A rapidly screened ovarian cancer nucleic acid aptamer and its application in the preparation and detection of ovarian cancer preparations
A technology of nucleic acid aptamer and ovarian cancer, applied in measuring devices, biological testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of difficult detection of pathological tissue and poor detection, and achieve low cost, time-saving and low cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
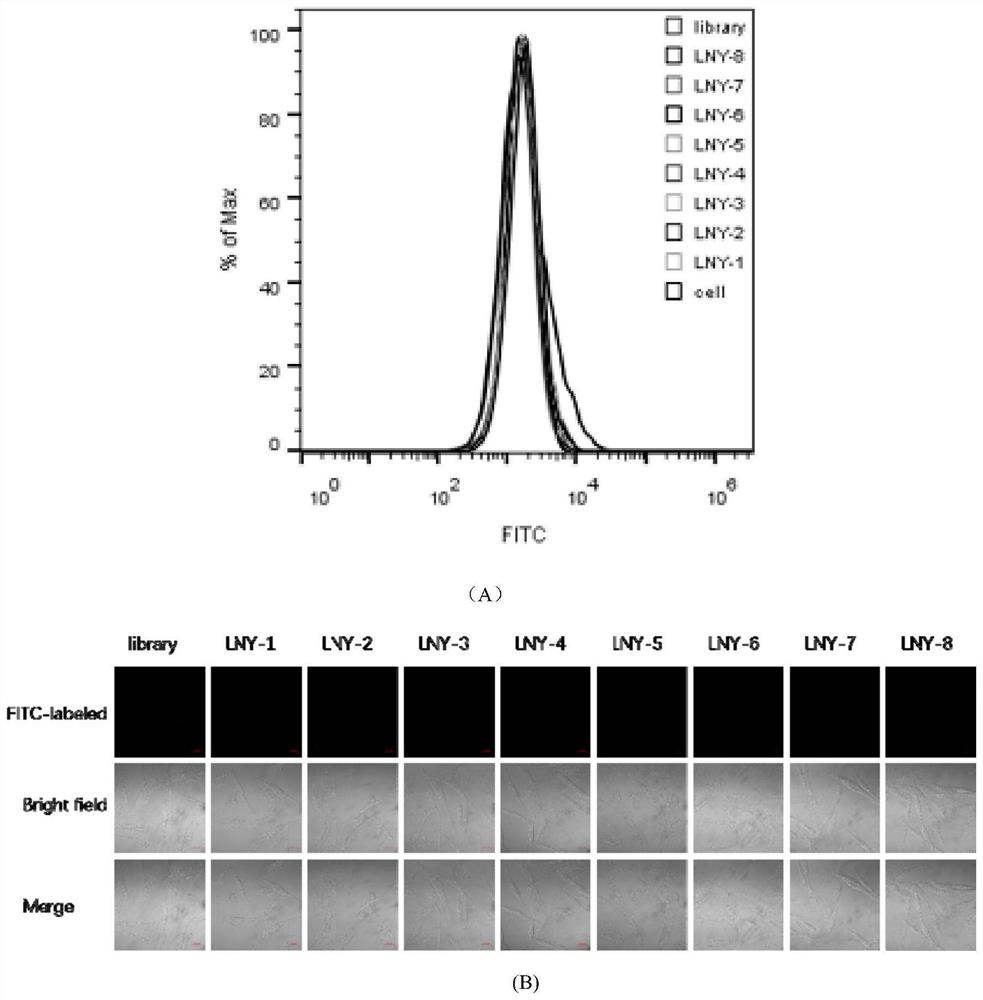
[0026] Example 1: Nucleic acid aptamer screening of clinical ovarian cancer tissue
[0027] Based on Tissue-SELEX technology, positive screening is performed on clinical ovarian cancer tissues, and negative screening is performed on ovarian cancer paracancerous tissues to obtain the expected target sequence. Synthesize the X-Aptamer library with affinity group modification first. In the first round of screening, the initial library was incubated with ovarian cancer paracancerous tissues, and the isolated and retained binding library was the negative screening library. The non-binding library was incubated with ovarian cancer tissues, and the binding library that was isolated and retained was a positive screening library. In the second round of screening, the positive screening library and negative screening library in the first round of screening were mixed with sterile deionized water (blank group), ovarian cancer tissue (positive group), and ovarian cancer adjacent tissue (...
Embodiment 2
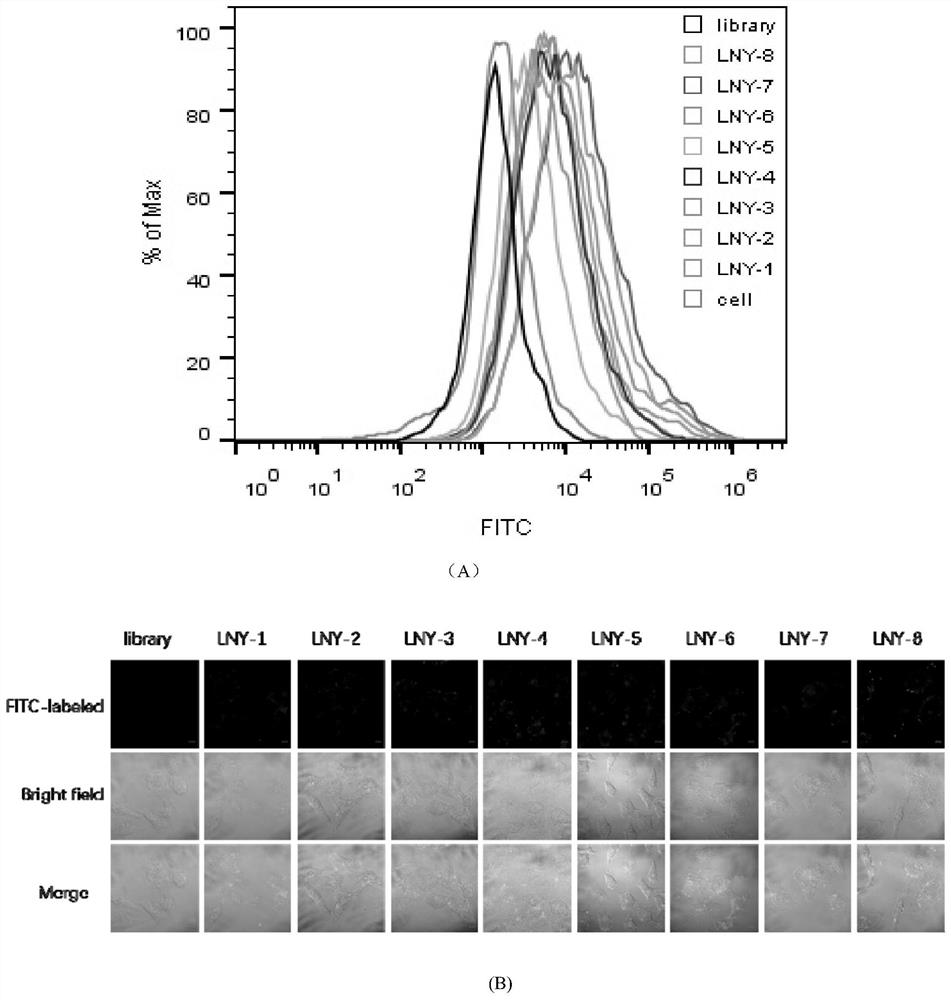
[0031] Example 2: Determining the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to the HO-8910 cell line
[0032] Centrifuge the powder of the 8 nucleic acid aptamer sequences and the control library chain, dilute it with sterile deionized water to a final concentration of 250nM, denature it in a metal bath at 95°C for 5min, refold it on ice for 10min, and place it at room temperature. At the same time, the HO-8910 adherent cells were washed twice with DPBS, and 0.2% EDTA was added to digest the cells at 37°C. After washing twice with DPBS, the cells were collected by pipetting with washing buffer (Washing buffer, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) into a centrifuge tube. After centrifugation and washing, add binding buffer (Binding Buffer: DPBS, 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride, 100mg / L tRNA, 1g / L BSA) and the processed nucleic acid aptamer sequence and library. Mix by pipetting and incubate on a shaker at 4°C for 1 hour. After incubation, wash...
Embodiment 3
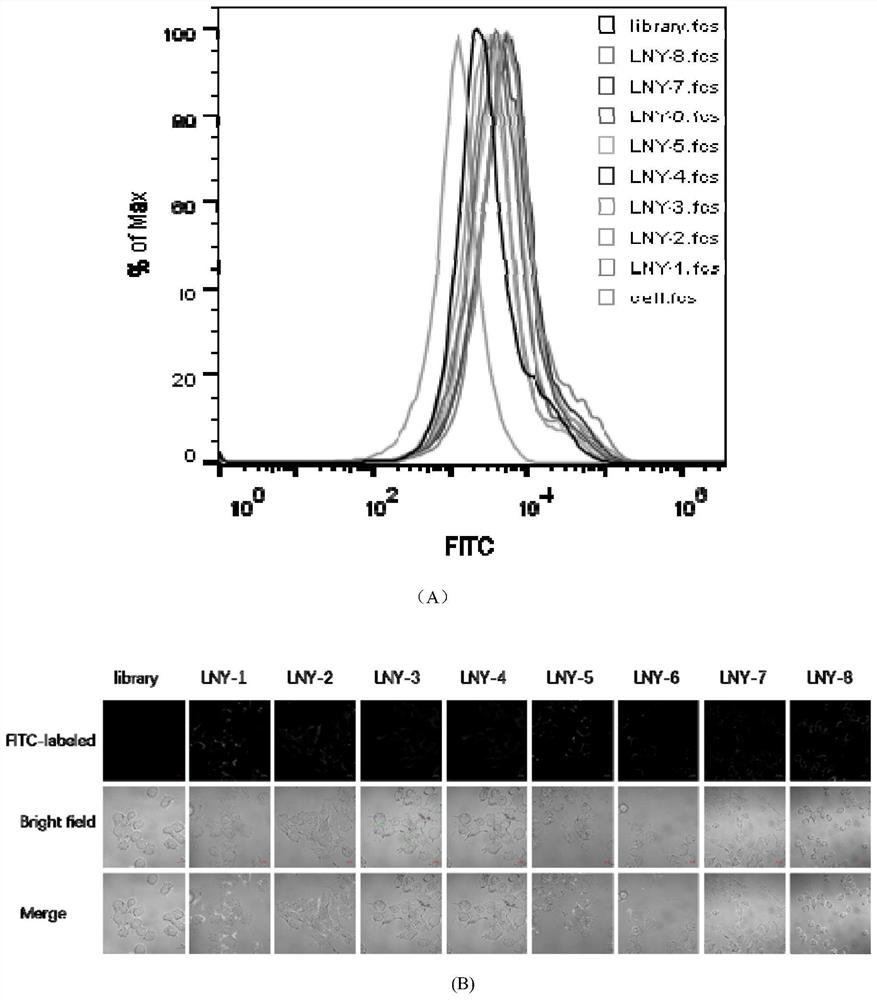
[0035] Example 3: Determining the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to the A2780 cell line
[0036] Centrifuge the powder of the 8 nucleic acid aptamer sequences and the control library chain, dilute it with sterile deionized water to a final concentration of 250nM, denature it in a metal bath at 95°C for 5min, refold it on ice for 10min, and place it at room temperature. At the same time, the A2780 adherent cells were washed twice with DPBS, and 0.2% EDTA was added to digest the cells at 37°C. After washing twice with DPBS, the cells were collected by pipetting with washing buffer (Washing buffer, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) into a centrifuge tube. After centrifugation and washing, add binding buffer (Binding Buffer: DPBS, 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride, 100mg / LtRNA, 1g / L BSA) and the processed nucleic acid aptamer sequence and library. Mix by pipetting and incubate on a shaker at 4°C for 1 hour. After incubation, wash with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com