Ethanol-tolerant, high-temperature-tolerant and high-permeability-tolerant multi-tolerance fermentation strain and construction method
A technology for fermenting strains and construction methods, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fungi, etc., which can solve the problems of easily changing performance, not suitable for industrial production conditions, unsatisfactory fermentation ability of multi-tolerant strains, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
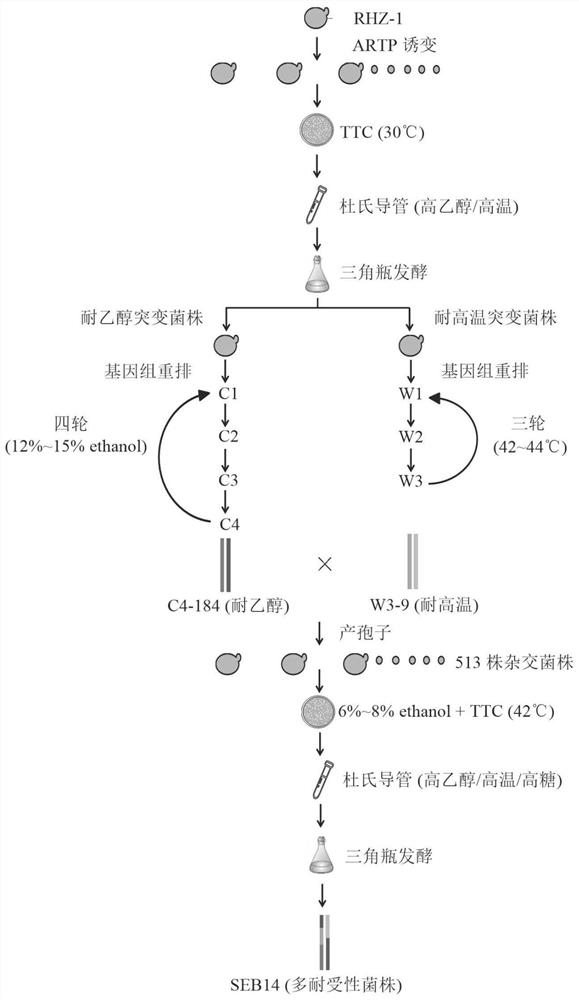
[0037] refer to figure 1 , the present embodiment provides a method for constructing a multi-tolerant fermentation strain resistant to ethanol, high temperature and hypertonicity, comprising the steps of:
[0038] Step 1, the construction of the starting strain
[0039]The spores produced by SEB1 and IR-2 were fused by protoplasts to obtain flocculant fusogen RHZ-1, of which SEB1 was preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, and the preservation number was CGMCC NO.11321; the IR-2 strain was isolated Fermented food from Indonesia, with ethanol production capacity and flocculation, the source is described in the following documents: Hiroshi K, Yoshio S, Toshio M, Harumi K, Yorikazu S.1985.Continuous ethanolfermentation with cell recycling using flocculatingyeast.J.Ferment .Technol.63:159-165; the translated name of this document is: use flocculating yeast to carry out continuous ethanol fermentation with cell...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment verifies the fermentation performance of the multi-tolerant bacterial strain SEB14 under high temperature conditions, and the specific verification process and results are as follows:
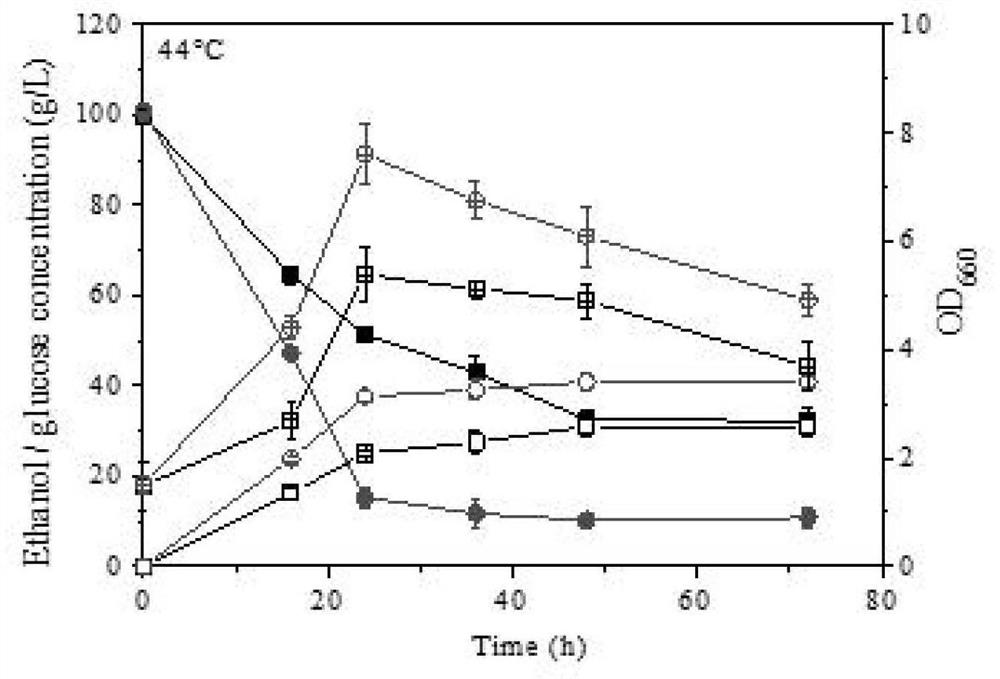
[0054] Under the fermentation conditions of 42°C and 43°C (10% YPD), both strains RHZ-1 and SEB14 could consume glucose within 24h and 48h, indicating that the starting strain RHZ-1 itself has better high temperature tolerance. When the fermentation temperature increased to 44 °C, the ethanol concentration of SEB14 was significantly higher than that of RHZ-1 ( image 3 ). After 72 hours of fermentation, the ethanol concentration and glucose concentration of SEB14 were 40.98g / L and 10.71g / L, respectively. Compared with RHZ-1, it increased by 33.36% and decreased by 66.72% (Table 2). This result shows that SEB14 has stronger high temperature resistance.
[0055] Table 2 Comparison of strains fermented for 72 hours at 44°C
[0056]
[0057] Note: The same letter in th...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This example verifies the fermentation performance of the multi-tolerant strain SEB14 at high temperature and contains ethanol. The specific verification process and results are as follows:
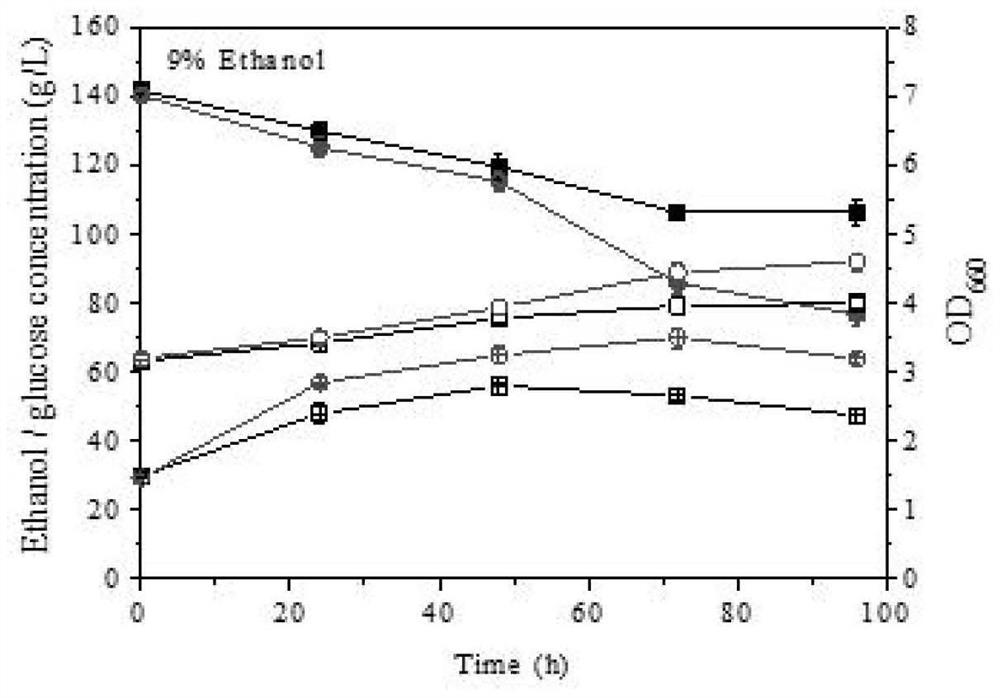
[0060] In the late stage of SSF fermentation, the yeast should not only tolerate high temperature, but also gradually increase the concentration of ethanol at the same time. In this study, we found that SEB14 also exhibited better fermentation performance than the parental strain RHZ-1 under the co-fermentation conditions of initial addition of 3% ethanol and high temperature at 43°C, indicating that the strain SEB14 can well withstand the dual effects of high temperature and ethanol. Coercion ( Figure 4 ,table 3).
[0061] Table 3 Comparison of results of 72h fermentation of strains with initial addition of 3% ethanol and 43°C
[0062]
[0063] Note: The same letter in the same column means no significant difference, different letters mean significant difference, P<0.05(t-te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com