Gene therapies for neurodegenerative disease
An active, viral vector technology for use in gene therapy for neurodegenerative diseases, addressing issues such as limited treatment options
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Example 1: rAAV vector
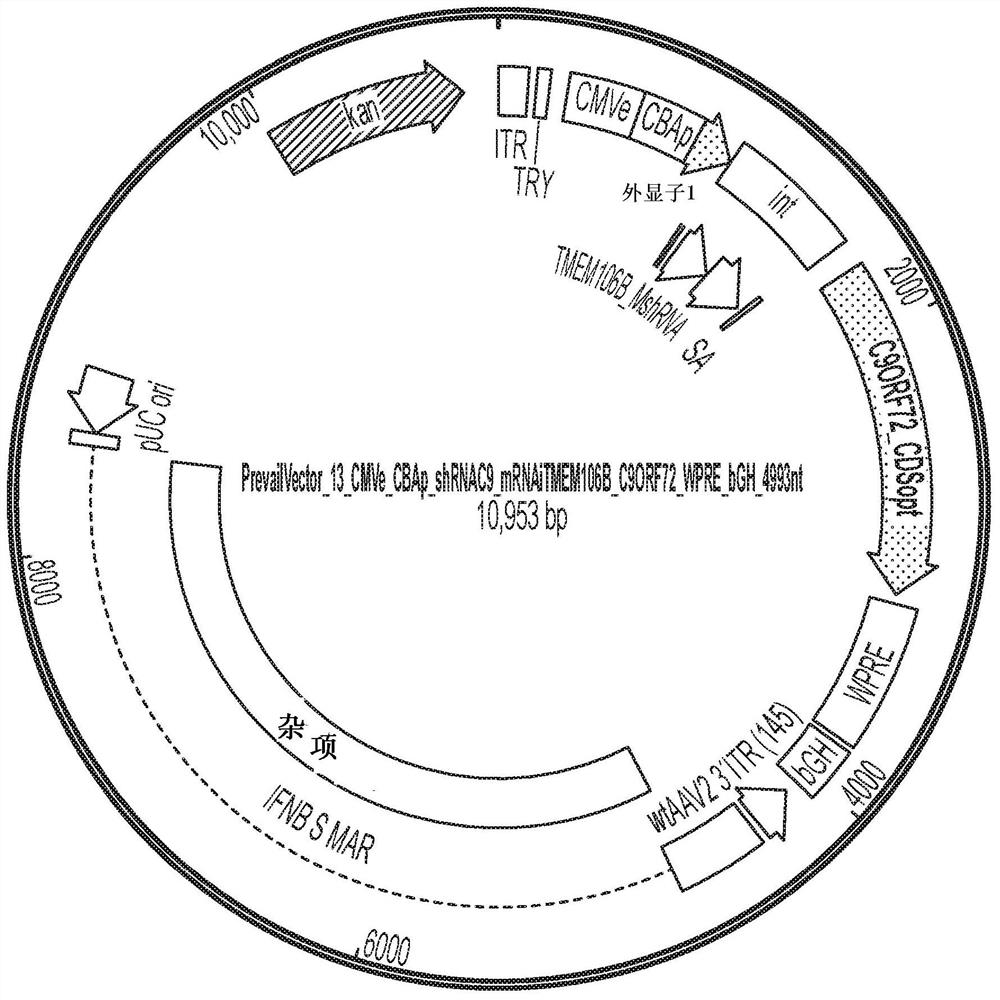
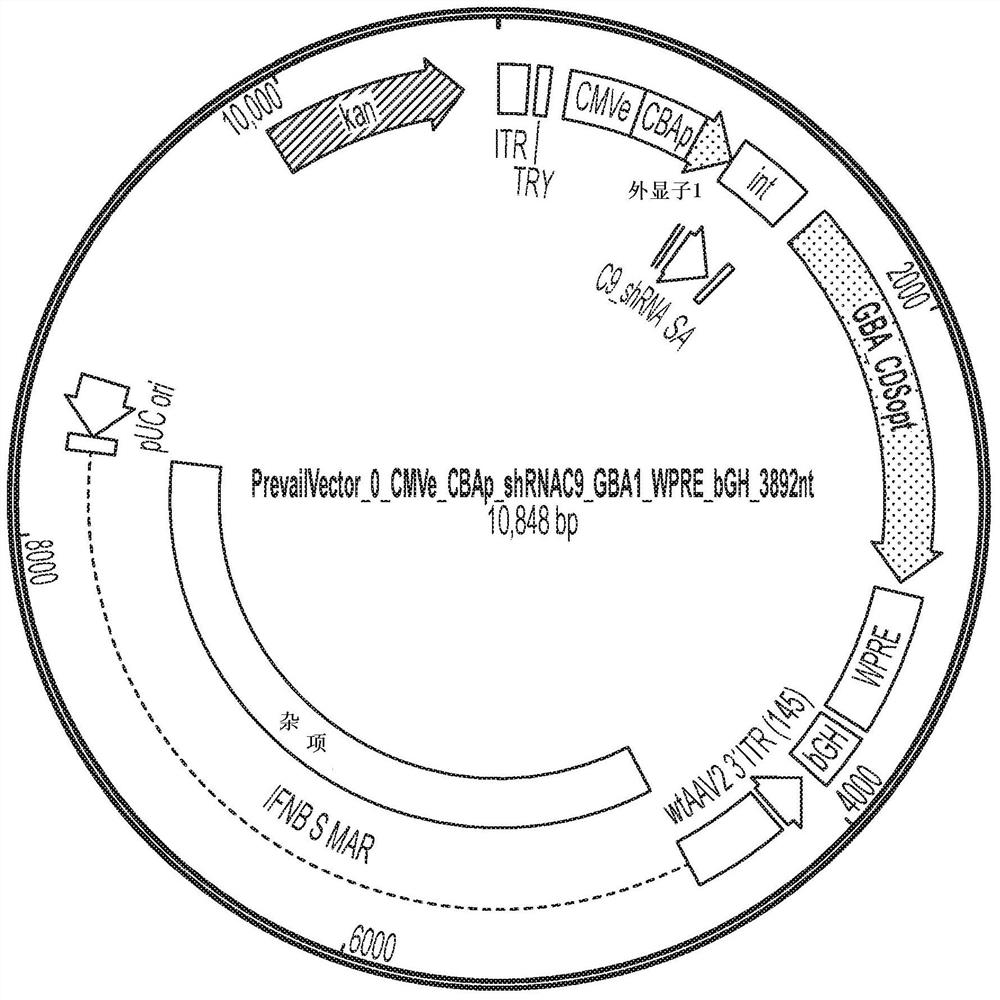
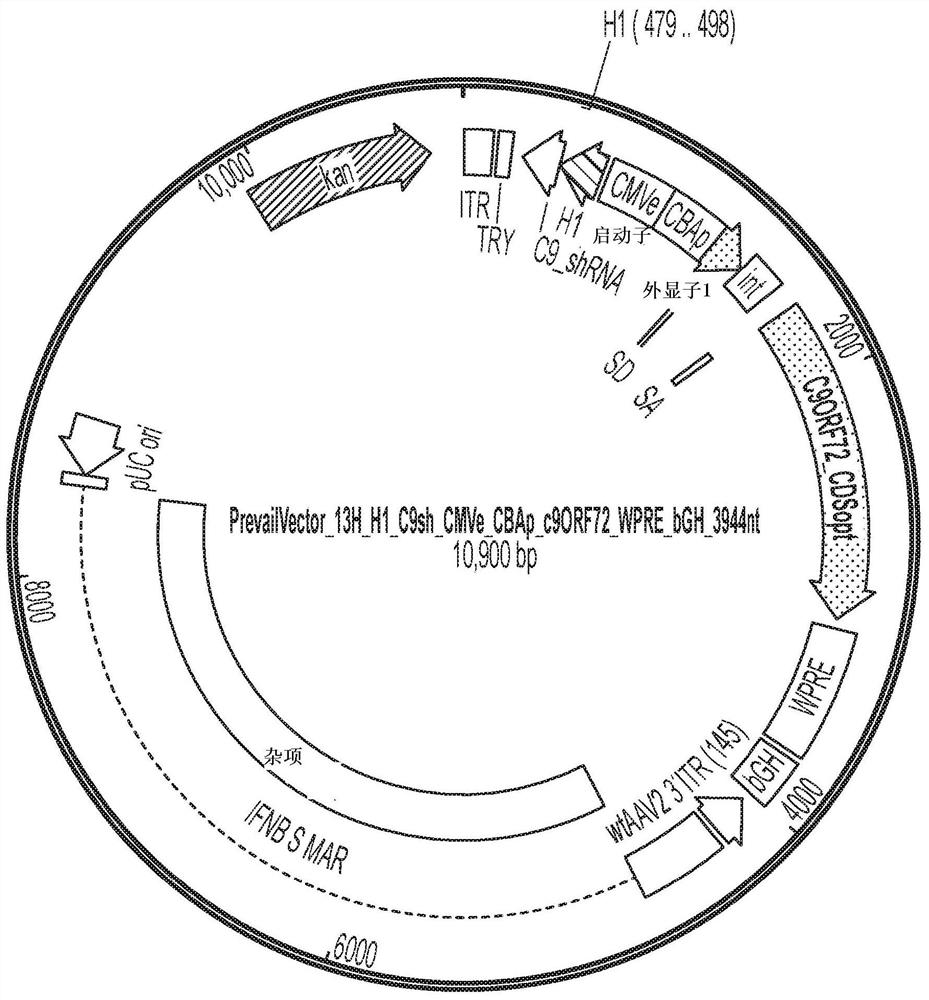
[0111] AAV vectors are produced using cells such as HEK293 cells for triple plasmid transfection. ITR sequences flank expression constructs containing promoter / enhancer elements, 3' polyA signals, and post-translational signals such as WPRE elements for each transgene of interest. Multiple gene products, such as C9orf72 protein or GBA1 protein, and one or more inhibitory nucleic acids (e.g., inhibitory nucleic acids targeting C9orf72 and / or TMEM106B) can be expressed simultaneously, e.g., by using a single expression cassette or separate expression cassettes Express. The presence of highly spliced short intronic sequences upstream of the expressed gene can increase expression levels. Inhibitory RNAs (eg, miRNAs, shRNAs, etc.) and other regulatory RNAs can potentially be included in these sequences. Examples of expression constructs described in this disclosure are shown in Figure 1-17 and 20-21 and in Table 1 below.
[0112] Table 1
[...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Example 2: Cell-Based Assay for Viral Transduction in ALS / FTD Cells
[0116] Cells characterized by the repeat expansion of C9orf72 are obtained as, for example, fibroblasts, monocytes or hES cells from ALS / FTD patients or patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells accumulate RNA foci and proteins translated from RAN.
[0117] Using these cell models, cellular disease is quantified based on the accumulation of protein aggregates, such as aggregates of the RAN protein, using anti-RAN protein antibodies, followed by fluorescence microscopy imaging. Abnormal accumulation of RAN protein was quantified using Western blot and / or ELISA.
[0118] Therapeutic endpoints (eg, reduction of ALS / FTD-associated disease) are measured in the context of transduced expression of AAV vectors to confirm and quantify activity and function. Reduction in endogenous (eg, pathogenic repeat expansion-containing) C9orf72 mRNA levels can be quantified, eg, using quantitat...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Example 3: In vitro studies
[0120] This example describes in vitro testing of the C9orf72 rAAV vector described in this disclosure. The effects of C9orf72 knockdown and overexpression were studied in mammalian cells. Examples of constructs tested are listed in Table 2.
[0121] ID Promoter knock down Promoter Overexpression I00017 H1 C9_sh CMV opt-C9 I00018 CMV C9_sh, TMEM_mi CMV opt-C9 I00030 CMV_intronic C9_sh(cons) CMV opt-C9 I00031 CMV_intronic C9repeat_sh CMV opt-C9 I00032 CMV_intronic C9_sh (validated) CMV opt-C9 I00037 CMV_intronic C9r_sh, ATXN_sh CMV opt-C9
[0122] Gene knockdown and overexpression were determined by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and ELISA. Figure 19A Representative data shown demonstrates statistically significant silencing of C9orf72 by rAAV vectors. Figure 19B Representative data shown demonstrates a statistically significant increase in wild-type C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com