Production process for reducing content of trichloropropanol in original soy sauce
A technology of trichloropropanol and production process is applied in the field of production technology for reducing the content of trichloropropanol in original brewed soy sauce, and achieves the effects of reducing starch content and reducing the generation of 3-MCPD
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Comparing the constant temperature fermentation process of inoculating single yeast with different raw material ratios
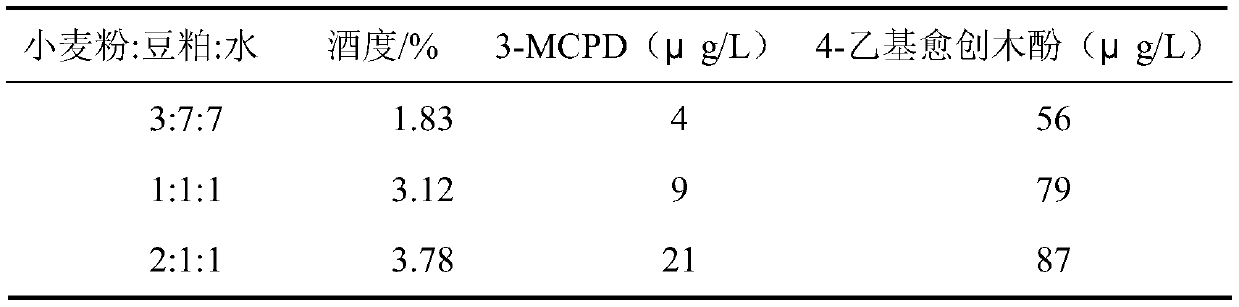
[0018] Mix wheat flour, soybean meal, and water in different proportions in Table 1, then sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, cool to below 40°C, inoculate Aspergillus oryzae As 3.042 into the material at an inoculum amount of 1‰, control the temperature at 30°C, and the humidity at 95 % under the condition of culturing for 48 hours to prepare koji; then add salt water with a salt concentration of 22% to the koji according to the ratio of 1:1.8, and then transfer it to a fermentation tank to start fermentation.
[0019] When the moromi pH drops to 5.0, according to 10 9 CFU / mL bacterial concentration was added with Zygomyces luteus, and fermented at 30°C for 6 months to obtain the finished soy sauce, and its 3-MCPD and ethanol content were detected. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0020] Table 1 Comparison of 3-MCPD and ethanol content in ferment...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Comparison of different raw material ratios to inoculate a single yeast variable temperature fermentation process
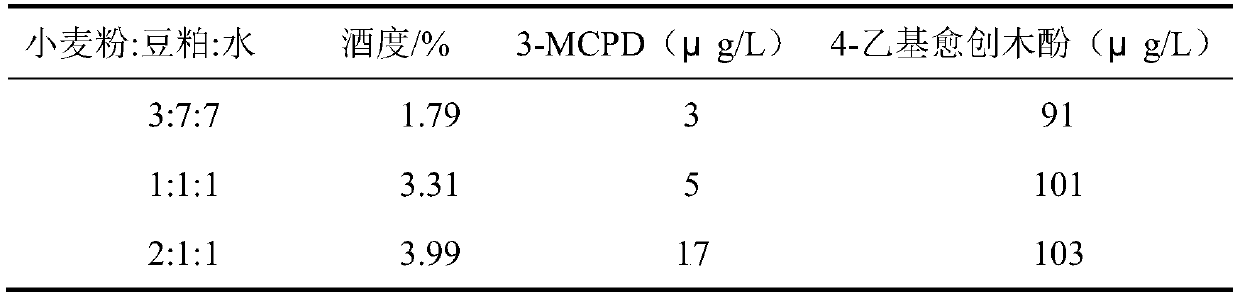
[0024] Mix wheat flour, soybean meal, and water according to the different ratios in Table 2, sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, cool to below 40°C, inoculate Aspergillus oryzae As 3.042 into the material at an inoculum amount of 1‰, control the temperature at 30°C, and the humidity at 95 % under the condition of culturing for 48h, made into koji. Add brine with a salt concentration of 22% to the finished koji at a ratio of 1:1.8, and then transfer it to a fermentation tank to start fermentation.
[0025] After the pH of the moromi drops to 5.0, follow the 10 9 CFU / mL bacterial concentration Add Zygomyces luschii, ferment at 16°C for 30 days, raise the temperature to 32°C, ferment for 3 months, and finally ferment at 23°C for 2 months to obtain the finished soy sauce, test its 3 - MCPD, ethanol content and flavor compounds in soy sauce. The results are ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Comparing the ratio of different raw materials to inoculate compound strains for variable temperature fermentation
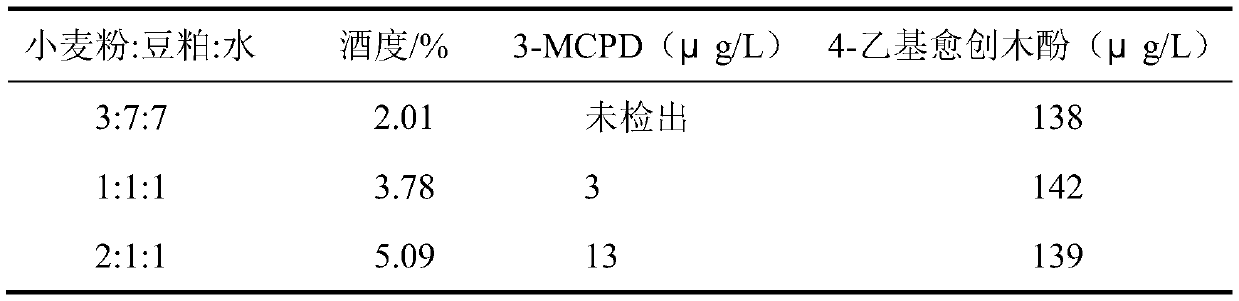
[0030] Mix wheat flour, soybean meal, and water according to the different ratios in Table 3, then sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, cool to below 40°C, inoculate Aspergillus oryzae As 3.042 into the material at an inoculum amount of 1‰, control the temperature at 30°C, and the humidity at 95 % under the condition of culturing for 48h, made into koji. Add brine with a salt concentration of 22% to the finished koji at a ratio of 1:1.8, and then transfer it to a fermentation tank to start fermentation.
[0031] After fermenting the moromi for one week, follow the 10 6 CFU / mL bacterial concentration was added with tetradococcus halophilus, and fermented at 16°C for 30 days. After the pH of the moromi dropped to 5.0, the 5 CFU / mL bacterial concentration was added with Saccharomyces luteus, fermented at 32°C for 3 months, and finally according to 10 7 CFU / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com