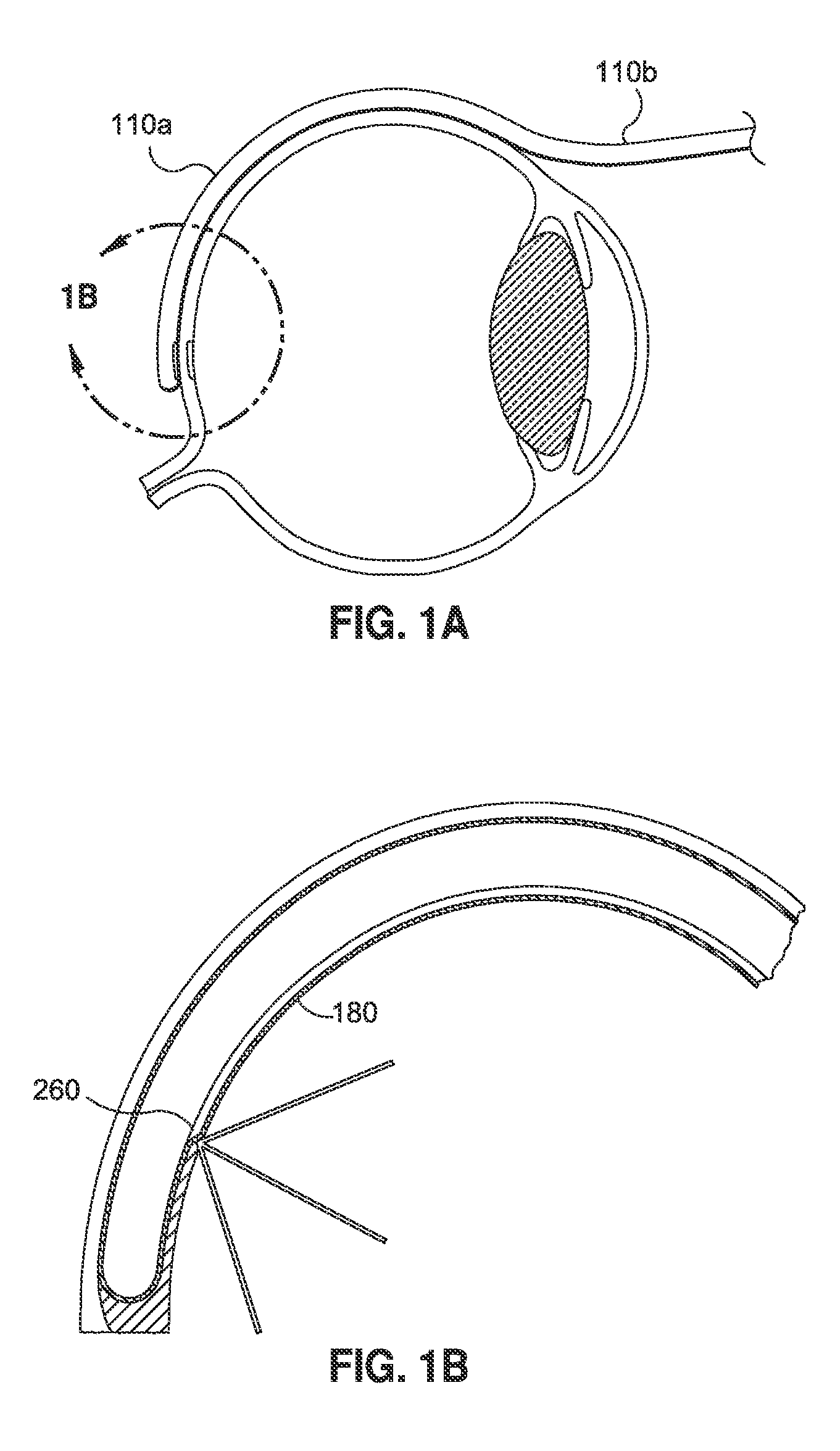
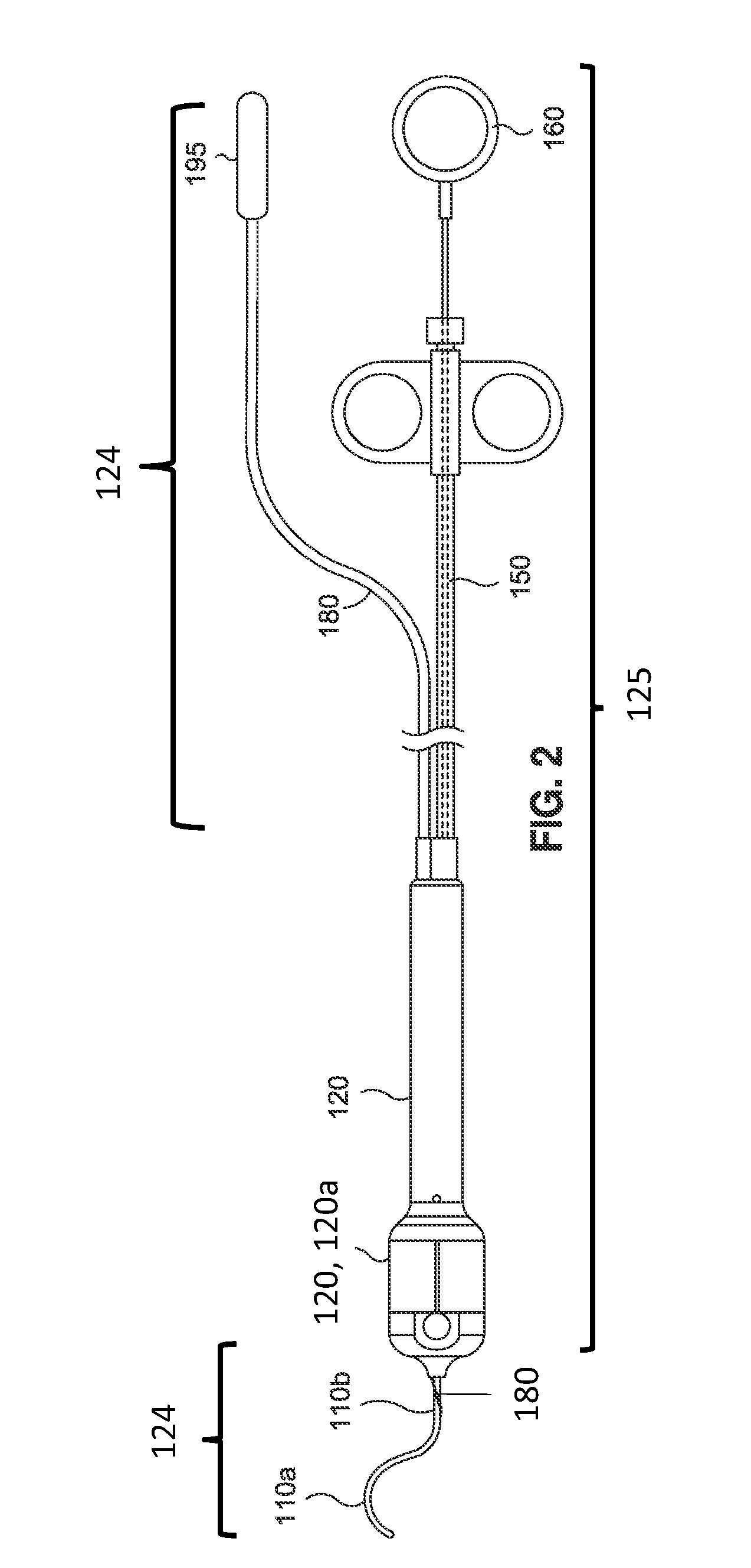
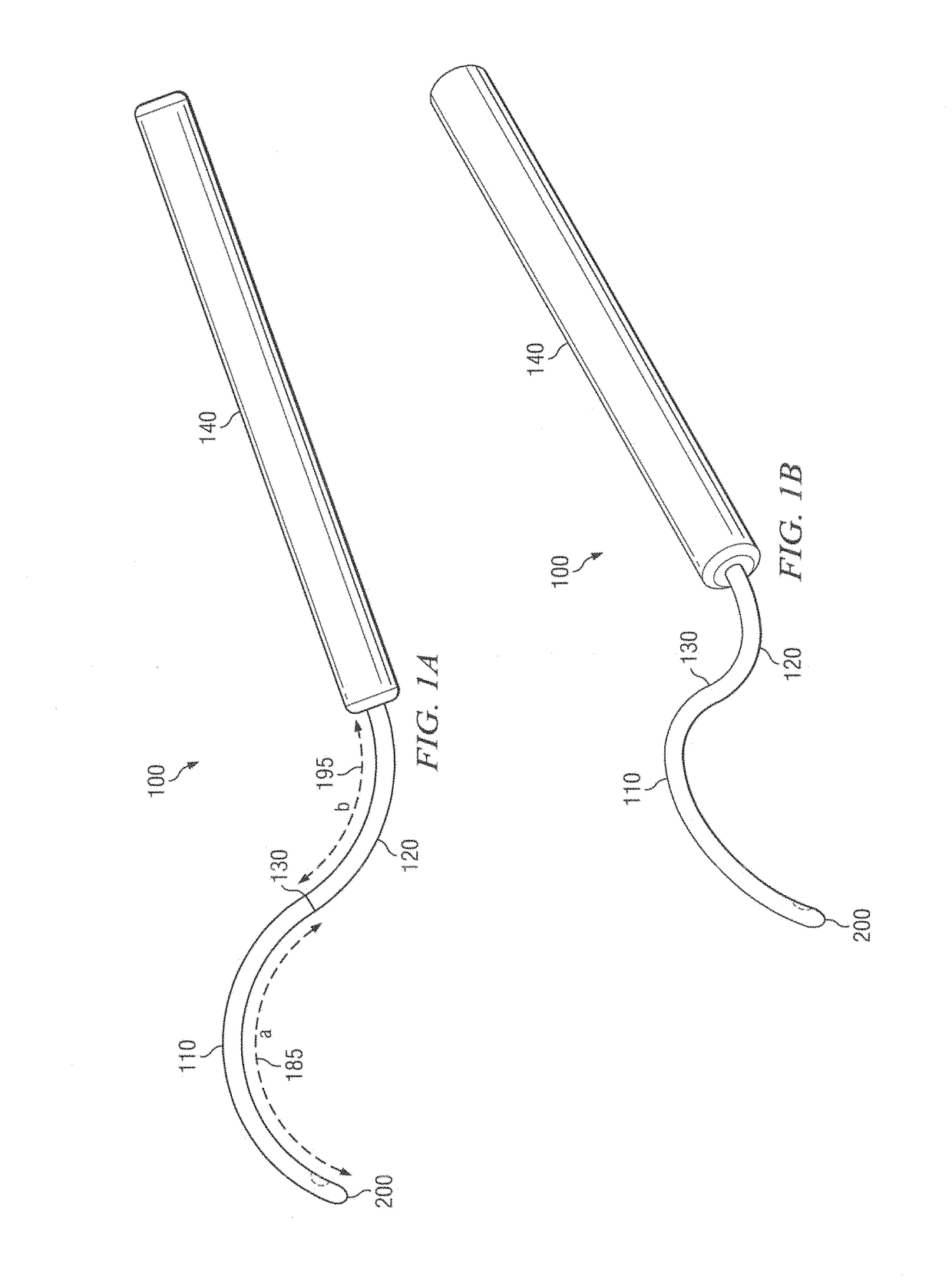
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive extraocular delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye
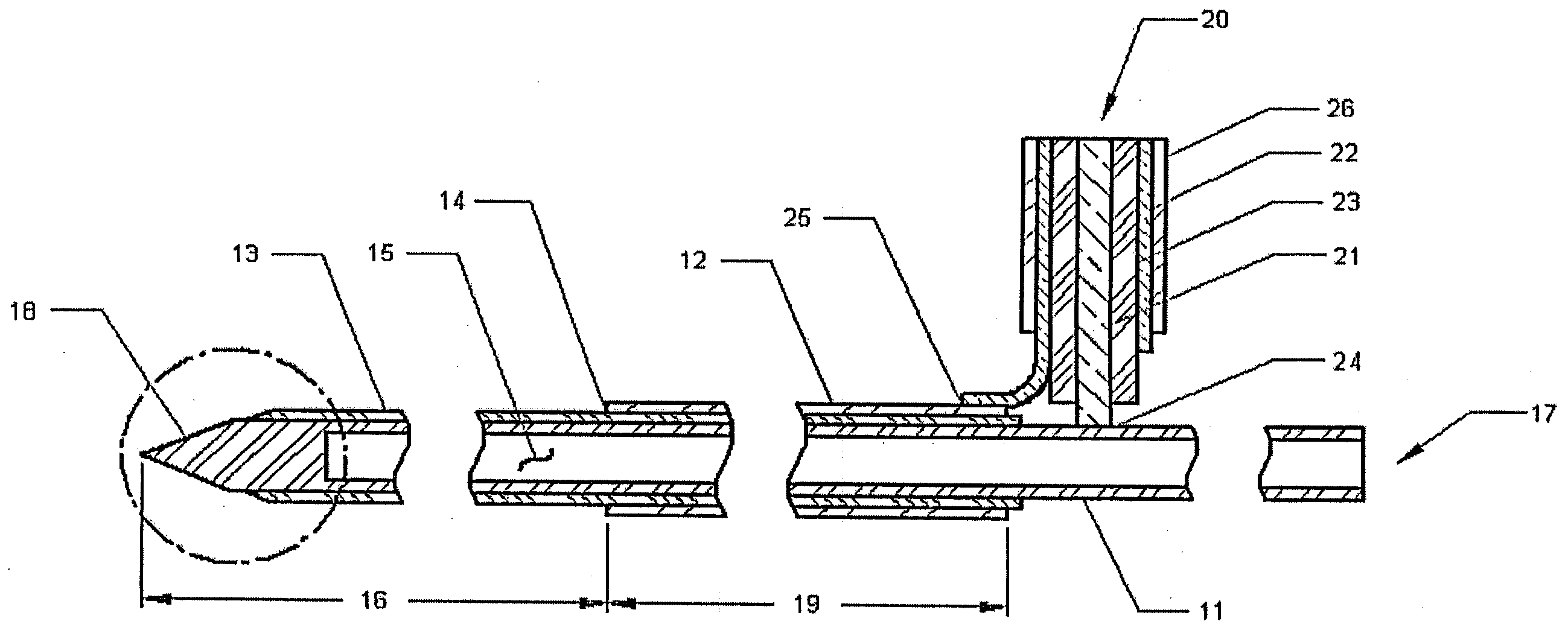
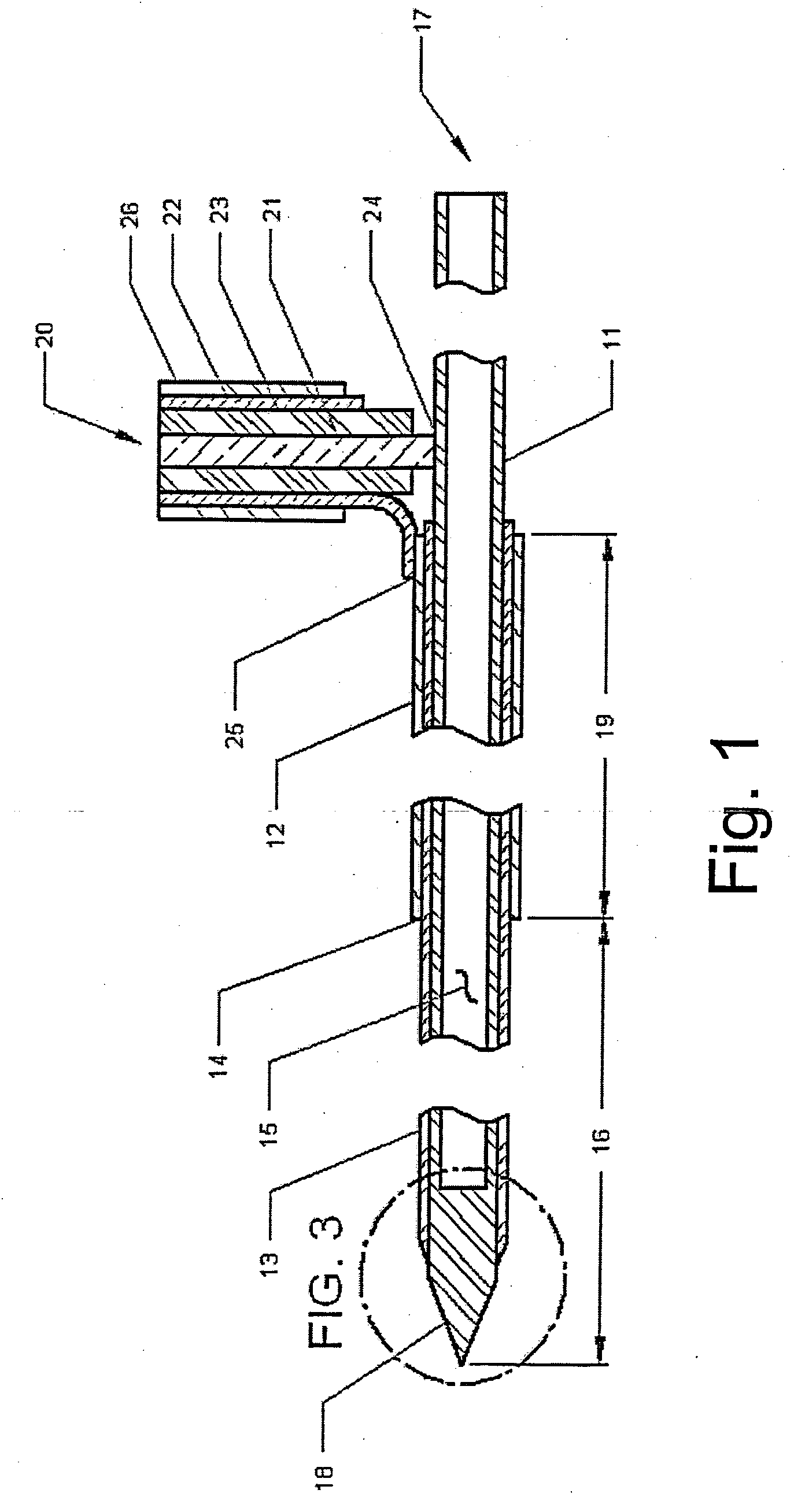
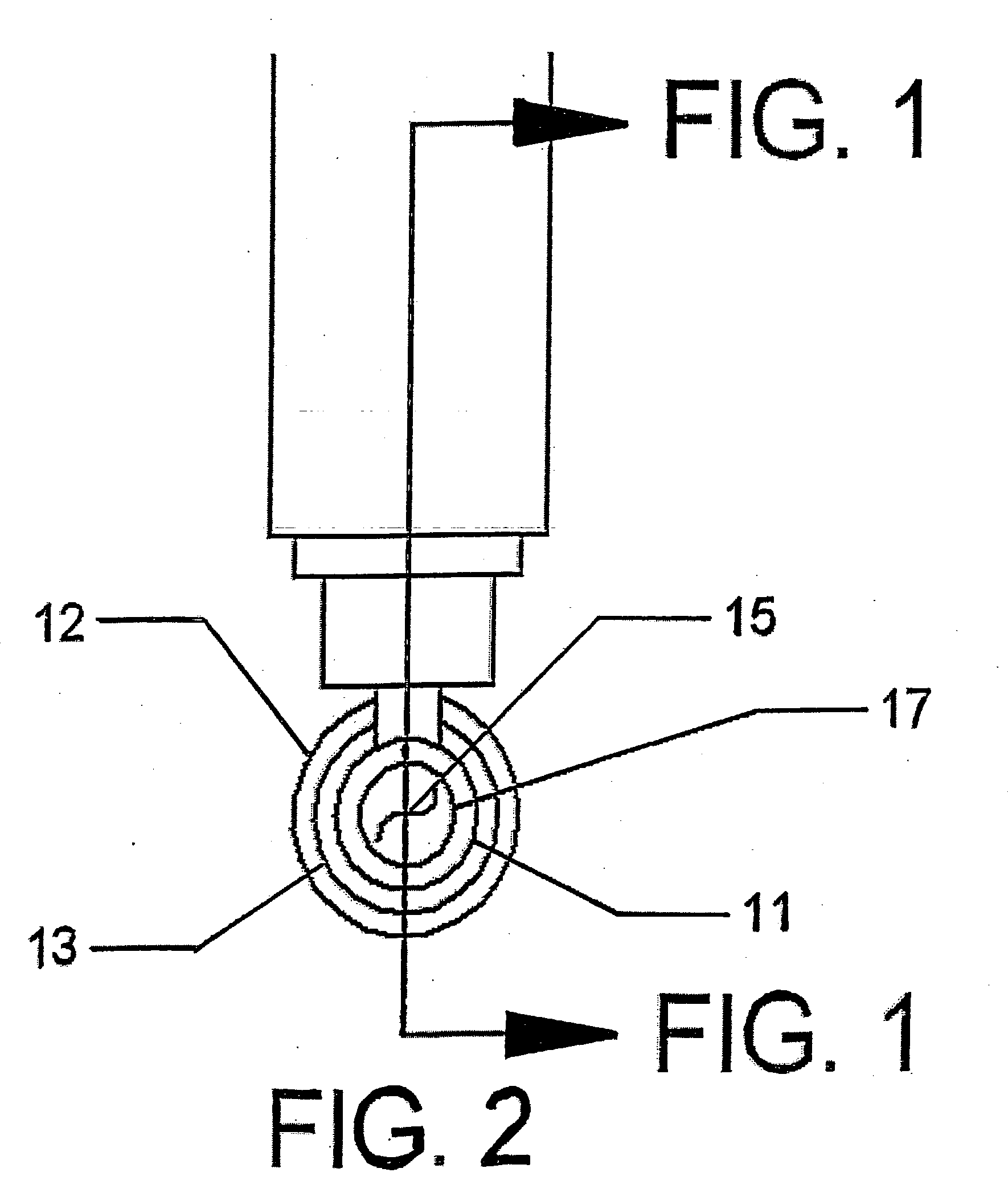
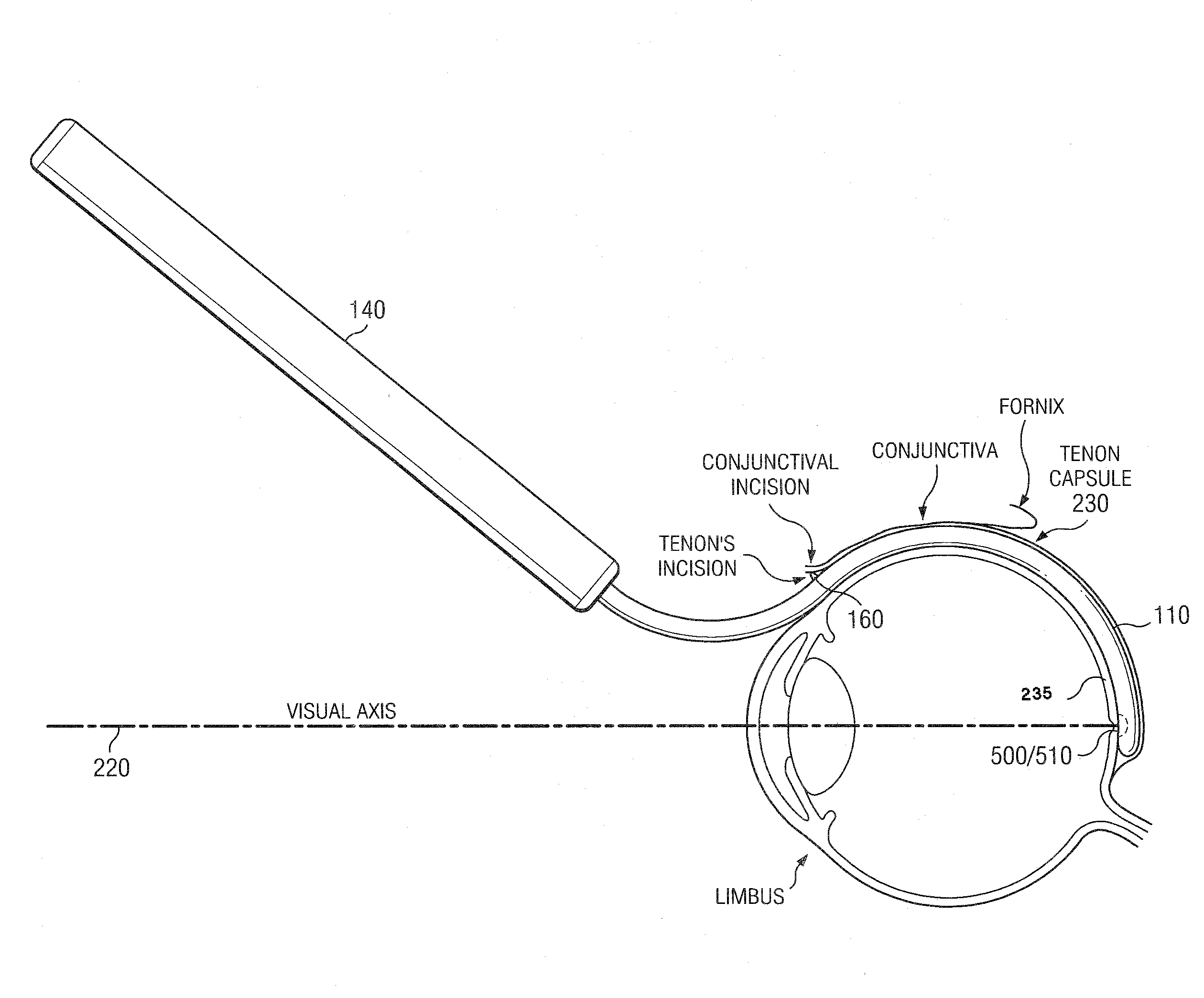
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye including a cannula comprising a distal portion connected to a proximal portion and a means for advancing a radionuclide brachytherapy source (RBS) toward the tip of the distal portion; a method of introducing radiation to the human eye comprising inserting a cannula between the Tenon's capsule and the sclera of the human eye and emitting the radiation from the cannula on an outer surface of said sclera.
Owner:SALUTARIS MEDICAL DEVICES INC
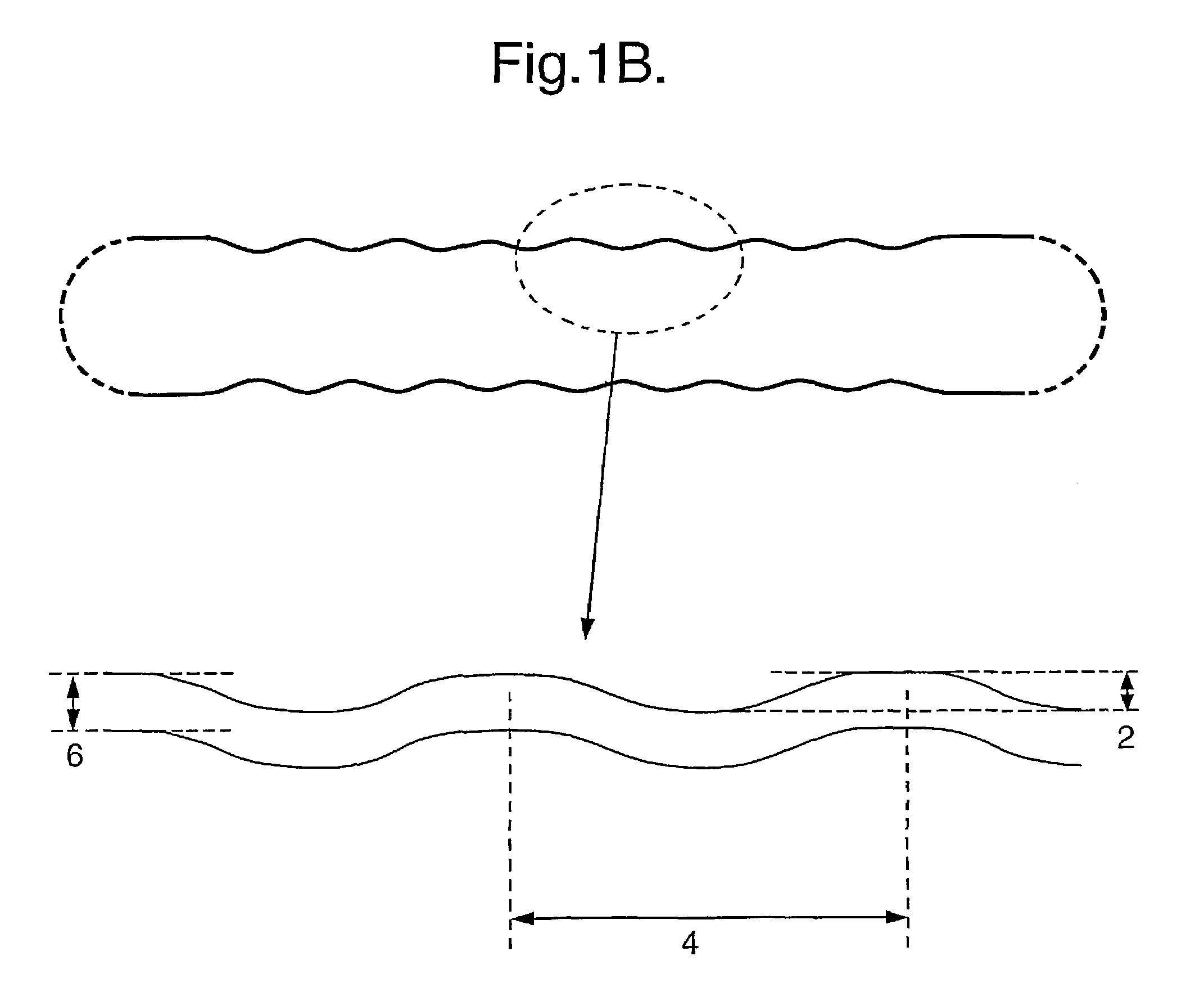
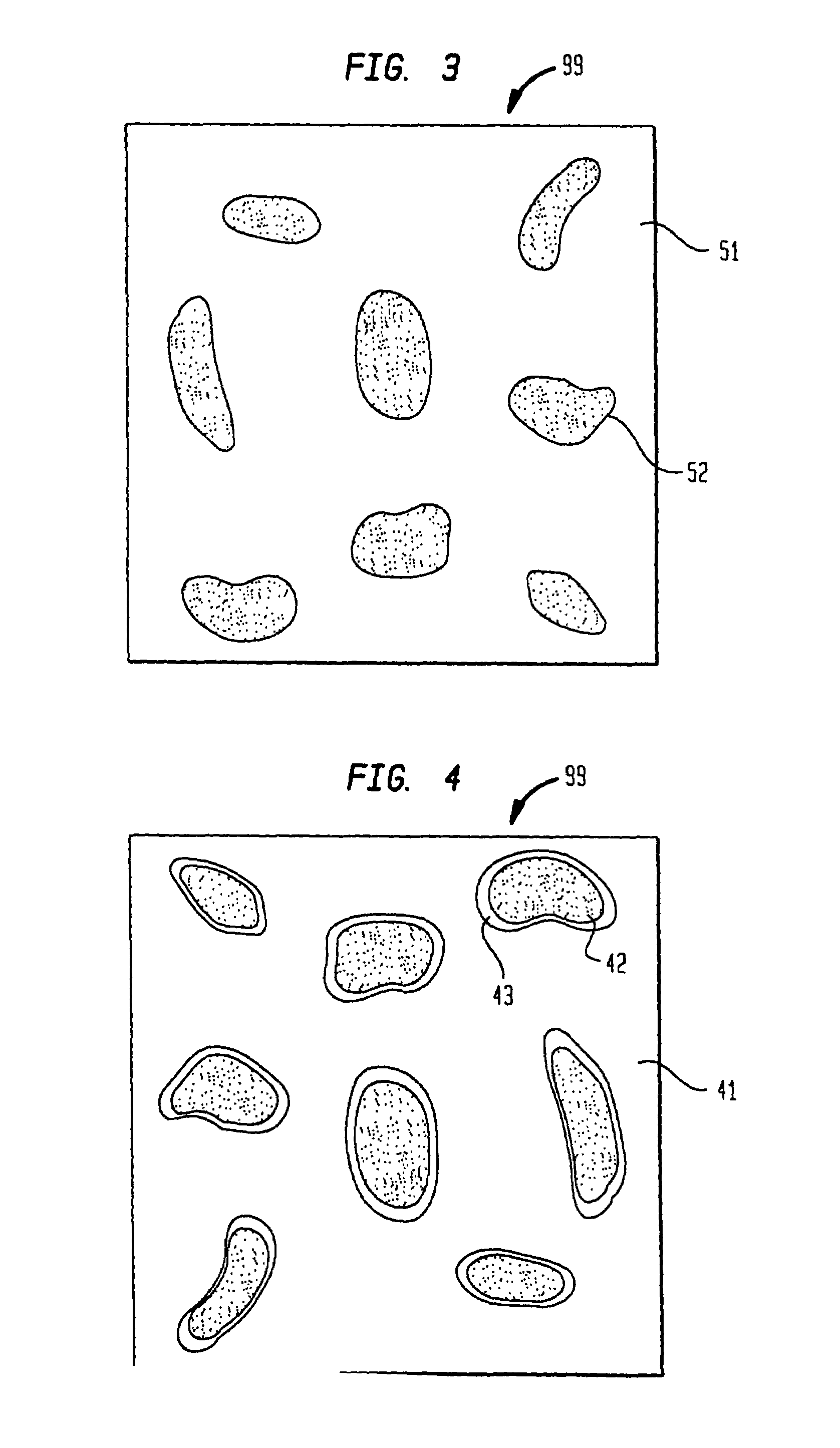
Grooved brachytherapy sources
InactiveUS7083566B2Increase ultrasound visibilityIncrease reflectionDiagnosticsSurgeryVisibilityBrachytherapy source
Radioactive sources, preferably radioactive seeds, for use in brachytherapy comprising a radioisotope within a sealed biocompatible container, wherein at least one part of the outer surface of the container is grooved, preferably with a curved groove. The grooved outer surface is preferably substantially free from angularities. Such grooves enhance the echogenicity of the source using medical ultrasound at a greater range of angles to the ultrasound probe, thus enhancing the ultrasound visibility of the source. Preferred radioisotopes are palladium-103 and iodine-125.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Invasive microwave antenna array for hyperthermia and brachytherapy
InactiveUS6957108B2Increase oxygenationSpeed up the flowMicrowave therapySurgical instruments using microwavesElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:PYREXAR MEDICAL
Methods And Devices For Minimally-Invasive Extraocular Delivery of Radiation To The Posterior Portion Of The Eye
InactiveUS20100004499A1Easy to implementNot impose risk of damageEye surgeryMedical devicesHuman eyeBrachytherapy source
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye including a cannula comprising a distal portion connected to a proximal portion and a means for advancing a radionuclide brachytherapy source (RBS) toward the tip of the distal portion; a method of introducing radiation to the human eye comprising inserting a cannula between the Tenon's capsule and the sclera of the human eye and emitting the radiation from the cannula on an outer surface of said sclera.
Owner:SALUTARISMD
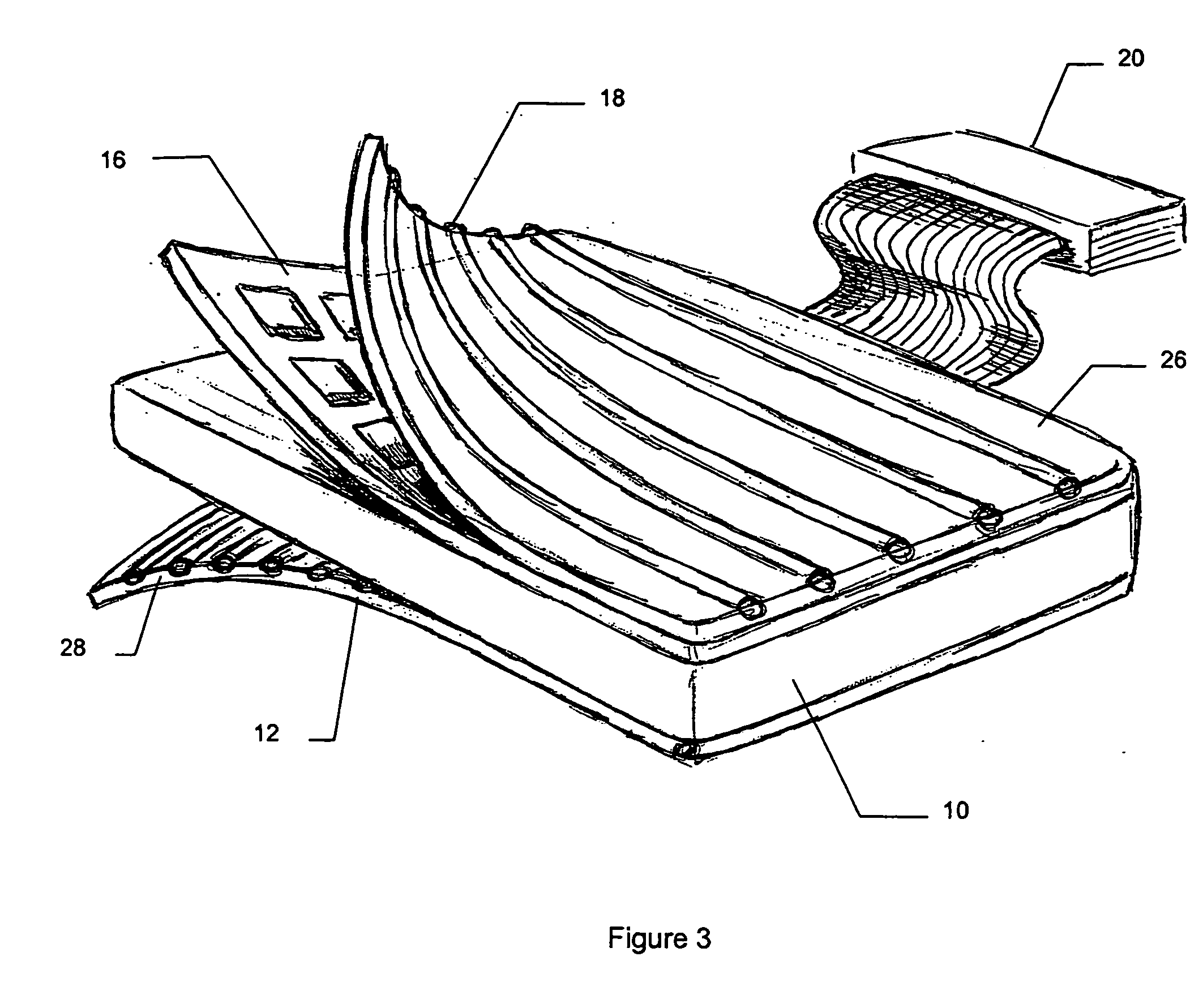
Apparatus for hyperthermia and brachytherapy delivery
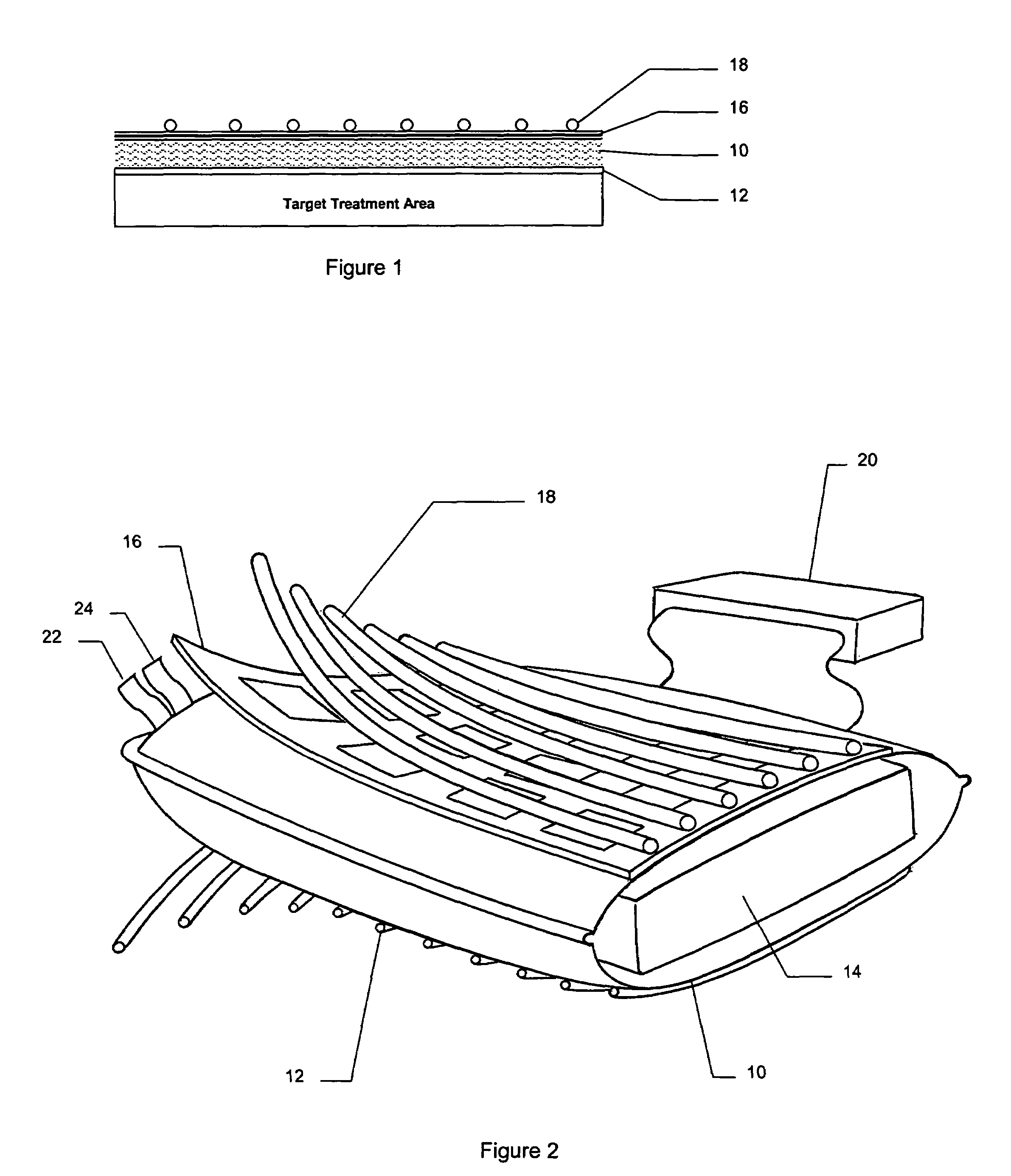
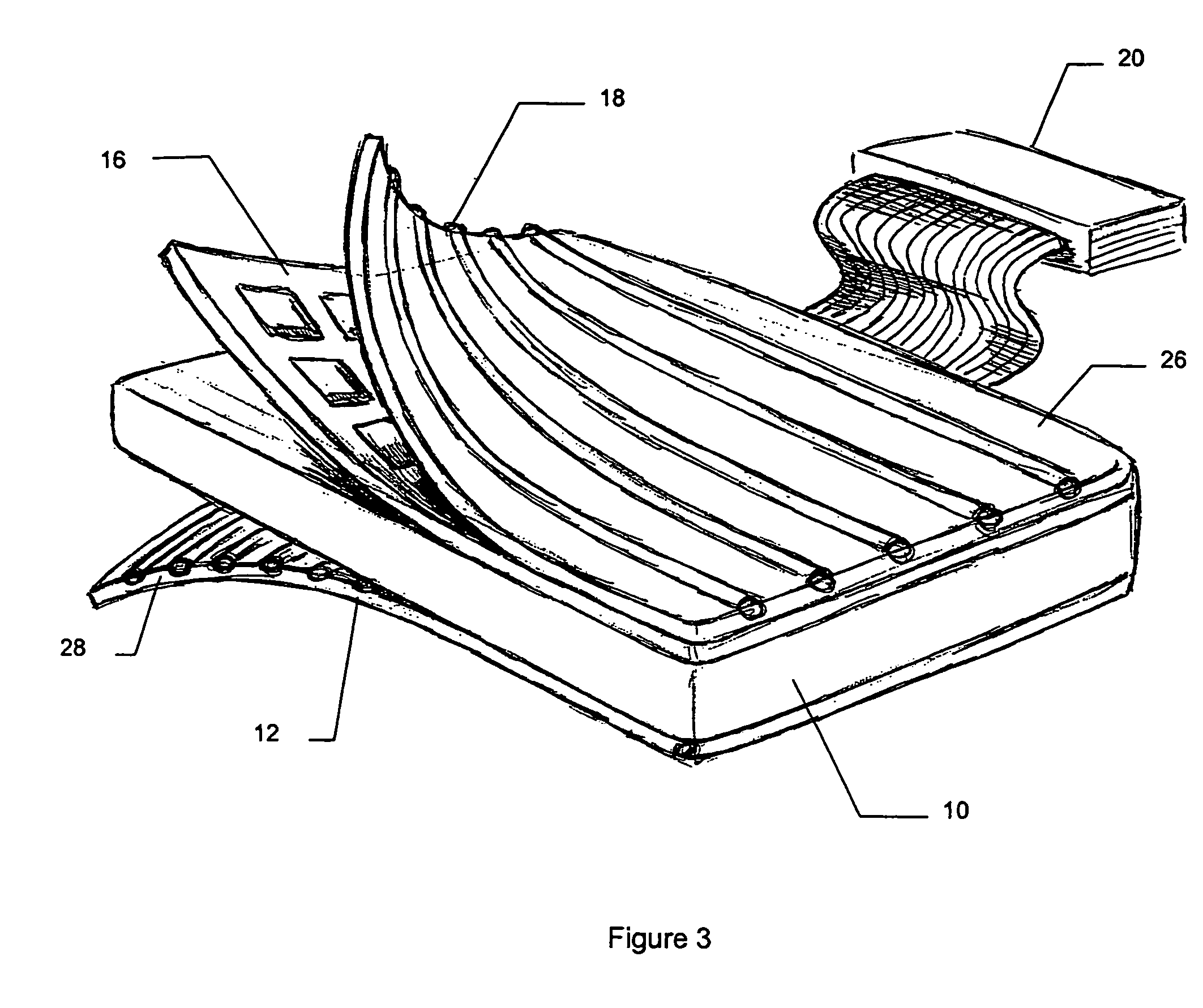
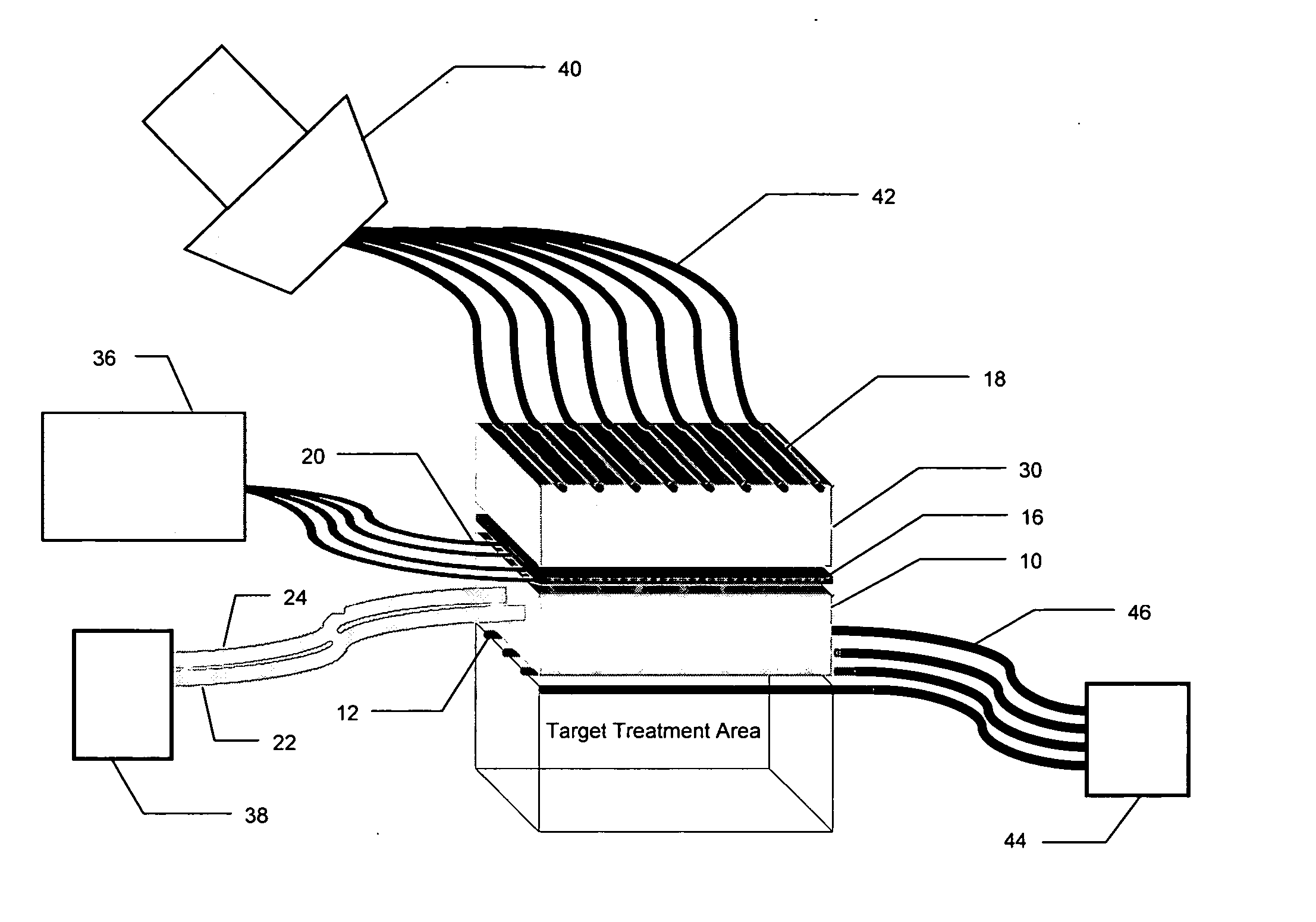
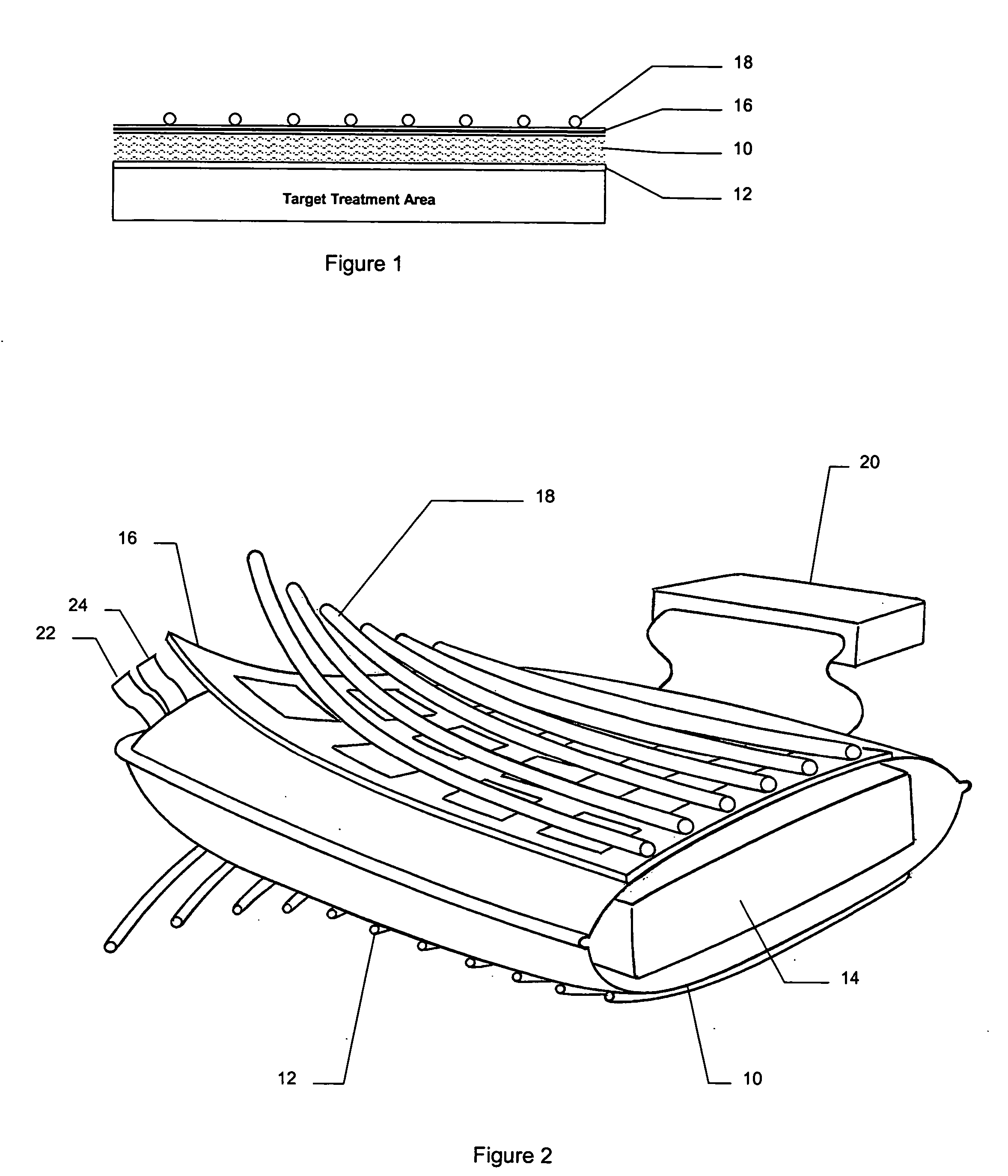
A combination applicator is able to deliver heat and radiation, either simultaneously or sequentially, for the treatment of cancer or other disease. The combination applicator is flexible and able to conform to contoured anatomy of the patient. The combination applicator comprises a flexible, dielectric containing compartment having a tissue-engaging surface and an opposite, non-tissue-engaging surface. A heating surface comprising one or more RF or microwave antennas or ultrasound transducers is supported adjacent to the non-tissue-engaging surface. In addition, a plurality of conduits are also supported on the dielectric containing compartment, the conduits being adapted to communicate with at least one brachytherapy source. Additional conduits may be located on the tissue contacting surface of the dielectric containing compartment to accommodate moving or stationary temperature monitoring sensors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Apparatus for hyperthermia and brachytherapy delivery
A combination applicator is able to deliver heat and radiation, either simultaneously or sequentially, for the treatment of cancer or other disease. The combination applicator is flexible and able to conform to contoured anatomy of the patient. The combination applicator comprises a flexible, dielectric containing compartment having a tissue-engaging surface and an opposite, non-tissue-engaging surface. A heating surface comprising one or more RF or microwave antennas or ultrasound transducers is supported adjacent to the non-tissue-engaging surface. In addition, a plurality of conduits are also supported on the dielectric containing compartment, the conduits being adapted to communicate with at least one brachytherapy source. Additional conduits may be located on the tissue contacting surface of the dielectric containing compartment to accommodate moving or stationary temperature monitoring sensors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods and devices for delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye
ActiveUS8602959B1ElectrotherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDistal portionOphthalmology
Methods and devices for delivering radiation to a target at a posterior portion of an eye using a brachytherapy-administering device adapted to be inserted into a suprachoroidal space of the eye including a brachytherapy source and a means of advancing the brachytherapy source from a storage position to a radiation position corresponding to a position in a distal portion of the device, positioning the device appropriately such that the distal portion of the device is in close proximity to the target, exposing the target to the brachytherapy source for a predetermined length of time then removing the device and closing incisions made during a surgical procedures to reach the suprachoroidal space of the eye.
Owner:PARK ROBERT +2
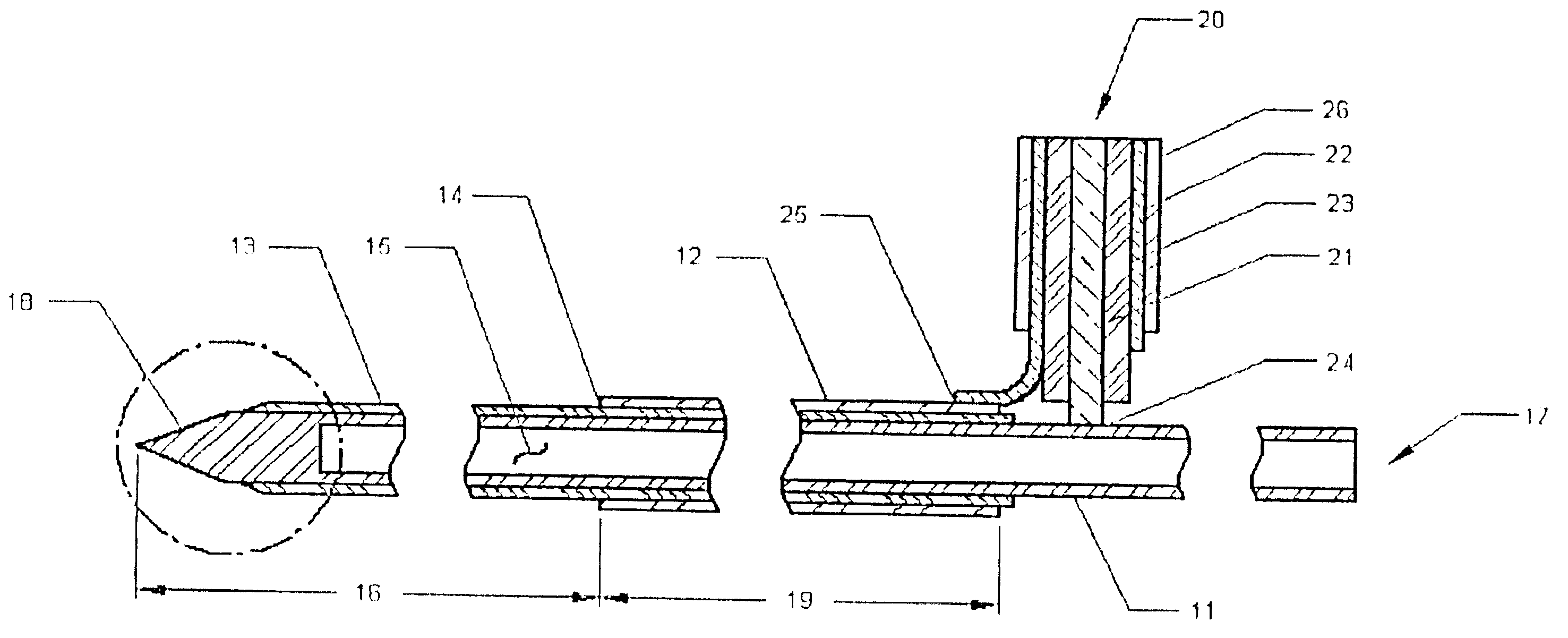
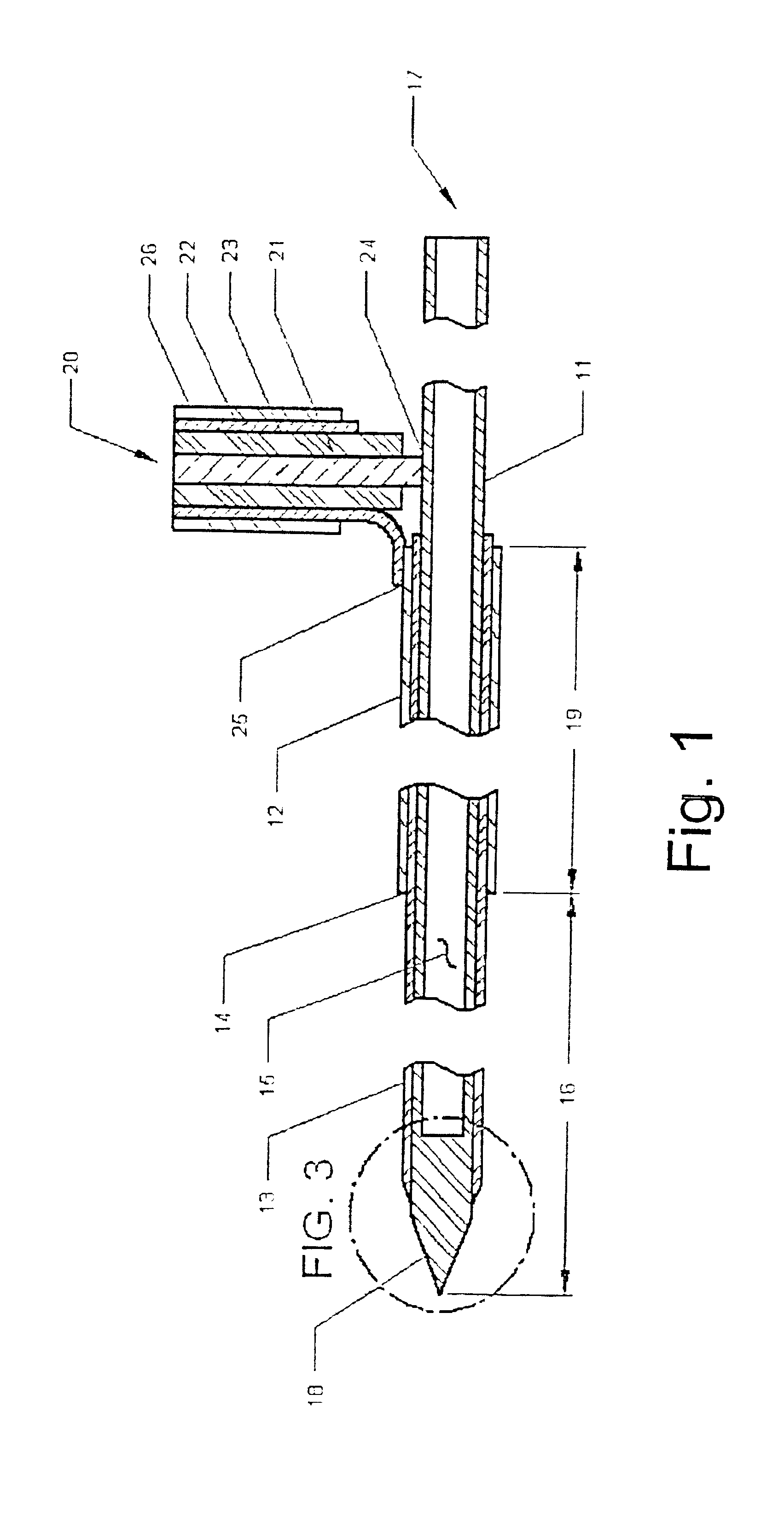
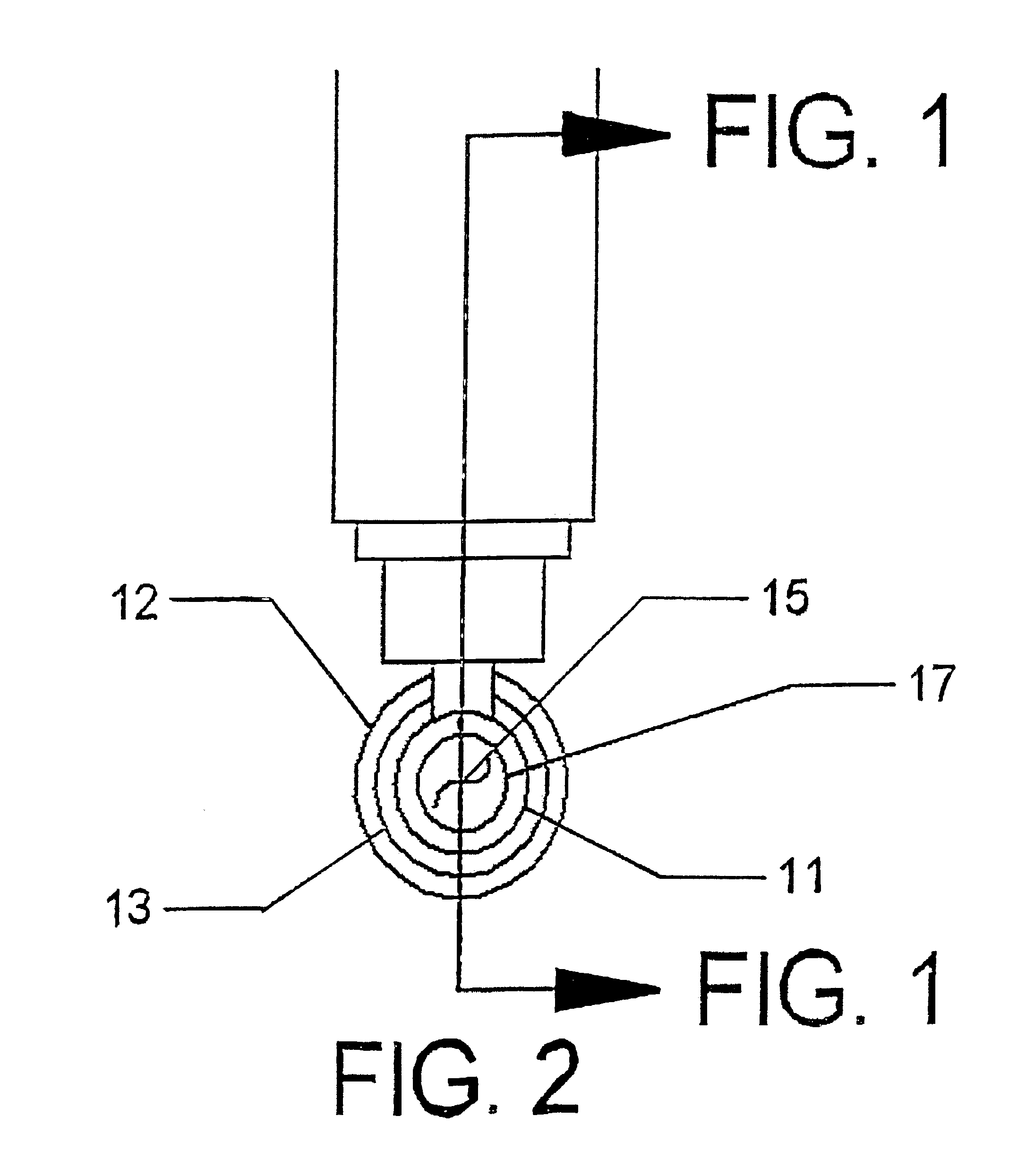
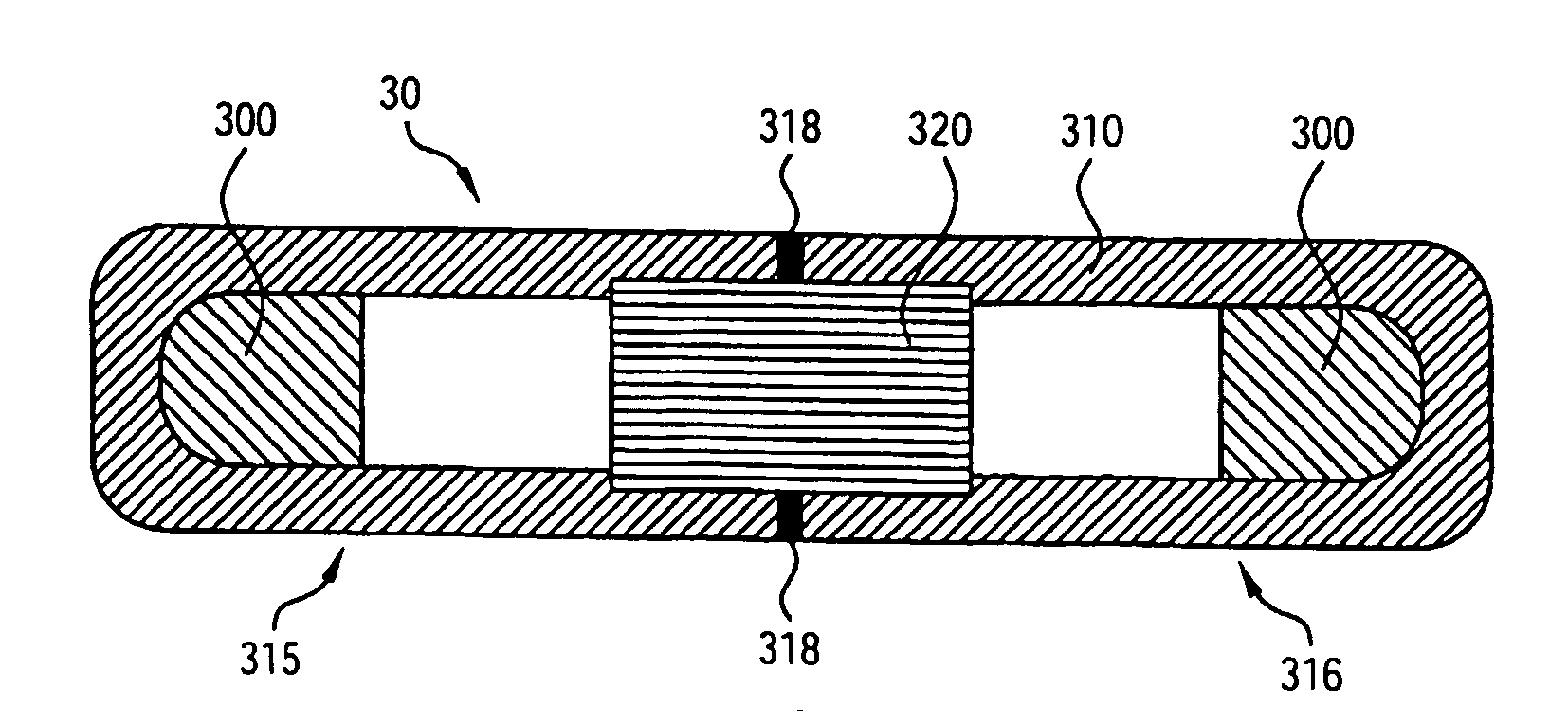
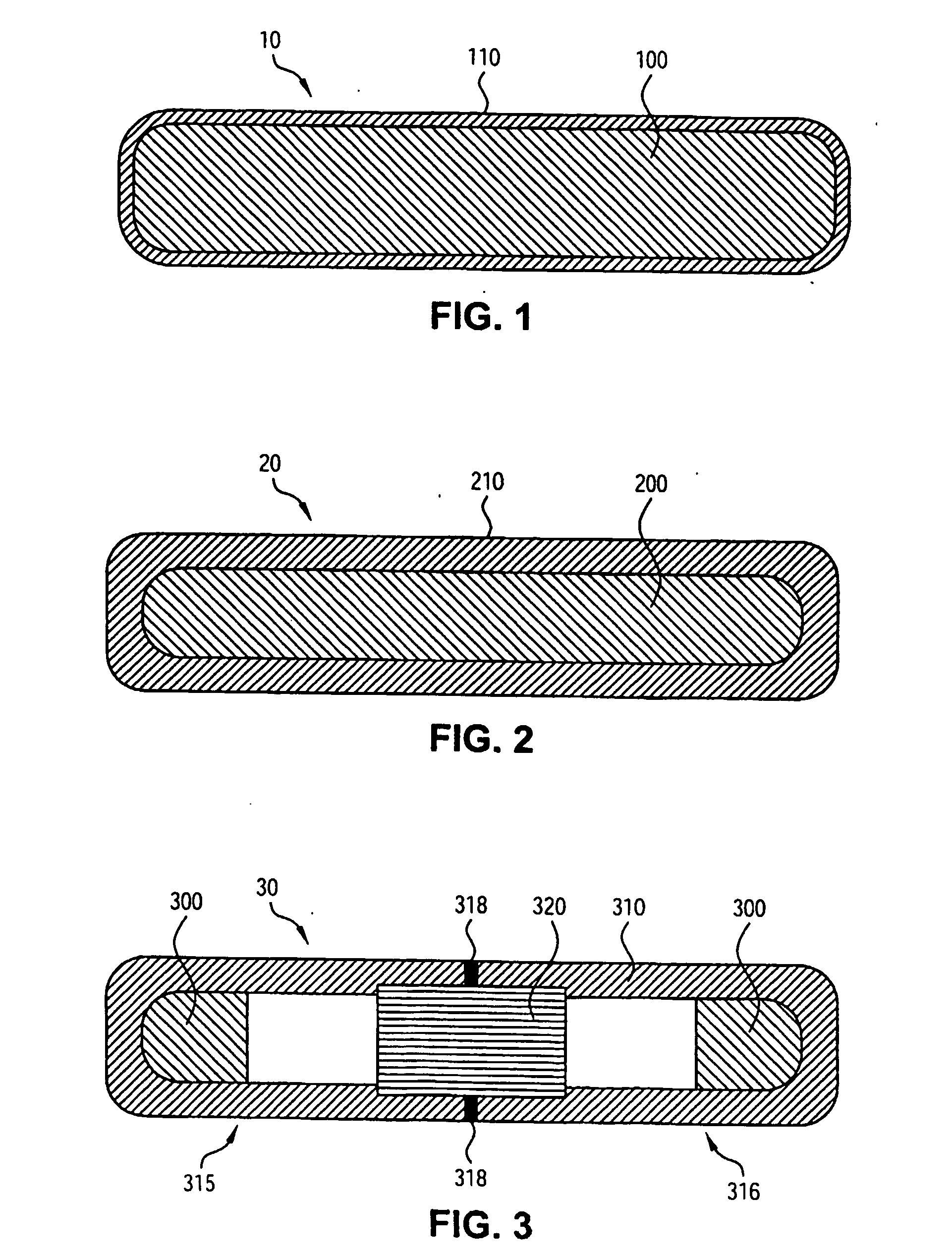
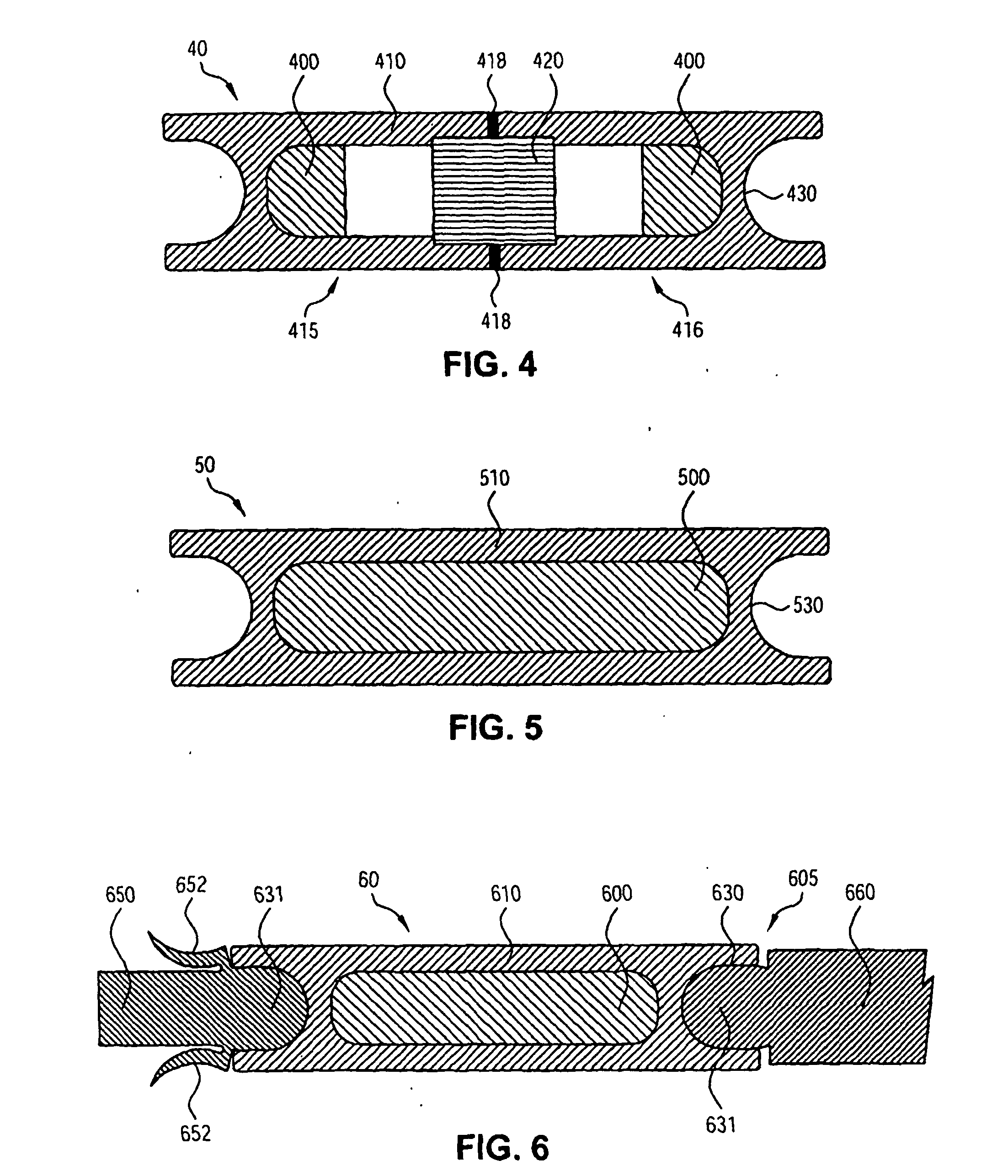
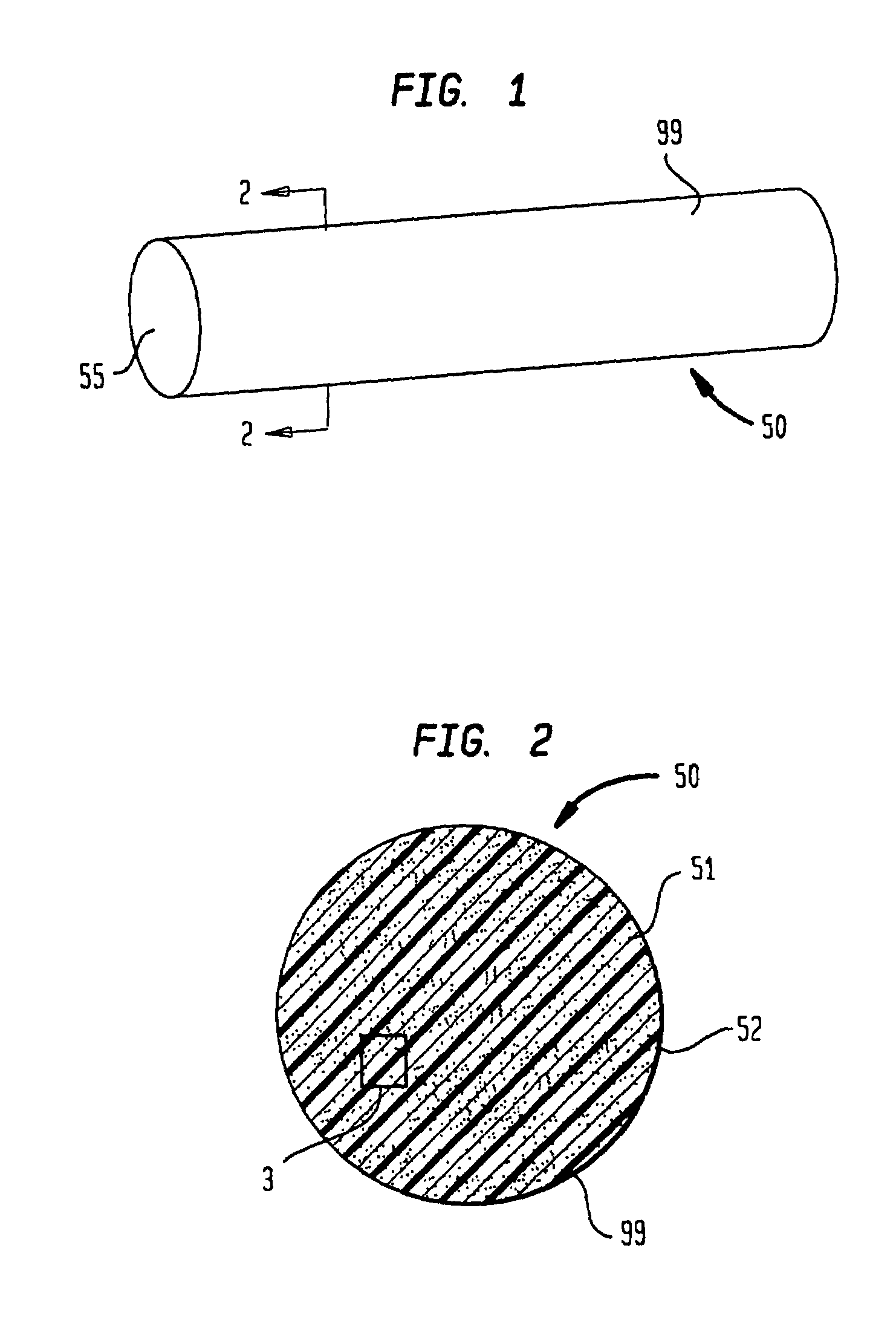
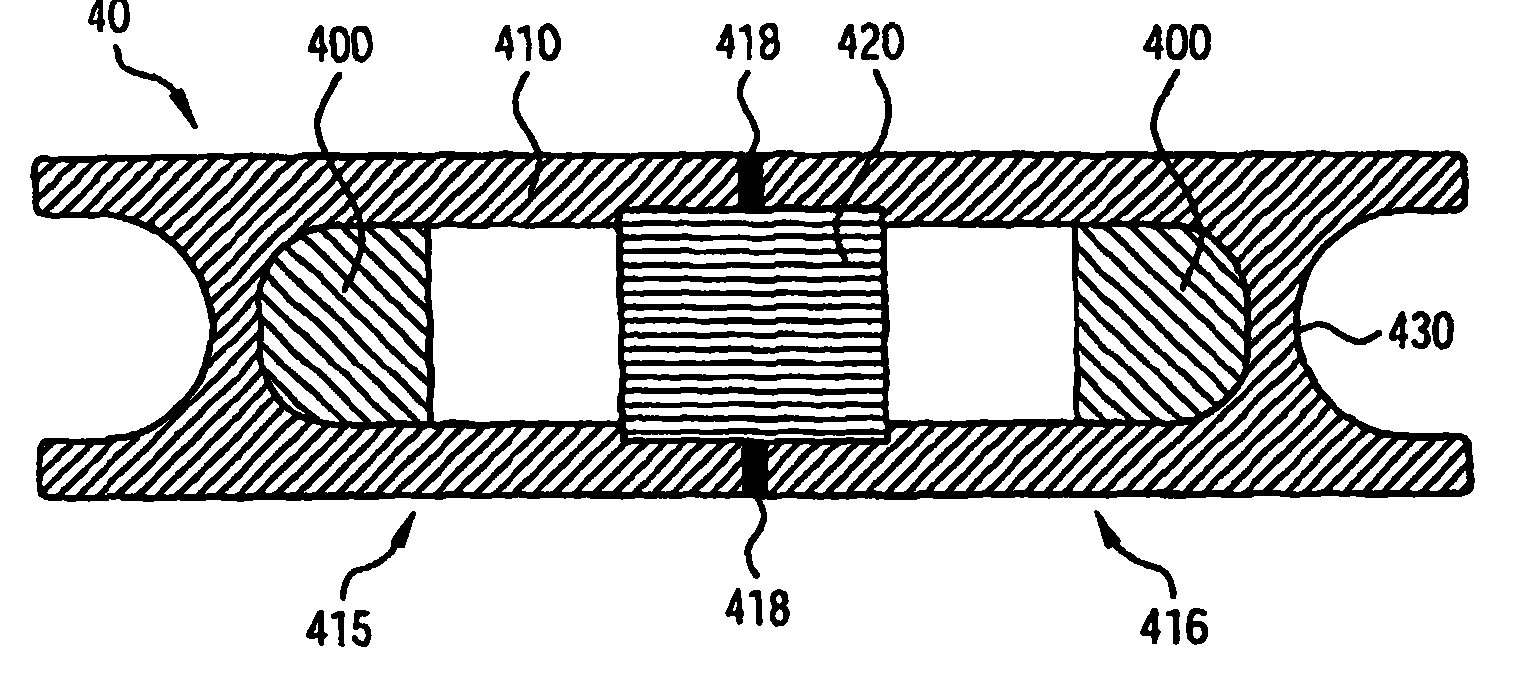
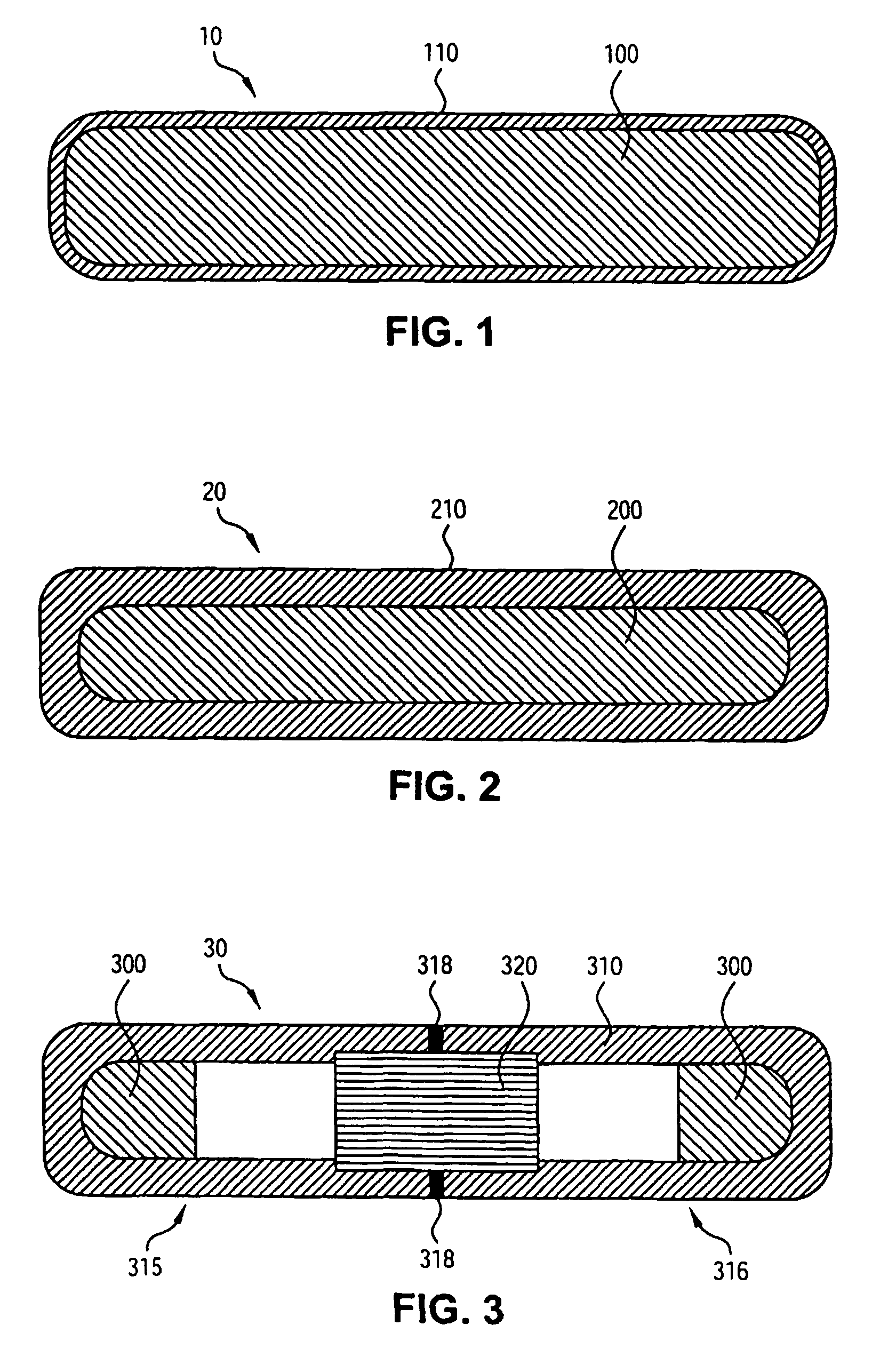
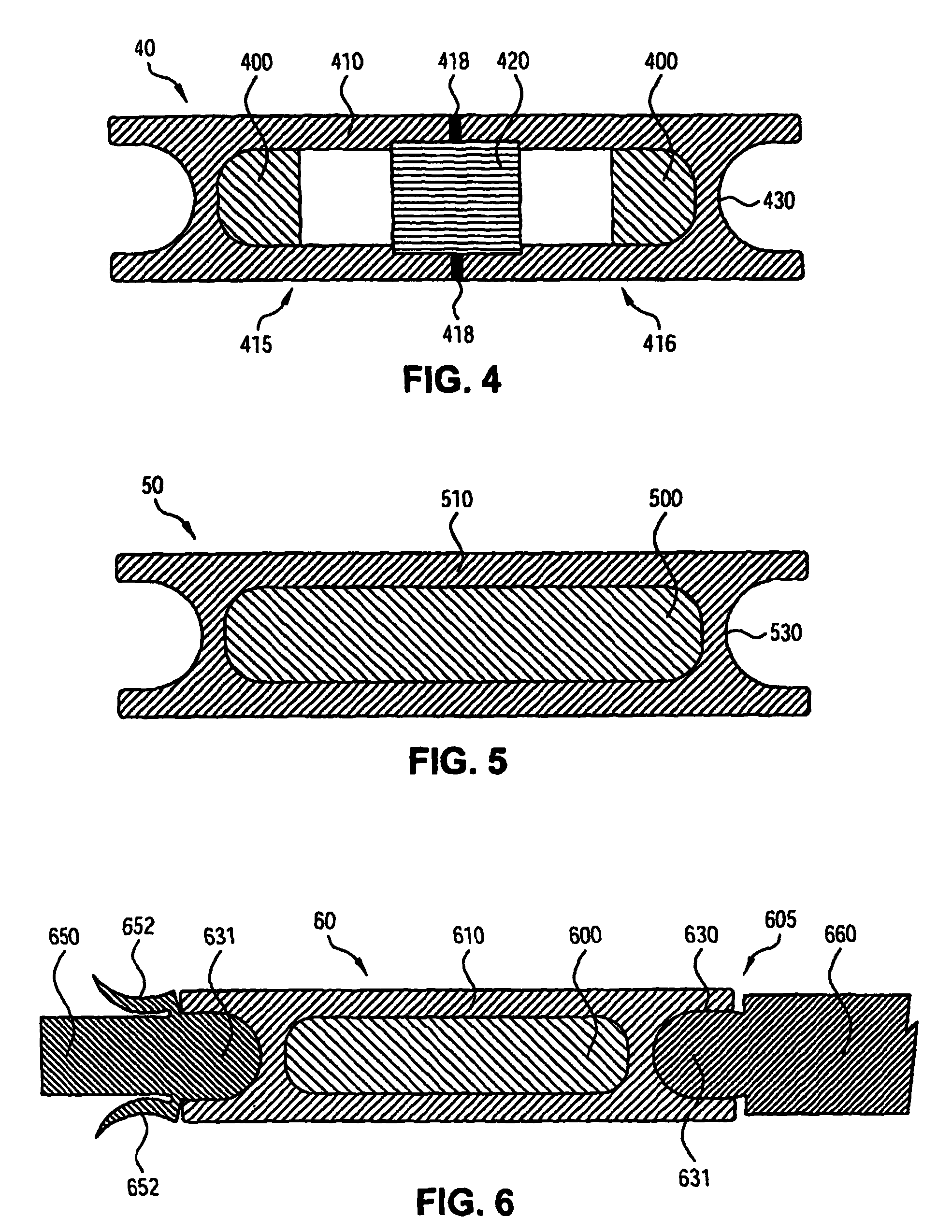
Plastic brachytherapy sources
InactiveUS20060224035A1Less materialEconomic advantageX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPolyether ether ketoneBrachytherapy source
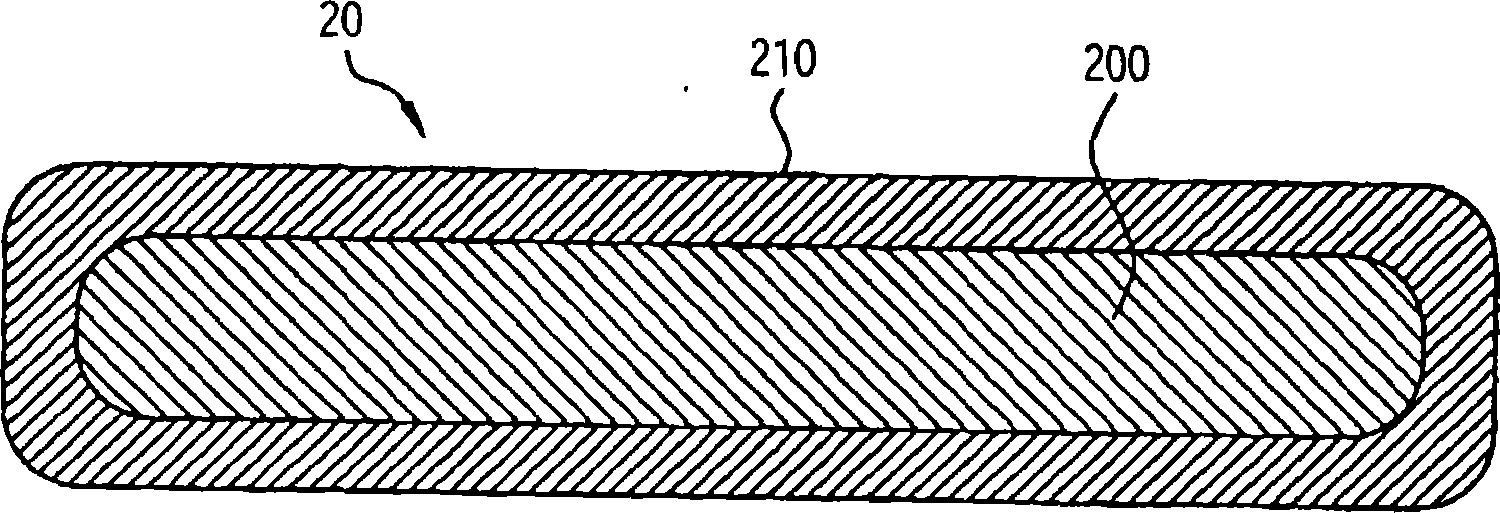
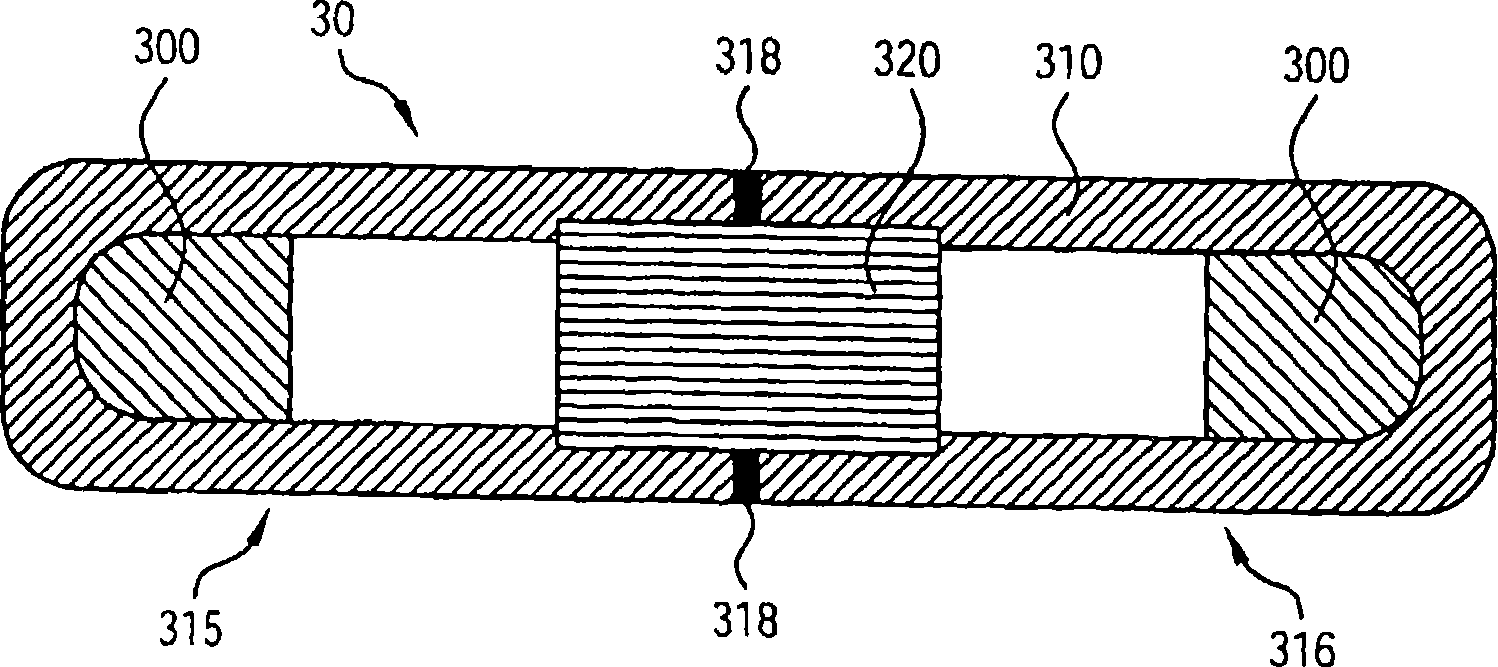
An implantable source (40) of therapeutic radiation for brachytherapy is provided as a sealed, biocompatible capsule (410) of plastic (e.g. polyethylene or PEEK) transparent to the radiation. The capsule contains a radiation source (400) comprising particles of a radioactive isotope (e.g. Pd103, I125, Cs131) in a fluid carrier that is resistant to radiation polymerization but solidifies at elevated temperature. It also has a marker (420), and desirably has a socket (430) which accommodates attaching spacers (660) and makes possible linear strands and planar arrays of the capsules. The spacers may be functional, e.g. heat-generating or medication-releasing.
Owner:ECKERT & ZIEGLER BEBIG
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive extraocular delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye including a cannula comprising a distal portion connected to a proximal portion and a means for advancing a radionuclide brachytherapy source (RBS) toward the tip of the distal portion; a method of introducing radiation to the human eye comprising inserting a cannula between the Tenon's capsule and the sclera of the human eye and emitting the radiation from the cannula on an outer surface of said sclera.
Owner:SALUTARIS MEDICAL DEVICES INC
Brachytherapy dose computation system and method
InactiveUS20090063110A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVoxelCritical structure
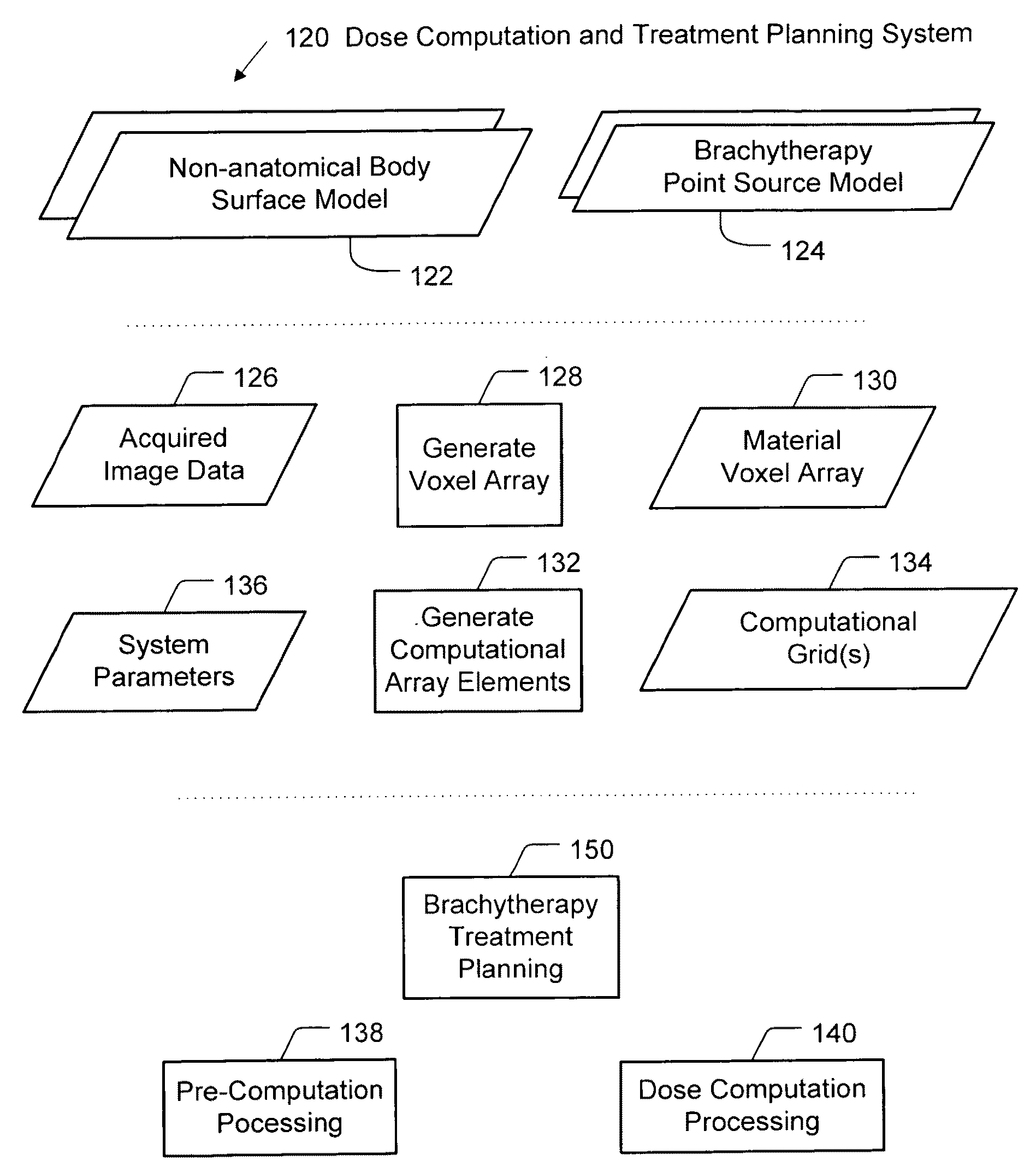
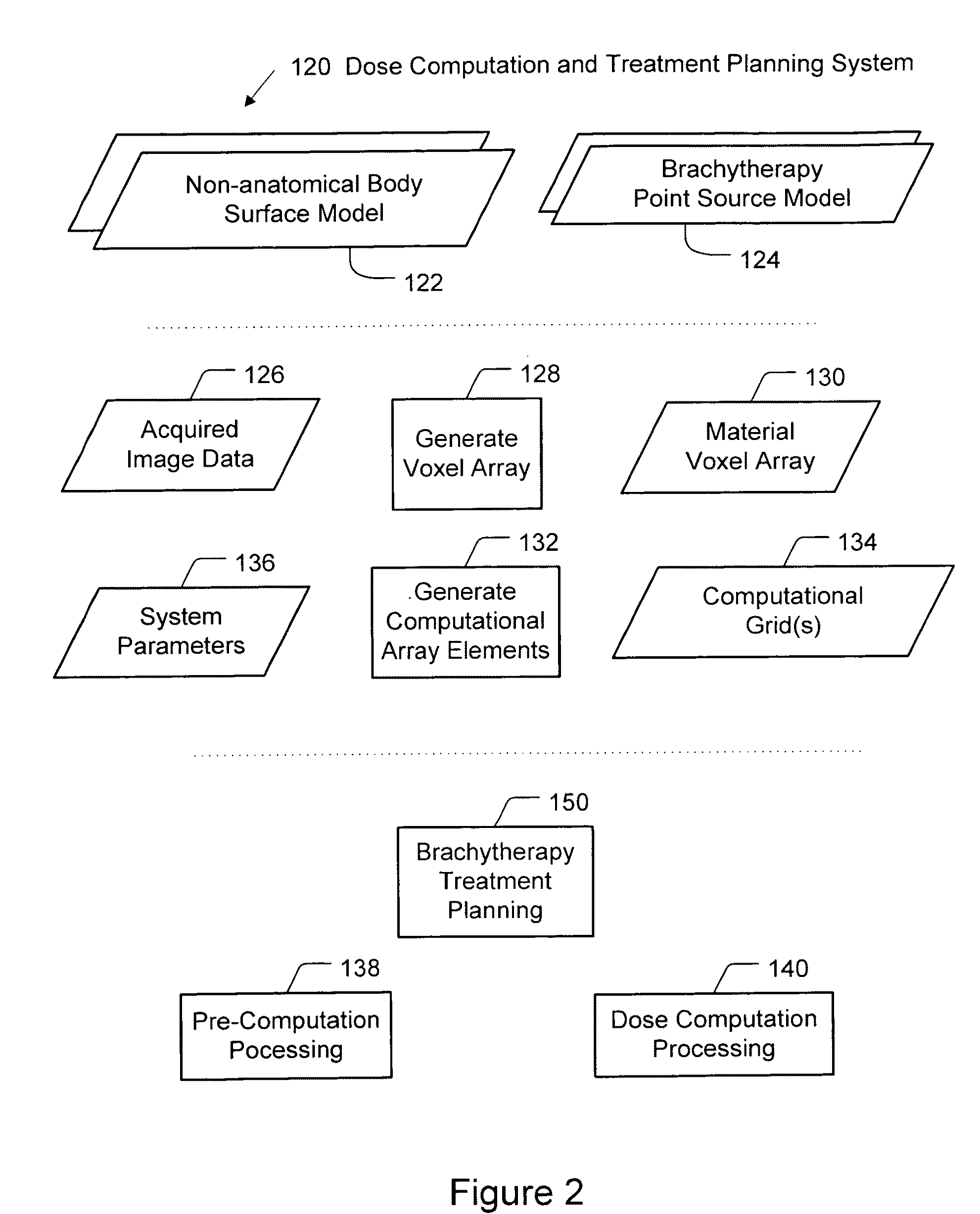
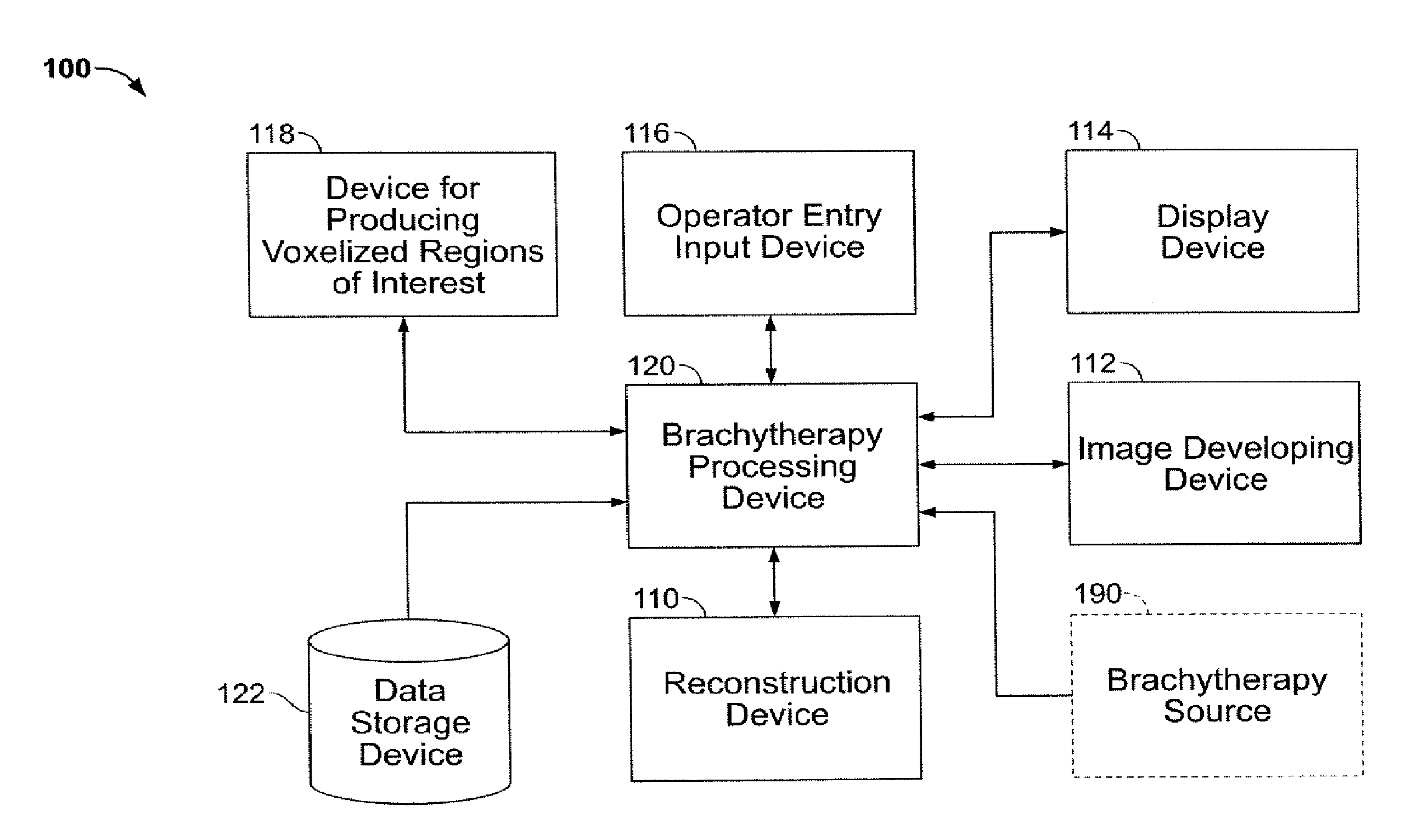
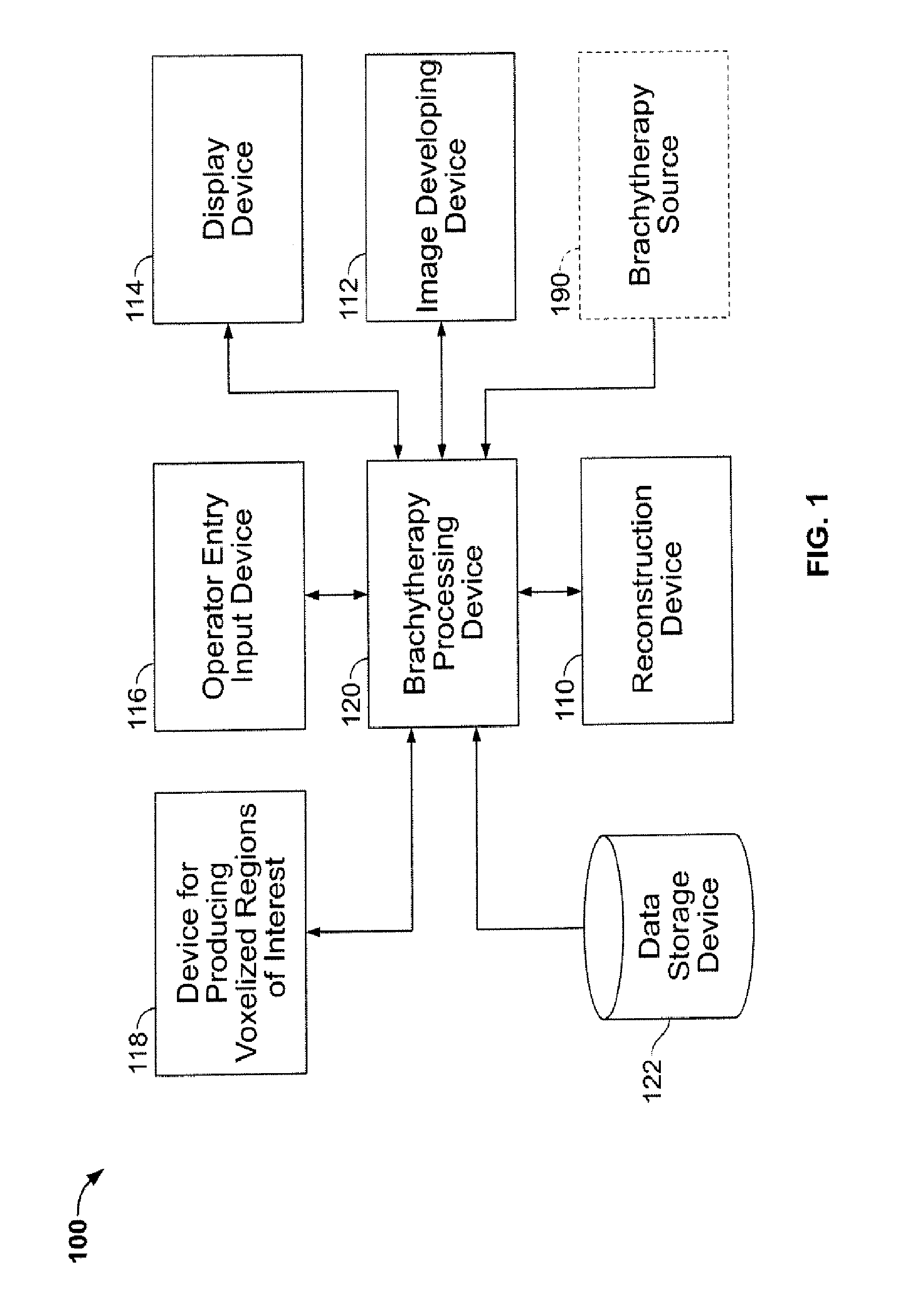
Brachytherapy dose attributable to a brachytherapy source is computed for portions of a patient treatment volume corresponding to a pathological target volume and critical structures. Patient image data is accessed to derive a material voxel array. Multiple computation grids are derived. Primary particle fluence is computed for each first grid element using a ray tracing process from which a primary dose and a first scattered particle source are derived. Scattered particle fluence of the first scattered particle source is derived for each second grid element from which a secondary dose is derived. Each first grid element corresponds to a plurality of second grid elements. Primary dose and scattered dose combine to provide total dose at specific volumes. Brachytherapy source models and non-anatomical body surface models may be applied as applicable.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
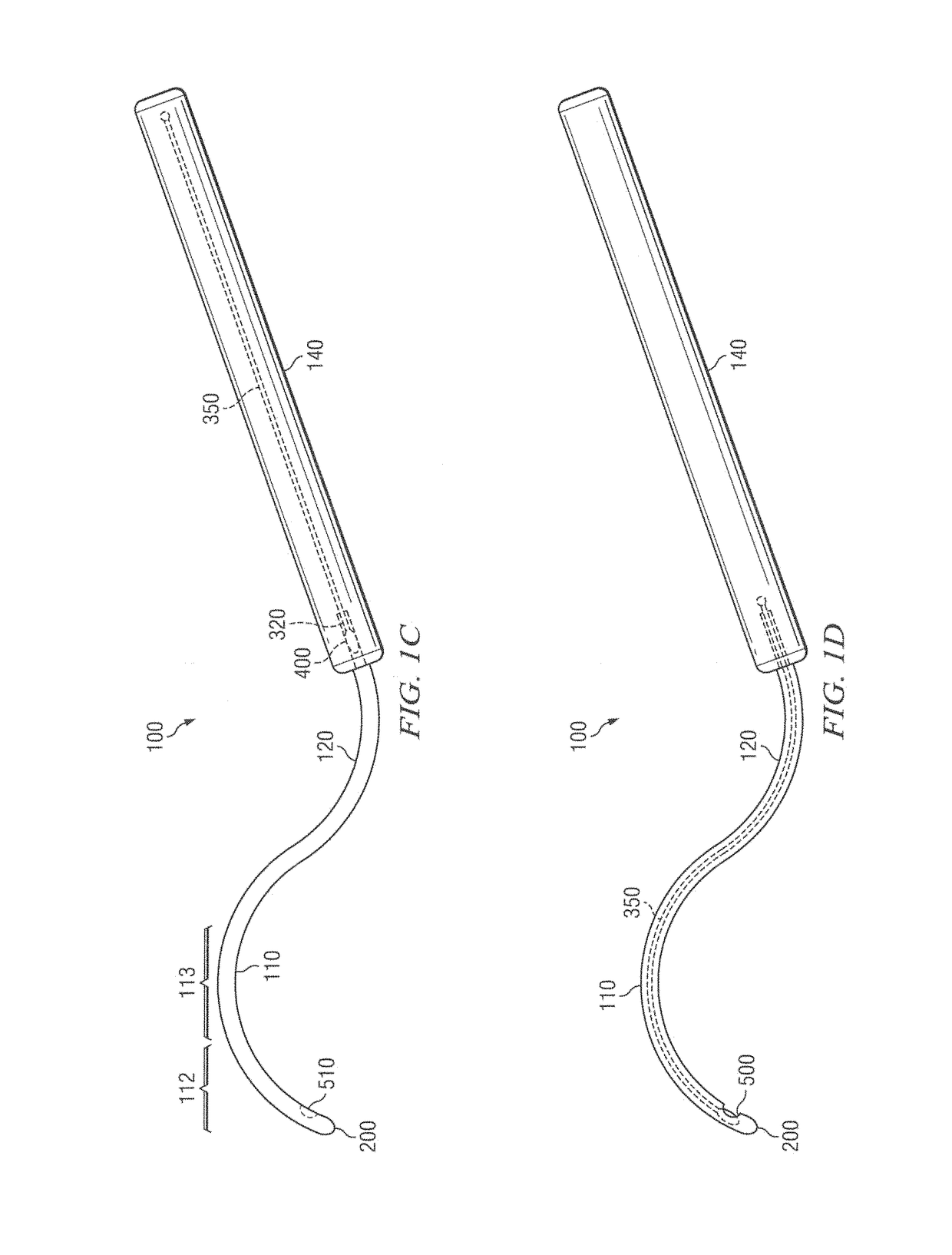
Methods And Devices For Delivering Appropriate Minimally-Invasive Extraocular Radiation
InactiveUS20110207987A1Avoid insufficient thicknessDiagnosticsSurgeryBrachytherapy sourceBiomedical engineering
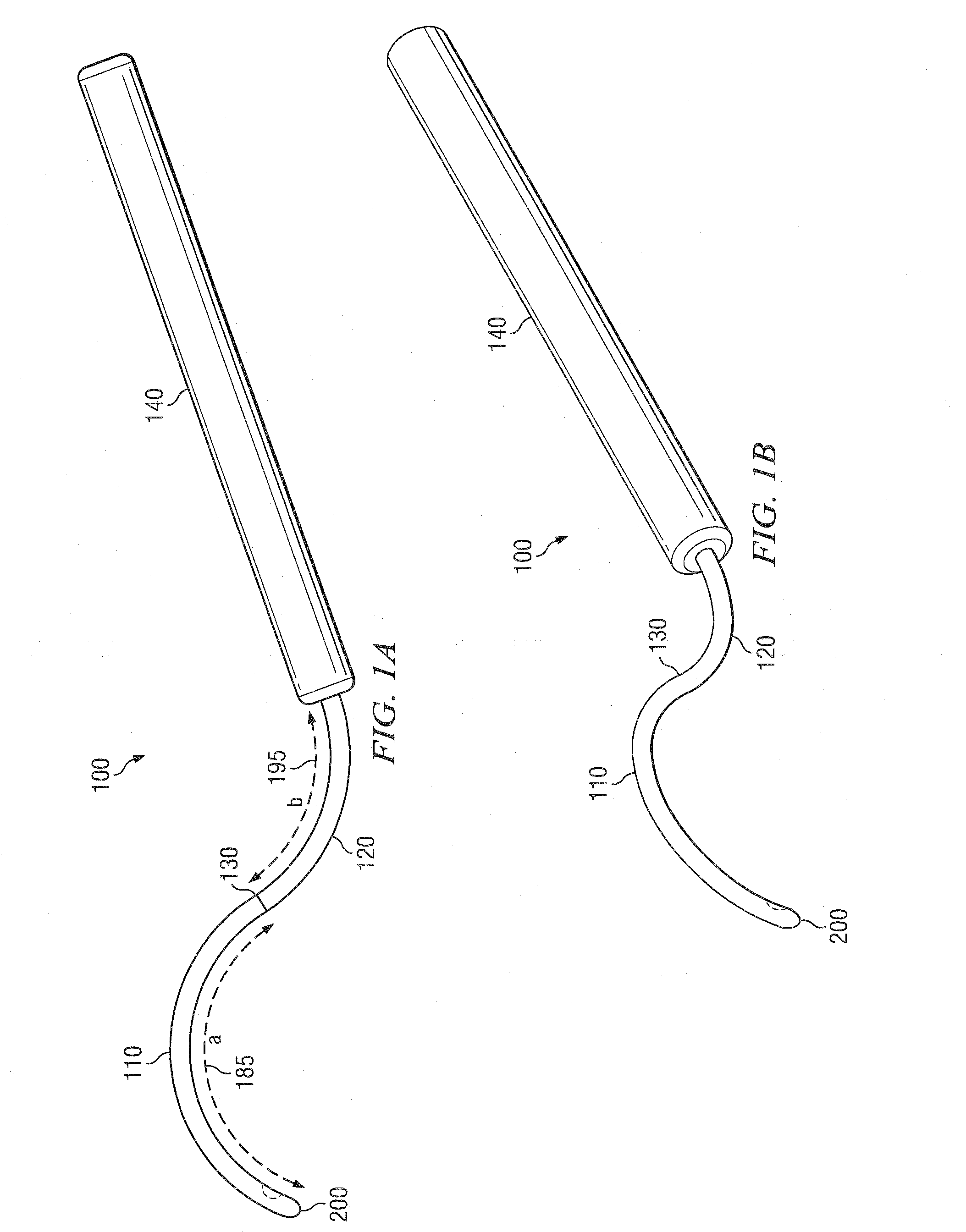
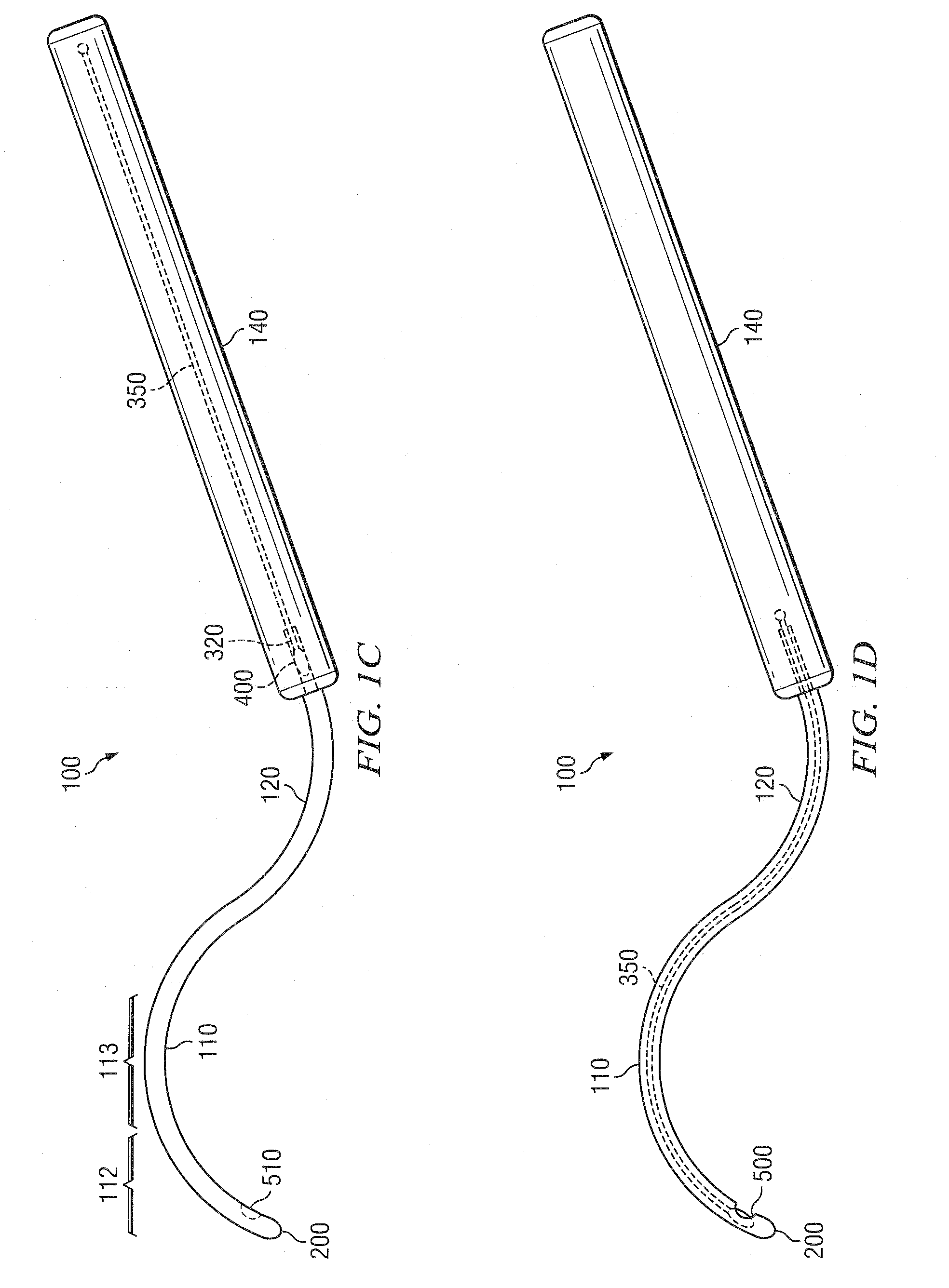
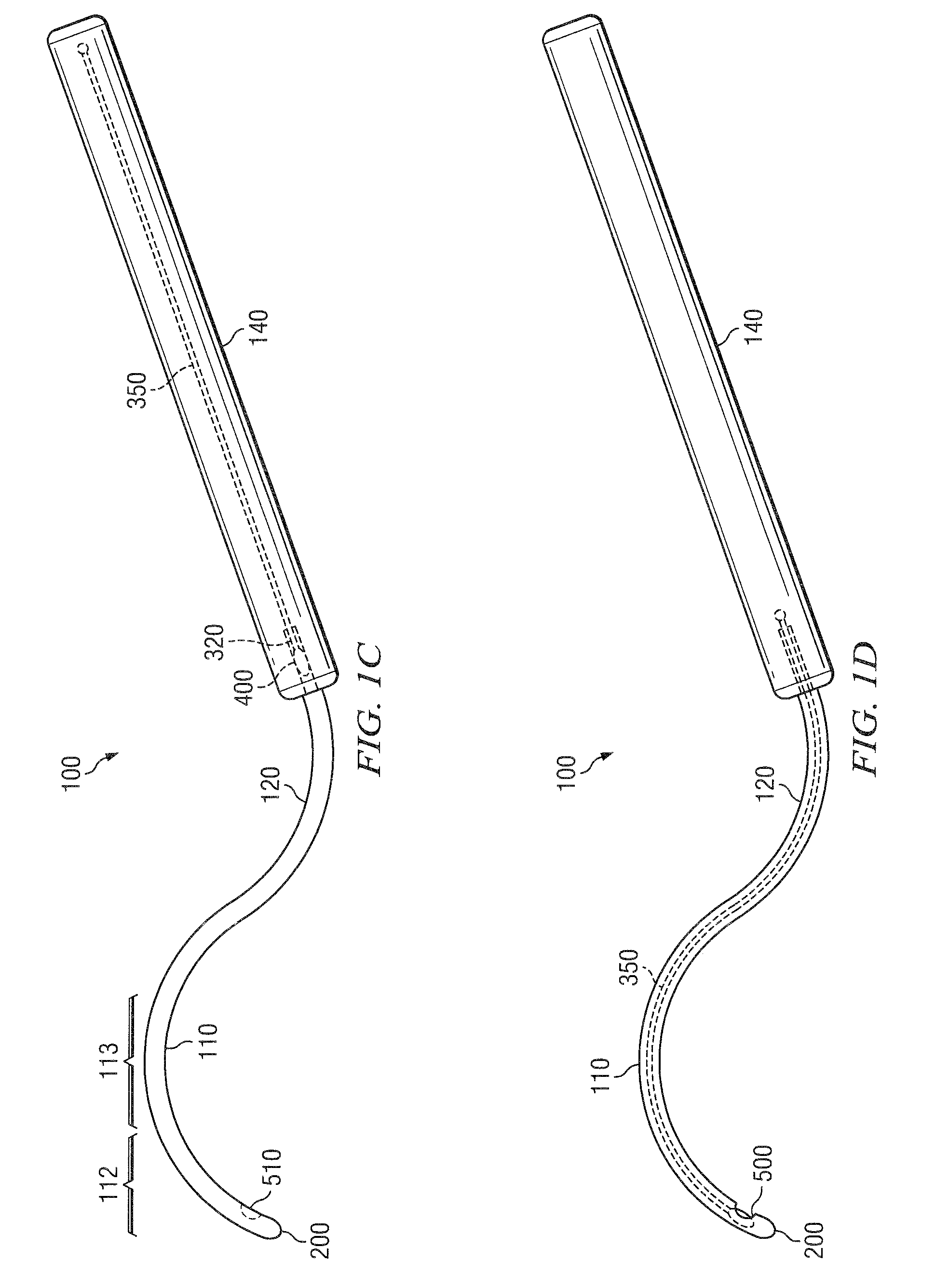
The present invention also features a brachytherapy system comprising a spiral cut tube having a first end and a second end; a radioactive brachytherapy source (RBS) disposed on the first end of the spiral cut tube; and a handle and a generally hollow cannula disposed on the handle, wherein a channel is disposed in the handle aligned with the hollow cannula, and the spiral cut tube and RBS are adapted to slide within the channel and the hollow cannula.
Owner:SALUTARIS MEDICAL DEVICES
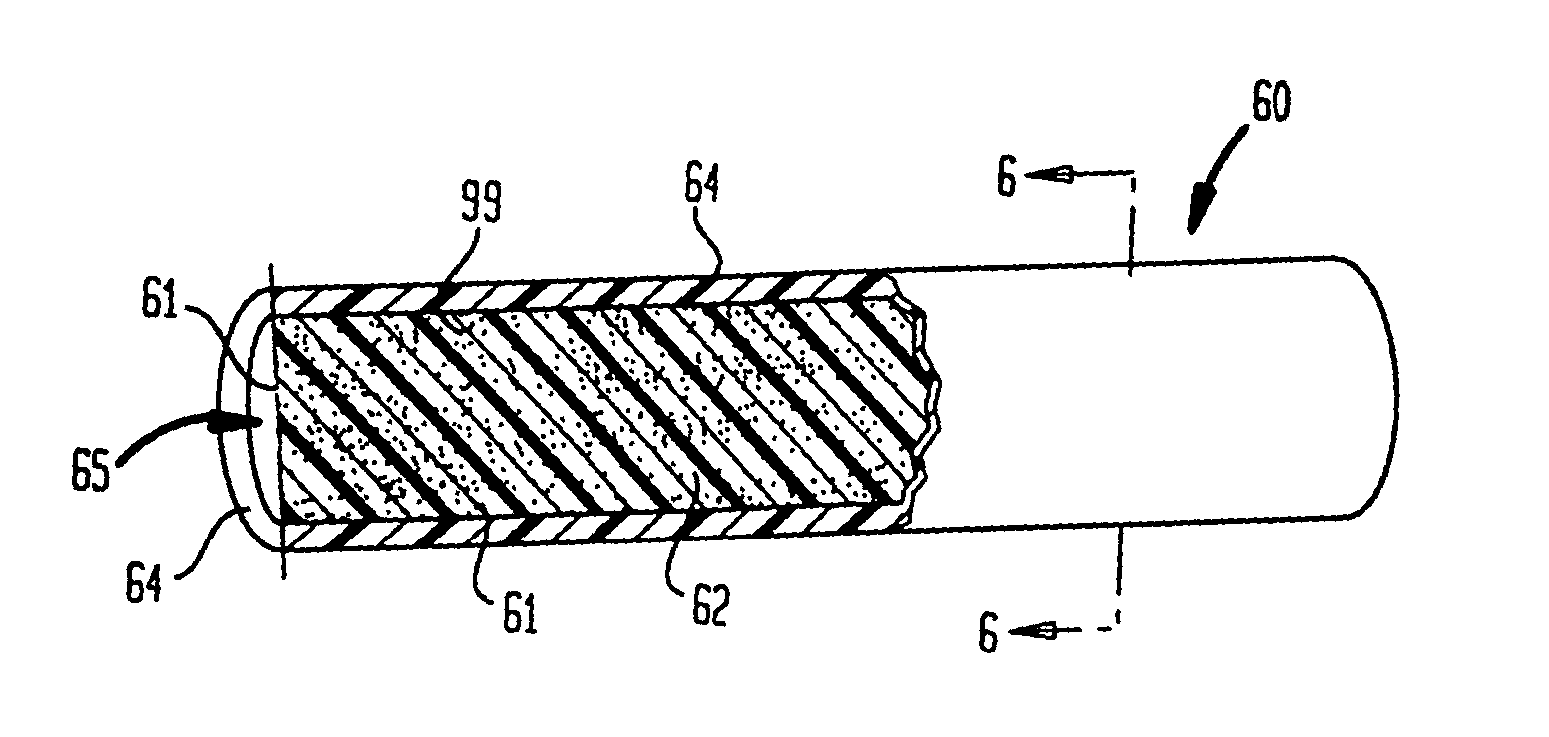
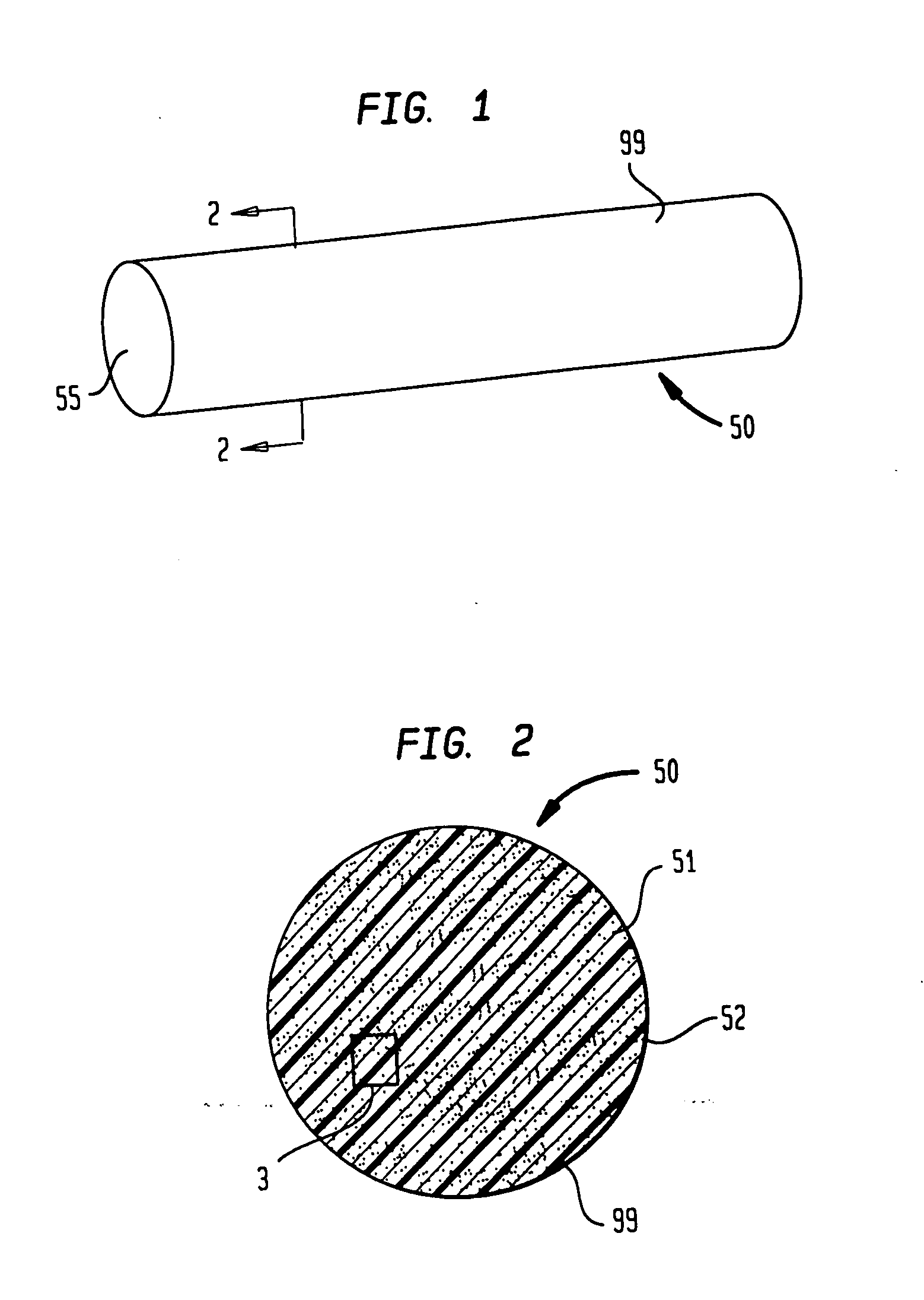
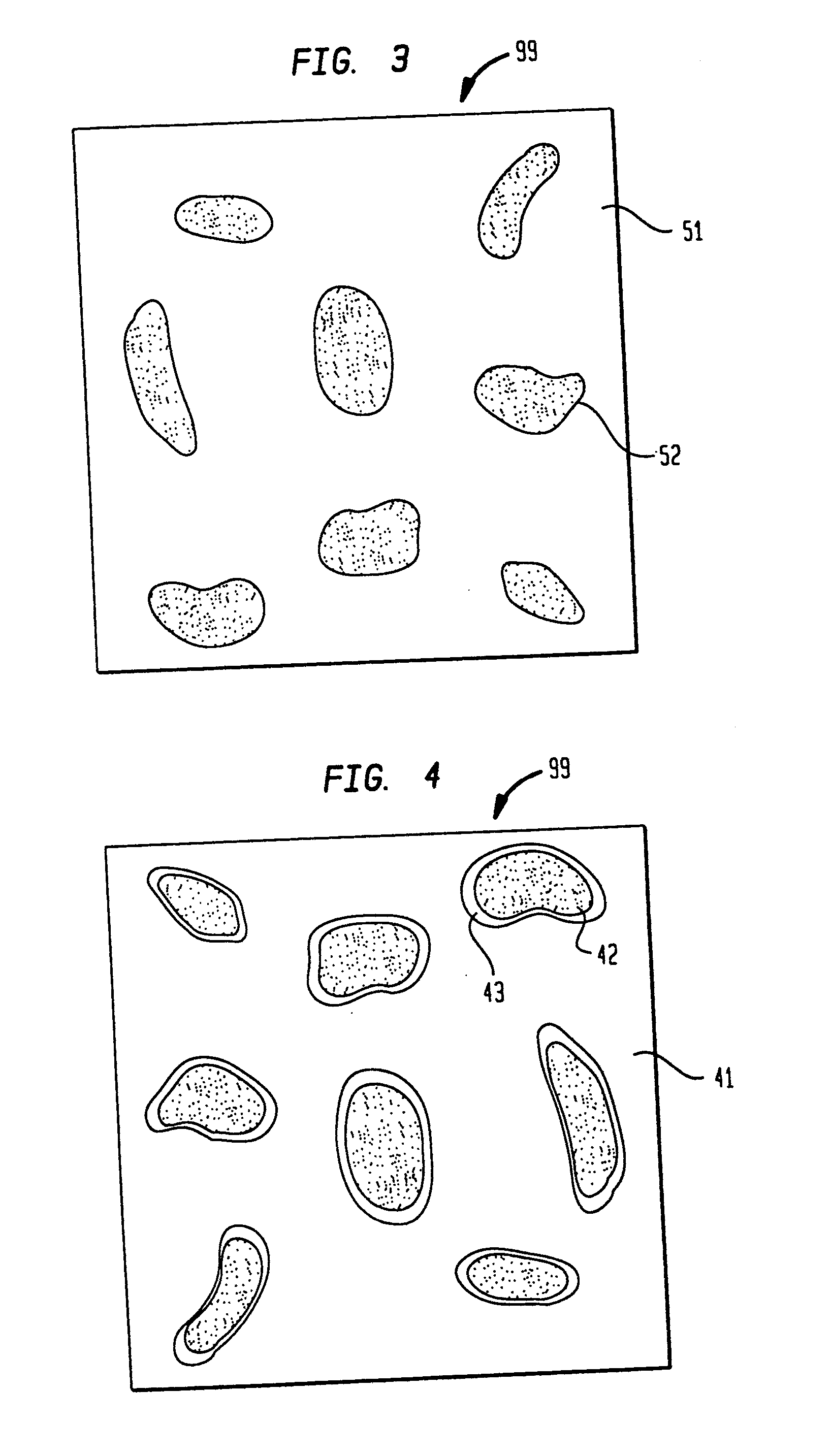
Polymeric-matrix brachytherapy sources
InactiveUS6986880B2Simply and inexpensivelyDegree of flexibilityRadioactive preparation formsRadioactive sourcesGlobular shapedBrachytherapy source
Therapeutic sources for use in the practice of brachytherapy comprise a radioactive composite that includes (a) a polymeric matrix and (b) a radioactive powder, e.g. Pd-103 or I-125, consisting essentially of very fine radioactive particles that are randomly and essentially uniformly dispersed within the polymeric matrix. The composite may be in the shape of one or more solid cylindrical rods surrounded by a non-radioactive sleeve. Alternatively it may be a hollow rod, suture, film, sheet, or microspheroidal particles. The composite may be shaped by molding, extrusion or other methods, may be made with a flexibility suitable to its intended use or may be encapsulated in a metallic capsule.
Owner:INT BRACHYTHERAPY
Shielded treatment environment for brachytherapy source
InactiveUS7276716B1Reduce radiation exposureReduce exposureShieldingPortable shielded containersGamma rayBrachytherapy source
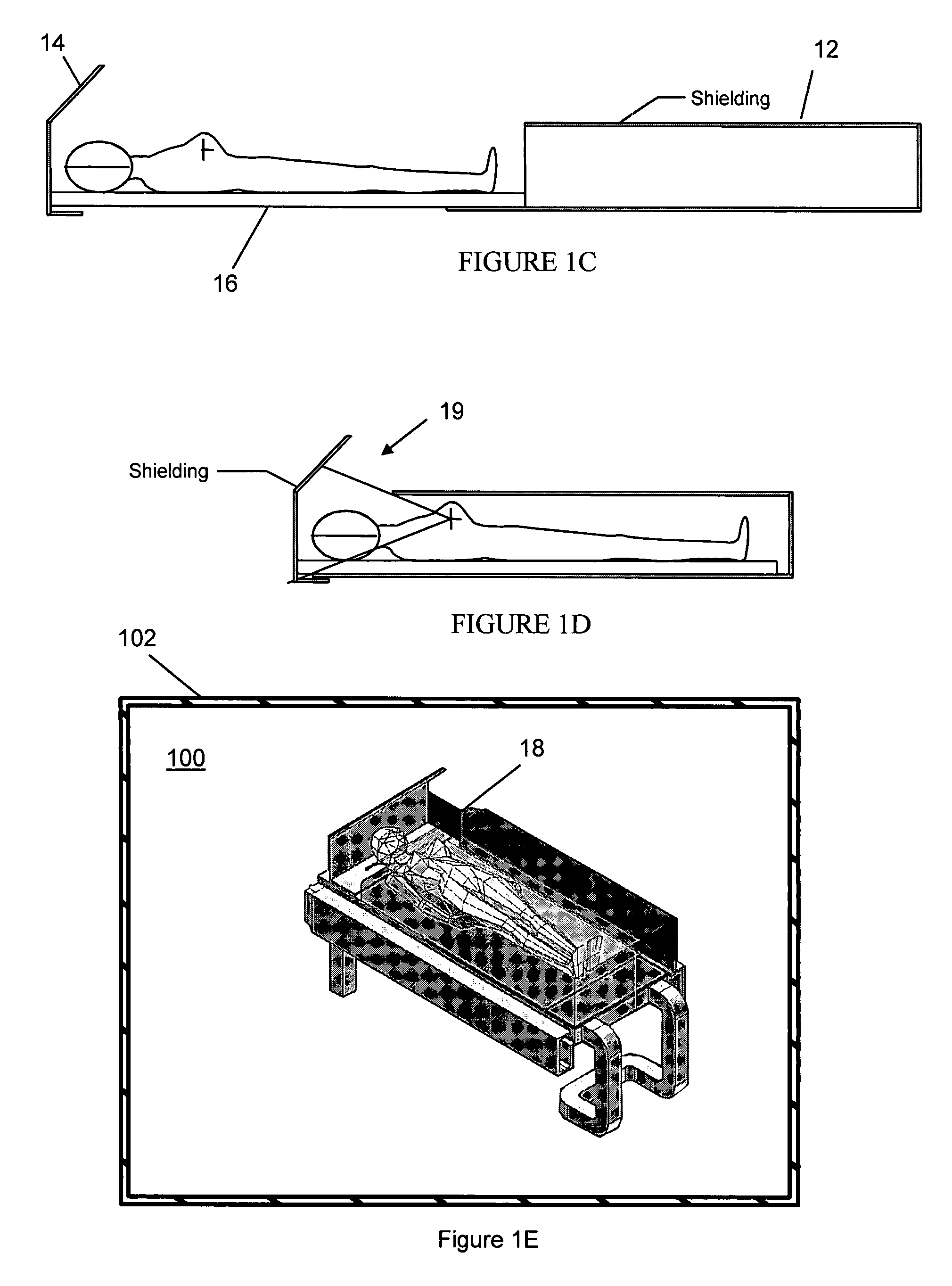
A radiation protection system for shielding medical personnel from a gamma ray source being used to provide brachytherapy to a patient is provided by disposing shielding material between the source of radiation and locations outside the radiation protection system in such a manner as to provide shielding for the primary radiation in directions from which radiation from the source may emerge, while providing the patient an open viewing area with a large field of view for the patient to view the locations outside the radiation protection system. The described system reduces the radiation exposure of staff in the treatment room, thereby permitting physicians and therapists to observe the patient without being exposed to excessive amounts of radiation. The opening in the radiation protection system around the head of the patient provides the ability for the patient to see his surroundings and to eliminate the anxiety resulting from the feeling of being closed in.
Owner:IMPLANT SCI
System and method of clinical treatment planning of complex, monte carlo-based brachytherapy dose distributions
InactiveUS20110184283A1Error minimizationImprove spatial resolutionRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAxis of symmetryProgram planning
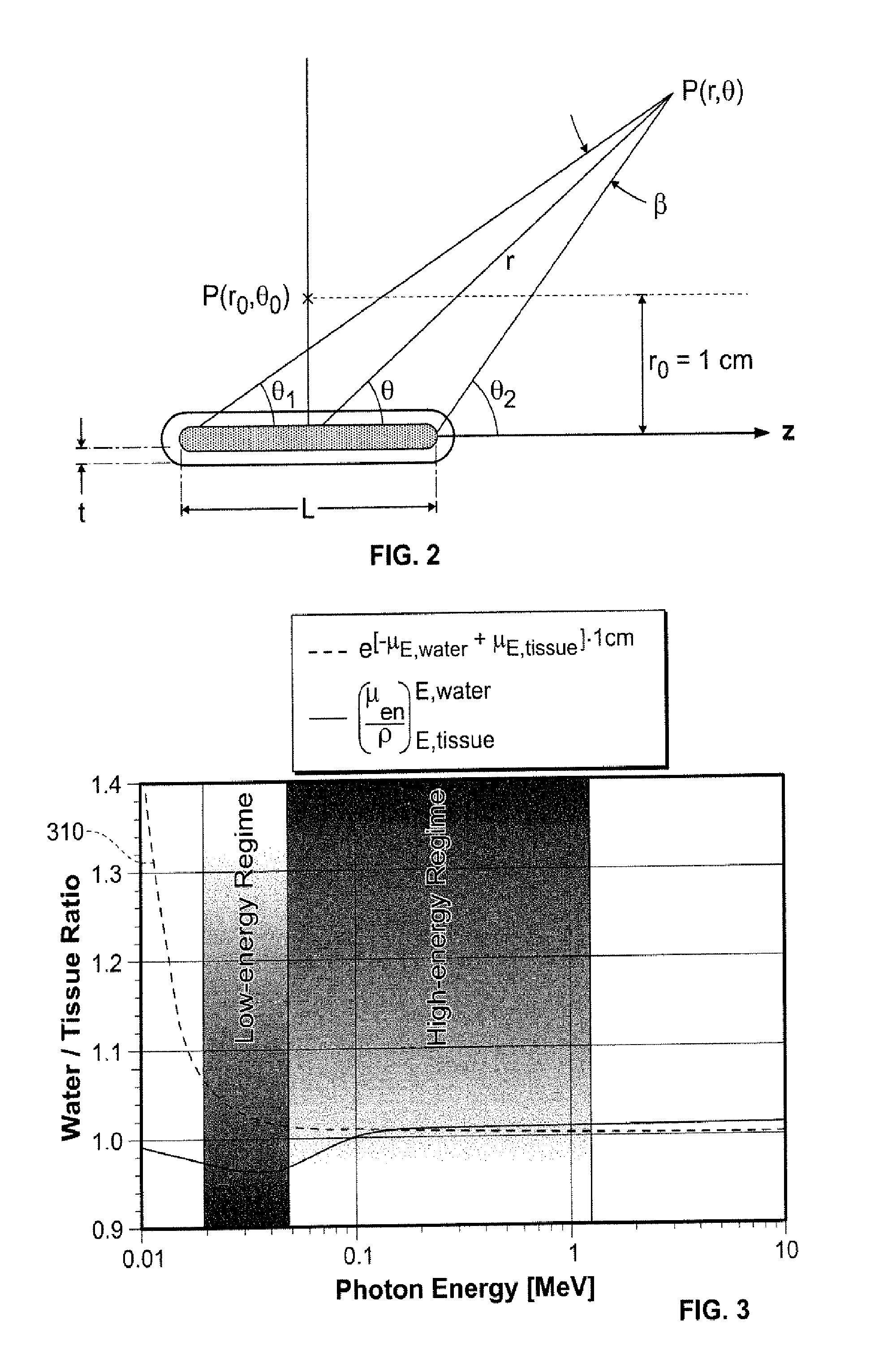
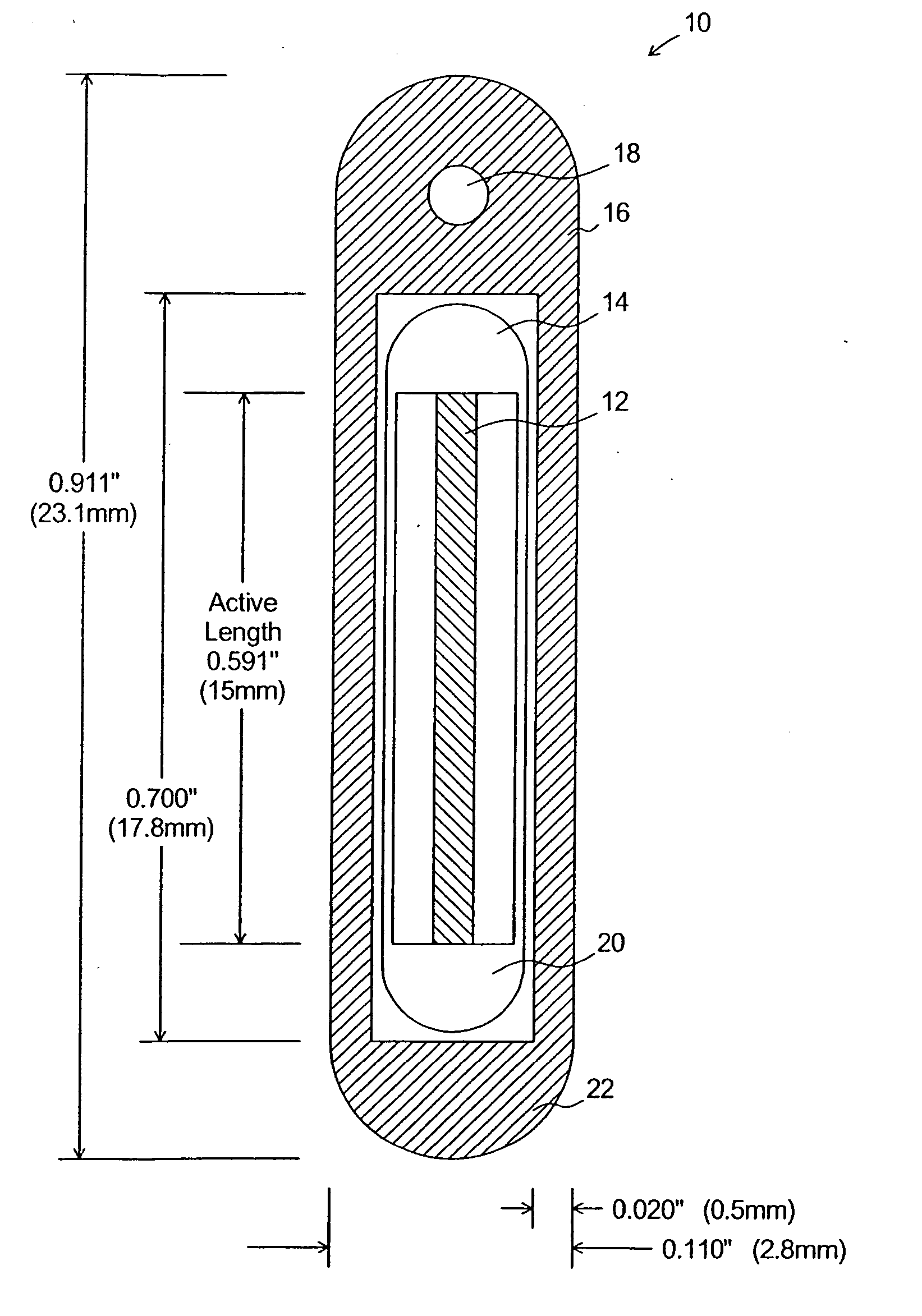
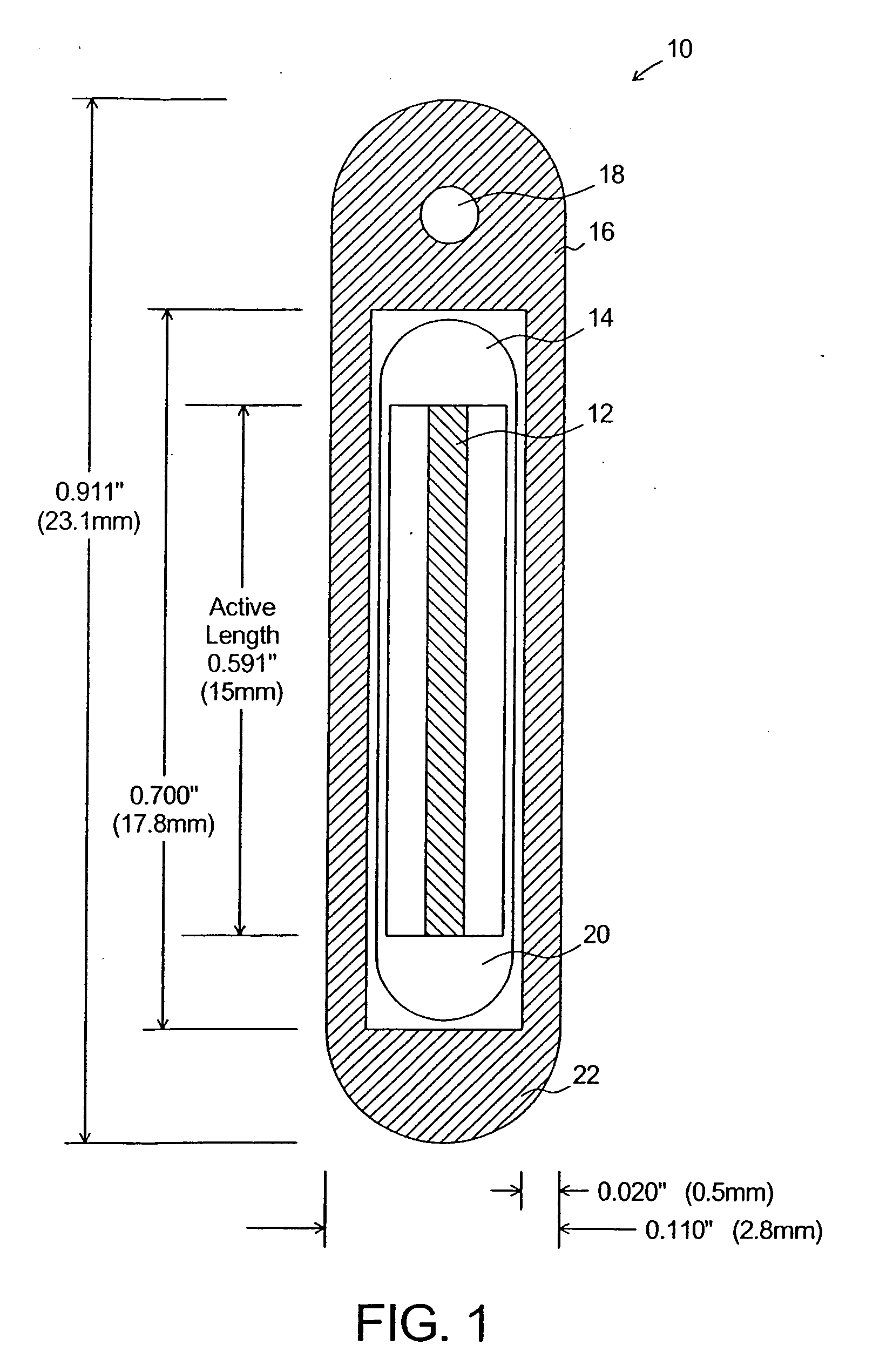
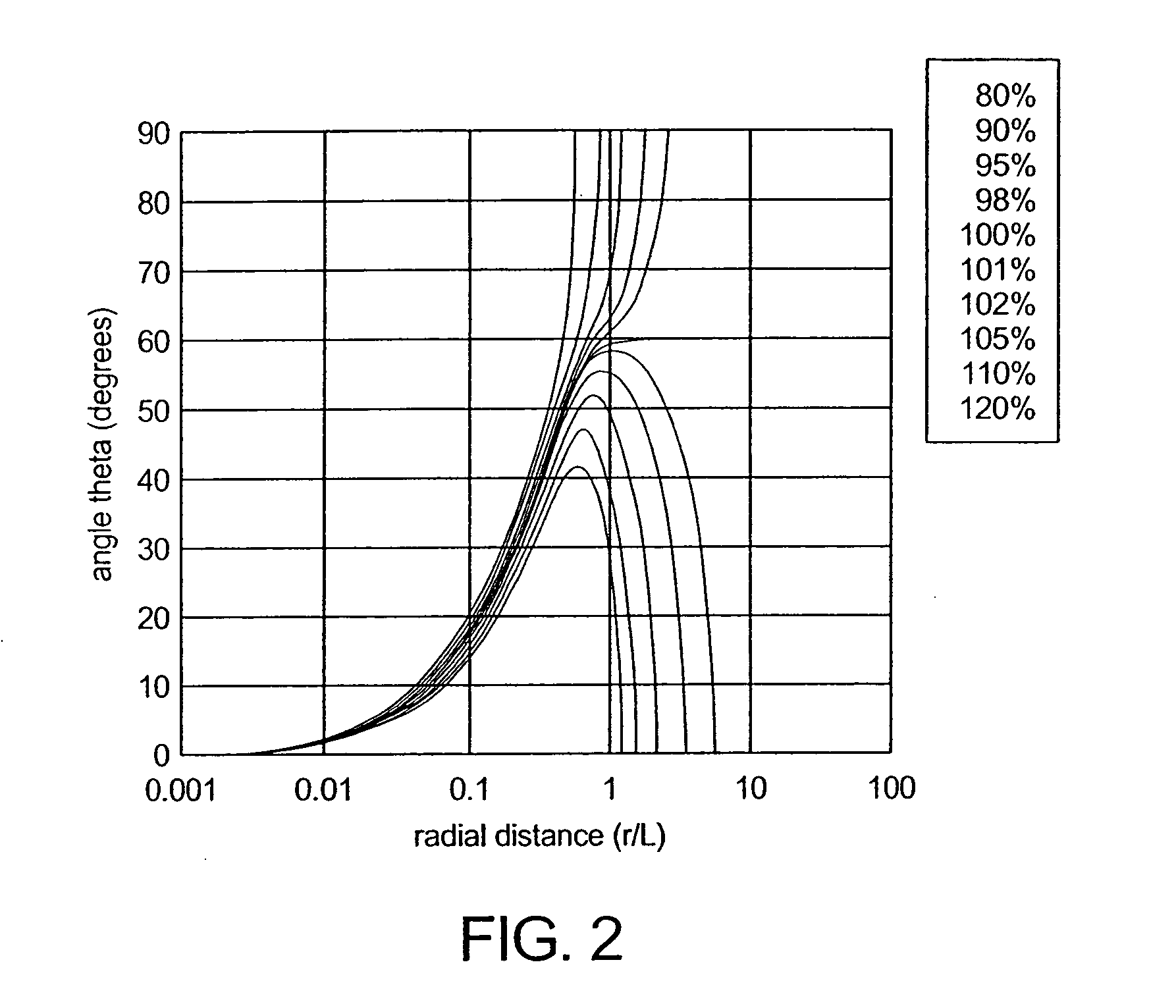
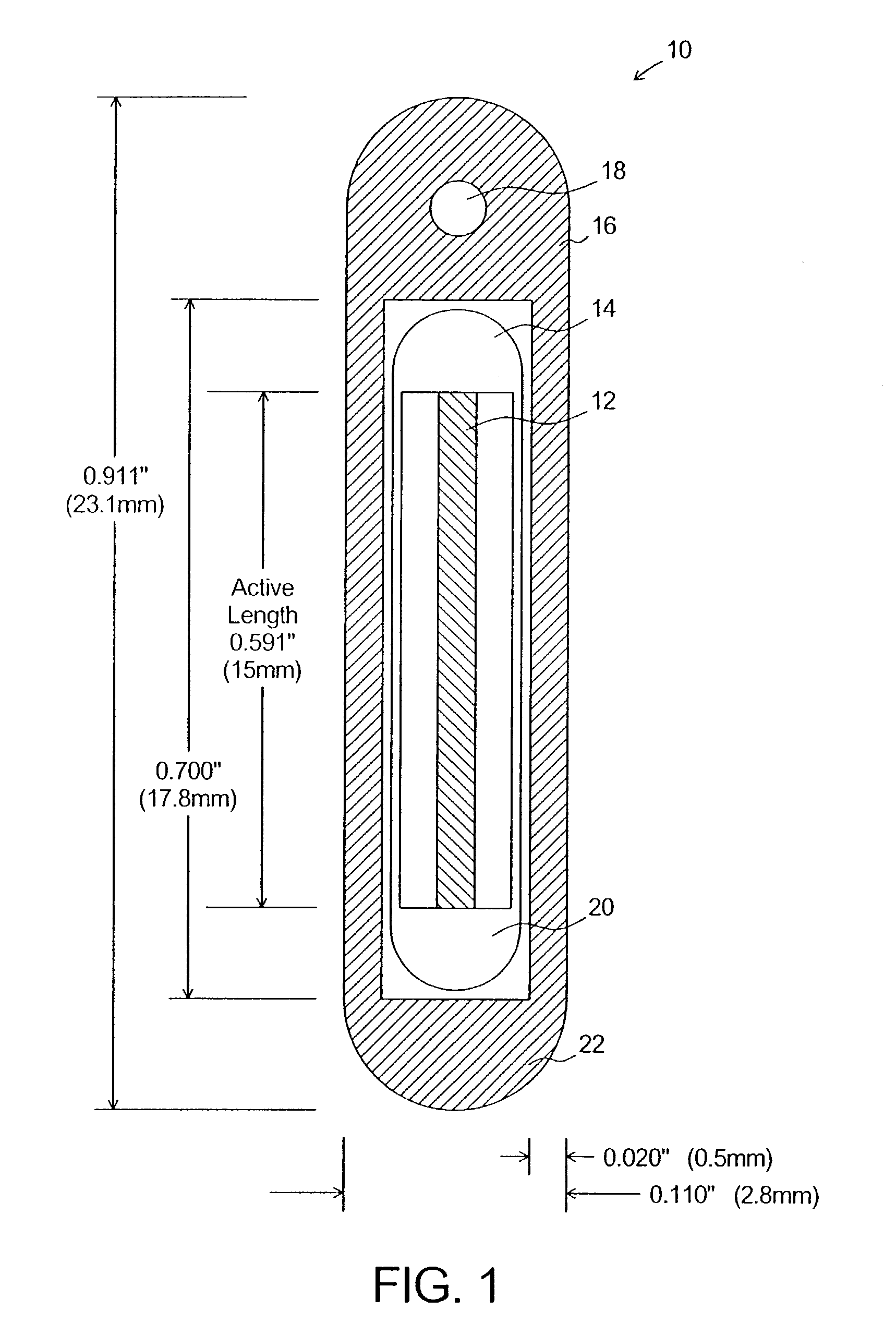
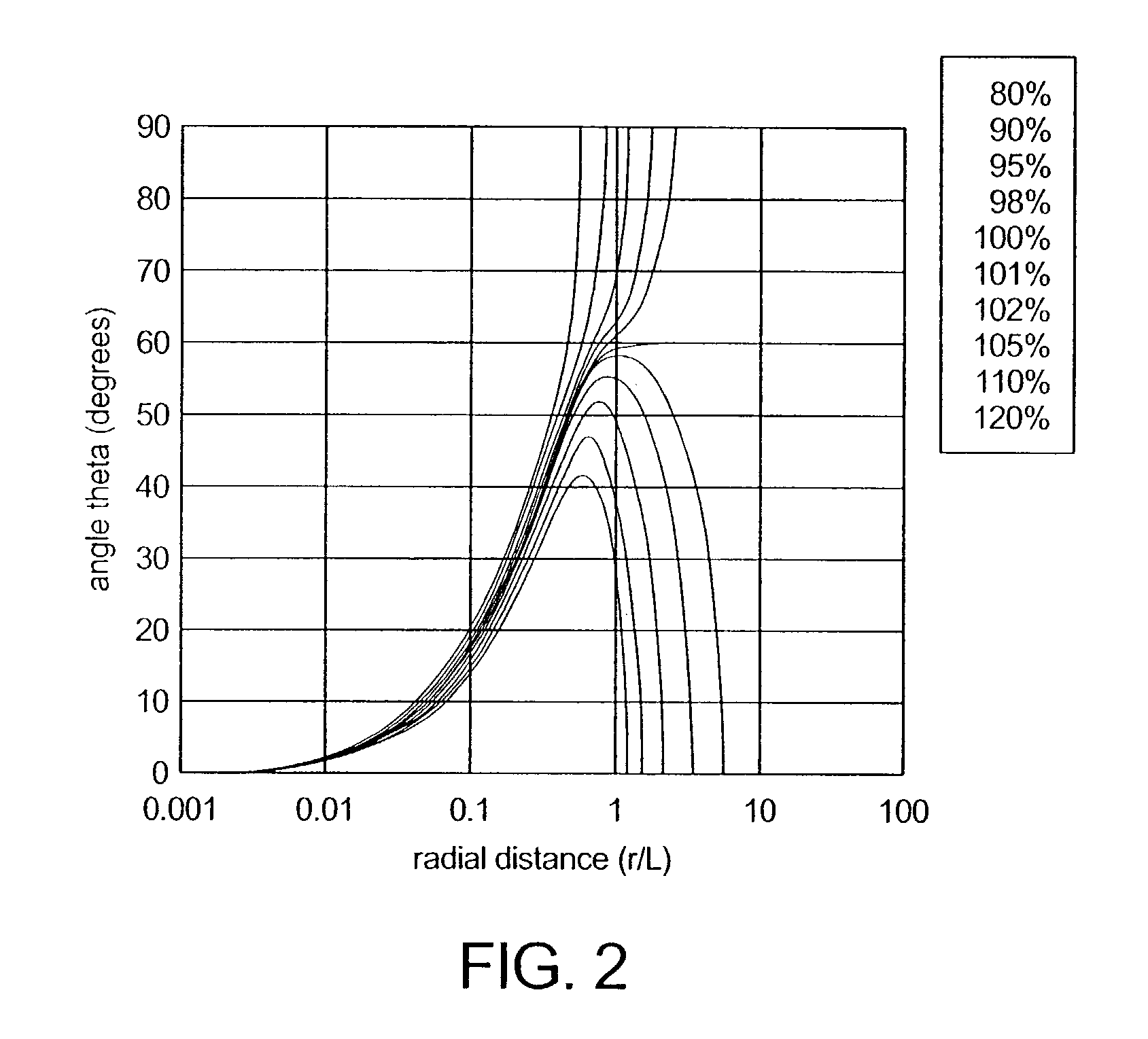
A system, method, and computer program product of clinical treatment planning implements complex Monte Carlo (MC) based brachytherapy dose distributions using conventional brachytherapy treatment planning systems (TPS). Dose distributions from complex brachytherapy source configurations determined with MC methods are used as inputs. Radial dose functions and 2D anisotropy functions are obtained by positioning the coordinate system origin along the dose distribution cylindrical axis of symmetry. Origin to tissue distance and active length are chosen to minimize TPS interpolation errors. A 2D anisotropy function is determined, and a brachytherapy dose rate constant is selected. A virtual brachytherapy source dose distribution is calculated based upon the complex treatment configuration. Additional dosimetry parameters may be considered as well, and dose distributions may be calculated and compared to the original MC-derived dose distributions. The present techniques may calculate dose to a specific tissue type instead of dose to water as used in the TG-43 formalism
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Dosimetry for californium-252 (252Cf) neutron-emitting brachytherapy sources and encapsulation, storage, and clinical delivery thereof
The present invention discloses a methodology for the characterization and determination of mixed-field dosimetry for 252Cf Applicator Tube (AT)-type medical sources, utilizing ionization chambers, GM counters, and Monte Carlo methods. Unlike the previous methodologies, the present invention discloses a specification of dose to muscle, rather than dose to water, for clinical dosimetry of 252Cf medical sources. A dosimetry protocol, similar to that utilized for ICRU-45, with parameters determined specifically for 252Cf brachytherapy is disclosed. Neutron isodose distributions and data necessary for clinical implementation of 252Cf AT sources are also disclosed herein. Additionally, novel methods for the encapsulation, storage, and delivery / implantation of 252Cf radionuclide sources are disclosed.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND MEDICAL CENT HOSPITALS
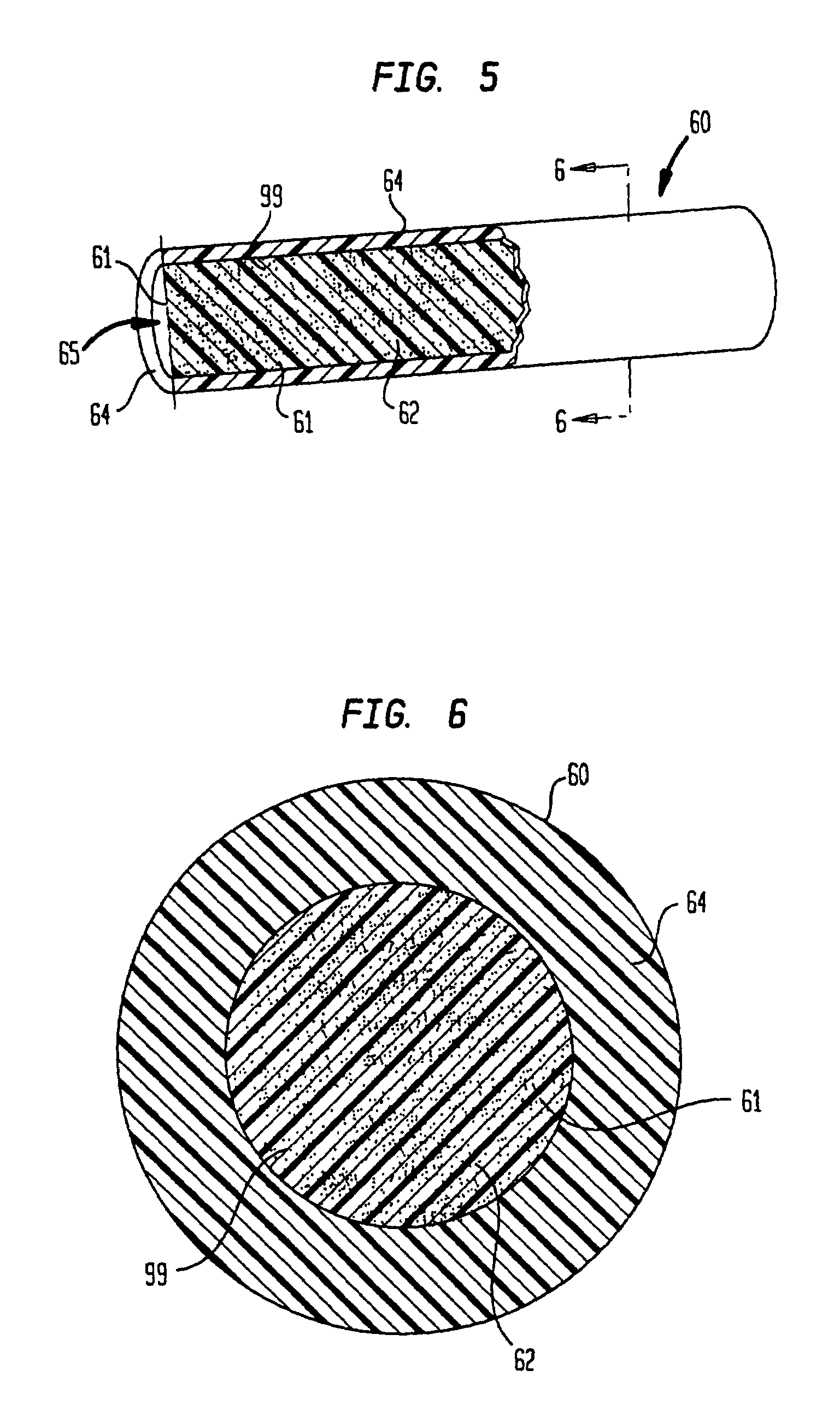
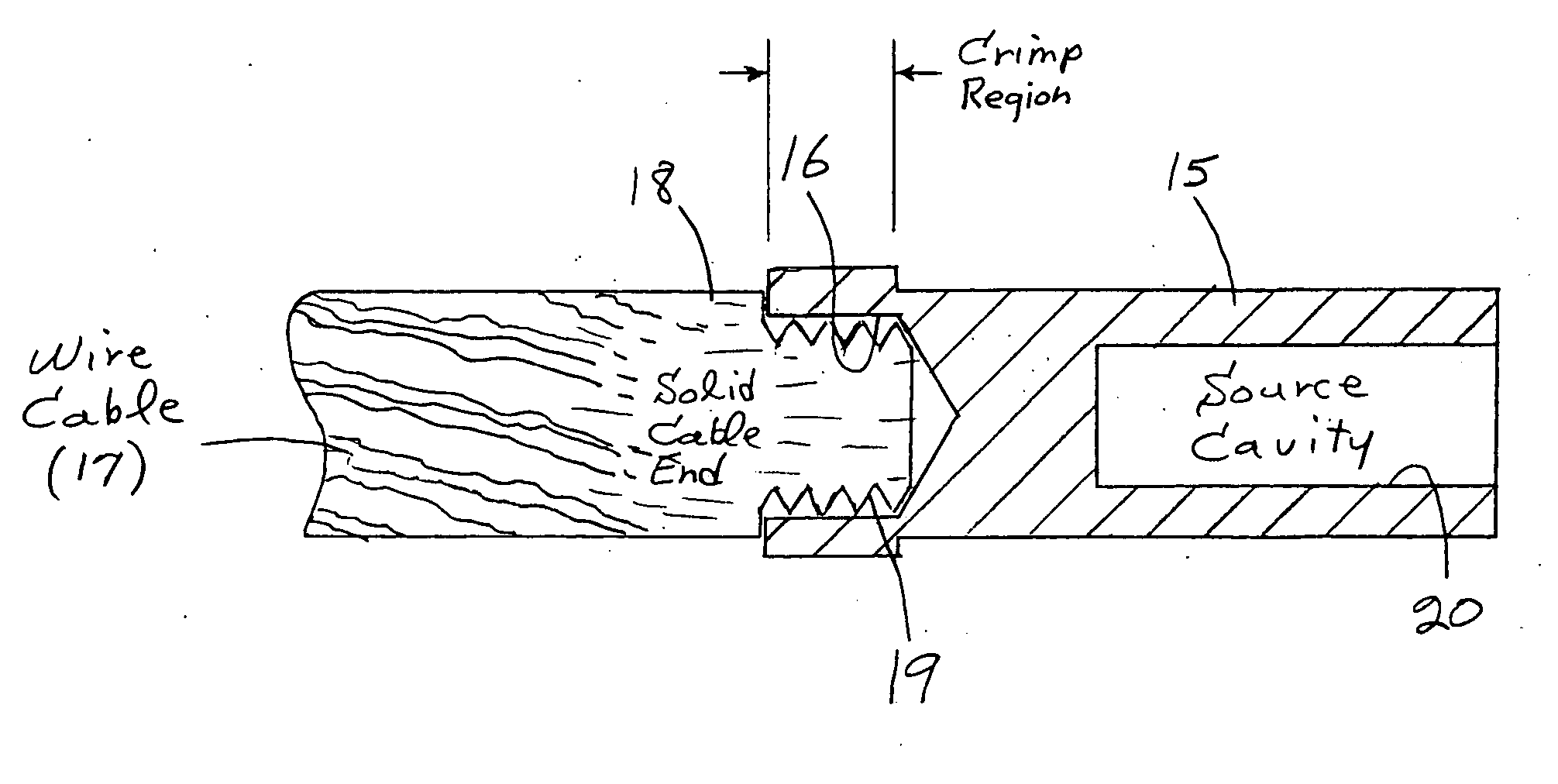
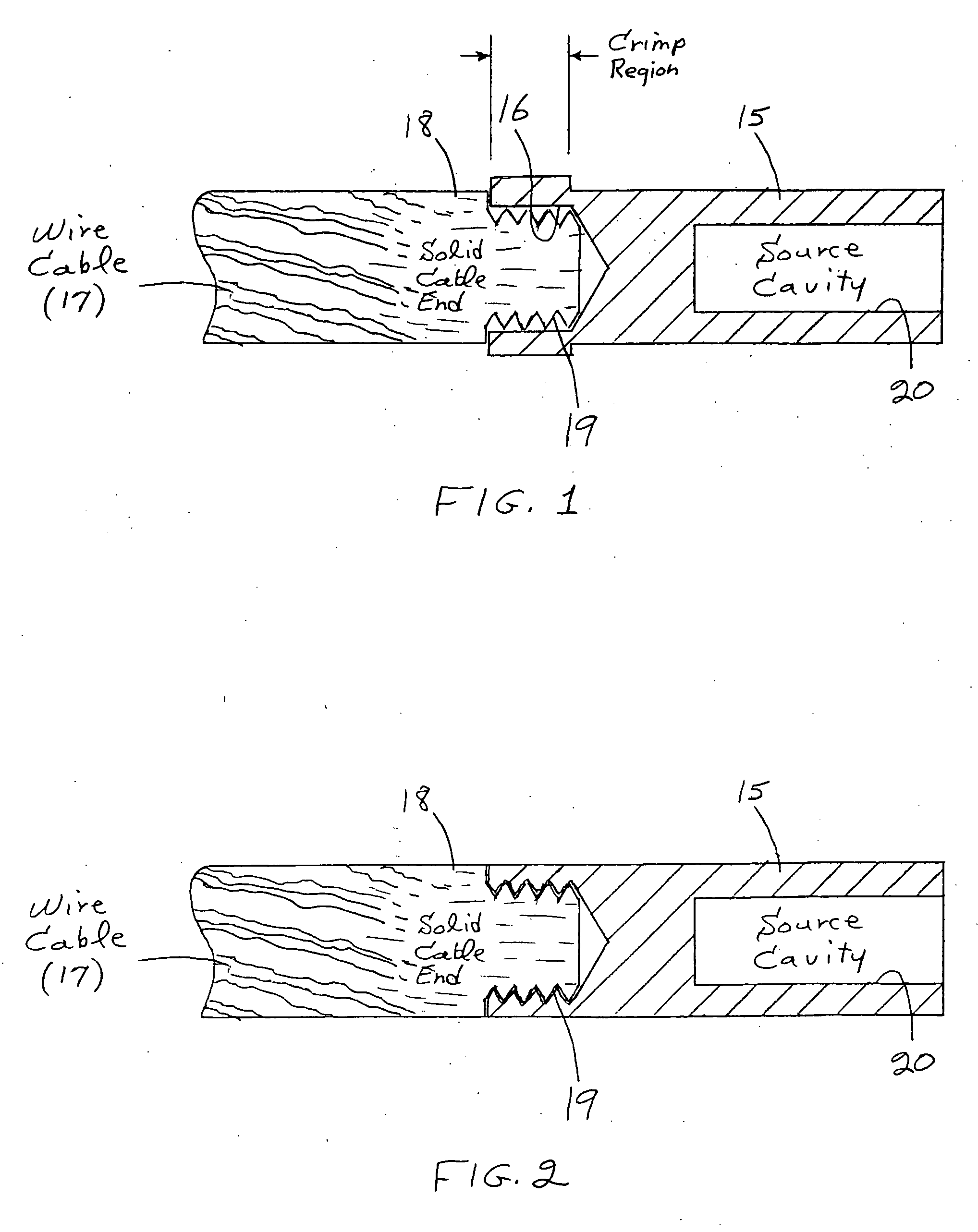
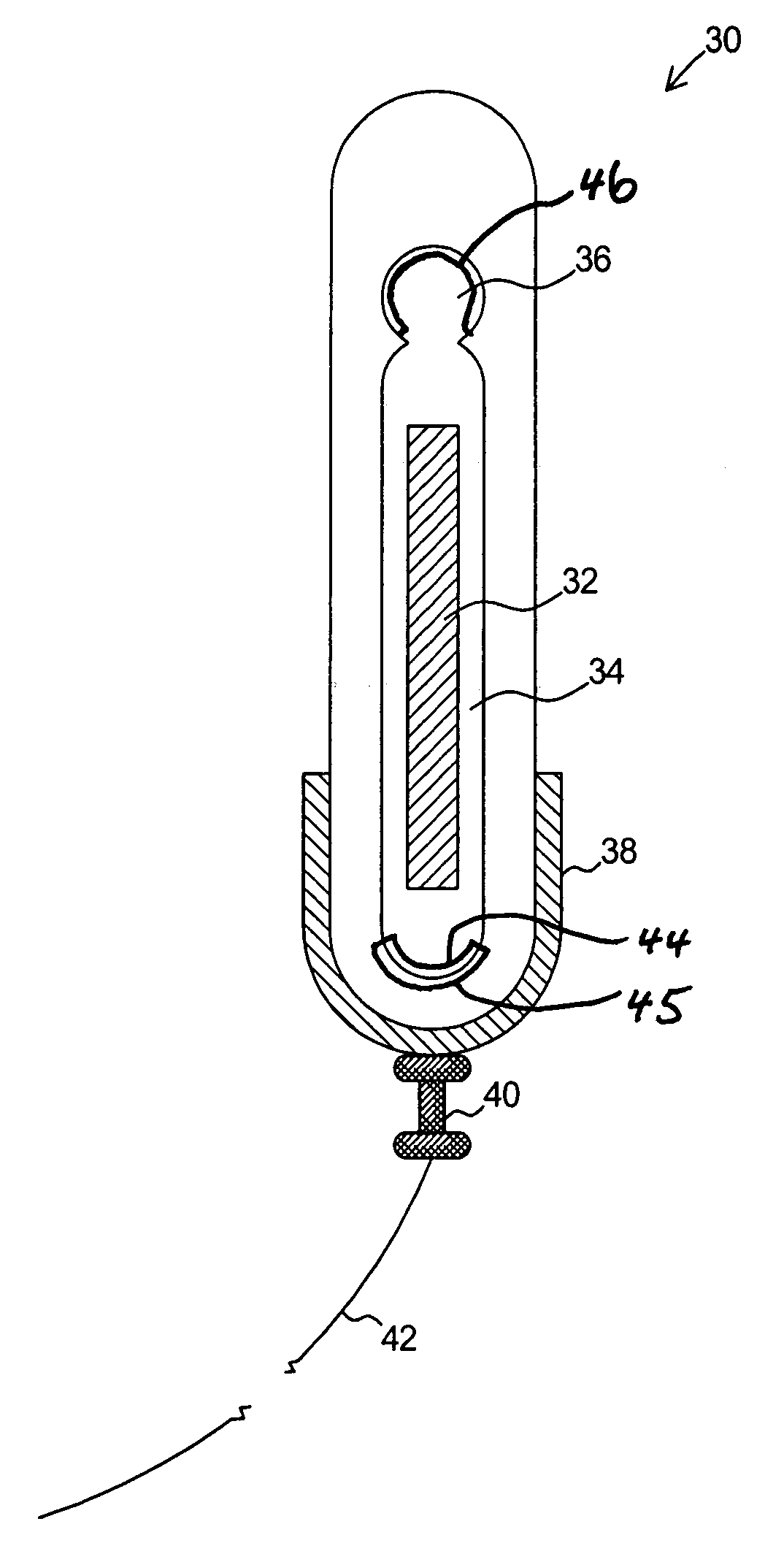
Cable attachment for a radioactive brachytherapy source capsule
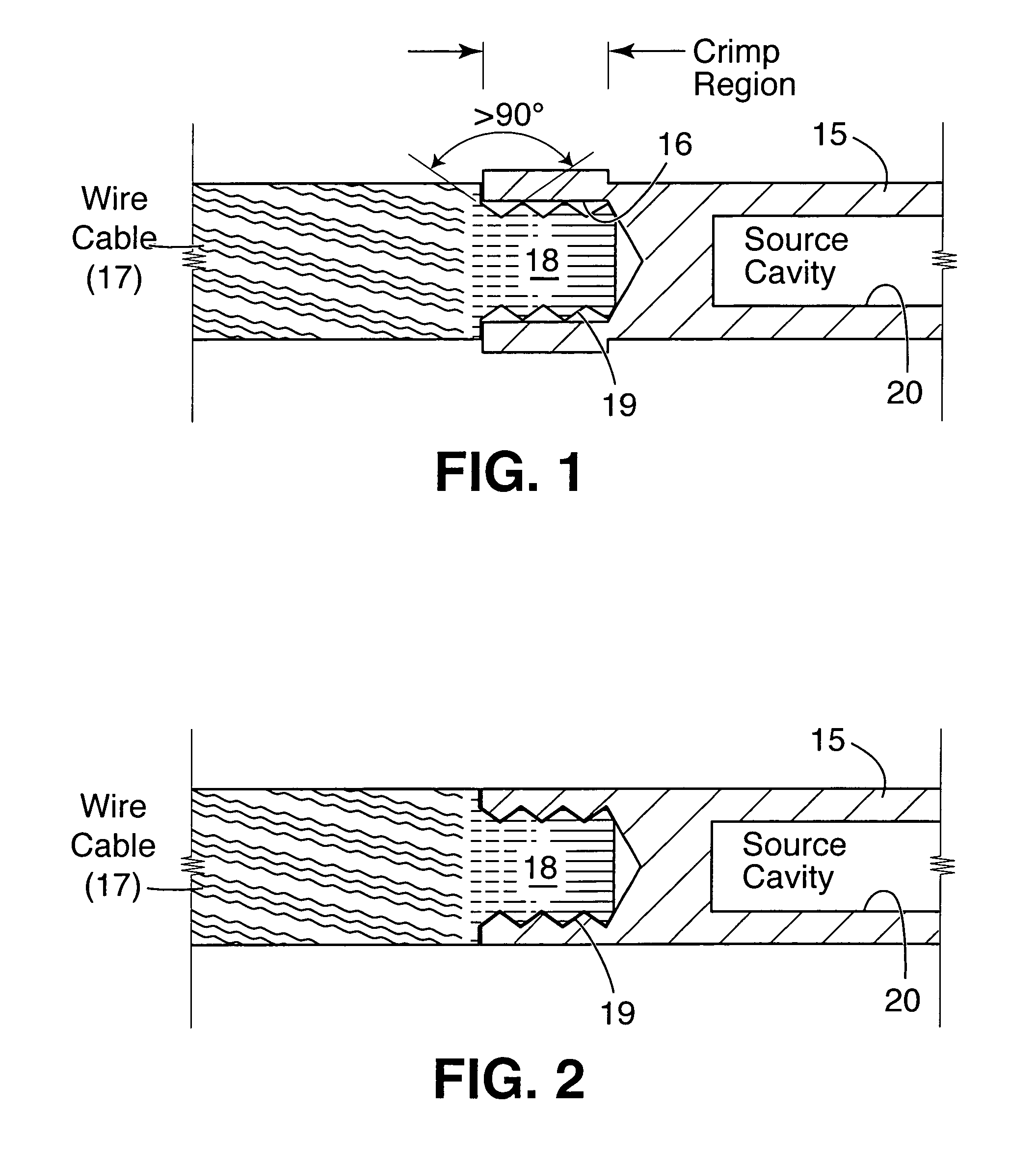
InactiveUS20060058568A1No dimensional variability in the final productMaximized strengthRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyCouplings for rigid shaftsHot cellEngineering
In cancer brachytherapy treatment, a small californium-252 neutron source capsule is attached to a guide cable using a modified crimping technique. The guide cable has a solid cylindrical end, and the attachment employs circumferential grooves micromachined in the solid cable end. The attachment was designed and tested, and hardware fabricated for use inside a radioactive hot cell. A welding step typically required in other cable attachments is avoided.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for preparing particles of radioactive powder containing cesium-131 for use in brachytherapy sources
ActiveUS20060167332A1Easy to holdPowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAbnormal tissue growthBrachytherapy source
The present invention provides a method of preparing Cesium-131 (Cs-131) as a dispersed radioisotope. Uses of the dispersed Cs-131 prepared by the method include cancer research and treatment, such as for the use in brachytherapy. Cs-131 is particularly useful in the treatment of faster growing tumors.
Owner:ISORAY MEDICAL INC
Plastic brachytherapy sources
InactiveUS7922646B2Less materialEconomic advantageX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapy sourceTherapeutic radiation
Owner:ECKERT & ZIEGLER BEBIG
Method for manufacturing radioactive brachytherapy source material, brachytherapy source material and encapsulated radioactive brachytherapy source
The invention relates to a method for producing a radioactive brachytherapy source material comprising indium-114m in radioactive equilibrium with indium-114 as main radioactive isotopes. A new radioactive brachytherapy source material comprises indium-114m in radioactive equilibrium with indium-114 as main radioactive isotopes. A new encapsulated radioactive brachytherapy source comprises the new radioactive brachytherapy source material.
Owner:NUCLETRON
Method for preparing particles of radioactive powder containing Cesium-131 for use in brachytherapy sources
ActiveUS7316644B2Powder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBrachytherapy sourceRadioactive waste
The present invention provides a method of preparing Cesium-131 (Cs-131) as a dispersed radioisotope. Uses of the dispersed Cs-131 prepared by the method include cancer research and treatment, such as for the use in brachytherapy. Cs-131 is particularly useful in the treatment of faster growing tumors.
Owner:ISORAY MEDICAL INC
Brachytherapy devices, kits and methods of use
InactiveUS20130030238A1Reduce radiation doseLittle penaltyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapy deviceX-ray
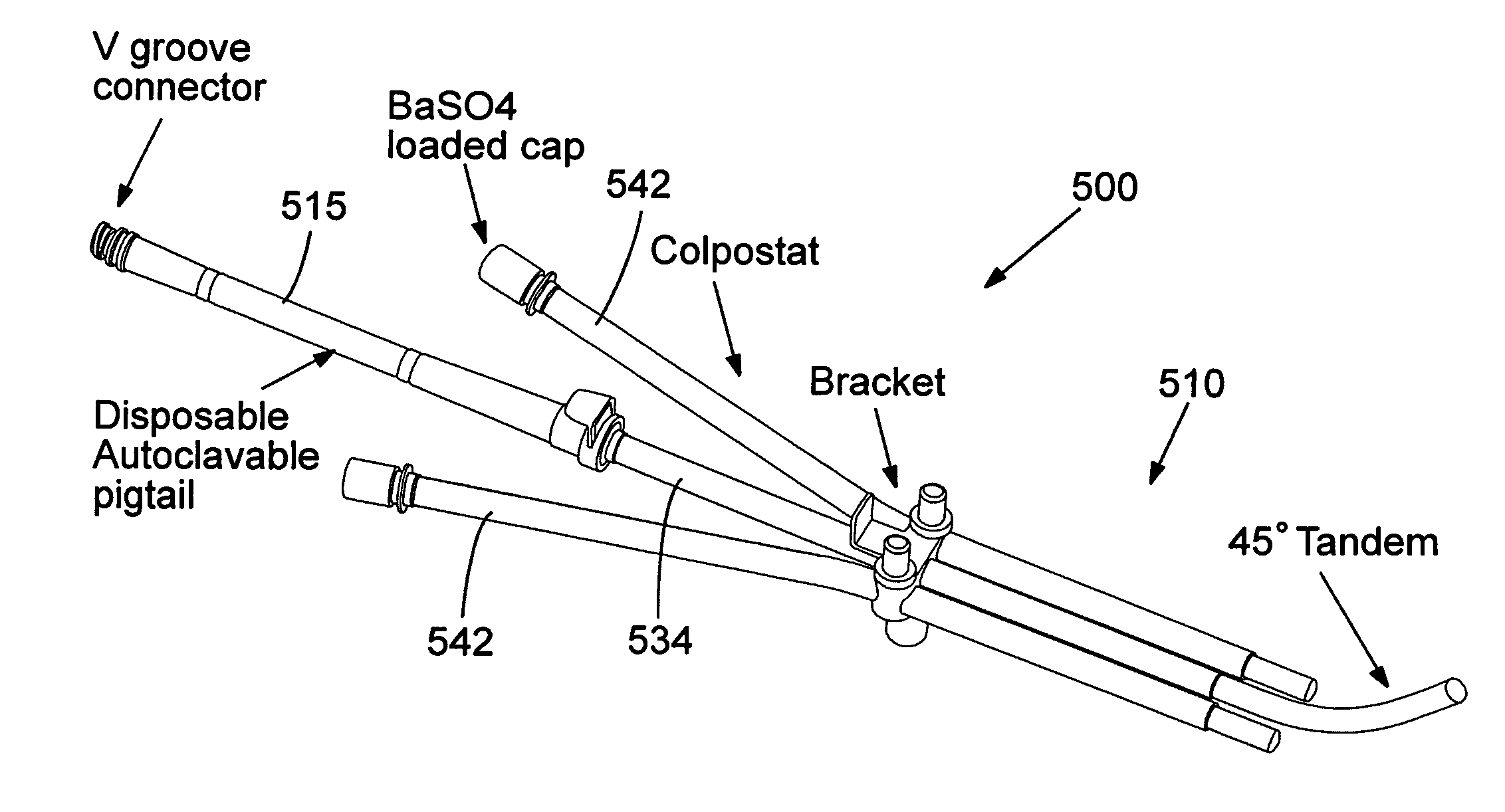
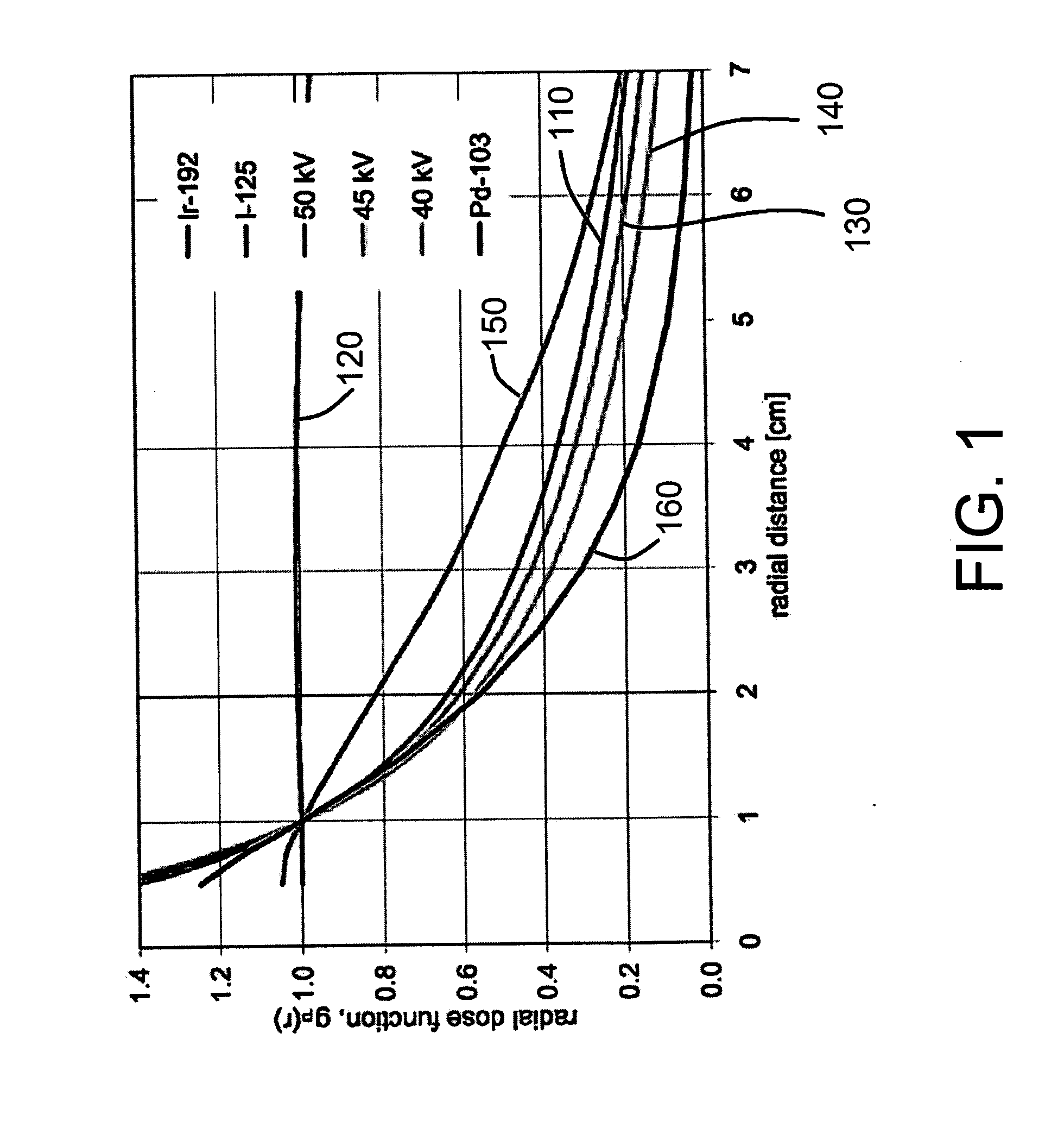
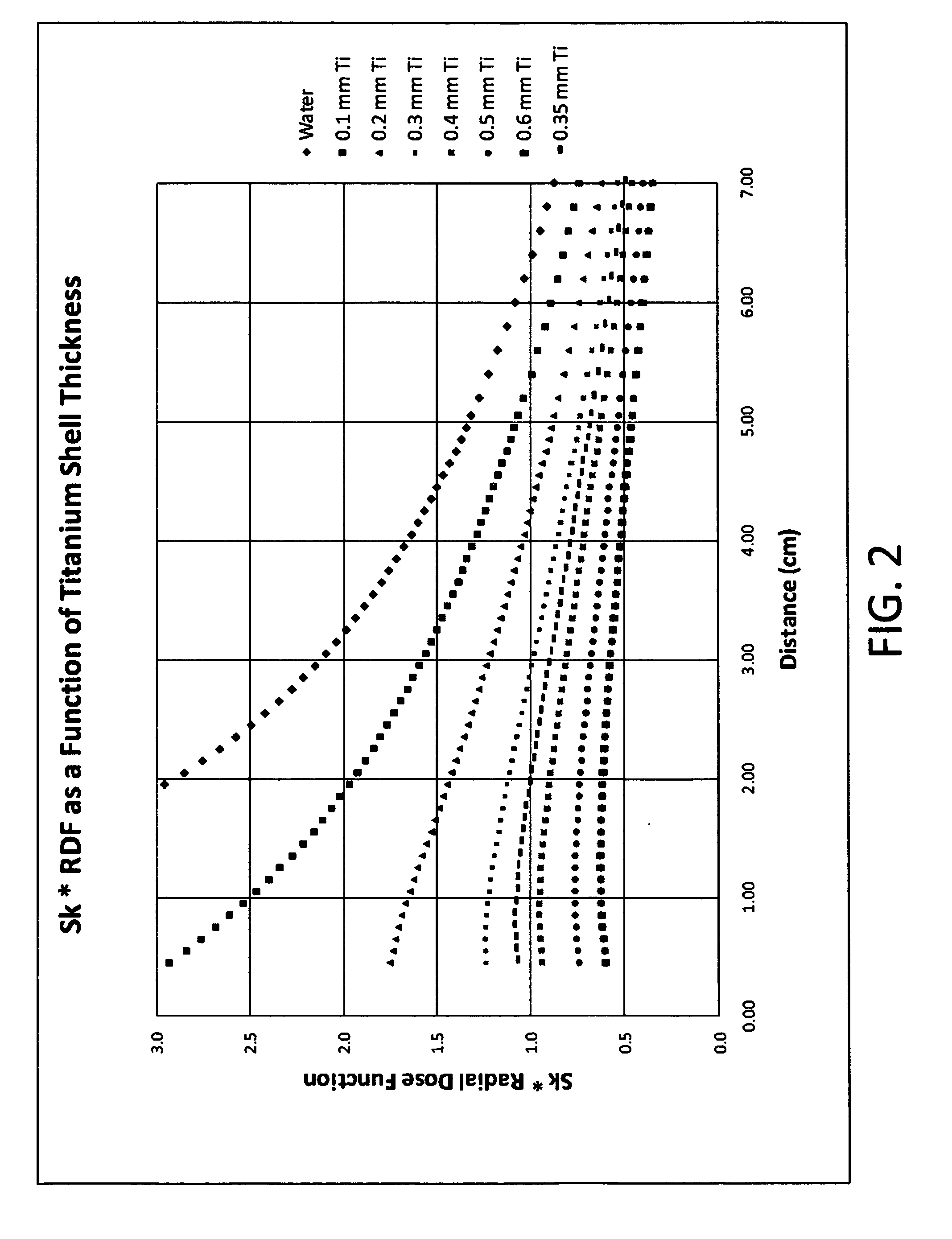
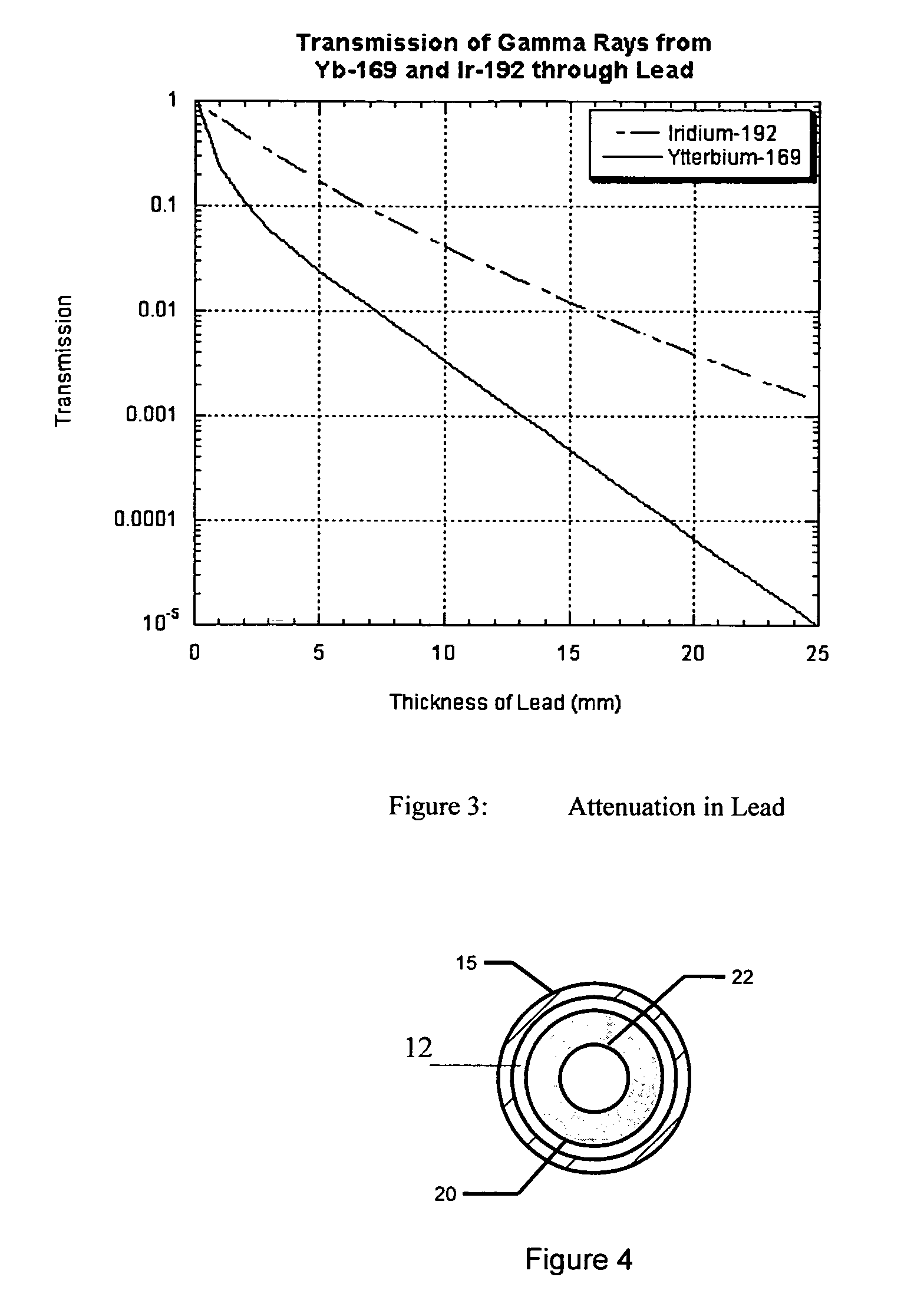
The radial dose function of an electronic x-ray brachytherapy source is flattened by filtering with transition metals in the fourth row of the periodic table, i.e. titanium through nickel. Titanium-walled applicator devices of small diameter, under 10 mm, and with wall thicknesses of about 0.2 mm to 0.6 mm, are disclosed. The walls can be of titanium or alloys thereof, providing adequate strength and flattening the radial dose function curve particularly for x-rays in an energy range of about 45 kV to 55 kV.
Owner:ICAB
X-ray and gamma ray emitting temporary high dose rate brachytherapy source
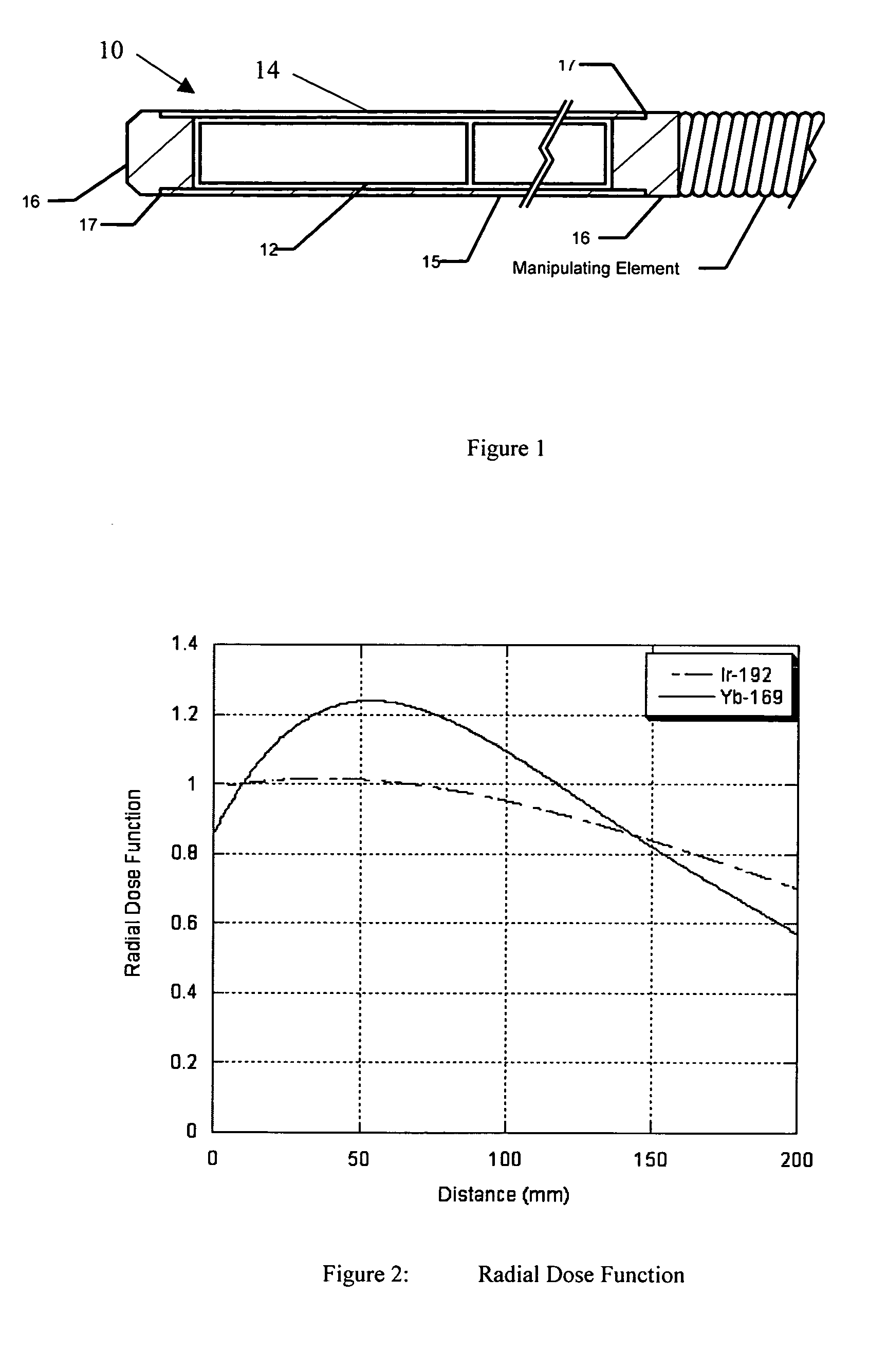
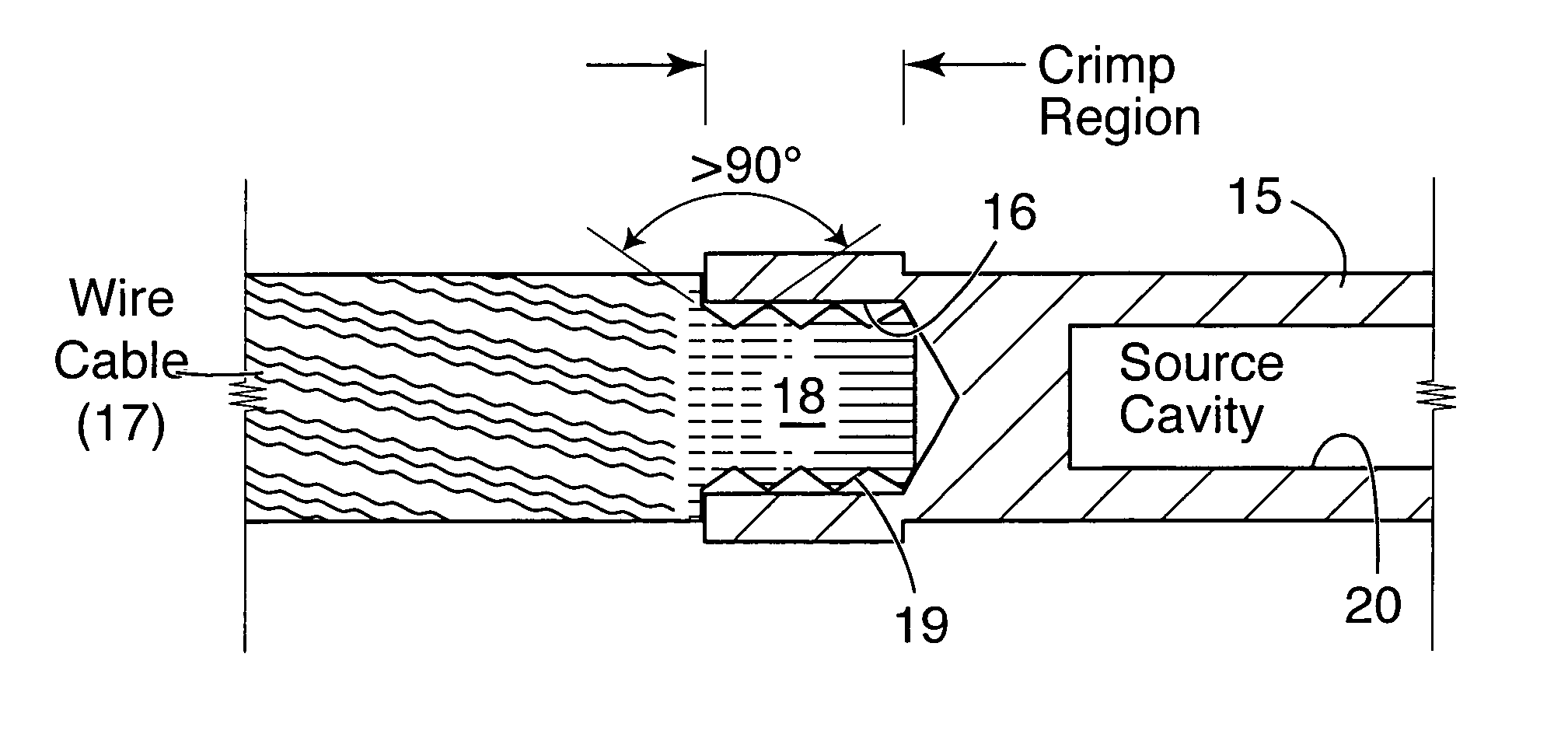
ActiveUS7530941B2Short half-lifeRadioactive sourcesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadioactive agentX-ray
Radioactive sources are manufactured for treating a tumor or cancerous area occurring around a conduit or duct in the body by emitting X-rays to destroy or reduce the tumors. The sources contain ytterbium which is substantially enriched in 168Ytterbium and which is activated by exposure to neutron flux so as to contain a minor, but significant, fraction of X-ray and gamma-emitting 169Ytterbium. The radioactive 169Ytterbium source is inserted through a catheter or applicator or needle to the site of the cancer where it is maintained in position for a period of time to reduce the occurrence of cancer. The ytterbium also acts as an X-ray-opaque marker to facilitate external visualization of the sources during their delivery to the treatment site. The sources are encased in a shell to prevent direct contact of the radioactive material with human tissue. This encapsulation may be formed by welding a pair of end caps to a tubular member.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Cable attachment for a radioactive brachytherapy source capsule
InactiveUS7077800B2No dimensional variability in the final productMaximized strengthRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyCouplings for rigid shaftsHot cellEngineering
In cancer brachytherapy treatment, a small californium-252 neutron source capsule is attached to a guide cable using a modified crimping technique. The guide cable has a solid cylindrical end, and the attachment employs circumferential grooves micromachined in the solid cable end. The attachment was designed and tested, and hardware fabricated for use inside a radioactive hot cell. A welding step typically required in other cable attachments is avoided.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Dosimetry for californium-252 (252Cf) neutron-emitting brachytherapy sources and encapsulation, storage, and clinical delivery thereof
InactiveUS7118524B2Maximize efficacyMaximize accuracyNeutron capture therapyPortable shielded containersClinical dosimetryNeutron emission
The present invention discloses a methodology for the characterization and determination of mixed-field dosimetry for 252Cf Applicator Tube (AT)-type medical sources, utilizing ionization chambers, GM counters, and Monte Carlo methods. Unlike the previous methodologies, the present invention discloses a specification of dose to muscle, rather than dose to water, for clinical dosimetry of 252Cf medical sources. A dosimetry protocol, similar to that utilized for ICRU-45, with parameters determined specifically for 252Cf brachytherapy is disclosed. Neutron isodose distributions and data necessary for clinical implementation of 252Cf AT sources are also disclosed herein. Additionally, novel methods for the encapsulation, storage, and delivery / implantation of 252Cf radionuclide sources are disclosed.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND MEDICAL CENT HOSPITALS
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive delivery of radiation to the eye
ActiveUS10022558B1Precise positioningFor accurate placementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDistal portionBrachytherapy source
Methods and devices for minimally-invasive delivery of radiation to the posterior portion of the eye including a cannula comprising a distal portion connected to a proximal portion and a means for advancing a radionuclide brachytherapy source (RBS) toward the tip of the distal portion; a method of introducing radiation to the human eye comprising inserting a cannula between the Tenon's capsule and the sclera of the human eye and emitting the radiation from the cannula.
Owner:SALUTARIS MEDICAL DEVICES
System for placing brachytherapy source in airway
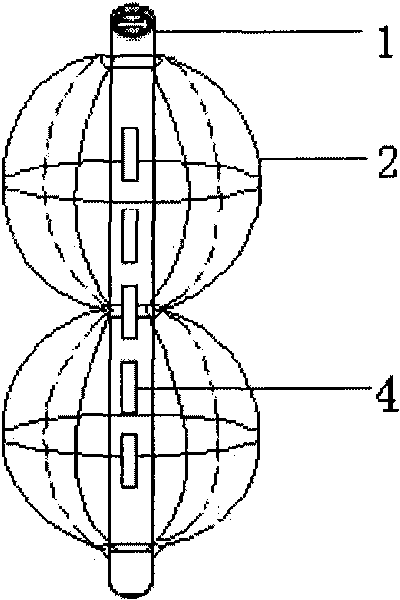
InactiveCN101700197AEasy to adjustAccurate adjustment positionDiagnosticsSurgeryHand heldBrachytherapy source
The invention relates to a system for placing brachytherapy source in the airway, comprising a fixed part (2) in the airway, a particle carrying part (1) and a pusher (3). The particle carrying part (1) is in the structure of a hollow pillar; the top end of the particle carrying part (1) is closed, and the bottom end is provided with an internal thread opening; the pusher (3) consists of a hand-held part (5), an outer sheath (6) and a push rod (7), wherein the front end of the push rod (7) is provided with a screw which matches with the internal thread opening; the fixed part (2) in the airway is a bean-pod support which is woven by metal wires and is fixed on two ends of the particle carrying part (1) by metal wires; and the particle carrying part (1) and the metal wires are made of the nickel-titanium alloy. The invention can solve the problems existing in the prior art that the placement of the radioactive particles is troublesome, the adjustment of the dosage of the radiological agent is hard, the steps of placing the support are complex and the positioning of the support is difficult.
Owner:李强 +1
Polymeric-matrix brachytherapy sources
InactiveUS20060067882A1Reduce radiation doseEliminate needRadioactive preparation formsRadioactive sourcesBrachytherapy sourceRadioactive particles
Therapeutic sources for use in the practice of brachytherapy comprise a radioactive composite that includes (a) a polymeric matrix and (b) a radioactive powder, e.g. Pd-103 or I-125, consisting essentially of very fine radioactive particles that are randomly and essentially uniformly dispersed within the polymeric matrix. The composite may be in the shape of one or more solid cylindrical rods surrounded by a non-radioactive sleeve. Alternatively it may be a hollow rod, suture, film, sheet, or microspheroidal particles.
Owner:RUSSELL JOHN +1
Protective sleeve of brachytherapy source particle bin
PendingCN109550143AImprove the protective effectEasy to useX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadioactive agentBrachytherapy source
The invention provides a protective sleeve of a brachytherapy source particle bin. The protective sleeve comprises a cover body assembly and a base, wherein the cover body assembly is in cooperation connection with the base; the cover body assembly comprises a cover body, a pressing rod, an elastic device and a pressing block; the pressing rod penetrates through the top of the cover body, and is connected with the cover body through threads; the elastic device is arranged at the tail end of the pressing rod; the pressing block is arranged at one end away from the pressing rod, of the elastic device; a hollow cavity is formed in the base, and is used for accommodating the particle bin; the pressing rod can move relative to the cover body through the threads, and can actuate the elastic device to generate elastic force; and the elastic force is used for enabling the pressing block to be in contact with one end of the particle bin. According to the protective sleeve of the brachytherapy source particle bin provided by the invention, omnidirectional protection of the brachytherapy source particle bin can be completed, and high-efficiency and safe transportation and movement are performed; brachytherapy sources in the brachytherapy source particle bin are effectively protected from being extruded and deformed, array malposition cannot generate, and environmental pollution caused byoutward leakage of radioactive substances is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIBO BIO MEDICAL TECH
Plastic brachytherapy sources
InactiveCN1894002ACutting costsImprove visibilityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadio isotopesPharmaceutical drug
An implantable source (40) of therapeutic radiation for brachytherapy is provided as a sealed, biocompatible capsule (410) of plastic (e.g. polyethylene or PEEK) transparent to the radiation. The capsule contains a radiation source (400) comprising particles of a radioactive isotope (e.g. Pd<103>, I<125>, Cs<131>) in a fluid carrier that is resistant to radiation polymerization but solidifies at elevated temperature. It also has a marker (420), and desirably has a socket (430) which accommodates attaching spacers (660) and makes possible linear strands and planar arrays of the capsules. The spacers may be functional, e.g. heat-generating or medication-releasing.
Owner:INT BRACHYTHERAPY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com