Heat treatment method capable of realizing both precipitation strengthening and lower bainite phase-transformation strengthening
A heat treatment method and precipitation strengthening technology, which is applied in the field of heat treatment that takes into account both precipitation strengthening and lower bainite transformation strengthening, and can solve the problems that precipitation strengthening and lower bainite strengthening cannot be solved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
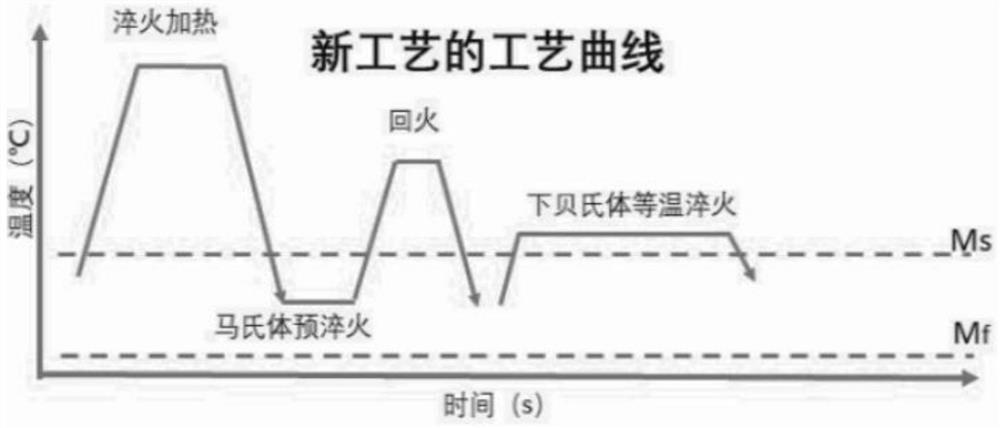
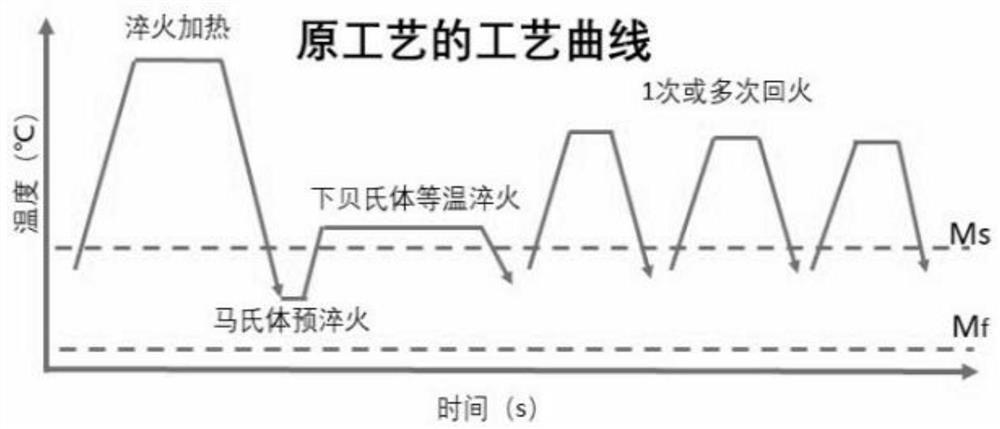
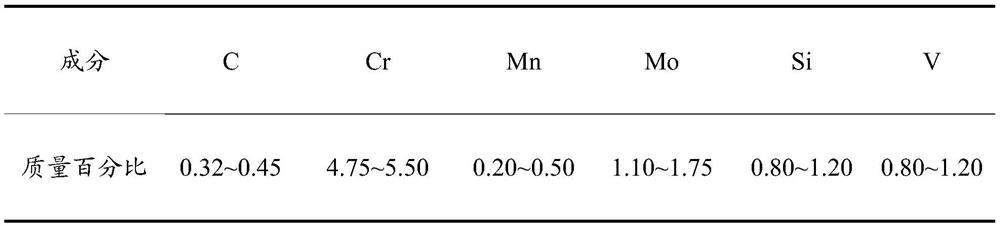
[0052] According to attached figure 1 The process curve in the heat treatment of H13 steel (brand, 4Cr5MoSiV1, see Table 1 for composition), the parameters of H13 steel are obtained from the TTT diagram of H13 steel, its Ac3 is 915 °C, and in the case of austenitization at 1050 °C, Ms is 320°C, Mf is 180°C, and the lower bainite transformation temperature range is 320°C to 400°C.
[0053] The heat treatment method is:
[0054] (1) Heating the H13 steel to 1050°C and holding it for 1 hour to obtain an austenitic alloy;
[0055] (2) cooling the austenitized alloy obtained in the step (1) to 260° C. and keeping it warm for 30 seconds to obtain a martensitic iron-based alloy;
[0056] (3) raising the temperature of the martensitic iron-based alloy obtained in the step (2) to 550° C. for 0.5 hours to obtain a tempered iron-based alloy;
[0057] (4) Water cooling the tempered iron-based alloy obtained in the step (3) to 340° C. for 2 hours, and then naturally cooling to room temp...
Embodiment 2
[0062] According to attached figure 1 The process curve in the heat treatment of 42CrMo steel (composition see Table 2), the parameters of 42CrMo steel are obtained from the TTT diagram of 42CrMo steel, its Ac3 is 800 ° C, in the case of austenitization at 840 ° C, its Ms is 310 ° C , Mf is 170°C, and the lower bainite transformation range is 310°C to 420°C.
[0063] The heat treatment method is:
[0064] (1) Heating 42CrMo steel to 840°C and holding it for 1 hour to obtain an austenitic alloy;
[0065] (2) cooling the austenitized alloy oil obtained in the step (1) to 200° C., and keeping it warm for 10 minutes to obtain a martensitic iron-based alloy;
[0066] (3) raising the temperature of the martensitic iron-based alloy obtained in the step (2) to 400° C. for 0.5 hours to obtain a tempered iron-based alloy;
[0067] (4) Cool the tempered iron-based alloy oil obtained in the step (3) to 340° C. for 2 hours, and then naturally cool to room temperature.
[0068] Properti...
Embodiment 3
[0073] According to attached figure 1 The process curve in the heat treatment of Cr12MoV steel (see Table 3 for composition), the parameters of Cr12MoV steel are obtained from the TTT diagram of Cr12MoV steel, its Accm is 855 ° C, it is austenitized at 1020 ° C, its Ms is 230 ° C, Mf The lower bainite temperature range is 230°C to 350°C.
[0074] The heat treatment method is:
[0075] (1) Heating the Cr12MoV steel to 1020°C and holding it for 1 hour to obtain an austenitic alloy;
[0076] (2) cooling the austenitized alloy oil obtained in the step (1) to 190° C., and keeping it warm for 1 minute to obtain a martensitic iron-based alloy;
[0077] (3) raising the temperature of the martensitic iron-based alloy obtained in the step (2) to 500° C. for 0.5 hours to obtain a tempered iron-based alloy;
[0078] (4) Cool the tempered iron-based alloy oil obtained in the step (3) to 240° C. for 2 hours, and then naturally cool to room temperature.
[0079] Properties of Cr12MoV ste...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Impact absorption energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impact absorption energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impact absorption energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com