Convolutional interleaving and de-interleaving FPGA implementation method and system without redundant data
A technology of convolutional interleaving and redundant data, applied in the field of digital signal transmission, can solve problems affecting system delay and system throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
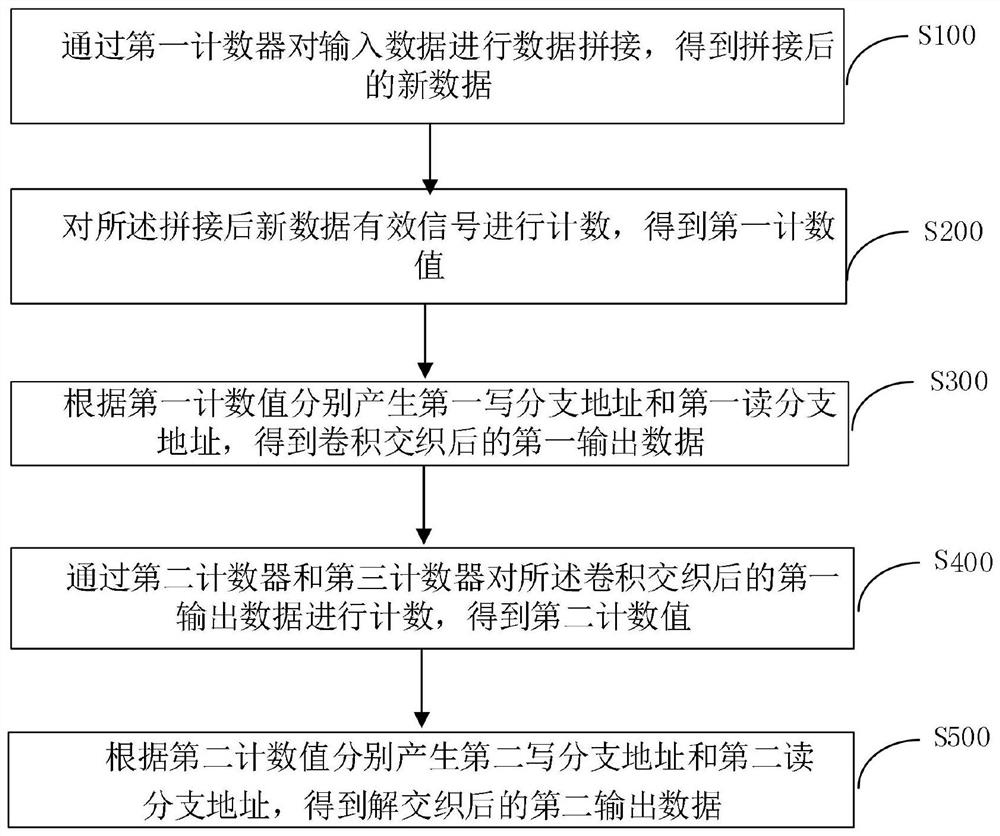
[0057] This embodiment discloses a method for implementing convolutional interleaving and deinterleaving FPGA without redundant data, such as figure 1 ,include:
[0058] S100. Perform data splicing on the input data to obtain spliced new data;
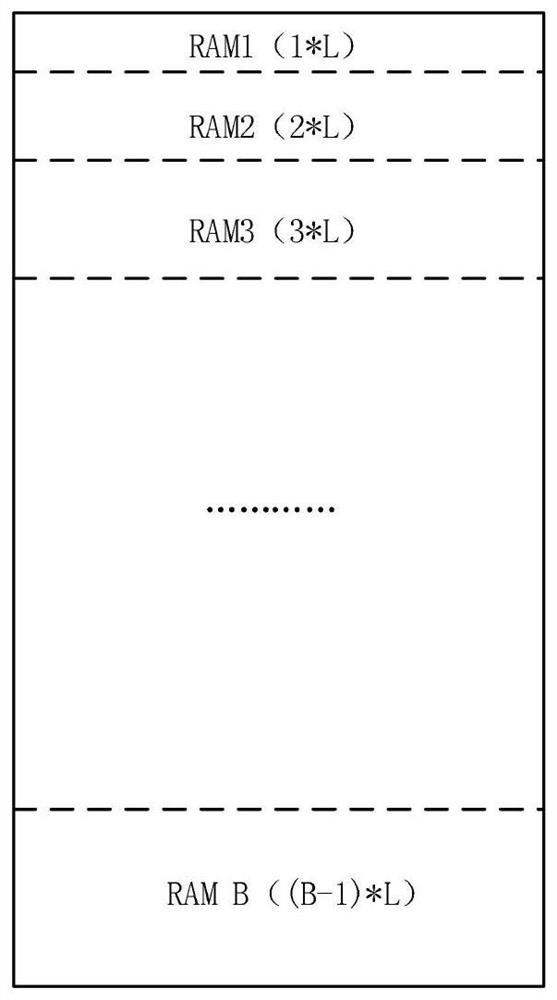
[0059] Specifically, the specific method of the S100 is: adding invalid data 0 of a certain length 1 to the input data; the length 1 of the invalid data 0 is related to the branch number (B) and the branch length (L) in the interleaving principle, The specific conversion relationship is:
[0060] l=[(B-1)+(B-2)+...+1]*L
[0061] S200. Count the spliced new data valid signal by using the first counter to obtain a first count value;
[0062] Specifically, the S200 method is: counting the valid signals of the new data after splicing, counting the columns, rows, and blocks of the data respectively, the counting rule is to first count the columns, and count the columns The range is 0~B-1, when the value of the column count is equal ...
Embodiment 2
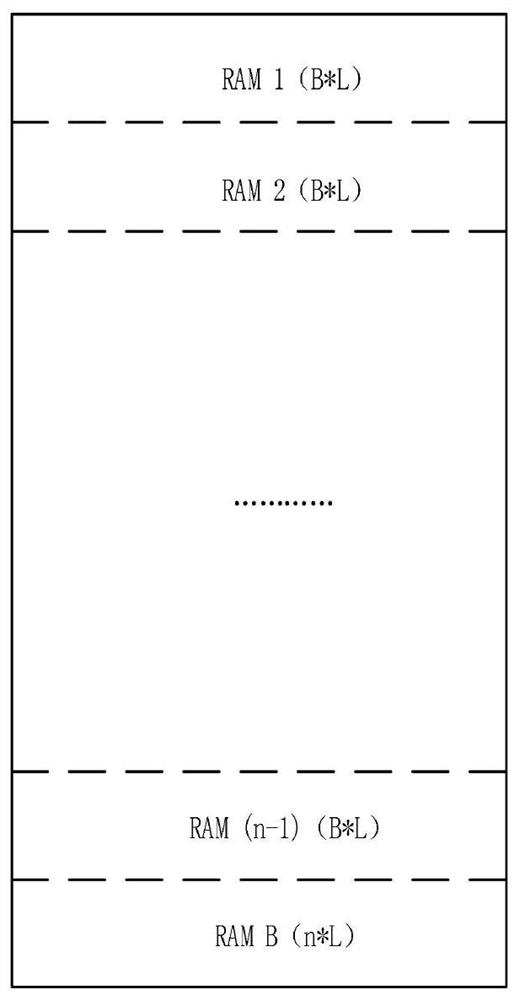
[0089] This embodiment discloses a convolutional interleaving and deinterleaving FPGA implementation system without redundant data. The specific system workflow block diagram is as follows Figure 4 , including: data splicing module, first counter module, first write RAM module, first read RAM module, first RAM storage module, second counter module, third counter module, second write RAM module, second read RAM module, the second RAM storage module.
[0090] The data splicing module performs data splicing on the input data to obtain spliced new data;
[0091] The first counter module counts the new data valid signals after the splicing to obtain the value of the first counter; specifically, the first counter module is divided into a column counter submodule, a row counter submodule, and a block counter submodule; Count the effective signals of the new data after splicing, and count the columns, rows, and blocks of the data respectively. The counting rule is to first count the...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap