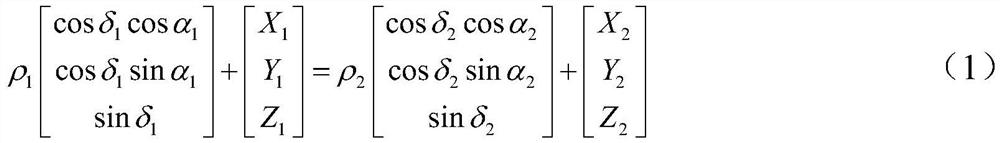Geometric method for determining space target initial orbit through optical telescope common-view observation and system
A technology of space target and geometric method, applied in the direction of navigation calculation tools, etc., can solve the problems of too expensive operation cost, uncertainty of speed deviation, unstable distance deviation of vector method, etc., and achieves high orbit determination accuracy and good real-time performance. , the effect of fast track setting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
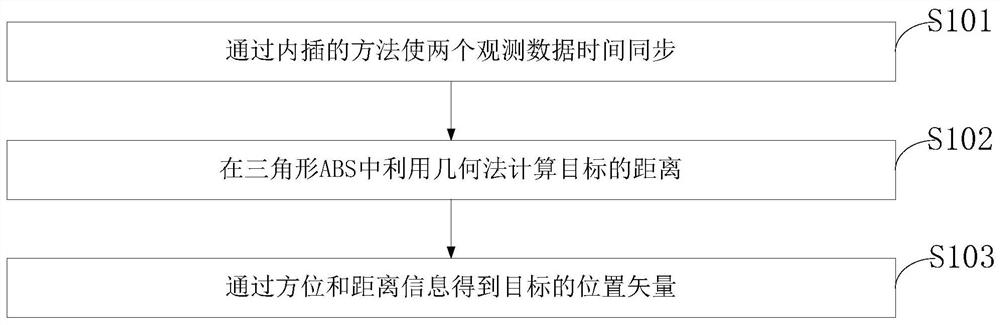
[0043] Aiming at the problems existing in the prior art, the present invention provides a geometric method and system for determining the initial orbit of a space object through common-view observation with optical telescopes. The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
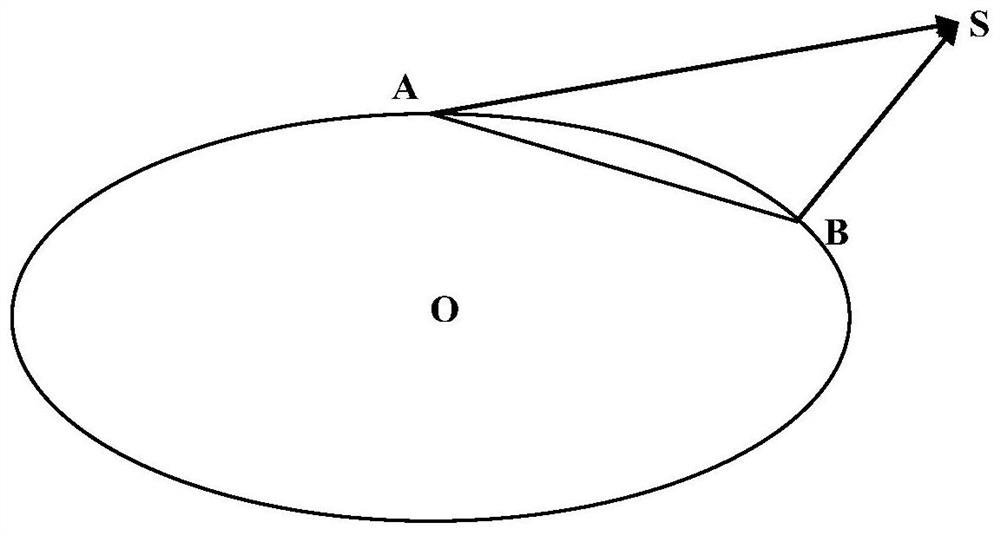
[0044] The geometric method for determining the initial orbit of a space object through common-view observation of optical telescopes provided by the present invention includes: directly solving the target position information in the triangle formed by the space object and two measuring stations bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com