BCR-ABL1 kinase structural domain mutation screening method
A BCR-ABL1 and kinase domain technology, applied in the field of BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutation screening, can solve the problems of inapplicable identification of low-level variants and inability to clearly distinguish them
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
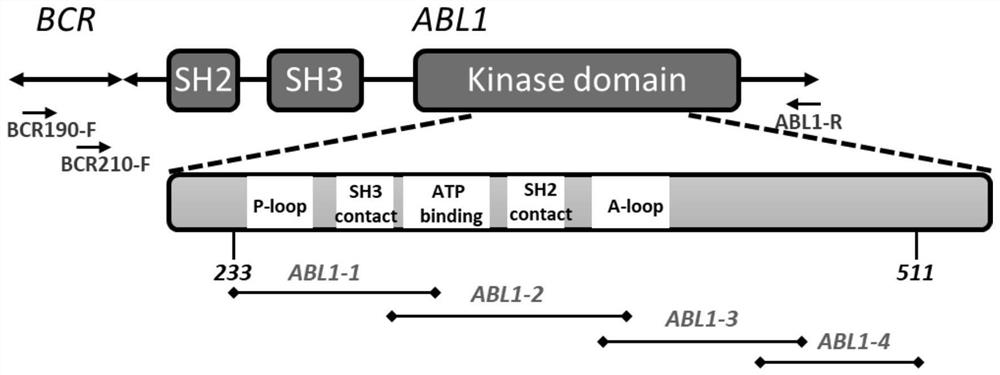
[0103] This embodiment provides a method for screening mutations in the kinase domain of BCR-ABL1, the screening method comprising the following steps:
[0104] (a) 6×10 cells were isolated from the patient’s bone marrow sample 6 mononuclear cells and extract RNA;
[0105] (b) Using the Maxima First Strand cDNA synthesis kit and random primers, 14 μl of RNA with a concentration of 50-200 ng / μl was reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and PCR reaction was performed, and then 30 μl of AMPureXP Beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA) was purified, and then eluted with 13 μl Low TE (Life Technologies Corp, USA) to obtain the amplified product including the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain, wherein:
[0106] The PCR reaction includes a nested first-round PCR reaction and a nested second-round PCR reaction, and the nested second-round PCR reaction uses the nested first-round PCR reaction product as a reaction raw material;
[0107] The primer sequences used in the first round of nested PCR reactions a...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Bone marrow samples at two time points were selected from two patients, and were screened according to the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutation screening method in Example 1. The screening results of samples at different time points in one of them were as follows: image 3 As shown, the screening results of samples from another person at different time points are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0142] In summary, by Figure 2 ~ Figure 4 It can be seen that the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutation screening method of the present invention can screen out a variant allele frequency with a minimum frequency of 4.7%, therefore, the screening method of the present invention has higher sensitivity; in addition, the screening method of the present invention can also Determine whether a patient carries a compound or polyclonal mutation and its variant allele frequency, to achieve the purpose of dynamically monitoring the patient's drug resistance mutation status.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com