Novel recombinant adeno-associated virus capsids with enhanced human pancreatic tropism
A capsid and virus technology, applied in the direction of viruses, viral peptides, viruses/bacteriophages, etc., can solve complex problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0381] Example 1: Directed evolution of AAV for human islet targeting
[0382] Introduction
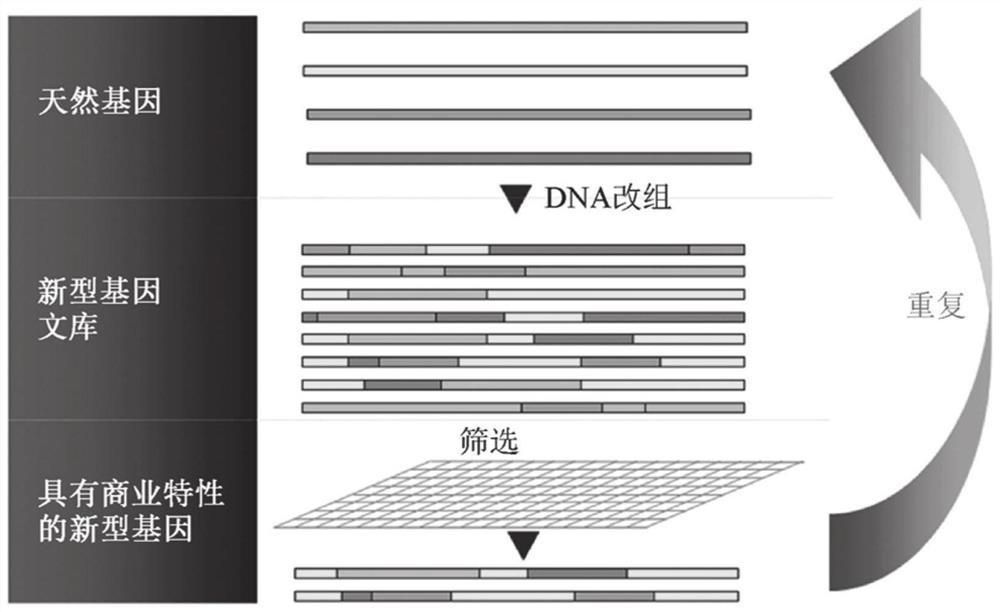
[0383]Adeno-associated virus (AAV) has attracted great interest as a potent vehicle for gene transfer into various cell types. Although AAV has several features that make itself a promising vehicle for human gene therapy, several disadvantages hinder the use of AAV in clinical applications, such as its promiscuous nature, limited transgene package size, and pre-existing neutralizing antibodies in the general population high prevalence. For gene therapy purposes, transduction needs to be both efficient and highly cell-type specific. AAV cell tropism and immunogenicity are determined by the sequences of the structural capsid proteins VP1, VP2 and VP3.
[0384] DNA shuffling is a powerful method for the evolution of molecules with specific functions in vitro and has applications in various fields such as medicine, pharmacy and agricultural research. Shuffling of AAV capsid sequences ...
example 2
[0391] Example 2: Novel recombinant adeno-associated virus capsids with enhanced human pancreatic tissue or human islet cell tropism
[0392] Purpose
[0393] The purpose of the present invention is to find rAAV vectors with enhanced ability to transduce human islet cells. This could be useful for new treatments targeting endocrine disorders, especially type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
[0394] Technical Description
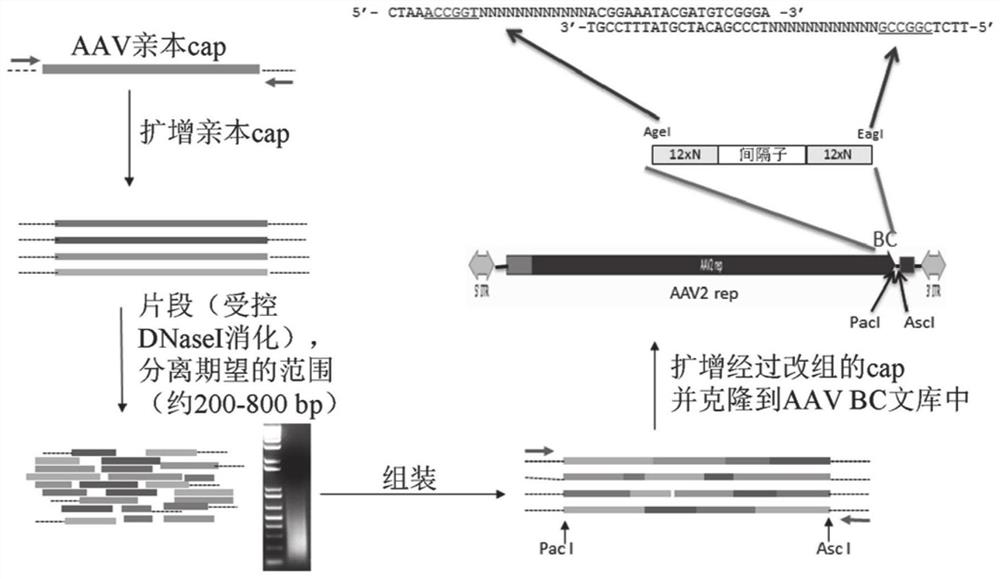
[0395] AAV capsid libraries were used to select for AAVs that selectively transduce dissociated or intact human islets. These capsid sequences were amplified using barcode-specific reverse primers and used to generate rAAV with GFP as the transgene ( Figure 18 ). Islets dissociated using Accumax were transduced at MOI = 1K or 10K μg / cell for 48 hours at 37°C (10% FBS / CMRL), plated 48 hours after transduction and analyzed by flow cytometry. Intact human islets were transduced on ice at MOI=10K μg / cell for 1-2 hours (2% FBS / CMRL), followed by suspension culture fo...
example 3
[0404] Example 3: Generation and screening of a barcoded adeno-associated virus capsid shuffling library for enhanced transduction of primary human islet cells
[0405] Summary
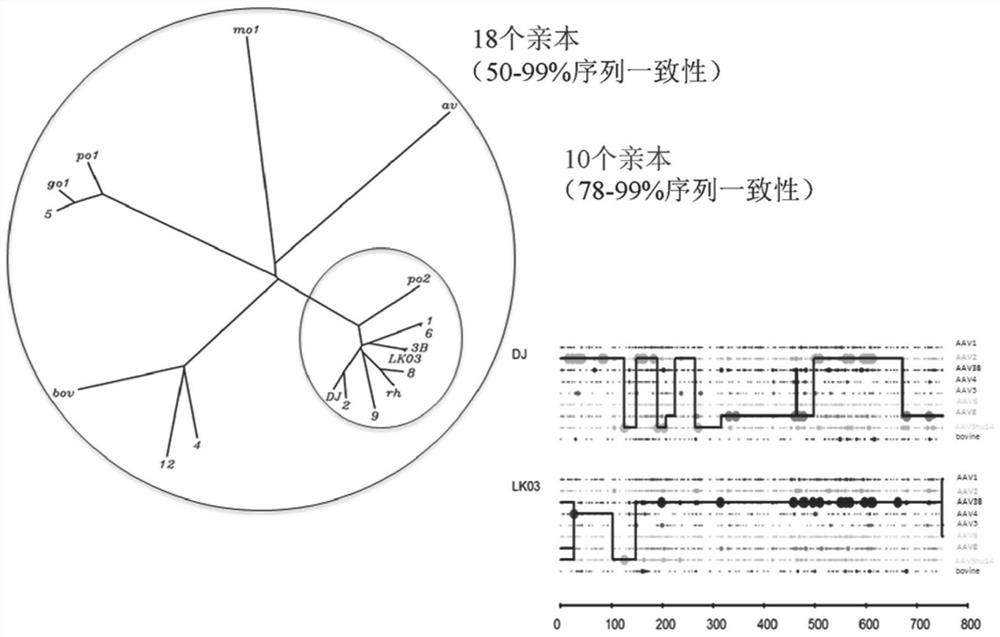
[0406] Safe and efficient gene transfer to Langerhans islets is a promising approach for treating diabetes. Recombinant AAV-mediated gene transfer into islets has been hampered by the lack of AAV serotypes that efficiently transduce these cells. To identify novel AAV serotypes with improved tropism for human islets, two highly complex, barcoded, replication-competent capsid libraries were constructed, diversity verified by single-molecule DNA sequencing, and performed on human islets sequence selection. The enriched barcodes were tracked by high-throughput sequencing, and three capsid variants were identified that were able to generate 5-fold to 10-fold better capsids than the best previously identified capsids. Highly efficient transduction of dissociated and intact islets. These novel AAV capsid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com