Molar back push device
A technique of molar and premolar, applied in dentistry, orthodontics, prosthetics, etc., can solve the problems of tooth rotation, molar buccal tilt, etc., to avoid tooth rotation, improve connection strength, and increase the effect of connection area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
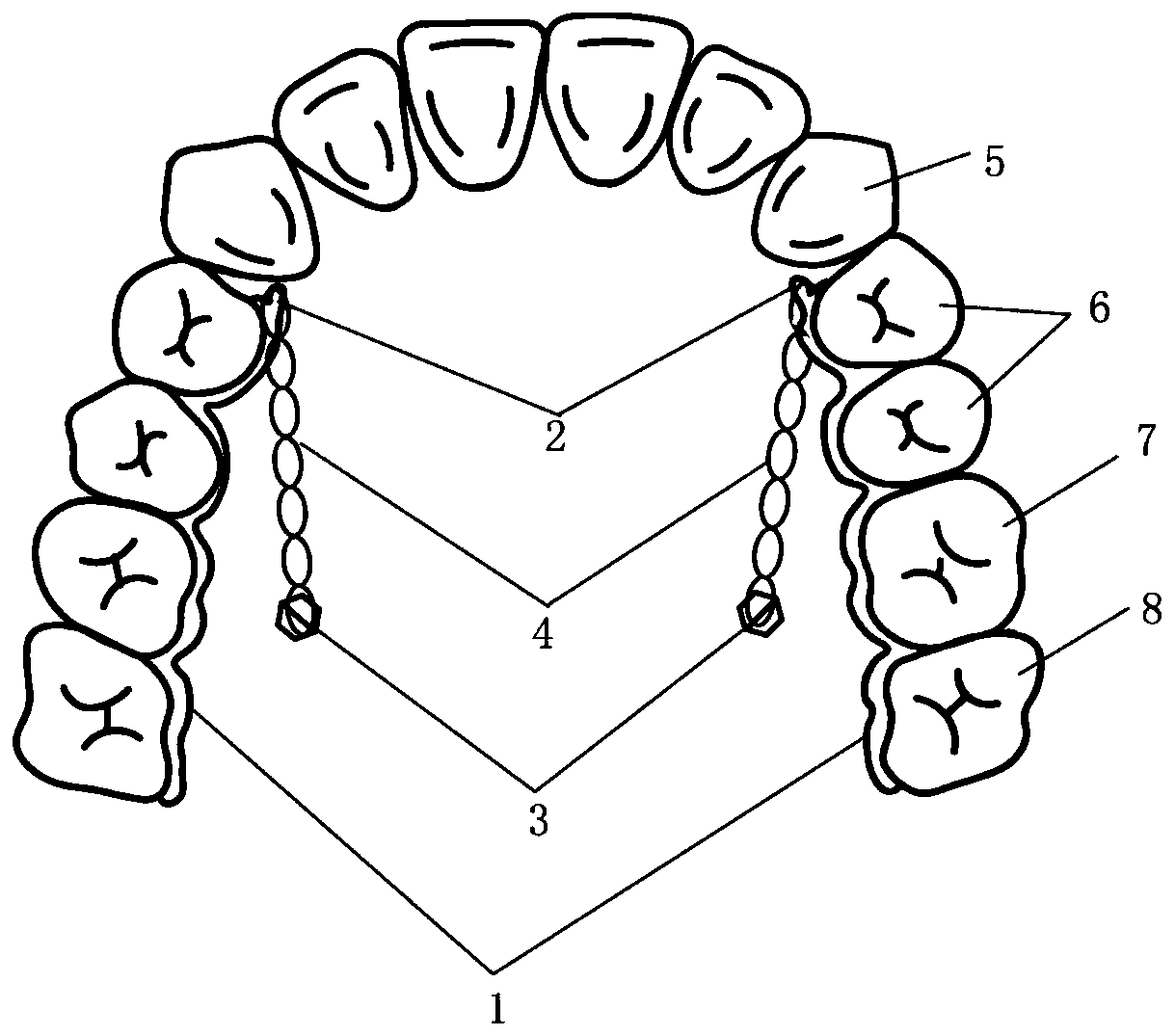
[0047] figure 1 A schematic structural view of the molar pushback device of this embodiment is shown.
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown, the pushback molar device includes:
[0049] A pair of retaining parts are respectively arranged on both sides of the upper jaw of the oral cavity. Each retaining part includes a retaining part 1 and a traction hook 2. The retaining part 1 is in the form of a sheet with a thickness of 0.4 mm and bonded by a resin adhesive On the crown-palatal side of the premolars 6, first molars 7, and second molars 8 on the maxillary side of the oral cavity, the traction hook 2 is cylindrical, with a diameter of 1 mm, and is arranged at the proximal end of the retainer 1, and extends toward the proximal Extending in the middle direction, wherein, the retainer 1 of each retainer part and the traction hook 2 are integrally formed;
[0050] Two implant nails 3, each implant nail 3 is located between the palatal roots of the first molar 7 and the second mol...
Embodiment 2
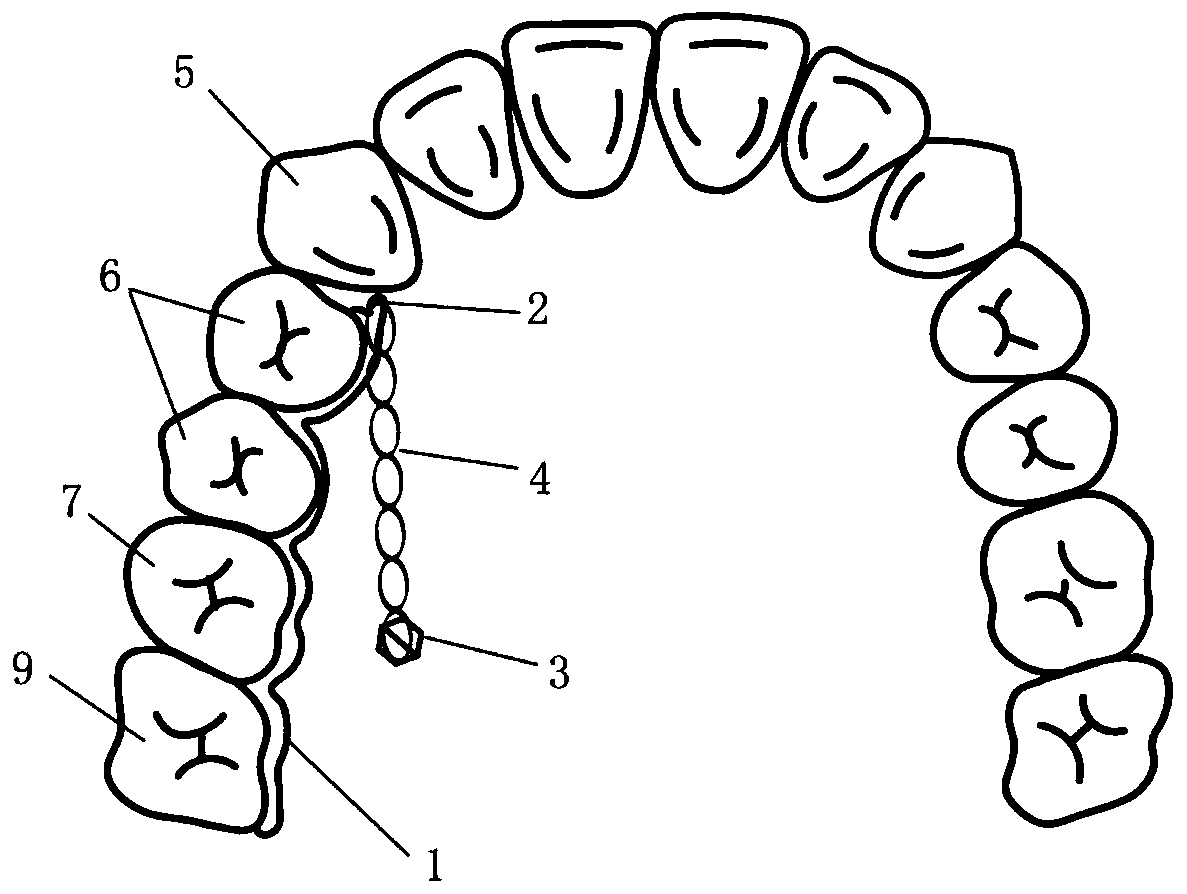
[0056] figure 2 A schematic structural view of the molar pushback device of this embodiment is shown.
[0057] Such as figure 2 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the retaining part, the implant nail 3 and the connecting part 4 are all one, and the retaining part 1 of the retaining part is bonded to the side of the upper jaw of the oral cavity through a resin adhesive. On the palatal side of the crowns of the premolars 6, the first molars 7 and the second molars 8, the connecting piece 4 is connected between the implant nail 3 and the traction hook 2 of the retaining part. For patients requiring only unilateral molar setback.
[0058] When designing, first use a computer to design a single-sided retention part that fits the patient's molar tooth surface according to the patient's dental arch data and does not affect the occlusion with the opposing jaw; then use 3D printing technology to print out the retention part in one piece . W...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com